Cisco Crosswork Hierarchical Controller Solution Overview
Available Languages
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
Cisco Crosswork Hierarchical Controller turns your complex multilayer and multivendor infrastructure into a unified, easily controlled network. The Crosswork Hierarchical Controller extends the architectural simplicity of Routed Optical Networking to fulfill and assure any transport service over any combination of IP, optical, and microwave network domains.
Service provider networks consist of multiple layers, such as optical and packet networks, stitched through many domains and vendors. Provisioning services in such complex environments requires intricate coordination between different management systems and organizations; assuring these services’ SLAs is virtually impossible.
Cisco’s Routed Optical Networking architecture solves these challenges by unifying the WDM, OTN, and packet transport layers into a single, easy-to-control network. However, while transitioning to this flat architecture, Routed Optical Networking becomes another network domain to manage, adding complexity. This is where the Crosswork Hierarchical Controller steps in, and extends some of the ease of operating a RON network to the rest of the transport network.
The Crosswork Hierarchical Controller provides an API and a single pane of glass for all the network components – from DWDM links to routers and from wavelength services to private line services. It controls your existing optical, microwave, and packet domains with the same unified approach. Rather than making your network control more complex, Routed Optical Networking with Crosswork Hierarchical Controller dramatically simplifies it. Finally, it allows you to create services that meet strict low-latency and high-availability requirements.

● Create the ultimate network data source that can be relied on for safe operation and automation. Crosswork’s Hierarchical Controller is the only network controller that’s pre-integrated with most IP and optical vendors. And It’s the only controller that uses deep analytics to stitch all intra-and interdomain connectivity straight from the network, rather than relying on inaccurate inventory systems.
● Use a single intuitive user interface to deploy wavelength, private line, and packet services. Services paths are determined by Crosswork Hierarchical Controller’s sophisticated path computation engine, based on full understanding of all network layers.
● Troubleshoot failures across different domains and layers and quickly identify their root causes with a simple user interface to the entire transport network and all its services.
● Navigate back and forth in time: Rewind your network visibility to any point in the past to investigate events and faults. Use AI-based predictive analysis of its future state to avoid problems and improve planning.
● Easily integrate with OSS tools such as service orchestrators, inventory systems, and trouble ticket systems via standard-based RESTCONF APIs. Use an easy-to-use network query language to derive insights and reduce integration costs by up to 40 percent.
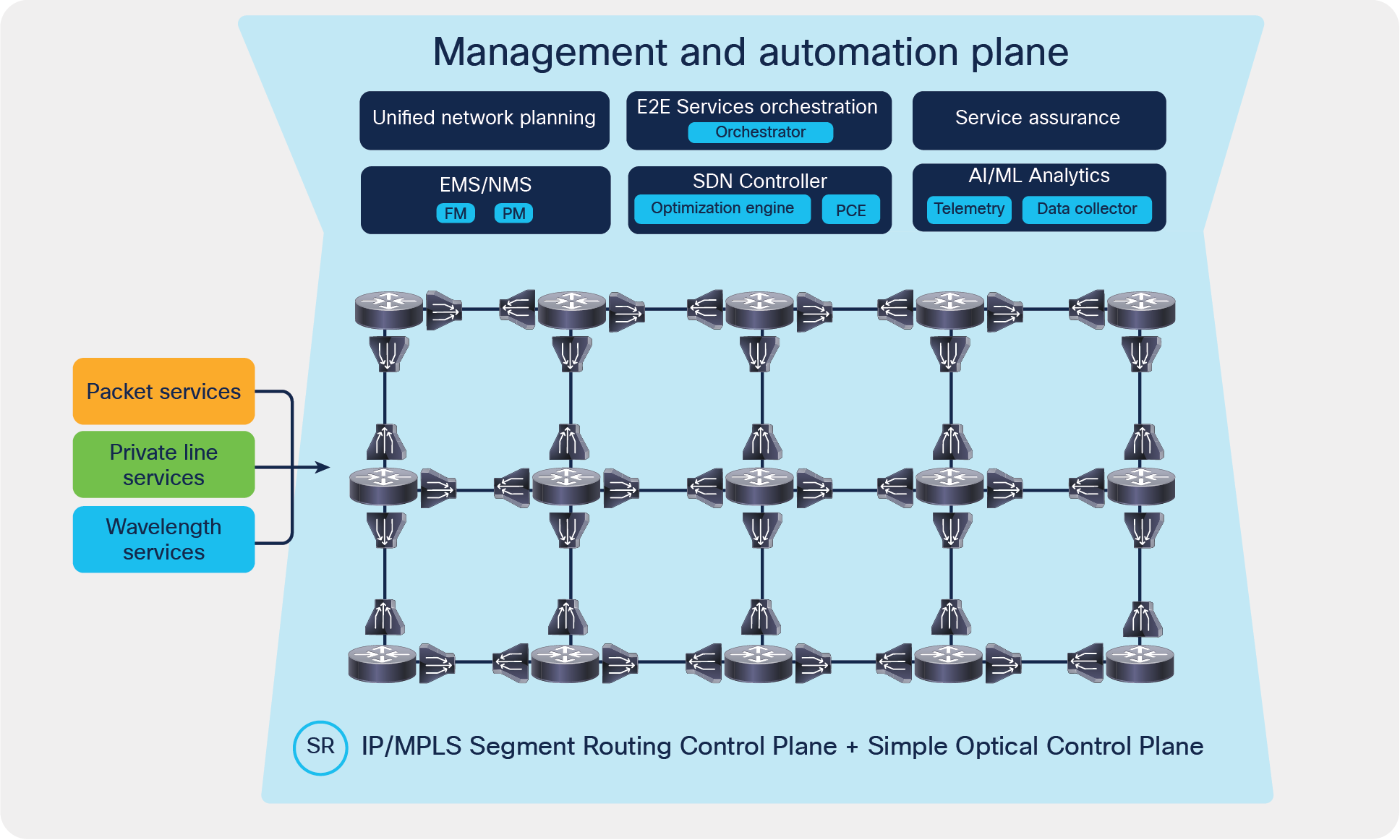
Cisco’s Routed Optical Networking Architecture
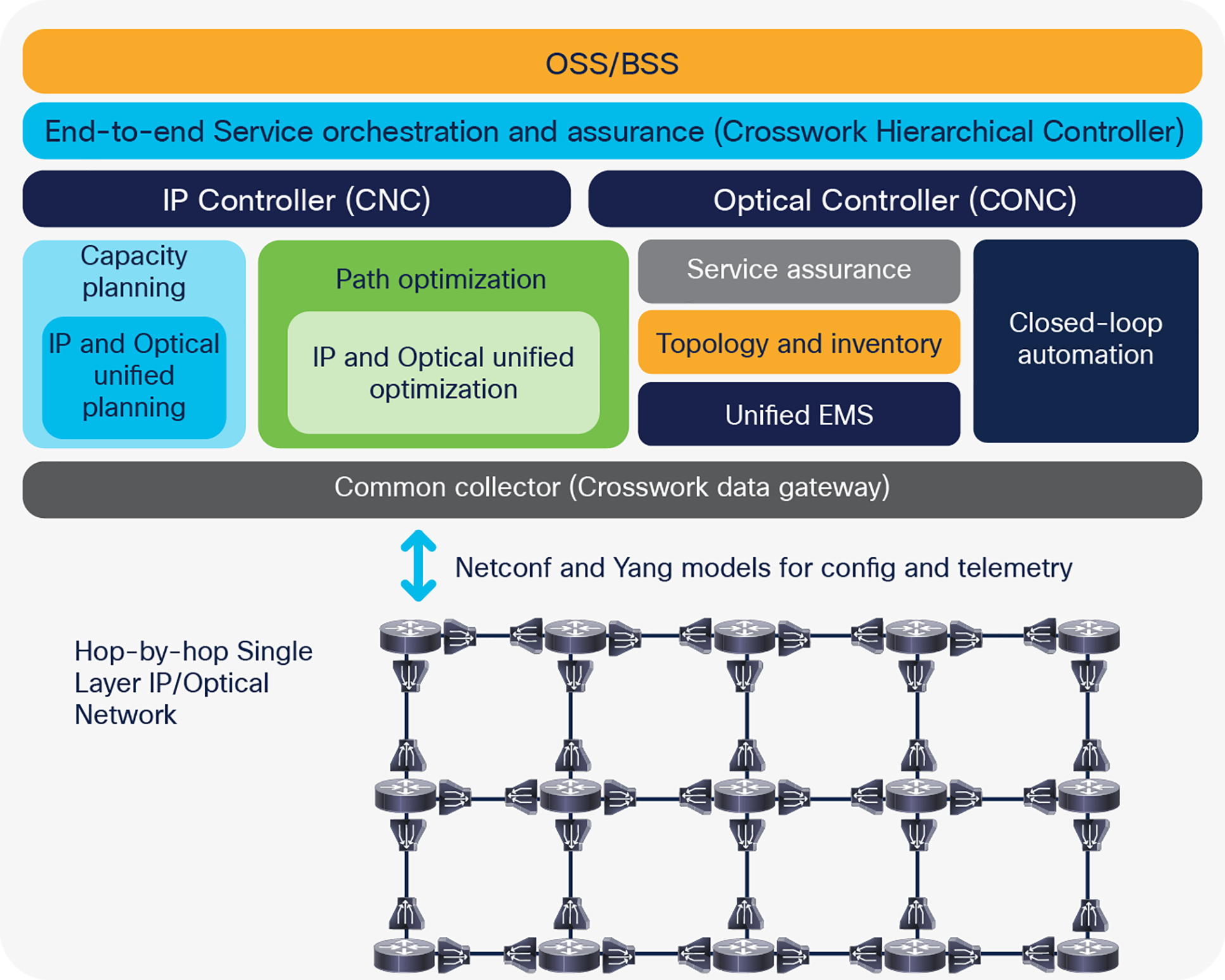
Cisco’s Routed Optical Networking’s control architecture with the Cisco Crosswork Hierarchical Controller
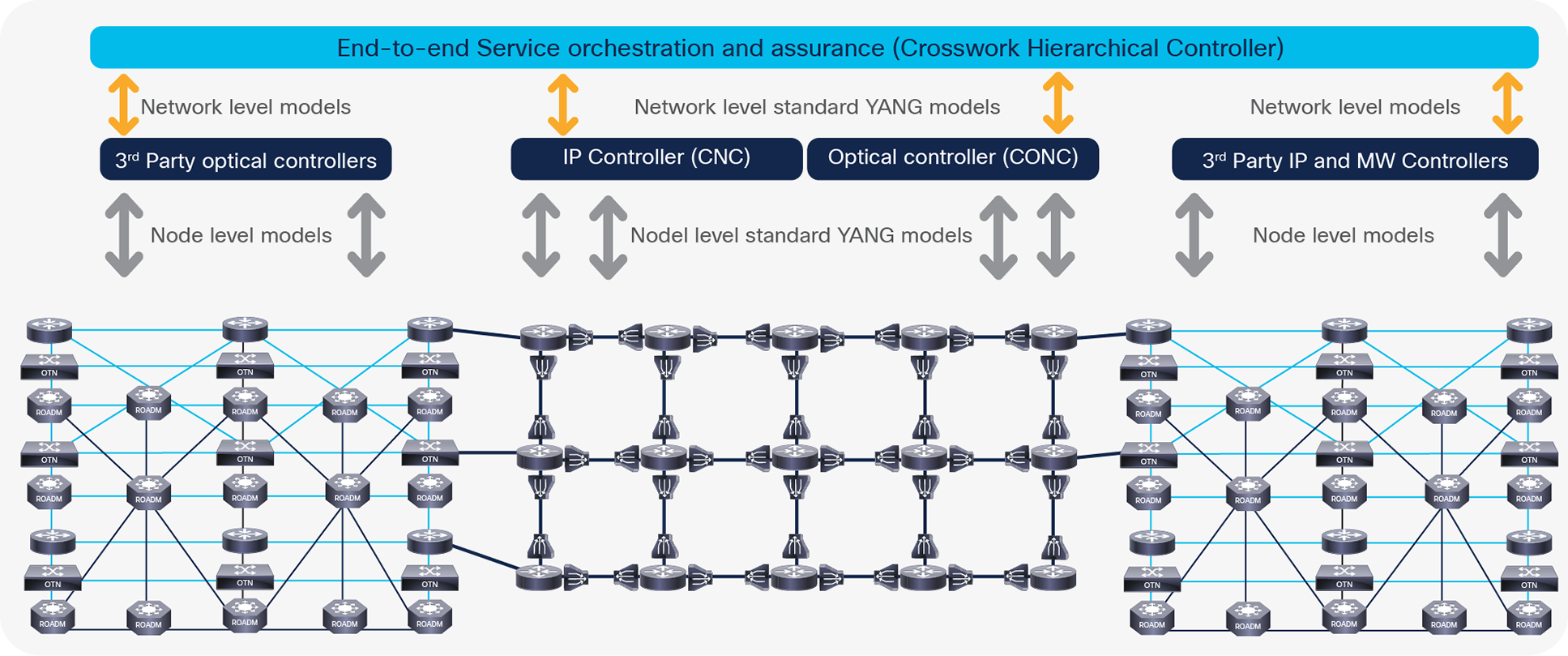
Controlling a hybrid network of Routed Optical Networking and legacy domains
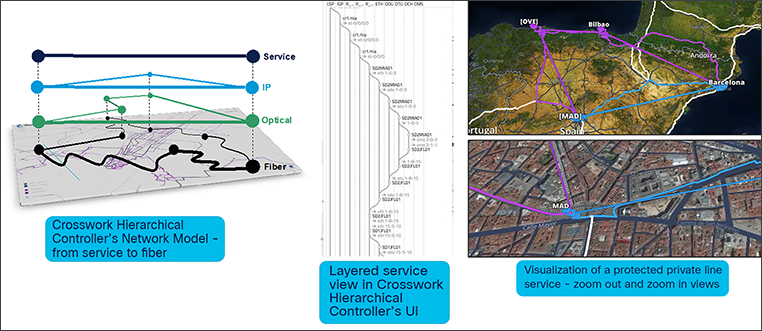
The Crosswork Hierarchical Controller’s visibility of all service layers, down to the fiber level
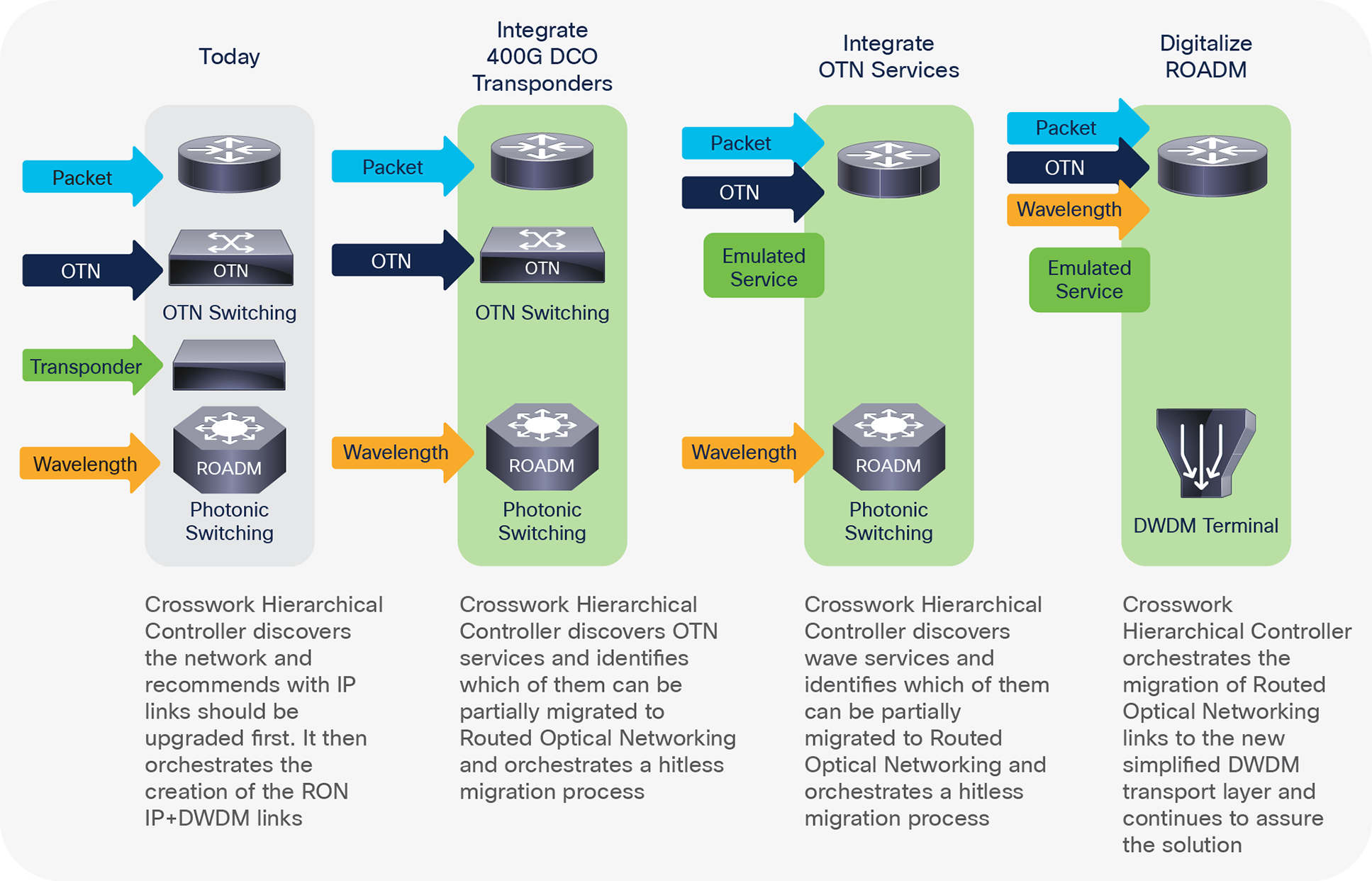
Cisco Crosswork Hierarchical Controller’s role in migrating to RON-based networks
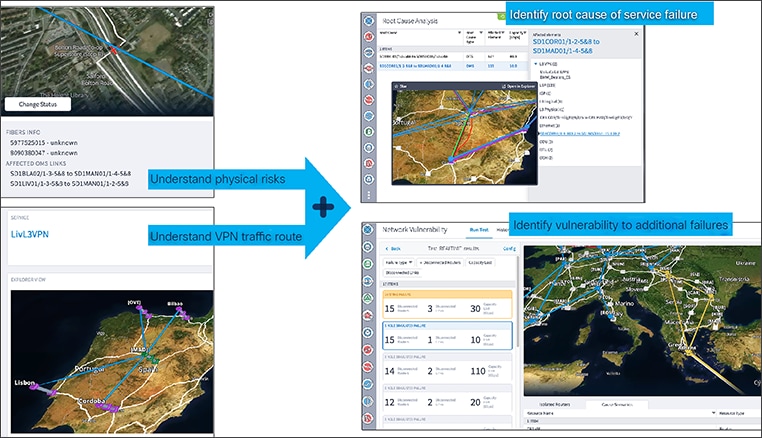
The Crosswork Hierarchical Controller’s visibility of all service layers, down to the fiber level
“5G and edge computing will usher in a new era of services enabled by network slicing and URLLC applications that cannot be delivered with the existing inflexible, disjointed, and manual network operations. As such, operators are transforming their networks and operations into software-defined and cloud-native infrastructures and highly automated processes, respectively, as they strive to become more digitalized, cost-efficient, and agile.”
Analysys Mason,
Automation in the WAN: The Critical Role of Multi-layer, Multi-vendor SDN Control Platforms, May 2019
“Awarded to the company that has developed a potentially market-leading optical/IP/Ethernet/FTTH product that, through engineering and technical excellence, enables the deployment of profitable next-generation telecom services.”
Light Reading Leading Lights 2018: Most Innovative Telecoms Product
Next-generation 5G network slices and machine-to-machine services have very different requirements than today’s manually built services with loose SLA requirements. They require a high degree to automation that allows rapid churn in services and strict adherence to latency, availability, and capacity requirements.
The vast majority of these services, as well as current service provider traffic, continues to be IP based. Consequently, service providers should optimize their next-generation network architectures for IP services with stringent SLAs rather than for legacy TDM services, whose volumes are small and decreasing.
When service providers do not optimize their network infrastructures for IP services, they incur high TCO because:
● Layered and siloed infrastructures rely on large volumes of line cards for traffic hand-off between networking layers.
● Each networking layer has its separate – and overlapping - resiliency scheme, resulting in high costs and low resource utilization.
● The network is excessively complex since each layer has independent switching points, control, and management planes.
● Every network silo requires manual service stitching across network domains, impeding end-to-end closed-loop automation and increasing service lead times.
Cross-domain services require a very high level of coordination. In today’s networks, each domain is managed by different systems and different teams. In this state, they cannot meet the stringent requirements of latency, capacity, and reliability of 5G and some machine-to-machine interactions.
Even if the network is optimized, it will still be challenging to operate without a control system that understands its different component technologies and without orchestrating their provisioning. Even worse, evolving from existing siloed multilayer networks to an optimized future state might make the network more complicated before it can become simpler. So, customers who want to migrate to a simpler network need a way to evolve without undertaking more complexity.
Routed optical networking solution components
Cisco's Routed Optical Networking Architecture is shown in Figure 2. Components relevant to this discussion are:
● Cisco® IP controller – Crosswork Network Controller
● Cisco optical controller – Cisco Optical Network Controller
● Crosswork Hierarchical Controller and optionally other Cisco Crosswork™ components
The architecture conforms to the SDN architecture defined by IETF and ONF and the 3GPP control architecture for network slicing defined by 3GPP. Within it, Crosswork Hierarchical Controller acts as an overall network controller, controlling the DWDM links of Routed Optical Networking via Cisco Optical Controller and the IP layer via Crosswork Network Controller. Crosswork Hierarchical Controller extends its controlling function to other network domains that are likely to be part of the network (optical, IP, or microwave domains). It executes it via standards-based network models defined in YANG over RESTCONF or through proprietary interfaces to various vendor controllers supported by Crosswork Hierarchical Controller (see Figure 3).
Thanks to this design, all services are provisioned in the same way, using a common set of policies, a shared UI, and the same API. A service can also be defined across multiple domains via a single operation, even if it spans different layers. Figure 3 presents an example of a private line that encompasses an OTN metro domain, a Routed Optical Networking core domain, and another Ethernet over microwave metro domain.
Crucially, the Crosswork Hierarchical Controller assures services across all domains, allowing operations to quickly pinpoint a problem to its correct domain and fix it quickly, even automatically. Figure 4 shows how Crosswork Hierarchical Controller visualizes a private line service all the way down to the physical fiber in the ground.
There is no one-size-fits-all solution for deploying a new architecture. The approach depends on the structure of the network and the goals of its owner. Thus, it is critical to have a flexible control platform that supports a phased deployment and a smooth evolution. Crosswork Hierarchical Controller facilitates it, as follows:
Greenfield RON deployment: When a new IP and optical network is deployed, RON hardware, together with its control architecture – including Crosswork Hierarchical Controller, Crosswork Network Controller (CNC), and Cisco Optical Network Controller (CONC), is installed from scratch (Figure 2). In fact, it may be useful to install Crosswork Hierarchical Controller ahead of time, in preparation for the RON deployment, over existing parts of the network, to help plan out the RON network based on accurate data about the existing services, network, and fiber assets.
Brownfield RON deployment: When RON routers are deployed over an existing DWDM network, Crosswork Hierarchical Controller is deployed over CNC and the existing DWDM optical controllers. Crosswork Hierarchical Controller creates IP links between RON routers by configuring the optical path through the optical controllers and terminates those paths on the DWDM transceivers in the routers.
Brownfield solution with NSO: In legacy networks that already use Cisco’s NSO for automating service provisioning, Crosswork Hierarchical Controller can be added as a network analytics and path computation engine (Figure 6). It will automate complex services that require topological understanding, such as services across different domains and services that require adherence to complex constraints.
Evolution from legacy networks to routed optical networks
Crosswork Hierarchical Controller can help in all the phases of migrating to RON, as shown in Figure 5. It provides visibility to network areas that need to be upgraded first and identifies all services that could be migrated to RON. It then orchestrates the migration process, using the SDN controllers of the legacy network domains to steer the service to RON and using CNC to build out the part of the service that goes over RON. The value that Crosswork Hierarchical Controller brings in all phases of this process is a cost-effective and safe process that minimizes service disruption. An example of such a service after the migration process is shown in Figure 3.
In legacy networks that already deploy Cisco Network Services Orchestrator (NSO) for service automation, Crosswork Hierarchical Controller can be added to the network to enhance automation without disrupting the existing workflows. In this case, Hierarchical Controller is deployed in read-only mode to discover all aspects of the network. Hierarchical Controller is connected to NSO through a path computation interface and allows Cisco NSO to select network paths that consider bandwidth availability, latency, and diversity requirements – all the way to the fiber duct.
Key capabilities
● Automatic discovery based on network data allows you to create a trustworthy digital twin of your network to help operations and to feed OSS tools.
● Multivendor control over IP, optical, and microwave networks lets you create services consistently across different domains.
● End-to-end assurance of service across all domains enables you to meet strict service requirements.
| Industry name |
Use case description |
| Any network operator |
● Operate your network using the same pane of glass, irrespective of equipment vendor or network layer
● Plan your network based on an accurate data source that includes both IP and optical layers stitched together as one network
● Troubleshoot the network by understanding its current and past state at all the layers
|
| Mobile operator |
● Understand how your traffic flows from eNodeB to the core via microwave, Ethernet, optical, and IP layers
● Pinpoint service issues to areas that are congested or failed
● Manage connectivity services that implement network slices while proactively assuring latency, capacity, and availability constraints
|
| Operators offering private line services |
● Manage private line services over optical, packet, and microwave networks, ensuring tight SLAs of latency and diversity
● Provide sales teams and customers with visibility into the service down to the physical route of fiber ducts
● Proactively warn against impending network issues or maintenance activities that will impact services
|
| Operators offering VPN services |
● Manage VPNs over all router vendors from a unified standards-based interface
● Ensure VPNs use the right underlay network resources to guarantee strict SLAs – differentiating them from over-the-top technologies such as SD-WAN
● Understand the impact of failures or maintenance activities on VPN services
|
| Large enterprise managing their own IP/optical network |
● Simple operation of the network without requiring IP and optical expertise
● Simple network planning without requiring specialized planning tools
● Easy and quick creation of all services from a single pane of glass or API
|
Flexible payment solutions to help you achieve your objectives
Cisco Capital makes it easier to get the right technology to achieve your objectives, enable business transformation and help you stay competitive. We can help you reduce the total cost of ownership, conserve capital, and accelerate growth. In more than 100 countries, our flexible payment solutions can help you acquire hardware, software, services and complementary third-party equipment in easy, predictable payments. Learn more.
Crosswork Hierarchical Controller is a flexible control platform that allows gradual deployment and expansion of Routed Optical Networking. From early in the transition, it brings network layers together, enabling a smooth network evolution.
Crosswork Hierarchical Controller acts as an overall network controller, controlling the Routed Optical Networking DWDM via Cisco Optical Controller and the IP layer via Crosswork Network Controller. This architecture conforms to the SDN architecture defined by IETF and ONF and to the 3GPP architecture for network slicing defined by 3GPP.
In legacy networks that already deploy NSO, Crosswork Hierarchical Controller enhances automation without disrupting existing workflows. Deploying Crosswork Hierarchical Controller as a PCE allows NSO to select paths that take into account bandwidth, latency, and diversity.
End-to-end service orchestration and assurance
The Cisco Crosswork Hierarchical Controller simplifies operations of Cisco’s Routed Optical Networking to increase visibility and control third party optical resources.
Cisco’s Routed Optical Networking with Cisco Crosswork Hierarchical Controller is the only solution that fully integrates optical circuit switching and packet switching while unifying control, making transport networks substantially easier to operate versus a siloed approach of optical and IP domains. It’s the only solution based on 100 percent accurate network visibility, facilitating deep analytics and safe automation. Cisco Crosswork Hierarchical Controller is deployed and preintegrated with most network transport vendors in multiple Tier 1 operators, so deployment risk is very low.
Accelerate your journey to next-generation networking
If your network needs to deliver high-bandwidth services with uncompromising diversity and latency SLAs and dramatically lower costs, you’ll be interested in Cisco’s RON solution with Crosswork Hierarchical Controller.
For more information on Cisco’s network automation portfolio for Service Providers please visit www.cisco.com/go/crosswork. To learn more about Crosswork Hierarchical Controller or to schedule a demonstration contact your Cisco sales representative.