Feature Summary and Revision History
Summary Data
|
Applicable Product(s) or Functional Area |
SMF |
|
Applicable Platform(s) |
SMI |
|
Feature Default Setting |
Disabled – Configuration Required |
|
Related Changes in this Release |
Not Applicable |
|
Related Documentation |
Not Applicable |
Revision History
|
Revision Details |
Release |
|---|---|
|
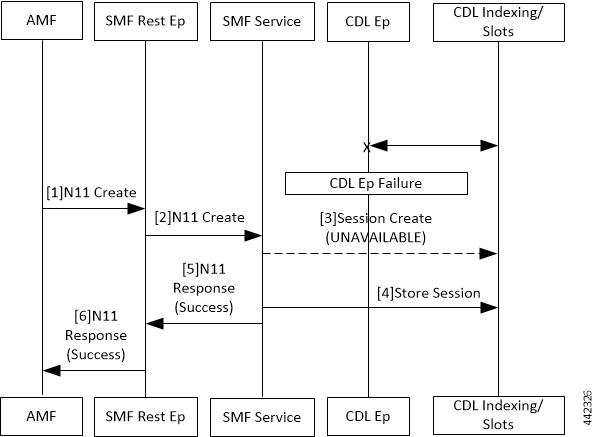
Added the failure handling support. |
2023.03.0 |
|
Added the procedures for configuration and verification of the event trace data in the CDL database record. |
2021.02.0 |
|
First introduced. |
Pre-2020.02.0 |
 Feedback
Feedback