Product Overview (Version 1.0)
Available Languages
Table Of Contents
What Is Media Gateway Control Protocol?
What Is the Cisco MGCP IP Phone?
Dialing and Messaging Features
Product Overview
This chapter contains the following information about the Cisco MGCP IP Phone:
•
What Is Media Gateway Control Protocol?
•
What Is the Cisco MGCP IP Phone?
What Is Media Gateway Control Protocol?
Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP) is the Internet Engineering Task Force's (IETF's) standard for multimedia conferencing over IP. MGCP is an ASCII-based, application-layer control protocol (defined in RFC 2705) that can be used to establish, maintain, and terminate calls between two or more endpoints.
Like other VoIP protocols, MGCP is designed to address the functions of signaling and session management within a packet telephony network. Signaling allows call information to be carried across network boundaries. Session management provides the ability to control the attributes of an end-to-end call.
One aspect of MGCP that differs from other VoIP protocols is that MGCP relies on a control server, or call agent (CA) to control call progression, tones to apply, and call characteristics. MGCP endpoints carry out instructions from the CA, which controls how calls proceed.
MGCP provides the capabilities to allow a Control Server to:
•
Determine the location of the target endpoint.
•
Determine the media capabilities of the target endpoint. Using Session Description Protocol (SDP), MGCP determines the lowest level of common service between the endpoints. Conferences are established using only the media capabilities that can be supported by all endpoints.
•
Determine the availability of the target endpoint.
•
Establish a session between the originating and target endpoint. If the call can be completed, MGCP establishes a session between the endpoints. MGCP also supports mid-call changes, such as the addition of another endpoint to the conference or the changing of a media characteristic or codec.

Note
Conferences can consist of two or more users and can be established using multicast or multiple unicast sessions. The term conference means an established session (or call) between two or more endpoints. In this document, the terms conference and call are used interchangeably.
MGCP is a client-server protocol. The CA handles all aspects of setting up calls to and from endpoints. CAs or control servers provide the feature capabilities that a particular endpoint will be able to use. Endpoints connected to different CAs will likely have a different set of features they can use. Since all of the call control features are in the control server, each control server vendor decides which features are most important, and therefore different control server vendors differ in "essential features."
What Is the Cisco MGCP IP Phone?
The Cisco Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP) Internet Protocol (IP) Phone provides voice communication over an IP network. It functions much like a traditional phone, allowing you to place and receive telephone calls.
The Cisco MGCP IP phone works with a third-party CA that uses MGCP for call control and eXtensible Markup Language (XML) for control of the phone's displays and feature keys. This document describes the phone features that are controlled by the phone. Refer to your CA documentation for descriptions of all other phone features, displays, and applications.
Cisco MGCP IP phones are full-featured telephones that can be plugged directly into an IP network and used very much like a standard private branch exchange (PBX) telephone. The Cisco MGCP IP phone model terminals can attach to the existing in place data network infrastructure, via 10BaseT/100BaseT interfaces on an Ethernet switch. When used with a voice-capable Ethernet switch (one that understands Type of Service [ToS] bits and can prioritize VoIP traffic), the phones eliminate the need for a traditional proprietary telephone set and key system/PBX.
Figure 1-1 illustrates physical features of the Cisco MGCP IP phone:
Figure 1-1 Cisco MGCP IP Phone Physical Features
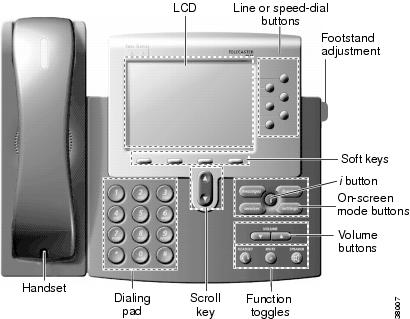
The main components of the Cisco MGCP IP Phone are defined in Table 1-1.
Supported Features
The MGCP phone supports the following features. Depending on the features that your CA supports, some of these may not be available on your phone.
Physical Features
•
Hearing-aid compatible handset
•
Headset compatibility
•
Integrated two-port Ethernet switch that allows the telephone and a computer to share a single Ethernet jack
•
Direct connection to a 10BaseT or 100BaseT Ethernet (RJ-45) network (half- or full-duplex connections are supported)
•
Large (4.25 x 3 in.) display with adjustable contrast
Network Features
•
Interoperability with third-party CAs.
•
Up to six MGCP connections and call appearances.
•
IP address assignment—Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) client or manually configured via a local setup menu
•
Network startup using DHCP and Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP)
•
Domain Name System (DNS): The MGCP phone uses DNS lookups to locate its communication partners (for example, a TFTP server or a CA. If a CA is unreachable, the MGCP phone queries the DNS server for an alternate CA.)
•
Telnet support—Allows the user to use telnet to connect directly to the Cisco MGCP IP Phone to debug and troubleshoot the phone. See "Configuring the Cisco MGCP IP Phone" section on page 4-1 for more information on configuration parameters.
•
Ping support—Allows the user to use ping to see if a Cisco MGCP IP Phone is operational and how long the response time is from the phone.
•
Traceroute support—Allows the user to use traceroute to see the path that a Cisco MGCP IP phone traverses in the route to its desired destination.
Codec and Protocol Support
•
Basic phone service including MGCP 0.1 and MGCP 1.0 headers.
•
G.711 u-law codec.
•
G.711 a-law codec.
•
G.729a codec.
•
DTMF out-of-band for G.729a codec compliant to RFC 2833.
•
Local Connection Options (LCOs):
–
G.729a codec: supports low-bandwidth access for multitenant deployment.
–
Voice activity detection (VAD) support.
–
Type of service (ToS) bit for Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP)
•
XML support.
Dialing and Messaging Features
•
Message Waiting Indication—Lights to indicate that a new voice message is in a subscriber's mailbox. If the subscriber listens to the message but does not save or delete the message, the light remains on. If a subscriber listens to the new message or messages, and saves or deletes them, the light goes off. The message waiting indicator (MWI) is controlled by the voicemail server. The indication will be saved over a phone upgrade or reboot.
•
Notified entity: A CA can direct an endpoint to send notify messages to an alternate destination.
•
Call waiting, call transfer, call forward (unconditional, busy, no answer), announcement, music on hold, and volume control. (Must be supported by the CA.)
•
Three-way calling using an external multipoint control unit (MCU). (Must be supported by the CA.)
Supported Protocols
The Cisco MGCP IP phone supports the following standard protocols:
•
Domain Name System (DNS)—Used in the Internet for translating names of network nodes into addresses. The MGCP IP Phone uses DNS to resolve the host names of endpoints to IP addresses.
•
Dynamic Host Control Protocol (DHCP)—Used to dynamically allocate and assign IP addresses. DHCP allows you to move network devices from one subnet to another without administrative attention. If using DHCP, you can connect Cisco MGCP IP phones to the network and become operational without having to manually assign an IP address and additional network parameters.
The Cisco MGCP IP phone complies with the DHCP specifications documented in RFC 2131. By default, Cisco MGCP IP phones are DHCP-enabled.
•
Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)—A network layer Internet protocol that enables hosts to send error or control messages to other hosts. ICMP also provides other information relevant to IP packet processing.
The Cisco MGCP IP phone supports ICMP as it is documented in RFC 792.
•
Internet Protocol (IP)—A network layer protocol that sends datagram packets between nodes on the Internet. IP also provides features for addressing, type-of-service (ToS) specification, fragmentation and reassembly, and security.
The Cisco MGCP IP phone supports IP as it is defined in RFC 791.
•
Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP)—Transports real-time data (such as voice data) over data networks. RTP also has the ability to obtain Quality of Service (QoS) information.
The Cisco MGCP IP phone supports RTP as a media channel.
•
Session Description Protocol (SDP)—An ASCII-based protocol that describes multimedia sessions and their related scheduling information.
The Cisco MGCP IP phone uses SDP for session description.
•
Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP)—Synchronizes computer clocks on an IP network. The Cisco MGCP IP phones use SNTP for their date and time support.
•
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)—Provides a reliable byte-stream transfer service between two endpoints on an internet. The Cisco IP Phone 7960 supports TCP for telnet sessions only.
•
Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP)—Allows files to be transferred from one computer to another over a network. The Cisco MGCP IP phone uses TFTP to download configuration files and software updates.
•
User Datagram Protocol (UDP)—A simple protocol that exchanges data packets without acknowledgments or guaranteed delivery. MGCP can use UDP as the underlying transport protocol. If UDP is used, retransmissions are used to ensure reliability.
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback