Multi-Site Remote Border
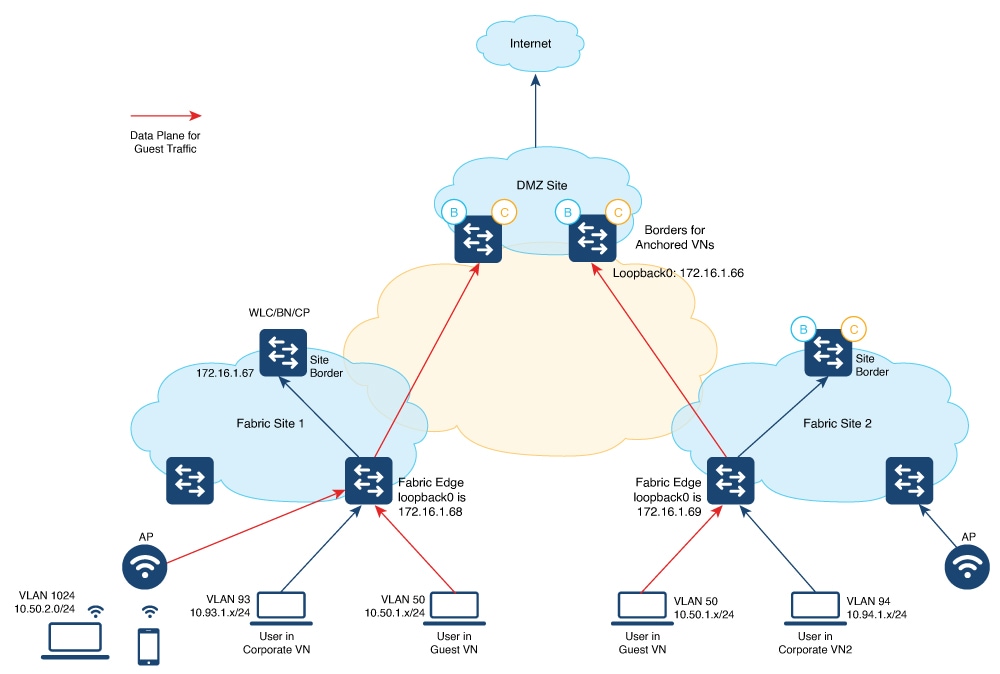
A multi-site remote border enables the fabric network to isolate untrusted traffic to a central location like a firewall or a DMZ (demilitarized zone). For example, if the network has a guest virtual network (VN) that is stretched across multiple sites, all the guest traffic can be tunneled to a remote border at the DMZ, thus isolating the guest traffic from the enterprise traffic.
In a multi-site network deployment, you can designate a common border (multi-site remote border) to route the traffic to and from a particular VN that is stretched across multiple sites. This allows you to deploy a VN across multiple fabric sites but have a single subnet across all these sites. Preserving the subnets across multiple fabric sites helps in conserving the IP address space.
Here are some common terms that are used in the context of a multi-site remote border:
Anchor Virtual Network (VN): A virtual network that exists across multiple fabric sites in a network. The associated IP subnet and segment are common across these multiple sites.
Anchor Site: The fabric site that hosts the common border and control plane for an Anchor VN. Anchor Site handles the ingress and egress traffic for the Anchor VN.
Anchoring Sites: Fabric sites other than the Anchor Site where the Anchor VN is deployed.
Anchor Border Node or Multi-Site Remote Border: The fabric border node at the Anchor Site that provides the ingress and egress location for traffic to and from the Anchor VN.
Anchor Control Plane Node: The fabric control plane node at the Anchor Site that accepts registrations and responds to requests for endpoints in the Anchor VN.

 Feedback
Feedback