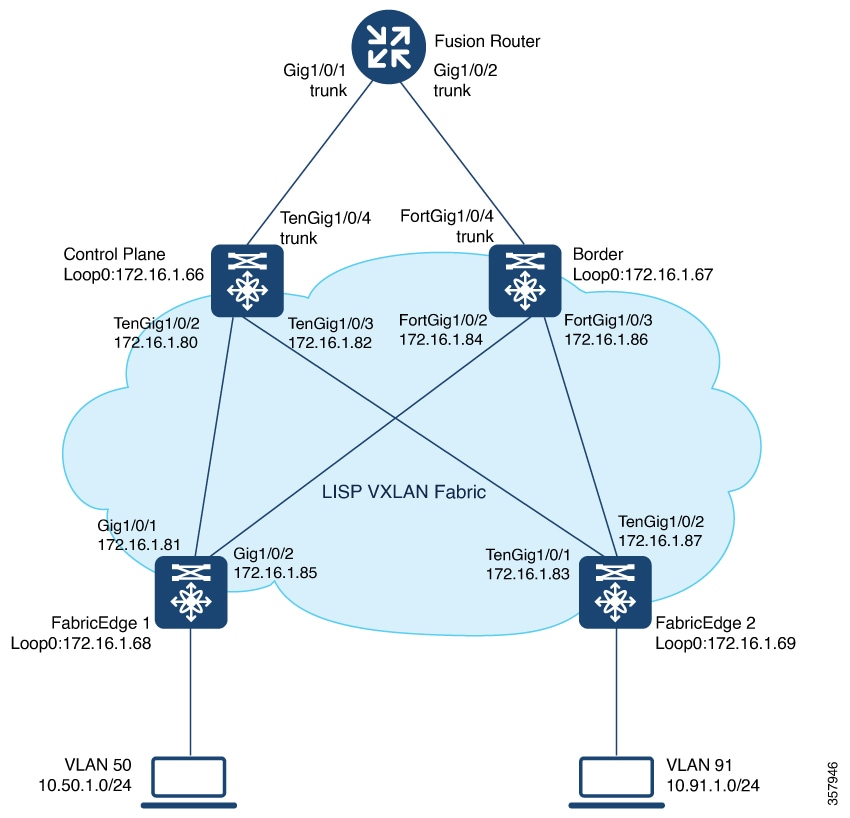
View a summary of the LISP sessions that are created on the edge node:
FabricEdge# show lisp session
Sessions for VRF default, total: 2, established: 2
Peer State Up/Down In/Out Users
172.16.1.66:4342 Up 1d04h 27/9 14
172.16.1.67:4342 Up 1d03h 19/9 14
FabricEdge#
View the LISP session with the Control Plane Node (172.16.1.66) :
FabricEdge# show lisp session 172.16.1.66 port 4342
Peer address: 172.16.1.66:4342
Local address: 172.16.1.69:27785
Session Type: Active
Session State: Up (1d04h)
Messages in/out: 27/9
Bytes in/out: 1666/276
Fatal errors: 0
Rcvd unsupported: 0
Rcvd invalid VRF: 0
Rcvd override: 0
Rcvd malformed: 0
Sent deferred: 0
SSO redundancy: N/A
Auth Type: None
Accepting Users: 0
Users: 14
Type ID In/Out State
Pubsub subscriber lisp 0 IID 4097 AFI IPv4 1/0 Idle
Pubsub subscriber lisp 0 IID 4097 AFI IPv6 1/0 Idle
Pubsub subscriber lisp 0 IID 4099 AFI IPv4 1/0 Idle
Pubsub subscriber lisp 0 IID 4099 AFI IPv6 1/0 Idle
Pubsub subscriber lisp 0 IID 8194 AFI MAC 2/0 Idle
Pubsub subscriber lisp 0 IID 8197 AFI MAC 2/0 Idle
Capability Exchange N/A 1/1 waiting
ETR Reliable Registration lisp 0 IID 4097 AFI IPv4 0/1 TCP
ETR Reliable Registration lisp 0 IID 4097 AFI IPv6 0/1 TCP
ETR Reliable Registration lisp 0 IID 4099 AFI IPv4 0/1 TCP
ETR Reliable Registration lisp 0 IID 4099 AFI IPv6 0/1 TCP
ETR Reliable Registration lisp 0 IID 8194 AFI MAC 0/1 TCP
ETR Reliable Registration lisp 0 IID 8197 AFI MAC 0/1 TCP
ETR Reliable Registration lisp 0 IID 16777214 AFI IPv4 13/2 TCP
FabricEdge#
View the Locator set information:
FabricEdge# show lisp locator-set
LISP Locator-set information:
172.16.1.68, local, reachable, loopback
View the dynamic interfaces that are created after configuring LISP instances:
FabricEdge# show ip interface brief | i LISP
L2LISP0 172.16.1.68 YES unset up up
L2LISP0.8194 172.16.1.68 YES unset up up
L2LISP0.8197 172.16.1.68 YES unset up up
LISP0 unassigned YES unset up up
LISP0.4097 172.16.1.68 YES unset up up
LISP0.4099 10.50.1.1 YES unset up up
FabricEdge#
View the IPv4 map-cache entries:
FabricEdge# show lisp instance-id 4099 ipv4 map-cache
LISP IPv4 Mapping Cache for LISP 0 EID-table vrf VN3 (IID 4099), 2 entries
0.0.0.0/0, uptime: 18:03:23, expires: 00:12:10, via map-reply, unknown-eid-forward
action: send-map-request + Encapsulating to proxy ETR
PETR Uptime State Pri/Wgt Encap-IID Metric
172.16.1.67 18:03:23 up 10/10 - 0
10.50.1.0/24, uptime: 19:59:51, expires: never, via dynamic-EID, send-map-request
Negative cache entry, action: send-map-request
View the LISP EID statistics related to packet encapsulations, decapsulations, map requests, map replies, map registers, and
other LISP-related packets:
FabricEdge# show lisp service ipv4 statistics
LISP EID Statistics for all EID instances - last cleared: never
Control Packets:
Map-Requests in/out: 2/2465
Map-Requests in (5 sec/1 min/5 min): 0/0/0
Encapsulated Map-Requests in/out: 0/2465
RLOC-probe Map-Requests in/out: 2/0
SMR-based Map-Requests in/out: 2/0
Extranet SMR cross-IID Map-Requests in: 0
Map-Requests expired on-queue/no-reply 0/493
Map-Resolver Map-Requests forwarded: 0
Map-Server Map-Requests forwarded: 0
Map-Reply records in/out: 0/0
Authoritative records in/out: 0/0
Non-authoritative records in/out: 0/0
Negative records in/out: 0/0
RLOC-probe records in/out: 0/0
Map-Server Proxy-Reply records out: 0
WLC Map-Subscribe records in/out: 0/11
Map-Subscribe failures in/out: 0/0
WLC Map-Unsubscribe records in/out: 0/0
Map-Unsubscribe failures in/out: 0/0
Map-Register records in/out: 0/150
Map-Registers in (5 sec/1 min/5 min): 0/0/0
Map-Server AF disabled: 0
Not valid site eid prefix: 0
Authentication failures: 0
Disallowed locators: 0
Miscellaneous: 0
WLC Map-Register records in/out: 0/0
WLC AP Map-Register in/out: 0/0
WLC Client Map-Register in/out: 0/0
WLC Map-Register failures in/out: 0/0
Map-Notify records in/out: 24/0
Authentication failures: 0
WLC Map-Notify records in/out: 0/0
WLC AP Map-Notify in/out: 0/0
WLC Client Map-Notify in/out: 0/0
WLC Map-Notify failures in/out: 0/0
Publish-Subscribe in/out:
Subscription Request records in/out: 0/0
IID subscription requests in/out: 0/0
Pub-refresh subscription requests in/out: 0/0
Policy subscription requests in/out: 0/0
Subscription Request failures in/out: 0/0
Subscription Status records in/out: 0/0
End of Publication records in/out: 0/0
Subscription rejected records in/out: 0/0
Subscription removed records in/out: 0/0
Subscription Status failures in/out: 0/0
Solicit Subscription records in/out: 21/0
Solicit Subscription failures in/out: 0/0
Publication records in/out: 0/0
Publication failures in/out: 0/0
Errors:
Mapping record TTL alerts: 0
Map-Request invalid source rloc drops: 0
Map-Register invalid source rloc drops: 0
DDT Requests failed: 0
DDT ITR Map-Requests dropped: 0 (nonce-collision: 0, bad-xTR-nonce: 0)
Cache Related:
Cache entries created/deleted: 7/4
NSF CEF replay entry count 0
Number of rejected EID-prefixes due to limit: 0
Forwarding:
Number of data signals processed: 0 (+ dropped 0)
Number of reachability reports: 0 (+ dropped 0)
Number of SMR signals dropped: 0
LISP RLOC Statistics - last cleared: never
Control Packets:
RTR Map-Requests forwarded: 0
RTR Map-Notifies forwarded: 0
DDT-Map-Requests in/out: 0/0
DDT-Map-Referrals in/out: 0/0
Errors:
Map-Request format errors: 0
Map-Reply format errors: 0
Map-Referral format errors: 0
LISP Miscellaneous Statistics - last cleared: never
Errors:
Invalid IP version drops: 0
Invalid IP header drops: 0
Invalid IP proto field drops: 0
Invalid packet size drops: 0
Invalid LISP control port drops: 0
Invalid LISP checksum drops: 0
Unsupported LISP packet type drops: 0
Unknown packet drops: 0
FabricEdge#
View a summary of the IPv4 service instances on the fabric edge node:
FabricEdge# show lisp service ipv4 summary
Router-lisp ID: 0
Instance count: 5
Key: DB - Local EID Database entry count (@ - RLOC check pending
* - RLOC consistency problem),
DB no route - Local EID DB entries with no matching RIB route,
Cache - Remote EID mapping cache size, IID - Instance ID,
Role - Configured Role
Interface DB DB no Cache Incom Cache
EID VRF name (.IID) size route size plete Idle Role
default LISP0.4097 1 0 1 0.0% 0.0% ETR-PITR
VN3 LISP0.4099 1 0 2 0.0% 0.0% ETR-PITR
Number of eid-tables: 2
Total number of database entries: 2 (inactive 0)
Maximum database entries: 214528
EID-tables with inconsistent locators: 0
Total number of map-cache entries: 3
Maximum map-cache entries: 214528
EID-tables with incomplete map-cache entries: 0
EID-tables pending map-cache update to FIB: 0
FabricEdge#
View the details of the routing table that is created when a Layer 3 VRF is configured:
FabricEdge# show ip route vrf VN3
Routing Table: VN3
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, m - OMP
n - NAT, Ni - NAT inside, No - NAT outside, Nd - NAT DIA
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
H - NHRP, G - NHRP registered, g - NHRP registration summary
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, l - LISP
a - application route
+ - replicated route, % - next hop override, p - overrides from PfR
& - replicated local route overrides by connected
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 10.50.1.0/24 is directly connected, Vlan50
L 10.50.1.1/32 is directly connected, Vlan50
FabricEdge#

 Feedback
Feedback