Understanding Malware Protection and File Control
License: Protection, Malware, or Any
Using the advanced malware protection feature, you can configure the ASA FirePOWER module to detect, track, analyze, and optionally block malware files being transmitted on your network.
The system can detect and optionally block malware in many types of files, including PDFs, Microsoft Office documents, and others. ASA FirePOWER modules monitor specific application protocol-based network traffic for transmissions of those file types. When the ASA FirePOWER module detects an eligible file, the ASA FirePOWER module then performs a malware cloud lookup using the file’s SHA-256 hash value. Based on these results, the Cisco cloud returns a file disposition to the ASA FirePOWER module.
If a file has a disposition in the cloud that you know to be incorrect, you can add the file’s SHA-256 value to a file list:
-
To treat a file as if the cloud assigned a clean disposition, add the file to the clean list .
-
To treat a file as if the cloud assigned a malware disposition, add the file to the custom detection list.
If the system detects a file’s SHA-256 value on a file list, it takes the appropriate action without performing a malware lookup or checking the file disposition. Note that you must configure a rule in the file policy with either a Malware Cloud Lookup or Block Malware action and a matching file type to calculate a file’s SHA value. You can enable use of the clean list or custom detection list on a per-file-policy basis.
To inspect or block files, you must enable a Protection license on the ASA FirePOWER module. To add files to a file list, you must also enable a Malware license.
Understanding File Dispositions
The system determines file dispositions based on the disposition returned by the Cisco cloud. A file can have one of the following file dispositions returned by the Cisco cloud, as a result of addition to a file list, or due to threat score:
-
Malware indicates that the cloud categorized the file as malware.
-
Clean indicates that the cloud categorized the file as clean, or that a user added the file to the clean list.
-
Unknown indicates that a malware cloud lookup occurred before the cloud assigned a disposition. The cloud has not categorized the file.
-
Custom Detection indicates that a user added the file to the custom detection list.
-
Unavailable indicates that the ASA FirePOWER module could not perform a malware cloud lookup. You may see a small percentage of events with this disposition; this is expected behavior.
 Tip |
If you see several Unavailable malware events in quick succession, check your cloud connection and port configuration. For more information, see Security, Internet Access, and Communication Ports. |
Based on the file disposition, the ASA FirePOWER module either blocks the file or blocks its upload or download. To improve performance, if the system already knows the disposition for a file based on its SHA-256 value, your appliance uses the cached disposition rather than querying the Cisco cloud.
Note that file dispositions can change. For example, the cloud can determine that a file that was previously thought to be clean is now identified as malware, or the reverse—that a malware-identified file is actually clean. When the disposition changes for a file for which you performed a malware lookup in the last week, the cloud notifies the ASA FirePOWER module so the system can take appropriate action the next time it detects that file being transmitted. A changed file disposition is called a retrospective disposition.
File dispositions returned from a malware cloud lookup have a time-to-live (TTL) value. After a file disposition has been held for the duration specified in the TTL value without update, the system purges the cached information. Dispositions have the following TTL values:
-
Clean—4 hours
-
Unknown—1 hour
-
Malware—1 hour
If a malware cloud lookup against the cache identifies a cached disposition that timed out, the system performs a fresh lookup to determine a file disposition.
Understanding File Control
If your organization wants to block not only the transmission of malware files, but all files of a specific type (regardless of whether the files contain malware), the file control feature allows you to cast a wider net. As with malware protection, the ASA FirePOWER module monitors network traffic for transmissions of specific file types, then either blocks or allows the file.
File control is supported for all file types where the system can detect malware, plus many additional file types. These file types are grouped into basic categories, including multimedia (swf, mp3), executables (exe, torrent), and PDFs. Note that file control, unlike malware protection, does not require queries of the Cisco cloud.
Configuring Malware Protection and File Control
License: Protection or Malware
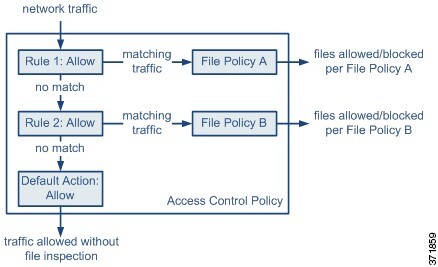
You configure malware protection and file control as part of your overall access control configuration by associating file policies with access control rules. This association ensures that before the system passes a file in traffic that matches an access control rule’s conditions, it first inspects the file.
A file policy, like its parent access control policy, contains rules that determine how the system handles files that match the conditions of each rule. You can configure separate file rules to take different actions for different file types, application protocols, or directions of transfer.
When a file matches a rule, the rule can:
-
allow or block files based on simple file type matching
-
block files based on malware file disposition
In addition, the file policy can automatically treat a file as if it is clean or malware based on entries in the clean list or custom detection list
As a simple example, you could implement a file policy that blocks your users from downloading executable files. For detailed information on file policies and associating them with access control rules, see Understanding and Creating File Policies.
Logging Events Based on Malware Protection and File Control
License: Protection or Malware
The ASA FirePOWER module logs records of the system’s file inspection and handling file events, and malware events:
-
File events represent files that the system detected, and optionally blocked, in network traffic.
-
Malware events represent malware files detected, and optionally blocked, in network traffic by the system.
-
Retrospective malware events represent files whose malware file dispositions have changed.
When the system generates a malware event based on detection or blocking of malware in network traffic, it also generates a file event, because to detect malware in a file the system must first detect the file itself.

 that indicates the number of files (including malware files) detected in the connection; click the icon to see a list of those
files and, for malware files, their file dispositions.
that indicates the number of files (including malware files) detected in the connection; click the icon to see a list of those
files and, for malware files, their file dispositions.
 Feedback
Feedback