Overview of Cisco LTE and 5G
Only the C8151-G2 and C8161-G2 routers support Cisco LTE and 5G using Pluggable Interface Modules (PIMs):
|
Pluggable Interface Modules |
Pluggable Interface Modules technology |
|---|---|
|
P-5GS6-R16SA-GL |
5G Sub-6 GHz Pluggable Interface Module |
|
P-LTEA7-NA |
CAT7 LTE Pluggable for North America |
|
P-LTEA7-JP |
CAT7 LTE Advanced PIM for Japan |
|
P-LTEA7-EAL |
CAT7 LTE Advanced PIM for EMEA, APAC, LATAM |
Cisco LTE/5G supports the following modes:
-
5G —5G is the next step in the evolution of mobile communications. It is a new global wireless standard after 1G, 2G, 3G, and 4G networks. 5G wireless technology is meant to deliver higher multi-Gbps peak data speeds, ultra low latency, increased availability, massive network capacity, more reliability, and a more uniform user experience to more users.
-
4G LTE —4G LTE mobile specification provides multi-megabit bandwidth, more efficient radio network, latency reduction, and improved mobility. LTE solutions target new cellular networks. These networks initially support up to 300 Mb/s peak rates in the downlink and up to 50 Mb/s peak rates in the uplink.
The following table describes the Cisco 4G LTE Cat 7 SKUs:
|
Radio Access Technology (RAT) |
Bands |
|---|---|
|
LTE |
B2, B4, B5, B7, B12, B13, B14, B25, B26, B41, B42, B43, B48, B66, B71 |
|
WCDMA |
B2, B4, B5 |
|
Radio Access Technology (RAT) |
Bands |
|---|---|
|
5GNR Sub-6G |
n1, n2, n3, n5, n7, n8, n12, n13, n14, n18, n20, n25, n26, n28, n29, n30, n38, n39, n40, n41, n48, n66, n70, n71, n75, n76, n77, n78, n79 |
|
LTE |
B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B7, B8, B12, B13, B14, B18, B19, B20, B21, B25, B26, B28, B29, B30, B32, B34, B38, B39, B40, B41, B42, B43, B46, B48, B66, B71 |
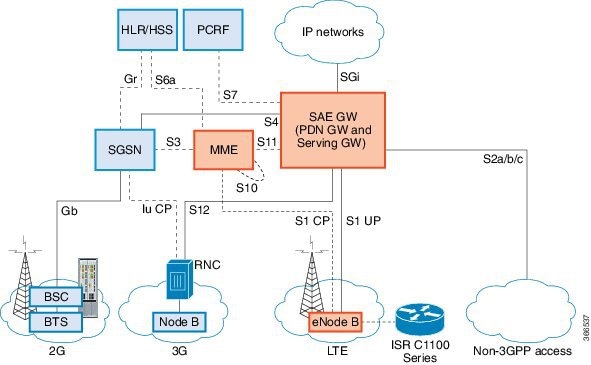
The following figure explains the 4G LTE packet core network architecture.
|
Gateways |
The Serving Gateway (SGW) routes and forwards user data packets, while also acting as the mobility anchor for the user plane, and is the anchor for mobility between LTE and other 3GPP technologies. The Packet Data Network (PDN) Gateway (PGW) provides connectivity from the User Equipment (UE) to external packet data networks by being the point of exit and entry of traffic for the UE. A UE may have simultaneous connectivity with more than one PGW for accessing multiple PDNs. The PGW performs policy enforcement, packet filtering for each user, charging support, lawful interception, and packet screening. Another key role of the PGW is to act as the anchor for mobility between 3GPP and non-3GPP technologies such as WiMAX and 3GPP2 (CDMA 1X and EvDO). The System Architecture Evolution GW (SAE GW) is the entity that covers the PGW and SGW functionality in the Evolved Packet Core (EPC). |
|
RNC |
The Radio Network Controller (RNC) is responsible for controlling the Radio Access Network (RAN) that are connected to it. The RNC carries out radio resource management and some of the mobility management functions and is the point where encryption is done before user data is sent to and from the mobile. The RNC connects to the Circuit-Switched Core Network through the Media Gateway (MGW). |
|
BTS |
Base Transceiver Station. |
|
BSC |
Base Station Controller. |
|
SGSN |
Service GPRS Support Node. |


 Feedback
Feedback