- Preface
- New and Changed Information
- Understanding the Carrier Packet Transport System
- Hardware
- Configuring Ethernet Virtual Circuit
- Configuring Multiprotocol Label Switching
- Configuring MPLS–Transport Profile
- Configuring Pseudowire
- Configuring Virtual Private LAN Services
- Configuring Quality of Service
- Configuring High Availability
- Configuring Resilient Ethernet Protocol
- Configuring Link Aggregation Group and Link Aggregation Control Protocol
- Configuring Span
- Configuring MAC Learning
- Configuring Multicast VLAN Registration
- Configuring IGMP Snooping
- Configuring Ethernet OAM, Connectivity Fault Management, and Y.1731
- Configuring Synchronous Ethernet
- Configuring Performance Monitoring, RMON, OTN, and Port Provisioning
- Configuring Local Authentication
- Configuring Cisco Discovery Protocol
- Alarm Troubleshooting
- SNMP
- CPT Error Messages
- Support for MSTP Cards
- Network Element Defaults
- Index
- Ethernet Link OAM Overview
- Understanding Ethernet Link OAM
- Ethernet Link OAM Features
- Discovery
- Link Monitoring
- DLP-J321 Enable or Disable Link Monitoring Support on an Interface Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J315 Enable or Disable Link Monitoring Support on an Interface Using CTC
- DLP-J322 Enable or Disable Link Monitoring on an Interface Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J316 Enable or Disable Link Monitoring on an Interface Using CTC
- DLP-J323 Configure Link Monitoring Parameters on an Interface Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J317 Configure Link Monitoring Parameters on an Interface Using CTC
- Remote Failure Indication
- Remote Loopback
- Understanding Maintenance End Points
- Understanding Up MEPs
- Understanding Down MEPs
- Understanding Port MEPs
- Understanding the Cross-Check Function
- DLP-J310 Create a Port MEP Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J321 Create an MEP for an EFP Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J319 Define MEPs Statically within a Maintenance Association Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J318 Specify the Number of MEPs in a Maintenance Association Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J323 Configure Cross-Check for an MEP Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J306 Create an MEP Using CTC
- Understanding Continuity Check Messages
- DLP-J316 Enable the Transmission of Continuity Check Messages Using Cisco IOS Commands
- Understanding Loopback Messages
- Understanding Linktrace Messages
- DLP-J324 Send CFM Loopback and Linktrace Messages Using Cisco IOS Commands
- NTP-J107 Perform ping and traceroute Operations on Services Using CTC
- NTP-J116 Configure Y.1731 Fault Management Parameters
- DLP-J349 Configure ETH-AIS Parameters Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J350 Clear AIS Alarms Using CTC
- DLP-J351 Configure ETH-LCK Parameters Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J352 Lock an MEP or an Interface Using CTC
- DLP-J353 Enable Y.1731 Fault Management Parameters Using CTC
- NTP-J117 Configure and Schedule Two-Way Delay Measurement
- DLP-J354 Configure and Schedule Two-Way Delay Measurement Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J355 Configure and Schedule Two-Way Delay Measurement Using CTC
- DLP-J356 Display IP SLA Configuration and Statistics Using CTC
- Troubleshooting an IP SLA Session
- Show Commands
Configuring Ethernet OAM, Connectivity Fault Management, and Y.1731
This chapter describes Ethernet OAM, Connectivity Fault Management (CFM), and Y.1731 features. This chapter also describes procedures to configure Ethernet OAM, CFM, and Y.1731.
This chapter includes the following topics:
- Ethernet Link OAM Overview
- Understanding Ethernet Link OAM
- Ethernet Link OAM Features
- Understanding Ethernet OAM Messages
- Understanding Connectivity Fault Management
- CFM Limitations and Restrictions in CPT
- NTP-J106 Configure CFM Using Cisco IOS Commands
- NTP-J105 Configure CFM Using CTC
- DLP-J305 Enable or Disable CFM on the CPT System Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J299 Enable or Disable CFM on the CPT System Using CTC
- DLP-J308 Enable or Disable CFM on an Interface Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J300 Enable or Disable CFM for Each Port or Channel Group Using CTC
- DLP-J312 Enable Caching of CFM Data Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J313 Enable Caching of CFM Data Using CTC
- Understanding Maintenance Domain
- Understanding Maintenance Association
- Understanding Maintenance Point
- Understanding Maintenance Intermediate Points
- Understanding CFM Messages
- Understanding Continuity Check Traps and Cross-Check Traps
- Understanding Y.1731
- Understanding Y.1731 Fault Management
- Understanding Y.1731 Performance Monitoring
Ethernet Link OAM Overview
Ethernet Link Operations, Administration, and Maintenance (OAM) is a protocol for installing, monitoring, and troubleshooting Ethernet metropolitan-area networks (MANs) and Ethernet WANs. It relies on an optional sublayer in the data link layer of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model, as specified in IEEE 802.3ah-2004 Clause 57.
Ethernet Link OAM enables service providers to monitor and troubleshoot a single physical (or emulated) Ethernet link. It supports link level verification, monitoring, and troubleshooting between two Ethernet devices. It is particularly valuable in the 'first mile' connection to the customer demarcation.
Understanding Ethernet Link OAM
Ethernet link OAM can be implemented on any full-duplex point-to-point or emulated point-to-point Ethernet link. A system-wide implementation is not required; OAM can be deployed for part of a system; that is, on specific interfaces.
Normal link operation does not require Ethernet link OAM. OAM frames, called OAM protocol data units (PDUs), use the slow protocol destination MAC address 0180.c200.0002. They are intercepted by the MAC sublayer and cannot propagate beyond a single hop within an Ethernet network.
Ethernet link OAM is a relatively slow protocol with modest bandwidth requirements. The frame transmission rate is limited to a maximum of 10 frames per second; therefore, the impact of OAM on normal operations is negligible. However, when link monitoring is enabled, the CPU must poll error counters frequently. In this case, the required CPU cycles will be proportional to the number of interfaces that have to be polled.
Two major components, the OAM client and the OAM sublayer, make up Ethernet Link OAM. The following two sections describe these components.
OAM Client
The OAM client is responsible for establishing and managing Ethernet link OAM on a link. It also enables and configures the OAM sublayer. During the OAM discovery phase, the OAM client monitors OAM PDUs received from the remote peer and enables OAM functionality on the link based on the local and remote state as well as configuration settings. After the discovery phase (at steady state), the OAM client is also responsible for managing the rules of response to OAM PDUs and the OAM remote loopback mode.
OAM Sublayer
The OAM sublayer presents two standard IEEE 802.3 MAC service interfaces: one facing the superior sublayers, which include the MAC client (or link aggregation), and the other interface facing the subordinate MAC control sublayer. The OAM sublayer provides a dedicated interface for passing OAM control information and OAM PDUs to and from a client. The OAM sublayer is made up of three components: control block, multiplexer, and packet parser (p-parser).
The control block provides the interface between the OAM client and other blocks internal to the OAM sublayer. The control block runs the discovery process, which detects the existence and capabilities of remote OAM peers. It also includes the transmit process that governs the transmission of OAM PDUs to the multiplexer and a set of rules that govern the receipt of OAM PDUs from the p-parser.
The multiplexer manages frames generated (or relayed) from the MAC client, control block, and p-parser. The multiplexer passes through frames generated by the MAC client untouched. It passes OAM PDUs generated by the control block to the subordinate sublayer; such as the MAC sublayer. Similarly, the multiplexer passes loopback frames from the p-parser to the same subordinate sublayer when the interface is in OAM remote loopback mode.
The p-parser classifies frames as OAM PDUs, MAC client frames, or loopback frames and then dispatches each class to the appropriate entity. OAM PDUs are sent to the control block; MAC client frames are passed to the superior sublayer; and loopback frames are dispatched to the multiplexer.
- Benefits of Ethernet Link OAM
- NTP-J114 Configure EFM Using Cisco IOS Commands
- NTP-J115 Configure EFM Using CTC
- DLP-J320 Enable or Disable Ethernet Link OAM on an Interface Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J314 Enable or Disable Ethernet Link OAM on a Port Using CTC
Benefits of Ethernet Link OAM
Ethernet Link OAM provides the following benefits:
NTP-J114 Configure EFM Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure configures EFM using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
NTP-J115 Configure EFM Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure configures EFM using CTC. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
DLP-J320 Enable or Disable Ethernet Link OAM on an Interface Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure enables or disables Ethernet Link OAM on an interface using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
DLP-J314 Enable or Disable Ethernet Link OAM on a Port Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure enables or disables Ethernet link OAM on a port using CTC. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node where you want to enable or disable Ethernet link OAM on a port. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Step 3 | The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. Click the Provisioning > EFM > Configuration tabs. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Step 4 | In the Configuration area, expand the appropriate slot and select the port where you want to enable the Ethernet link OAM. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Step 5 | From the EFM State drop-down list, choose Enabled to enable Ethernet link OAM on the selected port. Choose Disabled to disable Ethernet link OAM on the selected port.
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Step 6 | In the Configuration area, expand the appropriate slot and modify any of the parameters as described in the following table.
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Step 7 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
Ethernet Link OAM Features
The Cisco CPT supports the following Ethernet link OAM features:
Discovery
Discovery is the first phase of Ethernet link OAM where it identifies the devices in the network and their OAM capabilities. Discovery uses information OAM PDUs. During the discovery phase, the following information is advertised within periodic information OAM PDUs:
OAM mode—Conveyed to the remote OAM entity. The mode can be either active or passive and can be used to determine device functionality.
OAM configuration (capabilities)—Advertises the capabilities of the local OAM entity. With this information a peer can determine what functions are supported and accessible; for example, loopback capability.
OAM PDU configuration—Includes the maximum OAM PDU size for receipt and delivery. This information along with the rate limiting of 10 frames per second can be used to limit the bandwidth allocated to the OAM traffic.
Platform identity—Specifies a combination of an organization unique identifier (OUI) and 32-bits of vendor-specific information. OUI allocation, controlled by the IEEE, is typically the first three bytes of a MAC address.
Discovery includes an optional phase in which the local station can accept or reject the configuration of the peer OAM entity. For example, a node may require its partner support loopback capability to be accepted in the management network. These policy decisions may be implemented as vendor-specific extensions.
Link Monitoring
Link monitoring in Ethernet Link OAM detects and indicates link faults under a variety of conditions. Link monitoring uses the event notification OAM PDU and sends events to the remote OAM entity when there are problems detected on the link. The error events include the following:
Error Frame (error frames per second)—The number of frame errors detected during a specified period that exceed a threshold.
Error Frame Period (error frames per n frames)—The number of frame errors within the last n frames that exceed a threshold.
Error Frame Seconds Summary (error seconds per m seconds)—The number of error seconds (1-second intervals with at least one frame error) within the last m seconds that exceed a threshold.
Because IEEE 802.3ah OAM does not provide a guaranteed delivery of any OAM PDU, the event notification OAM PDU may be sent multiple times to reduce the probability of a lost notification. A sequence number is used to recognize duplicate events.
- DLP-J321 Enable or Disable Link Monitoring Support on an Interface Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J315 Enable or Disable Link Monitoring Support on an Interface Using CTC
- DLP-J322 Enable or Disable Link Monitoring on an Interface Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J316 Enable or Disable Link Monitoring on an Interface Using CTC
- DLP-J323 Configure Link Monitoring Parameters on an Interface Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J317 Configure Link Monitoring Parameters on an Interface Using CTC
DLP-J321 Enable or Disable Link Monitoring Support on an Interface Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure enables or disables link monitoring support on an interface using Cisco IOS Commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
DLP-J315 Enable or Disable Link Monitoring Support on an Interface Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure enables or disables support for link monitoring on an interface using CTC. This procedure helps establish an OAM session for performing OAM functions, such as remote loopback. For example, if the device is connected to a third-party device that does not support link monitoring, then link monitoring support must be disabled on the device to establish an OAM session with the third-party device. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node where you want to enable or disable link monitoring support on an interface. |
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. |
| Step 3 | The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. Click the Provisioning > EFM > Link Monitoring tabs |
| Step 4 | In the Link Monitoring area, expand the appropriate slot and select the port where you want to enable link monitoring. |
| Step 5 | From the Support drop-down list, choose Support to enable link monitoring support or choose No support to disable link monitoring support on the interface. |
| Step 6 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
DLP-J322 Enable or Disable Link Monitoring on an Interface Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure enables or disables link monitoring on an interface using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
DLP-J316 Enable or Disable Link Monitoring on an Interface Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure enables or disables link monitoring on an interface using CTC. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
 Note | Link monitoring is enabled by default when Ethernet Link OAM is enabled on a interface. |
When link monitoring is enabled, the interface sends event OAM PDUs when errors occur and interprets event OAM PDUs from the remote peer. Link monitoring can be effective only if both the local client and remote peer agree to support it.
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node where you want to enable or disable link monitoring on an interface. |
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. |
| Step 3 | The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. Click the Provisioning > EFM > Link Monitoring tabs |
| Step 4 | In the Link Monitoring area, expand the appropriate slot and select the port where you want to enable link monitoring. |
| Step 5 | From the Enable drop-down list, choose Enable to enable link monitoring or choose Disable to disable link monitoring on the interface. |
| Step 6 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
DLP-J323 Configure Link Monitoring Parameters on an Interface Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure configures link monitoring parameters on an interface using Cisco IOS Commands.
|
||
| Tools/Equipment | None | ||
| Prerequisite Procedures | None | ||
| Required/As Needed | As needed | ||
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote | ||
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
DLP-J317 Configure Link Monitoring Parameters on an Interface Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure configures the link monitoring parameters on an interface using CTC. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node where you want to configure link monitoring parameters on an interface. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Step 3 | The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. Click the Provisioning > EFM > Link Monitoring tabs | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Step 4 | In the Link Monitoring area, expand the appropriate slot and modify any of the parameters as described in the following table.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Step 5 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
Remote Failure Indication
Faults in Ethernet connectivity that are caused by slowly deteriorating quality are difficult to detect. Ethernet Link OAM provides a mechanism for an OAM entity to convey these failure conditions to its peer via specific flags in the OAM PDU. The following failure conditions can be communicated:
Link Fault–Loss of signal is detected by the receiver. A link fault is sent every second in the information OAM PDU. Link fault applies only when the physical sublayer is capable of independently transmitting and receiving signals.
Dying Gasp–An unrecoverable condition has occurred; for example, a power failure. This type of condition is vendor specific. A notification about the condition may be sent immediately and continuously.
Critical Event–An unspecified critical event has occurred. This type of event is vendor specific. A critical event may be sent immediately and continuously.
- DLP-J325 Configure the Port for Remote Link Failure Indication Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J319 Configure the Port for Remote Link Failure Indication Using CTC
DLP-J325 Configure the Port for Remote Link Failure Indication Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure configures the port for remote link failure indication using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
DLP-J319 Configure the Port for Remote Link Failure Indication Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure configures the port for remote link failure indication using CTC. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node where you want to configure the port for remote link failure indication. | ||||||||||||
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. | ||||||||||||
| Step 3 | The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. Click the Provisioning > EFM > Configuration tabs | ||||||||||||
| Step 4 | In the Configuration area, expand the appropriate slot and modify any of the parameters as described in the following table.
| ||||||||||||
| Step 5 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
Remote Loopback
An OAM entity can put its remote peer into loopback mode using the loopback control OAM PDU. Loopback mode helps an administrator ensure the quality of links during installation or when troubleshooting. In loopback mode, every frame received is transmitted back on the same port except for OAM PDUs and pause frames. The periodic exchange of OAM PDUs must continue during the loopback state to maintain the OAM session.
The loopback command is acknowledged by responding with an information OAM PDU with the loopback state indicated in the State field. This acknowledgement allows an administrator, for example, to estimate if a network segment can satisfy a service-level agreement. Acknowledgement makes it possible to test delay, jitter, and throughput.
When an interface is set to the remote loopback mode the interface no longer participates in any other Layer 2 or Layer 3 protocols; for example Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) or Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). This is because when two connected ports are in a loopback session, no frames other than the OAM PDUs are sent to the CPU for software processing. The non-OAM PDU frames are either looped back at the MAC level or discarded at the MAC level.
From a user perspective, an interface in a loopback mode is in a link-up state.
- DLP-J367 Set Up Remote Loopback Timeout Period on an Interface Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J324 Enable Remote Loopback on an Interface Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J318 Enable Remote Loopback on an Interface Using CTC
DLP-J367 Set Up Remote Loopback Timeout Period on an Interface Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure sets up remote loopback timeout period on an interface using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
DLP-J324 Enable Remote Loopback on an Interface Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure enables remote loopback on an interface using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | DLP-J367 Set Up Remote Loopback Timeout Period on an Interface Using Cisco IOS Commands |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
DLP-J318 Enable Remote Loopback on an Interface Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure enables remote loopback on an interface using CTC. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node where you want to enable remote loopback on an interface. | |||||||||||||||
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. | |||||||||||||||
| Step 3 | The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. Click the Provisioning > EFM > Remote Loopback tabs | |||||||||||||||
| Step 4 | In the Remote Loopback area, expand the appropriate slot and modify any of the parameters as described in the following table.
|
Understanding Ethernet OAM Messages
Ethernet OAM messages or OAM PDUs are standard length, untagged Ethernet frames within the normal frame length bounds of 64 to 1518 bytes. The maximum OAM PDU frame size exchanged between two peers is negotiated during the discovery phase.
OAM PDUs always have the destination address of slow protocols (0180.c200.0002) and an Ethertype of 8809. OAM PDUs do not go beyond a single hop and have a hard-set maximum transmission rate of 10 OAM PDUs per second. Some OAM PDU types may be transmitted multiple times to increase the likelihood that they will be successfully received on a deteriorating link.
Four types of OAM messages are supported:
Information OAM PDU—A variable-length OAM PDU that is used for discovery. This OAM PDU includes local, remote, and organization-specific information.
Event notification OAM PDU—A variable-length OAM PDU that is used for link monitoring. This type of OAM PDU may be transmitted multiple times to increase the chance of a successful receipt; for example, in the case of high-bit errors. Event notification OAM PDUs also may include a time stamp when generated.
Loopback control OAM PDU—An OAM PDU fixed at 64 bytes in length that is used to enable or disable the remote loopback command.
Vendor-specific OAM PDU—A variable-length OAM PDU that allows the addition of vendor-specific extensions to OAM.
Understanding Connectivity Fault Management
Ethernet Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) is an end-to-end per-service Ethernet layer operations, administration, and maintenance (OAM) protocol. It includes proactive connectivity monitoring, fault verification, and fault isolation for large Ethernet metropolitan-area networks (MANs) and WANs.
CPT supports the IEEE 802.1ag standard implementation of CFM. It supports CFM over the following:
Point–to–multipoint bridge domain associated with Ethernet Flow Points (EFP)
Xconnect
Port Maintenance End Point (MEP)
All the CFM configurations specific to point–to–multipoint EFPs also apply to Xconnect.
Understanding IEEE CFM
IEEE CFM is an end-to-end per-service Ethernet layer OAM protocol that supports provider edge-to-provider edge (PE-to-PE) and customer edge-to-customer edge (CE-to-CE) services. A service is identified as an Ethernet virtual circuit (EVC) service.
Troubleshooting carrier networks offering Ethernet Layer 2 services is challenging. Customers contract with service providers for end-to-end Ethernet service and service providers may subcontract with operators to provide equipment and networks. Compared to enterprise networks, where Ethernet traditionally has been implemented, these constituent networks belong to distinct organizations or departments, are substantially larger and more complex, and have a wider user base. Ethernet CFM provides a competitive advantage to service providers for which the operational management of link uptime and timeliness in isolating and responding to failures is crucial to daily operations.
Benefits of IEEE CFM
CFM Limitations and Restrictions in CPT
CFM over the point–to–point bridge domain is not supported.
CFM over Virtual Private LAN Service (VPLS) is not supported.
Maximum number of Maintenance End Points (MEPs) supported on a CPT system is 16000 depending on the Continuity Check (CC) interval.
Maximum number of Maintenance Intermediate Points (MIPs) supported on a CPT system is 16000.
CFM alarms in CTC is not supported.
CFM over VLAN based forwarding is not supported.
CFM is not supported on a bridge domain that has the split horizon configured.
CFM handles blocked ports only for tagged packets as REP operates only on tagged packets.
The following table specifies the number of supported remote and local MEPs depending on the configured CC interval.
| CC Interval | Number of Remote MEPS | Number of Local MEPs |
|---|---|---|
| 100 milliseconds | 100 | 100 |
| 1 second | 1000 | 1000 |
| 10 seconds | 8000 | 8000 |
| 1 minute | 16000 | 16000 |
| 10 minutes | 16000 | 16000 |
NTP-J106 Configure CFM Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure configures CFM using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
NTP-J105 Configure CFM Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure configures CFM using CTC. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
DLP-J305 Enable or Disable CFM on the CPT System Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure enables or disables Ethernet CFM globally on the CPT system using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
Example: Enable or Disable CFM on the System
The following example shows how to enable CFM on the system using Cisco IOS commands:
Router> enable Router# configure terminal Router(config)# ethernet cfm global
The following example shows how to disable CFM on the system using Cisco IOS commands:
Router> enable Router# configure terminal Router(config)# no ethernet cfm global
DLP-J299 Enable or Disable CFM on the CPT System Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure enables or disables CFM on the CPT system using CTC. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
 Note | CFM is disabled globally on the system by default. This indicates that the CFM frames are transparently forwarded in the system. |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node where you want to enable or disable CFM on the CPT system. |
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. |
| Step 3 | Click the Provisioning tab. |
| Step 4 | In the left pane, click CFM. |
| Step 5 | Click the Global Settings tab. |
| Step 6 |
In the Global Settings area, check the Enable CFM check box to enable CFM on the CPT system. Uncheck the Enable CFM check box to disable CFM on the CPT system. |
| Step 7 | Check the MIP Filter Enable check box to configure a CFM MIP filter that drops all the CFM frames at a lower level irrespective of whether they originate from the wire or the bridge relay. |
| Step 8 | Enter a value in the MEP Cross Check Delay field to specify the number of seconds a device waits for remote MEPs to come up before the cross-check starts. The default value is 30. The range is from 1 to 65535. |
| Step 9 | Click Apply. |
| Step 10 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
DLP-J308 Enable or Disable CFM on an Interface Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure enables or disables CFM on an interface using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
Example: Enable or Disable CFM on an Interface
The following example shows how to enable CFM on an interface using Cisco IOS commands:
Router> enable Router# configure terminal Router(config)# interface TenGigabitEthernet 4/1 Router(config-if)# ethernet cfm interface
The following example shows how to disable CFM on an interface using Cisco IOS commands:
Router> enable Router# configure terminal Router(config)# interface TenGigabitEthernet 4/1 Router(config-if)# no ethernet cfm interface
DLP-J300 Enable or Disable CFM for Each Port or Channel Group Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure enables or disables CFM for each port or channel group using CTC. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
 Note | CFM is enabled on each port by default. If CFM is disabled on a port, the CFM packets on that port are dropped. |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node where you want to enable or disable CFM for each port or channel group. |
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. |
| Step 3 | Click the Provisioning tab. |
| Step 4 | In the left pane, click CFM. |
| Step 5 | Click the Global Settings tab. |
| Step 6 | In the Ethernet Interfaces area, expand the slot of the fabric card or the line card or the Fan–Out–Group (FOG) of the CPT 50 panel. |
| Step 7 | If you want to enable CFM on a specific port, check the Enable CFM check box against that port. Uncheck the Enable CFM check box against the port to disable CFM on the port. |
| Step 8 | In the Channel Groups area, if you want to enable CFM on a specific channel group, check the Enable check box against that channel group. |
| Step 9 | Click Apply to enable CFM on the port or the channel group. |
| Step 10 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
DLP-J312 Enable Caching of CFM Data Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure enables caching of CFM data using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
Example: Enable Caching of CFM Data
The following example shows how to set the maximum number of entries in the CFM traceroute cache table to 2500 using Cisco IOS commands:
Router> enable Router# configure terminal Router(config)# ethernet cfm traceroute cache size 2500
The following example shows how to set the retention time for entries in the CFM traceroute cache table to 5 minutes using Cisco IOS commands:
Router> enable Router# configure terminal Router(config)# ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time 5
DLP-J313 Enable Caching of CFM Data Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure enables caching of CFM data using CTC. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node where you want to enable caching of CFM data. |
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. |
| Step 3 | Click the Provisioning tab. |
| Step 4 | In the left pane, click CFM. |
| Step 5 | Click the Global Settings tab. |
| Step 6 | In the Cache Configuration area, check the Enable check box to enable caching of CFM data learned through traceroute messages. |
| Step 7 | Enter the time in minutes in the HoldTime field to set the amount of time that CFM traceroute cache entries are retained. The default value is 100 minutes. The range is from 1 to 65535 minutes. |
| Step 8 | Enter the cache size in the Size field to set the maximum size for the CFM traceroute cache table. The default value is 100. The range is from 1 to 4095. |
| Step 9 | Click Apply to enable caching of CFM data. |
| Step 10 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
Understanding Maintenance Domain
A maintenance domain is an administrative domain for managing and administering a network. The maintenance domain allows CFM to support multiple independent operators, each supporting service instances from multiple independent customers.
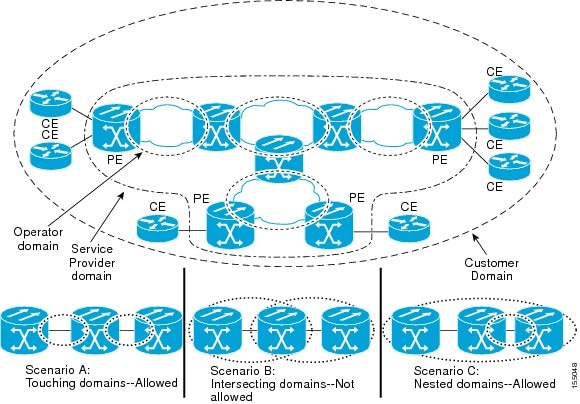
A unique maintenance level in the range of 0 to 7 is assigned to each maintenance domain by a network administrator. Maintenance levels and domain names are useful for defining the hierarchical relationship that exists among domains. The hierarchical relationship of domains parallels the structure of customer, service provider, and operator. The higher the domain level, the broader the scope of the domain. For example, a customer domain would be larger than an operator domain. The customer domain may have a maintenance level of 7 and the operator domain may have a maintenance level of 0. Typically, operators would have the smallest domains and customers the largest domains, with service provider domains in between these domains, varying in size. All levels of the hierarchy must operate together.
Domains must not intersect because intersecting would mean management by more than one entity, which is not allowed. Domains may nest or touch but when two domains nest, the outer domain must have a higher maintenance level than the domain nested within it. Nesting maintenance domains is useful in the business model where a service provider contracts with one or more operators to provide Ethernet service to a customer. Each operator would have its own maintenance domain and the service provider would define its domain that is a superset of the operator domains. Furthermore, the customer has its own end-to-end domain, which is in turn is a superset of the service provider domain. Maintenance levels of various nesting domains must be communicated among the administering organizations. For example, one approach would be to have the service provider assign maintenance levels to operators.
The following characteristics of maintenance domains are supported:
Maintenance domains are identified by a unique domain name that can be up to 154 characters.
The domain name as null is supported; the maintenance association name is used as the identifier.
Domain configuration is not required for devices that have only Maintenance Intermediate Points (MIPs).
Mix of Up (toward the bridge) and Down (toward the wire) Maintenance Association End Points (MEPs) is supported.
A domain can be removed when all the maintenance points within the domain have been removed and all the remote MEPs entries in the continuity check database (CCDB) for the domain have been purged.
The following figure illustrates a hierarchy of operator, service provider, and customer domains and also illustrates touching, intersecting, and nested domains.
- DLP-J309 Create a Maintenance Domain Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J301 Create and Modify a Maintenance Domain Profile Using CTC
- DLP-J302 Delete a Maintenance Domain Profile Using CTC
DLP-J309 Create a Maintenance Domain Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure creates a maintenance domain using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
Example: Create a Maintenance Domain
The following example shows how to define a domain named domain1 at level 6 and enters Ethernet CFM configuration mode:
Router> enable Router# configure terminal Router(config)# ethernet cfm domain domain1 level 6 Router(config-ecfm)#
DLP-J301 Create and Modify a Maintenance Domain Profile Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure creates or modifies a maintenance domain profile using CTC. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node where you want to create or modify a maintenance domain profile. |
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. |
| Step 3 | Click the Provisioning tab. |
| Step 4 | In the left pane, click CFM. |
| Step 5 | Click the Domain Profiles tab. |
| Step 6 | Click Add row(s). |
| Step 7 | Enter the name of the domain in the Domain Name field. |
| Step 8 | Enter the level of the domain profile in the Level field. The domain profile level ranges from 0 to 7. |
| Step 9 | Check the Sender Id check box to include the contents of the Sender ID time-length-value (TLV) field transmitted in CFM messages for members of a maintenance domain. |
| Step 10 | Check the Auto Create MIP check box to allow the automatic creation of an MIP at this maintenance domain level. |
| Step 11 | Check the Lower MEP check box. When this check box and Auto Create MIP check box are checked, auto MIPs are created at a specified level only where an MEP is configured at the next lower level for a maintenance domain. |
| Step 12 | Enter a value in the Archive Hold Timer field to specify the number of minutes that data from a missing MEP is kept before it is purged. The default value is 100 minutes. The range is from 1 to 65535 minutes. |
| Step 13 | Click Store. |
| Step 14 | In the CFM Profile Storing dialog box, choose the node and shelf where you want to store this domain profile and click OK. |
| Step 15 | To modify a maintenance domain profile, double-click the required parameters, change the values, and click Apply. |
| Step 16 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
DLP-J302 Delete a Maintenance Domain Profile Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure deletes a maintenance domain profile using CTC. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node where you want to delete a maintenance domain profile. |
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. |
| Step 3 | Click the Provisioning tab. |
| Step 4 | In the left pane, click CFM. |
| Step 5 | Click the Domain Profiles tab. |
| Step 6 | Click Load to load the maintenance domain profiles from the system. The CFM Profile Loading dialog box appears. |
| Step 7 | Choose the shelf and click OK. The domain profiles appear in the Domain Profiles tab. |
| Step 8 | Choose a domain profile to delete. |
| Step 9 | Check the On Node check box. |
| Step 10 | Click Delete Sel row(s). The CFM Profile Deleting dialog box appears. |
| Step 11 | Choose the shelf to delete the domain profile from and click OK. |
| Step 12 | Click Yes in the confirmation dialog box. |
| Step 13 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
Understanding Maintenance Association
There can be any number of maintenance associations (MA) within a maintenance domain. A maintenance association identifies a service that can be uniquely identified within the maintenance domains. The CFM protocol runs within a specific maintenance association.
The MA direction is specified when the MA is configured. The MA name must be configured on a domain before MEPs can be configured. Configuring an MA is not required for devices that have only MIPs.
- DLP-J334 Create a Maintenance Association Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J333 Configure CFM Encapsulation Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J303 Create and Modify a Maintenance Association Profile Using CTC
- DLP-J304 Delete a Maintenance Association Profile Using CTC
DLP-J334 Create a Maintenance Association Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure creates a maintenance association using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id Example:Router(config)# ethernet cfm domain Customer level 7 | Creates a maintenance domain at a specified level and enters Ethernet CFM configuration mode. |
| Step 4 | service {ma-name | number ma-num} {evc evc-name | port } [direction down] Example:Router(config-ecfm)# service Customer1 port | Creates a maintenance association within a maintenance domain and enters CFM service configuration mode. |
| Step 5 | exit Example:Router(config-ecfm)# exit | Returns to global configuration mode. |
| Step 6 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
Example: Create a Maintenance Association
The following example shows how to create a maintenance association using Cisco IOS commands:
Router> enable Router# configure terminal Router(config)# ethernet cfm domain operator level 5 Router(config-ecfm)# service operatorA port Router(config-ecfm)# exit
DLP-J333 Configure CFM Encapsulation Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure configures CFM encapsulation using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | interface type number Example:Router(config)# interface TenGigabitEthernet 4/1 | Specifies the interface to configure and enters interface configuration mode. |
| Step 4 | service instance id ethernet [evc-id] Example:Router(config-if)# service instance 101 ethernet | Configures an Ethernet service instance on an interface and enters service instance configuration mode. |
| Step 5 | encapsulation dot1q {any | vlan-id [vlan-id [-vlan-id]]} second-dot1q {any | vlan-id [vlan-id [-vlan-id]]} Example:Router(config-if-srv)# encapsulation dot1q 100-110 second dot1q 200 | Defines the matching criteria that maps the ingress dot1q, QinQ, or untagged frames on an interface to the appropriate service instance. |
| Step 6 | bridge-domain bridge-id [split-horizon ] Example:Router(config-if-srv)# bridge-domain 12 | Binds the Ethernet service instance to a bridge domain instance where bridge-id is the identifier for the bridge domain instance. |
| Step 7 | cfm encapsulation {dot1ad vlan-id | dot1q vlan-id} [dot1q vlan-id | second-dot1q vlan-id] Example:Router(config-if-srv)# cfm encapsulation dot1q 105 second dot1q 200 | Defines the matching criteria that maps the ingress dot1q, QinQ, or untagged frames on an interface to the appropriate service instance. |
| Step 8 | exit Example:Router(config-if-srv)# exit | Exits the service instance configuration mode. |
| Step 9 | exit Example:Router(config-if)# exit | Returns to global configuration mode. |
| Step 10 | end Example:Router(config)# end | Returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 11 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
DLP-J303 Create and Modify a Maintenance Association Profile Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure creates or modifies a maintenance association profile using CTC. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node where you want to create or modify a maintenance association profile. |
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. |
| Step 3 | Click the Provisioning tab. |
| Step 4 | In the left pane, click CFM. |
| Step 5 | Click the MA Profiles tab. |
| Step 6 | Click Add row(s). |
| Step 7 | Enter the name of the maintenance association profile in the Maintenance Profile Name field. |
| Step 8 | Enter the unique ID used to represent a service in the Service ID field. Service IDs identify customers within a domain. A service ID must be unique within a single maintenance domain. |
| Step 9 | Check the CC Enable check box to globally enable transmission of Continuity Check Messages (CCMs). |
| Step 10 | From the CC Interval drop-down list, choose the interval to transmit CCMs. The valid values are as follows: |
| Step 11 | Enter the number of CCMs that must be missed before declaring that a remote MEP is down, in the CC Threshold field. The range is from 2 to 255. The default value is 3. |
| Step 12 | Check the Direction Down check box to configure the service direction toward the LAN. |
| Step 13 | Enter the maintenance domain name in the Domain Name field to attach this maintenance association profile to a maintenance domain profile. |
| Step 14 | Check the Auto Create MIP check box to dynamically create an MIP. |
| Step 15 | Check the Port check box to create a port MEP. |
| Step 16 | Check the Lower MEP Only check box. When this check box and Auto Create MIP check box are checked, auto MIPs are created at a specified level only where an MEP is configured at the next lower level for a maintenance domain. |
| Step 17 | Check the CFM EFM Interaction check box to enable the CFM and EFM protocols to interoperate. CFM and EFM can interoperate together and can co-exist on the same port. CFM and EFM cannot interoperate together if CFM MEP is configured on the channel group. Use the oam protocol cfm domain domain-name to configure CFM and EFM to interoperate together using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Step 18 | Enter the static MEP ID or a list of static MEP IDs in the Static MEP Id field to statically specify the MEP IDs. The range is from 1 to 8191. |
| Step 19 | Check the MEP Cross Check Enable check box to enable cross-checking between the list of configured remote MEPs of a domain and MEPs learned through CCMs. |
| Step 20 | Enter the outer dot1q encapsulation tag value in the Outer CFM Encapsulation field. |
| Step 21 | Enter the inner dot1q encapsulation tag value in the Inner CFM Encapsulation field. |
| Step 22 | Click Store. |
| Step 23 | Choose the node and shelf where you want to store this maintenance association profile and click OK. |
| Step 24 | To modify a maintenance association profile, double-click the required parameters, change the values, and click Apply. |
| Step 25 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
DLP-J304 Delete a Maintenance Association Profile Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure deletes a maintenance association profile using CTC. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node where you want to delete a maintenance association profile. |
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. |
| Step 3 | Click the Provisioning tab. |
| Step 4 | In the left pane, click CFM. |
| Step 5 | Click the MA Profiles tab. |
| Step 6 | Click Load to load the maintenance association profiles from the system. The CFM Profile Loading dialog box appears. |
| Step 7 | Choose the shelf and click OK. The maintenance association profiles appear in the MA Profiles tab. |
| Step 8 | Choose an association profile to delete. |
| Step 9 | Check the On Node check box. |
| Step 10 | Click Delete Sel row(s). The CFM Profile Deleting dialog box appears. |
| Step 11 | Choose the shelf to delete the association profile from and click OK. |
| Step 12 | Click Yes in the confirmation dialog box. |
| Step 13 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
Understanding Maintenance Point
Any port of a bridge is referred to as a Maintenance Point. A maintenance point is a demarcation point on an interface or port that participates in CFM within a maintenance domain. Maintenance points must be explicitly configured on Cisco devices.
There are two classes of maintenance points:
- Understanding Maintenance End Points
- Understanding Up MEPs
- Understanding Down MEPs
- Understanding Port MEPs
- Understanding the Cross-Check Function
- DLP-J310 Create a Port MEP Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J321 Create an MEP for an EFP Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J319 Define MEPs Statically within a Maintenance Association Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J318 Specify the Number of MEPs in a Maintenance Association Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J323 Configure Cross-Check for an MEP Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J306 Create an MEP Using CTC
Understanding Maintenance End Points
MEPs reside at the edge of a maintenance domain and are active elements of CFM. They confine CFM messages within the domain through the maintenance domain level. MEPs periodically transmit and receive continuity check messages (CCMs) from other MEPs within the domain. MEPs also transmit linktrace and loopback messages at the request of the administrator.
MEP ID uniquely identifies each MEP along with those configured on a single MA. The MEP IDs range from 1 to 8191.
There are two types of MEPs:
MEP supports multicast loopbacks and pings. When a multicast ping is initiated for a particular domain or service, all the related remote MEPs reply to the ping.
MEP configurations can be removed after all pending loopback and linktrace replies are removed and the service on the interface is set to transparent mode. To set the service to transparent mode, MIP filtering must not be configured.
Understanding Up MEPs
An Up MEP is an MEP that resides in a bridge and transmits to and receives CFM messages from the direction of the bridge relay entity.
An Up MEP performs the following functions:
Sends and receives CFM frames at its level through the bridge relay and not through the wire connected to the port on which the MEP is configured.
Drops all CFM frames at its level (or lower level) that come from the direction of the wire.
Processes all CFM frames at its level coming from the direction of the bridge.
Drops all CFM frames at a lower level coming from the direction of the bridge.
Forwards all CFM frames transparently at a higher level, independent of whether they came in from the bridge or wire.
Understanding Down MEPs
A Down MEP is an MEP that resides in a bridge and transmits to and receives CFM messages from the direction of the wire.
A Down MEP performs the following functions:
Sends and receives CFM frames at its level through the wire connected to the port where the MEP is configured.
Drops all CFM frames at its level (or at a lower level) that come from the direction of the bridge.
Processes all CFM frames at its level coming from the direction of the wire.
Drops all CFM frames at a lower level coming from the direction of the wire.
Forwards all CFM frames transparently at a higher level, independent of whether they came in from the bridge or wire.
Understanding Port MEPs
CPT also supports Port MEP at the physical port. A port MEP can be created either on the physical port or on the port of a channel group. The port MEP takes higher precedence if both the port MEP and the Down MEP on untagged EFP is created on the same port.
Understanding the Cross-Check Function
The cross-check function is a timer-driven post-provisioning service verification between dynamically discovered MEPs (through CCMs) and expected MEPs (through configuration) for a service. The cross-check function verifies that all the endpoints of a multipoint or point-to-point service are operational. The function supports notifications when the service is operational; otherwise it provides alarms and notifications for unexpected or missing endpoints.
You must initiate the cross-check function each time you want a service verification. See DLP-J323 Configure Cross-Check for an MEP Using Cisco IOS Commands.
DLP-J310 Create a Port MEP Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure creates a port MEP using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | interface type number Example:Router(config)# interface TenGigabitEthernet 4/1 | Specifies the interface to configure and enters interface configuration mode. |
| Step 4 | ethernet cfm mep domain domain-name mpid mpid {port} Example:Router(config-if)# ethernet cfm mep domain Customer mpid 701 port | Sets a port as internal to a maintenance domain and creates a port MEP. A port MEP can be created only on a physical port or on a port of a channel group. |
| Step 5 | exit Example:Router(config-if)# exit | Returns to global configuration mode. |
| Step 6 | end Example:Router(config)# end | Returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 7 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
Example: Create a Port MEP
The following example shows how to set a port as internal to a maintenance domain and creates a port MEP:
Router> enable Router# configure terminal Router(config)# interface TenGigabitEthernet 4/1 Router(config-if)# ethernet cfm mep domain CustomerB mpid 5 port
DLP-J321 Create an MEP for an EFP Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure creates an MEP for an EFP using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | interface type number Example:Router(config)# interface TenGigabitEthernet 4/1 | Specifies the interface to configure and enters interface configuration mode. |
| Step 4 | service instance id ethernet [evc-id] Example:Router(config-if)# service instance 101 ethernet | Configures an Ethernet service instance on an interface and enters service instance configuration mode. |
| Step 5 | encapsulation dot1q {any | vlan-id [vlan-id [-vlan-id]]} second-dot1q {any | vlan-id [vlan-id [-vlan-id]]} Example:Router(config-if-srv)# encapsulation dot1q 100 second dot1q 200 | Defines the matching criteria that maps the ingress dot1q, QinQ, or untagged frames on an interface to the appropriate service instance. |
| Step 6 | bridge-domain bridge-id [split-horizon ] Example:Router(config-if-srv)# bridge-domain 12 | Binds the Ethernet service instance to a bridge domain instance where bridge-id is the identifier for the bridge domain instance. |
| Step 7 | cfm mep domain domain-name mpid mpid-value Example:Router(config-if-srv)# cfm mep domain Customer mpid 701 | Creates an MEP under the Ethernet service instance. |
| Step 8 | exit Example:Router(config-if-srv)# exit | Exits the service instance configuration mode. |
| Step 9 | exit Example:Router(config-if)# exit | Returns to global configuration mode. |
| Step 10 | end Example:Router(config)# end | Returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 11 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
Example: Create an MEP for an EFP
The following example shows how to create an MEP for an EFP using Cisco IOS commands:
Router> enable Router# configure terminal Router(config)# interface TenGigabitEthernet 4/1 Router(config-if)# service instance 101 ethernet Router(config-if-srv)# encapsulation dot1q 100 Router(config-if-srv)# bridge-domain 12 Router(config-if-srv)# cfm mep domain CustomerB mpid 5 Router(config-if-srv)# exit
DLP-J319 Define MEPs Statically within a Maintenance Association Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure statically defines MEPs within a maintenance association using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id Example:Router(config)# ethernet cfm domain Customer level 7 | Defines a CFM domain at a specified level and enters Ethernet CFM configuration mode. The range of maintenance domain level is from 0 to 7. |
| Step 4 | service {ma-name | number ma-num} {evc evc-name | port } [direction down] Example:Router(config-ecfm)# service Customer1 port | Configures a maintenance association within a maintenance domain for a port MEP or MEP for an EFP and enters CFM service configuration mode. |
| Step 5 | mep mpid mpid Example:Router(config-ecfm-srv)# mep mpid 702 | Statically defines the MEPs within a maintenance association. |
| Step 6 | exit Example:Router(config-ecfm-srv)# exit | Returns to Ethernet CFM configuration mode. |
| Step 7 | exit Example:Router(config-ecfm)# exit | Returns to global configuration mode. |
| Step 8 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
Example: Define the MEPs Statically within a Maintenance Association
The following example shows how to configure an MEP with an ID of 25 using Cisco IOS commands:
Router> enable Router# configure terminal Router(config)# ethernet cfm domain operator level 5 Router(config-ecfm)# service operatorA port Router(config-ecfm-srv)# mep mpid 25 Router(config-ecfm-srv)# exit Router(config-ecfm)# exit
DLP-J318 Specify the Number of MEPs in a Maintenance Association Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure allows you to specify the number of MEPs in a maintenance association using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id Example:Router(config)# ethernet cfm domain Customer level 7 | Defines a CFM domain at a specified level and enters Ethernet CFM configuration mode. The range of maintenance domain level is from 0 to 7. |
| Step 4 | service {ma-name | number ma-num} {evc evc-name | port} [direction down] Example:Router(config-ecfm)# service Customer1 port | Configures a maintenance association within a maintenance domain for a port MEP or MEP for an EFP and enters CFM service configuration mode. |
| Step 5 | maximum meps max-num Example:Router(config-ecfm-srv)# maximum meps 50 | Specifies the maximum number of MEPs in a maintenance association. The default is 100. The range is from 1 to 65535. |
| Step 6 | exit Example:Router(config-ecfm-srv)# exit | Returns the CLI to Ethernet CFM configuration mode. |
| Step 7 | exit Example:Router(config-ecfm)# exit | Returns to global configuration mode. |
| Step 8 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
Example: Specify the Number of MEPs in a Maintenance Association
The following example shows how to configure a maximum of 50 MEPs using Cisco IOS commands:
Router> enable Router# configure terminal Router(config)# ethernet cfm domain operator level 5 Router(config-ecfm)# service operatorA port Router(config-ecfm-srv)# maximum meps 50 Router(config-ecfm-srv)# exit Router(config-ecfm)# exit
DLP-J323 Configure Cross-Check for an MEP Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure configures cross-checking for an MEP using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id Example:Router(config)# ethernet cfm domain ServiceProvider level 4 | Creates a maintenance domain at a specified level and enters Ethernet CFM configuration mode. The range of maintenance domain level is from 0 to 7. |
| Step 4 | service {ma-name | number ma-num} {evc evc-name | port } [direction down] Example:Router(config-ecfm)# service Customer1 port | Configures a maintenance association within a maintenance domain and enters CFM service configuration mode. |
| Step 5 | mep mpid mpid Example:Router(config-ecfm-srv)# mep mpid 702 | Statically defines the MEPs within a maintenance association. |
| Step 6 | exit Example:Router(config-ecfm-srv)# exit | Returns to Ethernet CFM configuration mode. |
| Step 7 | exit Example:Router(config-ecfm)# exit | Returns to global configuration mode. |
| Step 8 | ethernet cfm mep crosscheck start-delay delay Example:Router(config)# ethernet cfm mep crosscheck start-delay 60 | Configures the maximum amount of time that the device waits for remote MEPs to come up before the cross-check operation is started. The default value is 30 seconds. The range is from 1 to 65535 seconds. |
| Step 9 | exit Example:Router(config)# exit | Returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 10 | ethernet cfm mep crosscheck {enable | disable} domain domain-name port Example:Router# ethernet cfm mep crosscheck enable domain cust4 port | Enables cross-checking between the list of configured remote MEPs of a domain and MEPs learned through CCMs. |
| Step 11 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
DLP-J306 Create an MEP Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure creates a maintenance end point using CTC. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node where you want to create a maintenance end point. | ||
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. | ||
| Step 3 | Click the Provisioning tab. | ||
| Step 4 | In the left pane, click CFM. | ||
| Step 5 | Click the MEP tab. | ||
| Step 6 | Click Create. The Create MEP dialog box appears. | ||
| Step 7 |
To create an MEP on an EFP: | ||
| Step 8 |
To create an MEP on a port:
| ||
| Step 9 |
To create an MEP on a channel group: | ||
| Step 10 | Click OK in the Create MEP dialog box to create an MEP. | ||
| Step 11 | To delete an MEP: | ||
| Step 12 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
Understanding Maintenance Intermediate Points
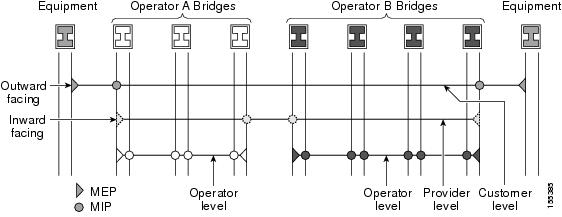
Maintenance intermediate points (MIPs) are internal to the maintenance domain and are passive elements of CFM. They store information received from MEPs and other MIPs and respond only to CFM linktrace and loopback messages. An MIP has only one level associated with it. MIPs forward CFM messages within a maintenance domain.
MIPs are defined as two MIP half functions (MHFs)—An Up MHF that resides above the port filtering entities and a Down MHF that resides below the port filtering entities. The same configuration parameters and characteristics apply to both MHFs of an MIP:
Can be created manually or dynamically (auto MIPs).
Dynamically created depending on configured policies at managed objects (MA, maintenance domain, or the default domain level).
Manual MIPs can be created under an interface and under a service instance within an interface.
Auto MIP commands can be issued globally or under a domain or service.
Can be created per MA, which means that an MIP in the MA can be lower level than an MEP in another MA.
CFM frames received from MEPs and other MIPs are cataloged and forwarded, using both the wire and the bridge relay.
When MIP filtering is enabled, all CFM frames at a lower level are stopped and dropped, independent of whether they originate from the wire or the bridge relay.
All CFM frames at a higher level are forwarded, independent of whether they arrive from the wire or from the bridge relay.
Passive points respond only when triggered by CFM linktrace and loopback messages.
The following figure illustrates MEPs and MIPs at the operator, service provider, and customer levels.
- DLP-J311 Create an MIP Dynamically Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J322 Create an MIP Manually Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J307 Create an MIP Using CTC
DLP-J311 Create an MIP Dynamically Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure creates an MIP dynamically using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
 Note | ethernet cfm mip auto-create command has lower precedence than the ethernet cfm mip level manual MIP command. For example, if you manually configure an MIP for a particular maintenance association, that configuration overrides the MIP created by the global ethernet cfm mip auto-create command for that maintenance association. |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | ethernet cfm mip {auto-create level level-id [lower-mep-only] [sender-id chassis] | filter} Example:Router(config)# ethernet cfm mip auto-create level 1 | Dynamically creates an MIP and provisions it globally at a specified maintenance level and enables level filtering. |
| Step 4 | end Example:Router(config)# end | Returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 5 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
Example: Create an MIP Dynamically
The following example shows how to dynamically create an MIP at maintenance level 6 using Cisco IOS commands:
Router> enable Router# configure terminal Router(config)# ethernet cfm mip auto-create level 6
DLP-J322 Create an MIP Manually Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure creates an MIP manually using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
 Note | You cannot configure an MIP at a level lower than the level of already configured maintenance endpoints (MEPs) on an interface. Configuring an MIP using this command is known as a manual MIP and has precedence over the ethernet cfm mip auto-create command. |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | interface type number Example:Router(config)# interface TenGigabitEthernet 4/1 | Specifies the interface to configure and enters interface configuration mode. |
| Step 4 | ethernet cfm mip level level-id Example:Router(config-if)# ethernet cfm mip level 1 | Creates an MIP manually at a specified maintenance level on an interface. The range of level is from 0 to 7. |
| Step 5 | exit Example:Router(config-if)# exit | Returns to global configuration mode. |
| Step 6 | end Example:Router(config)# end | Returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 7 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
Example: Create an MIP Manually
The following example shows how to provision an MIP manually at maintenance level 5 using Cisco IOS commands.
Router> enable Router# configure terminal Router(config)# interface TenGigabitEthernet 4/1 Router(config-if)# ethernet cfm mip level 5 Router(config-if)# exit
DLP-J307 Create an MIP Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure creates a maintenance intermediate point with a specific maintenance level using CTC. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node where you want to create a maintenance intermediate point. |
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. |
| Step 3 | Click the Provisioning tab. |
| Step 4 | In the left pane, click CFM. |
| Step 5 | Click the MIP tab. |
| Step 6 | Click Create. The Create MIP dialog box appears. |
| Step 7 | To create an MIP on an EFP: |
| Step 8 | To create an MIP on a channel group: |
| Step 9 | Click OK in the Create MIP dialog box to create an MIP. |
| Step 10 | To delete an MIP: |
| Step 11 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
Understanding CFM Messages
CFM uses standard Ethernet frames that can be distinguished by their EtherType and for multicast messages by their MAC address. CFM frames are sourced, terminated, processed, and relayed by bridges.
Bridges that cannot interpret CFM messages forward them as normal data frames. All CFM messages are confined to a maintenance domain and to a maintenance association. Three types of messages are supported:
- Understanding Continuity Check Messages
- DLP-J316 Enable the Transmission of Continuity Check Messages Using Cisco IOS Commands
- Understanding Loopback Messages
- Understanding Linktrace Messages
- DLP-J324 Send CFM Loopback and Linktrace Messages Using Cisco IOS Commands
- NTP-J107 Perform ping and traceroute Operations on Services Using CTC
Understanding Continuity Check Messages
CFM continuity check messages (CCMs) are multicast heartbeat messages exchanged periodically among MEPs. They allow MEPs to discover other MEPs within a domain and allow MIPs to discover MEPs. CCMs are confined to a domain.
CFM CCMs have the following characteristics:
Transmitted at a periodic interval by MEPs. The interval can be one of the following configurable values. The default is 10 seconds.
Cataloged by MIPs at the same maintenance level.
Terminated by remote MEPs at the same maintenance level.
Unidirectional and do not solicit a response.
Indicate the status of the bridge port on which the MEP is configured.
DLP-J316 Enable the Transmission of Continuity Check Messages Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure enables the transmission of continuity check messages (CCM) using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id Example:Router(config)# ethernet cfm domain Customer level 7 | Creates a CFM maintenance domain at a specified maintenance level and enters Ethernet CFM configuration mode. The range of maintenance domain level is from 0 to 7. |
| Step 4 | service {ma-name | number ma-num} {evc evc-name | port } [direction down] Example:Router(config-ecfm)# service Customer1 port | Configures a maintenance association within a maintenance domain for a port MEP or MEP for an EFP and enters CFM service configuration mode. |
| Step 5 | continuity-check [interval time | loss-threshold threshold | static rmep] Example:Router(config-ecfm-srv)# continuity-check | Enables the transmission of CCMs. |
| Step 6 | continuity-check [interval time | loss-threshold threshold | static rmep] Example:Router(config-ecfm-srv)# continuity-check interval 10s | Configures the time period between CCM transmissions. |
| Step 7 | continuity-check [interval time | loss-threshold threshold | static rmep] Example:Router(config-ecfm-srv)# continuity-check lossthreshold 10 | Sets the number of CCMs that must be missed before declaring that a remote MEP is down. |
| Step 8 | exit Example:Router(config-ecfm-srv)# exit | Returns to Ethernet CFM configuration mode. |
| Step 9 | mep archive-hold-time minutes Example:Router(config-ecfm)# mep archive-hold-time 60 | Sets the amount of time that data from a missing MEP is kept in the continuity check database or that entries are held in the error database before they are purged. The default value is 100 minutes. The range is from 1 to 65535 minutes. |
| Step 10 | exit Example:Router(config-ecfm)# exit | Returns to global configuration mode. |
| Step 11 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
Example: Enable the Transmission of Continuity Check Messages
The following example shows how to configure a loss threshold of 50 CCMs using Cisco IOS commands:
Router> enable Router# configure terminal Router(config)# ethernet cfm domain operator level 5 Router(config-ecfm)# service operatorA port Router(config-ecfm-srv)# continuity-check loss-threshold 50 Router(config-ecfm-srv)# exit Router(config-ecfm)# exit
Understanding Loopback Messages
CFM loopback messages (LBMs) are unicast frames that an MEP transmits, at the request of an administrator, to verify connectivity to a specific maintenance point. A loopback message reply (LBR) indicates whether a destination is reachable but does not allow hop-by-hop discovery of the path. A loopback message is similar in concept to an Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Echo (ping) message.
Since LBMs are unicast messages, they are forwarded like normal data frames except with the maintenance level restriction. If the outgoing port is known in the forwarding database of the bridge and allows CFM frames at the maintenance level of the image to pass through, the frame is sent out on that port. If the outgoing port is unknown, the message is broadcast on all the ports in that domain.
A CFM LBM can be generated on demand using the CLI. The source of a loopback message must be an MEP; the destination may be an MEP or MIP. Both CFM LBMs and LBRs are unicast. CFM LBMs specify the destination MAC address or MPID, VLAN, and maintenance domain.
Understanding Linktrace Messages
CFM linktrace messages (LTMs) are multicast frames that an MEP transmits, at the request of an administrator, to track the path (hop-by-hop) to a destination MEP. They are similar to Layer 3 traceroute messages. LTMs allow the transmitting node to discover vital connectivity data about the path and allow the discovery of all MIPs along the path that belong to the same maintenance domain. LTMs are intercepted by maintenance points along the path and processed, transmitted, or dropped. At each hop where there is a maintenance point at the same level, a linktrace message reply (LTR) is transmitted back to the originating MEP. For each visible MIP, linktrace messages indicate ingress action, relay action, and egress action. LTMs are multicast and LTRs are unicast.
DLP-J324 Send CFM Loopback and Linktrace Messages Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure allows you to send CFM loopback and traceroute messages to a destination MAC address using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | ping ethernet {mpid mpid | mac-address} {domain domain-name} {port | evc evc-name} [source source-mpid] [cos cos-value] Example:Router(config)# ping ethernet 1010.pcef.1010 level 2 evc evc5 | Sends CFM loopback messages to the destination MEP through MAC address or MPID. |
| Step 3 | traceroute ethernet {mpid mpid | mac-address} {domain domain-name} {port | evc evc-name} [cos cos-value] [fdb-only] Example:Router(config)# traceroute ethernet aabb.cc00.1010 level 4 evc evc_100 | Sends CFM traceroute messages to the destination MEP through MAC address or MPID. |
| Step 4 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
Example: Send CFM Loopback and Traceroute Messages
The following example shows how to send an Ethernet CFM loopback message to MAC address 1010.pcef.1010 on evc5:
Router> enable Router# ping ethernet 1010.pcef.1010 domain domain1 evc evc5
The following example shows how to send an Ethernet CFM traceroute message to MAC address aabb.cc00.1010 at maintenance level 4 on evc_100
Router> enable Router# traceroute ethernet aabb.cc00.1010 domain domain1 evc evc_100
NTP-J107 Perform ping and traceroute Operations on Services Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure performs ping and traceroute operations on services using CTC. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node on the network where you want to perform ping and traceroute operations. |
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. |
| Step 3 | Click the Maintenance tab. |
| Step 4 | In the left pane, click OAM. |
| Step 5 | From the Service drop-down list, choose TP Tunnel, TE Tunnel, Pseudowire, or EVC. |
| Step 6 | From the Command drop-down list, choose Ping or Traceroute. |
| Step 7 | If you choose TP Tunnel as the service, complete the following: |
| Step 8 | If you choose TE Tunnel as the service, complete the following: |
| Step 9 | If you choose Pseudowire as the service, complete the following: |
| Step 10 | If you choose EVC as the service, complete the following: |
| Step 11 | Click Execute to run the OAM operation for the specified service. Stop. You have completed this procedure. |
Understanding Continuity Check Traps and Cross-Check Traps
MEPs generate two types of Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) traps. They are Continuity Check (CC) traps and Cross-Check traps.
Continuity Check Traps
MEP up—Sent when a new MEP is discovered, the status of a remote port changes, or connectivity from a previously discovered MEP is restored after interruption.
MEP down—Sent when a timeout or last gasp event occurs.
Cross-connect—Sent when a service ID does not match the VLAN.
Loop—Sent when an MEP receives its own CCMs.
Configuration error—Sent when an MEP receives a continuity check with an overlapping MPID.
Cross-Check Traps
- DLP-J314 Enable CFM Traps Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J315 Enable SNMP Trap Generation for CFM Continuity Check Events Using Cisco IOS Commands
DLP-J314 Enable CFM Traps Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure enables CFM traps using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm alarm Example:Router(config)# snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm alarm | Enables CFM fault alarms (traps). |
| Step 4 | end Example:Router(config)# end | Returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 5 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
Example: Enable CFM Traps
The following example shows how to enable CFM traps using Cisco IOS commands:
Router> enable Router# configure terminal Router(config)# snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm alarm Router(config)# end
DLP-J315 Enable SNMP Trap Generation for CFM Continuity Check Events Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure enables SNMP trap generation for CFM Continuity Check events using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm cc [mep-up][mepdown][config] [loop] [cross-connect] Example:Router(config)# snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm cc mep-up mep-down config loop cross-connect | Enables SNMP trap generation for CFM mep-up, mep-down, config, loop, and cross-connect continuity check events. |
| Step 4 | snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm crosscheck [mepunknown|mep-missing| service-up] Example:Router(config)# snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm crosscheck mep-unknown | Enables SNMP trap generation for CFM mepunknown, mep-missing, and service-up continuity check events in relation to the cross-check operation between statically configured MEPs and those learned through CCMs. |
| Step 5 | end Example:Router(config)# end | Returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 6 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
Example: Enable SNMP Trap Generation for CFM Continuity Check Events
The following example shows how to enable SNMP trap generation for CFM continuity checks when a new remote MEP is discovered and learned by the device:
Router> enable Router# configure terminal Router(config)# snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm cc mep-up
The following example shows how to enable SNMP trap generation for CFM continuity check events when an unconfigured MEP comes up:
Router> enable Router# configure terminal Router(config)# snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm crosscheck mep-unknown
Understanding Y.1731
Y.1731 Fault Management and Performance Monitoring
Y.1731 is an extension of the Connectivity Fault Management (CFM). The ITU-T Y.1731 feature provides operations, administration, and maintenance (OAM) functions for fault management and performance monitoring to serve the needs of service providers in a large network.
CPT supports Ethernet Alarm Indication Signal (ETH-AIS), Ethernet Remote Defect Indication (ETH-RDI), and Ethernet Locked Signal (ETH-LCK) functionality for fault detection and isolation.
Y.1731 Performance Monitoring (PM) provides a standard Ethernet PM function that includes measurement of Ethernet frame delay, frame delay variation, frame loss, and frame throughput measurements specified by the ITU-T Y-1731 standard. To measure Service Level Agreement (SLA) parameters such as frame delay or frame delay variation, a small number of synthetic frames are transmitted along with the service to the maintenance end point (MEP).
CPT supports only two–way Ethernet frame Delay Measurement (ETH-DM) in Y.1731 performance monitoring. The CPT system sends, receives, and processes PM frames in intervals of 100 ms (10 frames per second) and 1 second.
 Note | CFM must be enabled in the network for Y.1731 to become operational. |
Y.1731 Limitations and Restrictions in CPT
CPT supports only Ethernet Alarm Indication Signal (ETH-AIS), Ethernet Remote Defect Indication (ETH-RDI), and Ethernet Locked Signal (ETH-LCK) functionality for fault detection, verification, and isolation.
ETH-LCK is supported on a channel group only at the MEP level and not at the interface level.
CPT supports only two–way Ethernet frame Delay Measurement (ETH-DM) in Y.1731 performance monitoring.
CPT does not support retransmission intervals of less than 100ms for delay measurement.
Port MEP is not supported for both fault management and delay measurement.
Y.1731 delay measurement is supported on UP MEP on xconnect configuration, and DOWN MEP on both xconnect and EVC configurations.
All the members of the channel group must be present on the same card to support delay measurement. After the delay measurement session is configured on the channel group, the members cannot be moved to a different card. The delay measurement session on the channel group must be unconfigured before moving the members to a different card.
Y.1731 is not supported for EVC encapsulation default and encapsulation untagged.
Understanding Y.1731 Fault Management
CPT supports Ethernet Alarm Indication Signal (ETH-AIS), Ethernet Remote Defect Indication (ETH-RDI), and Ethernet Locked Signal (ETH-LCK) functionality for fault detection and isolation.
ETH-AIS
The Ethernet Alarm Indication Signal function (ETH-AIS) is used to suppress alarms after defects are detected at an MEP. An MEP that receives a frame with ETH-AIS information suppresses alarms for all the peer MEPs, whether or not they are connected.
When an MEP detects a connectivity fault at a specific maintenance association level, it multicasts AIS frames in the direction away from the detected failure at the client maintenance association level. The frequency of AIS frame transmission is based on the AIS transmission period. The first AIS frame is always sent immediately following the detection of the defect condition.
When an MEP receives an AIS frame, it examines the AIS frame to ensure that the Maintenance Entity Group (MEG) level matches its own MEG and then detects the AIS default condition. After this detection, if AIS frames are not received for an interval of 3.5 times the AIS transmission period, the MEP clears the AIS defect condition. For example, if the AIS timer is set for 60 seconds, the AIS timer period expires after 3.5 times 60, or 210 seconds.
The AIS condition is terminated when a valid Continuity Check Message (CCM) is received with all the error conditions cleared or when the AIS period timer expires (the default time is 60 seconds).
ETH-RDI
When a downstream MEP detects a defect condition, such as receive signal failure or AIS , it sends Ethernet Remote Defect Indication (ETH–RDI) in the opposite upstream direction to its peer MEPs. RDI serves in informing the upstream MEPs that there has been a downstream failure and can be used as input to far-end performance monitoring.
When Ethernet OAM continuity check (ETH-CC) transmission is enabled, the Ethernet Remote Defect Indication (ETH-RDI) function uses a bit in the CFM CC message to communicate defect conditions to the MEP peers. For ETH-RDI functionality, you must configure the MEP MEG level, the ETH-CC transmission period, and the ETH-CC frame priority.
When an MEP receives frames with ETH-RDI information, it determines that its peer MEP has encountered a defect condition and sets the RDI files in the CCM frames for the duration of the defect condition. When the defect condition clears, the MEP clears the RDI field.
When an MEP receives a CCM frame, it examines the CCM frame to ensure that its MEG level is the same and if the RDI field is set, it detects an RDI condition. For point-to-point Ethernet connections, an MEP can clear the RDI condition when it receives the first frame from its peer MEP with the RDI field cleared. However, for multipoint Ethernet connectivity, the MEP cannot determine the associated subset of peer MEPs with which the sending MEP has seen the defect condition. It can clear the RDI condition after it receives CCM frames with the RDI field cleared from its entire list of peer MEPs.
ETH-LCK
The Ethernet Locked Signal (ETH-LCK) function communicates the administrative locking of an MEP and interruption of data traffic being forwarded to the MEP expecting the traffic. An MEP that receives frames with ETH-LCK information can differentiate between a defect condition and an administrative locking. ETH-LCK relies on loopback information (local, remote, port, and terminal loopback). The default timer for ETH-LCK is 60 seconds and the default level is the MIP level.
When an MEP is administratively locked, it sends LCK frames in a direction opposite to its peer MEPs, based on the LCK transmission period. The LCK transmission period is the same as the AIS transmission period. The first LCK frame is sent immediately following the administrative lock.
An MEP receiving a LCK frame verifies that the maintenance level matches its configured maintenance level and detects a LCK condition. When LCK frames are not received for an interval of 3.5 times the LCK transmission period, the MEP clears the LCK condition.
- NTP-J116 Configure Y.1731 Fault Management Parameters
- DLP-J349 Configure ETH-AIS Parameters Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J350 Clear AIS Alarms Using CTC
- DLP-J351 Configure ETH-LCK Parameters Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J352 Lock an MEP or an Interface Using CTC
- DLP-J353 Enable Y.1731 Fault Management Parameters Using CTC
NTP-J116 Configure Y.1731 Fault Management Parameters
| Purpose | This procedure configures Y.1731 fault management parameters. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
Stop. You have completed this procedure. |
DLP-J349 Configure ETH-AIS Parameters Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure configures ETH-AIS using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | NTP-J106 Configure CFM Using Cisco IOS Commands |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | ethernet cfm ais link-status global Example:Router(config)# ethernet cfm ais link-status global | Configures AIS specific commands for source MEP and enters config-ais-link-cfm mode. |
| Step 4 | level level-id Example:Router(config-ais-link-cfm)# level 3 | Configures the maintenance level to send AIS frames transmitted by the source MEP. The range is from 0 to 7. |
| Step 5 | period value Example:Router(config-ais-link-cfm)# period 1 | Configures the AIS transmission period interval for the source MEP. The allowable values are 1 second or 60 seconds. |
| Step 6 | exit Example: Router(config-ais-link-cfm)# exit | Returns to global configuration mode. |
| Step 7 | ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id Example:Router(config)# ethernet cfm domain customer level 7 | Creates a CFM maintenance domain at a specific maintenance level and enters Ethernet CFM configuration mode. The range of the maintenance domain level is from 0 to 7. |
| Step 8 | service {ma-name | number ma-num} {evc evc-name [direction down]} Example:Router(config-ecfm)# service Customer1 port | Creates a maintenance association within a maintenance domain and enters CFM service configuration mode. |
| Step 9 | ais period value Example: Router(config-ecfm-srv)# ais period 1 | Configures the specific AIS transmission period interval for the source MEP. The allowable values are 1 second or 60 seconds. |
| Step 10 | ais level level-id Example: Router(config-ecfm-srv)# ais level 4 | Configures the maintenance level to send AIS frames transmitted by the MEP. The range is from 0 to 7. |
| Step 11 | ais expiry-threshold value Example: Router(config-ecfm-srv)# ais expiry-threshold 20 | Sets the expiry threshold for the maintenance association. The range is from 2 to 255. The default value is 3.5. |
| Step 12 | ais suppress-alarms Example: Router(config-ecfm-srv)# ais suppress-alarms | Suppresses the AIS alarm on the MEP. |
| Step 13 | exit Example: Router(config-ecfm-srv)# exit | Returns to global configuration mode. |
| Step 14 | interface type number Example: Router(config)# interface TenGigabitEthernet 4/1 | Specifies the interface to configure and enters interface configuration mode. |
| Step 15 | ethernet cfm ais link-status Example: Router(config-if)# ethernet cfm ais link-status | Enables or disables sending AIS frames from the source MEP on the interface. |
| Step 16 | ethernet cfm ais link-status period value Example: Router(config-if)# ethernet cfm ais link-status period 60 | Configures the ETH-AIS transmission period generated by the source MEP on the interface. The allowable values are 1 second or 60 seconds. |
| Step 17 | ethernet cfm ais link-status level level-id Example: Router(config-if)# ethernet cfm ais link-status level 5 | Configures the maintenance level for sending AIS frames transmitted by the source MEP on the interface. The range is from 0 to 7. |
| Step 18 | end Example: Router(config-if)# end | Returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 19 | show ethernet cfm smep [interface type number] Example: Router# show ethernet cfm smep interface TenGigabitEthernet 4/1 | Displays CFM information for the source MEP. |
| Step 20 | show ethernet cfm errors Example: Router(config)# show ethernet cfm errors | Displays ETH-AIS frames that are received and other errors. |
| Step 21 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
DLP-J350 Clear AIS Alarms Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure enables you to clear the AIS alarm on an MEP or an interface using CTC. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | DLP-J353 Enable Y.1731 Fault Management Parameters Using CTC |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node where you want to clear the AIS alarm on an MEP or an interface. |
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. |
| Step 3 | Click the Provisioning tab. |
| Step 4 | In the left pane, click Y1731. |
| Step 5 | Click the Configuration > Execute Commands > Command Execution AIS tab. |
| Step 6 | Complete the following steps to clear the AIS alarm on an MEP. |
| Step 7 | Complete the following steps to clear the AIS alarm on an interface. |
| Step 8 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
What to Do Next
DLP-J351 Configure ETH-LCK Parameters Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure configures ETH-LCK using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | NTP-J106 Configure CFM Using Cisco IOS Commands |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | ethernet cfm lck link-status global Example:Router(config)# ethernet cfm lck link-status global | Configures LCK specific commands for source MEP and enters config-lck-link-cfm mode. |
| Step 4 | level level-id Example:Router(config-lck-link-cfm)# level 3 | Configures the maintenance level to send ETH-LCK frames transmitted by the source MEP. The range is from 0 to 7. |
| Step 5 | period value Example:Router(config-lck-link-cfm)# period 1 | Configures the ETH-LCK transmission period interval for the source MEP. The allowable values are 1 second or 60 seconds. |
| Step 6 | exit Example: Router(config-lck-link-cfm)# exit | Returns to global configuration mode. |
| Step 7 | ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id Example:Router(config)# ethernet cfm domain customer level 7 | Creates a CFM maintenance domain at a specific maintenance level and enters Ethernet CFM configuration mode. The range of the maintenance domain level is from 0 to 7. |
| Step 8 | service {ma-name | number ma-num} {evc evc-name [direction down]} Example:Router(config-ecfm)# service Customer1 port | Creates a maintenance association within a maintenance domain and enters CFM service configuration mode. |
| Step 9 | lck level level-id Example: Router(config-ecfm-srv)# lck level 3 | Configures the maintenance level for sending ETH-LCK frames transmitted by the MEP. The range is from 0 to 7. |
| Step 10 | lck period value Example: Router(config-ecfm-srv)# lck period 60 | Configure the MEP ETH-LCK frame transmission period interval. The allowable values are 1 second or 60 seconds. |
| Step 11 | lck expiry-threshold value Example: Router(config-ecfm-srv)# expiry-threshold 20 | Sets the expiry threshold for the maintenance association. The range is from 2 to 255. The default value is 3.5. |
| Step 12 | exit Example: Router(config-ecfm-srv)# exit | Returns to global configuration mode. |
| Step 13 | interface type number Example: Router(config)# interface TenGigabitEthernet 4/1 | Specifies the interface to configure and enters interface configuration mode. |
| Step 14 | ethernet cfm lck link-status Example: Router(config-if)# ethernet cfm lck link-status | Enables or disables sending ETH-LCK frames from the source MEP on the interface. |
| Step 15 | ethernet cfm lck link-status period value Example: Router(config-if)# ethernet cfm lck link-status period 60 | Configures the ETH-LCK transmission period generated by the source MEP on the interface. The allowable values are 1 second or 60 seconds. |
| Step 16 | ethernet cfm lck link-status level level-id Example: Router(config-if)# ethernet cfm lck link-status level 5 | Configures the maintenance level for sending ETH-LCK frames transmitted by the source MEP on the interface. The range is from 0 to 7. |
| Step 17 | end Example: Router(config-if)# end | Returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 18 | ethernet cfm lck start mpid local-mpid domain domain-name evc evc name [drop l2-bpdu] Example: Router# ethernet cfm lck start mpid test domain customer evc evc1 | Places an MEP in ETH-LCK condition. To put a MEP out of ETH-LCK condition, enter the ethernet cfm lck stop mpid local-mpid domain domain-name evc evc name privileged EXEC command. |
| Step 19 | ethernet cfm lck start interface type number direction {up | down} [drop l2-bpdu] Example: Router# ethernet cfm lck start interface TenGigabitEthernet 4/1 direction down | Places an interface in ETH-LCK condition. To put an interface out of ETH-LCK condition, enter the ethernet cfm lck stop interface type number direction {up | down} privileged EXEC command. |
| Step 20 | show ethernet cfm smep [interface type number] Example: Router# show ethernet cfm smep interface TenGigabitEthernet 4/1 | Displays CFM information for the source MEP. |
| Step 21 | show ethernet cfm errors Example: Router(config)# show ethernet cfm errors | Displays ETH-LCK frames that are received. |
| Step 22 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
DLP-J352 Lock an MEP or an Interface Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure enables you to start the ETH-LCK fault management function on an MEP or an interface using CTC. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | DLP-J353 Enable Y.1731 Fault Management Parameters Using CTC |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node where you want to start the ETH-LCK fault management function on an MEP or an interface. |
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. |
| Step 3 | Click the Provisioning tab. |
| Step 4 | In the left pane, click Y1731. |
| Step 5 | Click the Configuration > Execute Commands > Command Execution LCK tab. |
| Step 6 | Complete the following steps to place an MEP in ETH-LCK condition. |
| Step 7 | Complete the following steps to place an interface in ETH-LCK condition. |
| Step 8 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
What to Do Next
DLP-J353 Enable Y.1731 Fault Management Parameters Using CTC
| Purpose | Y.1731 fault management in CPT consists of ETH-LCK and ETH-AIS. This procedure enables ETH-LCK and ETH-AIS fault management functions using CTC. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | NTP-J105 Configure CFM Using CTC |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
 Note | ETH-AIS and ETH-LCK are enabled by default when CFM is enabled. |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node where you want to enable ETH-LCK and ETH-AIS fault management functions. |
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. |
| Step 3 | Click the Provisioning tab. |
| Step 4 | In the left pane, click Y1731. |
| Step 5 | Click the Configuration tab. |
| Step 6 | Complete the following steps to enable ETH-LCK and ETH-AIS configurations globally.
|
| Step 7 |
Complete the following steps to enable ETH-LCK and ETH-AIS configurations on an interface.
|
| Step 8 | Complete the following steps to enable ETH-LCK and ETH-AIS configurations at the MEP level. |
| Step 9 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
What to Do Next
Understanding Y.1731 Performance Monitoring
When service providers sell connectivity services to a subscriber, a Service Level Agreement (SLA) is reached between the buyer and seller of the service. The SLA defines the attributes offered by a provider and serves as a legal obligation on the service provider. As the level of performance required by subscribers increases, service providers need to monitor the performance parameters being offered. To capture the needs of service providers, organizations have defined various standards such as IEEE 802.1ag and ITU-T Y.1731 that define the methods and frame formats used to measure performance parameters.
Y.1731 Performance Monitoring (PM) provides a standard ethernet PM function that includes measurement of ethernet frame delay, frame delay variation, frame loss, and frame throughput measurements specified by the ITU-T Y-1731 standard. To measure SLA parameters such as frame delay or frame delay variation, a small number of synthetic frames are transmitted along with the service to the MEP.
 Note | CPT supports only two–way Ethernet frame Delay Measurement (ETH-DM) in Y.1731 performance monitoring. The CPT system sends, receives, and processes PM frames in intervals of 100ms (10 frames per second) and 1 second. |
The SLA delay measurement sessions are removed after the Stateful Switchover (SSO) of the fabric card. These sessions must be manually restarted after SSO.
Frame Delay and Frame Delay Variation
Ethernet frame Delay Measurement (ETH-DM) is used for on-demand Ethernet OAM to measure frame delay and frame delay variation. Ethernet frame delay and frame delay variation are measured by:
Sending periodic frames with Ethernet Delay Measurement Message (ETH-DMM) information to the peer MEP.
Receiving frames with Ethernet Delay Measurement Reply (ETH-DMR) information from the peer MEP.
During the interval, one or both MEPs in a maintenance association measures the frame delay and frame delay variation. Ethernet frame delay measurement also collects useful information, such as minimum and maximum delay over a fixed time, average delay, and average delay variation. Ethernet frame delay measurement supports hardware-based time stamping in the ingress direction. It provides a runtime display of delay statistics during a two-way delay measurement.
In two–way delay measurement, MEP transmits frames with ETH-DM request information to its peer MEP and receives frames with ETH-DM reply information from its peer MEP. Two–way frame delay and frame delay variation is measured using ETH-DMM and ETH-DMR frame combination.
- NTP-J117 Configure and Schedule Two-Way Delay Measurement
- DLP-J354 Configure and Schedule Two-Way Delay Measurement Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J355 Configure and Schedule Two-Way Delay Measurement Using CTC
- DLP-J356 Display IP SLA Configuration and Statistics Using CTC
- Troubleshooting an IP SLA Session
- Show Commands
NTP-J117 Configure and Schedule Two-Way Delay Measurement
| Purpose | This procedure configures and schedules two-way delay measurement. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
Stop. You have completed this procedure. |
DLP-J354 Configure and Schedule Two-Way Delay Measurement Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure configures and schedules two-way delay measurement using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | ip sla n Example:Router(config)# ip sla 1 | Enables the IP SLA configuration. |
| Step 4 | ethernet y1731 delay dmm domain domain-name {evc evc-name} {mpid | mac-address target-address} cos cos-value {source mpid | mac-address source-address} Example:Router(config-ip-sla)# ethernet y1731 delay dmm domain r3 evc e3 mpid 500 cos 3 source mpid 400 | Configures a two-way delay measurement on the sender.
|
| Step 5 | frame {interval | offset | size} bytes Example:Router(config-sla-y1731-delay)# frame interval 100 | Configures the following Y.1731 frame parameters: |
| Step 6 | history {interval} intervals-stored Example:Router(config-sla-y1731-delay)# history interval 5 | Configures the following Y.1731 history parameters: |
| Step 7 | aggregate {interval} seconds Example:Router(config-sla-y1731-delay)# aggregate interval 5 | Configures the following Y.1731 aggregation parameters: |
| Step 8 | distribution {delay | delay-variation} two-way number_of_bins comma_separated_values Example:Router(config-sla-y1731-delay)# distribution delay 5 10,30,500,700,1000 | Configures the following Y.1731 distribution parameters: |
| Step 9 | max-delay milliseconds Example: Router(config-sla-y1731-delay)# max-delay 1000 | Configures maximum delay which is allowed as a valid delay measurement. The values range from 1 to 65535 milliseconds. |
| Step 10 | owner owner-id Example: Router(config-sla-y1731-delay)#owner john | Specifies the operation owner. |
| Step 11 | exit Example: Router(config-sla-y1731-delay)# exit | Exits the Y.1731 submode and enters the global configuration mode. |
| Step 12 | ip sla schedule n [life {forever | seconds}] [start-time {hh:mm[:ss] [month day | day month] | now | after hh:mm:ss}] [ageout seconds] [recurring] Example: Router(config)# ip sla schedule 10 start-time now life forever | Schedules the two-way delay measurement on the sender.
See the Troubleshooting an IP SLA Session section if the IP SLA delay measurement session does not start. |
| Step 13 | exit Example: Router(config)# exit | Exits the global configuration mode. |
| Step 14 | show ip sla configuration Example: Router# show ip sla configuration | Displays the IP SLA configuration details. |
| Step 15 | show ip sla statistics [details] Example: Router# show ip sla statistics | Displays the IP SLA statistics. |
| Step 16 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
Example: Configure Two-Way Delay Measurement
The following example configures a two-way delay measurement using Cisco IOS commands:
Router# enable Router# configure terminal Router(config)# ip sla 1 Router(config-ip-sla)# ethernet y1731 delay DMM domain ifm_400 evc e1 mpid 401 cos 4 source mpid 1 Router(config-sla-y1731-delay)# frame interval 100 Router(config-sla-y1731-delay)# history interval 5 Router(config-sla-y1731-delay)# aggregate interval 60 Router(config-sla-y1731-delay)# exit Router(config)# ip sla schedule 1 start-time now life forever Router(config)# exit
DLP-J355 Configure and Schedule Two-Way Delay Measurement Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure configures and schedules two-way delay measurement using CTC. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node where you want to configure and schedule two-way delay measurement. |
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. |
| Step 3 | Click the Provisioning tab. |
| Step 4 | In the left pane, click Y1731. |
| Step 5 | Click the Delay Measurement > Configuration tab. |
| Step 6 | Click Create. |
| Step 7 | In the Basic area of the Create DM Config dialog box, specify the following mandatory parameters: |
| Step 8 | In the Advanced area of the Create DM Config dialog box, specify the following optional delay measurement parameters: |
| Step 9 | Click OK in the Create DM Config dialog box to configure a two-way delay measurement. |
| Step 10 | Complete the following steps to schedule a two-way delay measurement. See the Troubleshooting an IP SLA Session section if the IP SLA delay measurement session does not start. |
| Step 11 | Complete the following steps to start the IP SLA operation immediately. |
| Step 12 | (Optional) Complete the following steps to delete the IP SLA instance(s). |
| Step 13 | (Optional) Check the Enable IP SLA Trap check box to enable IP SLA traps. The traps need to be enabled only if SLA alarm needs to be configured. |
| Step 14 | Click Apply. |
| Step 15 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
DLP-J356 Display IP SLA Configuration and Statistics Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure enables you to display configuration values and statistics of IP SLA operations using CTC. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | DLP-J355 Configure and Schedule Two-Way Delay Measurement Using CTC |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node where you want to display configuration values and statistics of IP SLA operations. |
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. |
| Step 3 | Click the Maintenance tab. |
| Step 4 | In the left pane, click OAM. |
| Step 5 | From the Command drop-down list, choose Show IP-SLA. |
| Step 6 | Enter the IP SLA instance in the IP SLA ID field. The range is from 1 to 2147483647. |
| Step 7 | Complete the following steps to display the statistics of IP SLA operations. |
| Step 8 | Click the Configuration option to display the configuration values including all defaults for the IP SLA operations. |
| Step 9 | Click the Interval Statistics option to display the interval statistics of IP SLA operations. |
| Step 10 | Click Execute. |
| Step 11 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
Troubleshooting an IP SLA Session
The IP SLA sessions must have a delayed start of at least 10 minutes to allow adequate time for sessions to restart on node power cycle.
To start IP SLA automatically, check the following:
-
IP SLA aggregate interval should be above 300 seconds.
-
IP SLA start time should be equal to the time taken by all the cards of the node, to come up after node reload.
If an IP SLA delay measurement session does not start, check the following:
-
There are no CFM errors such as AIS and RDI on the source MEP or local MEP.
-
The remote MEP is visible locally.
-
If the local MEP is on a channel group, all its members are present on the same card.
-
MEPs between which the SLA session is configured do not have another SLA session for the same pair of MEP.
The following table describes the commands that can used to troubleshoot issues for an IP SLA delay measurement session.
| Command | Purpose |
|---|---|
| show ethernet cfm pm |
Displays mapping of SLA ID to delay measurement session ID. If there is no output from this command, it indicates that the session was not created or the ETH-DMR was not received. |
| show ethernet cfm pm session dm_session_id |
Displays the database of delay measurement. |
| clear ethernet cfm pm session dm_session_id |
Clears the database of delay measurement. |
|
|
Enables delay measurement engine logs. The debug ethernet cfm pm monitor command is applicable only on the fabric card. |
Show Commands
This section describes several show commands that can be used with IP SLA.
Display IP SLA Configuration
This command displays the configuration values including all defaults for all IP SLA operations or a specified operation.
Router# show ip sla configuration [operation-number]IP SLAs Infrastructure Engine-III Entry number: 1 Owner: Tag: Operation timeout (milliseconds): 5000 Ethernet Y1731 Delay Operation Frame Type: DMM Domain: Level1 Evc: PWEVC Target Mpid: 10 Source Mpid: 11 CoS: 7 Max Delay: 5000 Request size (Padding portion): 64 Frame Interval: 1000 Clock: Not In Sync Threshold (milliseconds): 5000 Schedule: Operation frequency (seconds): 900 (not considered if randomly scheduled) Next Scheduled Start Time: Start Time already passed Group Scheduled : FALSE Randomly Scheduled : FALSE Life (seconds): Forever Entry Ageout (seconds): never Recurring (Starting Everyday): FALSE Status of entry (SNMP RowStatus): Active Statistics Parameters Aggregation Period: 900 Frame offset: 1 Distribution Delay Two-Way: Number of Bins 10 Bin Boundaries: 5000,10000,15000,20000,25000,30000,35000,40000,45000,-1 Distribution Delay-Variation Two-Way: Number of Bins 10 Bin Boundaries: 5000,10000,15000,20000,25000,30000,35000,40000,45000,-1 History Number of intervals: 2
Display IP SLA Statistics
This command displays the current operational status and statistics of all IP SLAs operations or a specified operation.
Router# show ip sla statistics [operation-number] [details]IPSLAs Latest Operation Statistics IPSLA operation id: 1 Delay Statistics for Y1731 Operation 1 Type of operation: Y1731 Delay Measurement Latest operation start time: 05:50:54.467 PDT Sat Jul 8 2000 Latest operation return code: OK Distribution Statistics: Interval Start time: 05:50:54.467 PDT Sat Jul 8 2000 Elapsed time: 610 seconds Number of measurements initiated: 608 Number of measurements completed: 608 Flag: OK
Display IP SLA Aggregated Statistics
This command displays the aggregated statistical errors and distribution information for all IP SLAs operations or a specified operation.
Router# show ip sla statistics aggregated [operation-number] [details]
IPSLAs aggregated statistics
IPSLA operation id: 1
Delay Statistics for Y1731 Operation 1
Type of operation: Y1731 Delay Measurement
Latest operation start time: 05:50:54.467 PDT Sat Jul 8 2000
Latest operation return code: OK
Distribution Statistics:
Interval
Start time: 05:50:54.467 PDT Sat Jul 8 2000
Elapsed time: 787 seconds
Number of measurements initiated: 777
Number of measurements completed: 777
Flag: OK
Delay:
Number of TwoWay observations: 773
Min/Avg/Max TwoWay: 58/66/98 (microsec)
Time of occurrence TwoWay:
Min - 06:03:39.978 PDT Sat Jul 8 2000
Max - 06:02:54.975 PDT Sat Jul 8 2000
Delay Variance:
Number of TwoWay positive observations: 367
Min/Avg/Max TwoWay positive: 0/3/38 (microsec)
Time of occurrence TwoWay positive:
Min - 06:02:04.967 PDT Sat Jul 8 2000
Max - 06:02:54.975 PDT Sat Jul 8 2000
Number of TwoWay negative observations: 405
Min/Avg/Max TwoWay negative: 0/3/34 (microsec)
Time of occurrence TwoWay negative:
Min - 05:59:19.937 PDT Sat Jul 8 2000
Max - 05:53:49.821 PDT Sat Jul 8 2000
Display IP SLA Global Information
This command displays global information about IP SLAs.
Router# show ip sla application
IP Service Level Agreements
Version: Round Trip Time MIB 2.2.0, Infrastructure Engine-III
Supported Operation Types:
icmpEcho, path-echo, path-jitter, udpEcho, tcpConnect, http
dns, udpJitter, dhcp, ftp, 802.1agEcho VLAN, EVC, Port
802.1agJitter VLAN, EVC, Port, y1731Delay, y1731Loss, udpApp
wspApp
Supported Features:
IPSLAs Event Publisher
IP SLAs low memory water mark: 260261241
Estimated system max number of entries: 190621
Estimated number of configurable operations: 190620
Number of Entries configured : 1
Number of active Entries : 1
Number of pending Entries : 0
Number of inactive Entries : 0
Time of last change in whole IP SLAs: 09:23:56.488 PDT Sun Jul 2 2000
Display IP SLA Threshold Settings
This command displays the configured proactive threshold monitoring settings for all IP SLA operations or a specified operation.
Router# show ip sla reaction-configuration [operation-number]Entry number: 1 Index: 1 Reaction: rtt Threshold Type: Immediate Rising (milliseconds): 10 Falling (milliseconds): 10 Action Type: None
 Feedback
Feedback