- About this Guide
- Chapter 1, Install Shelf and Common Control Cards
- Chapter 2, Connect the PC and Log Into the GUI
- Chapter 3, Turn Up a Node
- Chapter 4, Perform Acceptance Tests
- Chapter 5, Turn Up a Network
- Chapter 6, Provision Channels and Circuits
- Chapter 7, Manage Alarms
- Chapter 8, Monitor Performance
- Chapter 9, Manage Node Settings
- Chapter 10, Change Card Settings
- Chapter 11, Maintain the Node
- Chapter 12, Power Down the Node
- Chapter 13, Shelf Hardware Reference
- Chapter 14, Card Reference
- Chapter 15, Node Reference
- Chapter 16, Network Reference
- Chapter 17, CTC Operation Reference
- Chapter 18, Security and Timing Reference
- Chapter 19, Network Connectivity Reference
- Chapter 20, Alarm Management Reference
- Appendix A, CTC Information and Shortcuts
- Appendix B, Shelf Specifications
- Appendix C, DWDM Extended State Model
Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Installation and Operations Guide, Release 4.7
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- Updated:
- March 20, 2015
Chapter: Chapter 3, Turn Up a Node
- Before You Begin
- NTP-G22 Verify Common Card Installation
- NTP-G23 Create Users and Assign Security
- NTP-G24 Set Up Name, Date, Time, and Contact Information
- NTP-G25 Set Power Monitor Thresholds
- NTP-G26 Set Up CTC Network Access
- NTP-G27 Set Up the ONS 15454 for Firewall Access
- NTP-G28 Set Up SNMP
- NTP-G29 Preprovision a Slot
- NTP-G30 Install the DWDM Cards
- NTP-G31 Install the DWDM Dispersion Compensating Units
- NTP-G32 Install the Transponder and Muxponder Cards
- NTP-G33 Create a Y-Cable Protection Group
- NTP-G34 Install Fiber-Optic Cables on DWDM Cards
- DLP-G65 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for OSC Link Terminations on All Nodes
- DLP-G66 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for a Hub Node
- DLP-G67 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for a Terminal Node
- DLP-G68 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for a Line Amplifier Node
- DLP-G69 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for an OSC Regeneration Node
- DLP-G70 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for an Amplified or Passive OADM Node
- DLP-G71 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for an ROADM Node
- NTP-G35 Route Fiber-Optic Cables
- NTP-G36 Calculate Cable Connections
- NTP-G37 Run Automatic Node Setup
- NTP-G38 Provision Terminations and Ring ID
- NTP-G39 Verify OSCM and OSC-CSM Transmit Power
- NTP-G40 Replace the Front Door
Turn Up a Node
This chapter explains how to provision a single Cisco ONS 15454 dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) node and turn it up for service, including node name, date and time, timing references, network attributes such as IP address and default router, users and user security, card installation, and DWDM connections.

Note ![]() Procedures in this chapter require that you have a network plan calculated for your DWDM network with Cisco MetroPlanner, Release 2.5. Cisco MetroPlanner is a DWDM planning tool that is available from your Cisco account representative. Cisco MetroPlanner prepares a shelf plan for each network node and calculates the power and attenuation levels for the DWDM cards installed in the node. For information about Cisco MetroPlanner, contact your Cisco account representative. For more information about MetroPlanner, refer to the Cisco MetroPlanner DWDM Installation and Operations Guide, Release 2.5.
Procedures in this chapter require that you have a network plan calculated for your DWDM network with Cisco MetroPlanner, Release 2.5. Cisco MetroPlanner is a DWDM planning tool that is available from your Cisco account representative. Cisco MetroPlanner prepares a shelf plan for each network node and calculates the power and attenuation levels for the DWDM cards installed in the node. For information about Cisco MetroPlanner, contact your Cisco account representative. For more information about MetroPlanner, refer to the Cisco MetroPlanner DWDM Installation and Operations Guide, Release 2.5.

Note ![]() Unless otherwise specified, "ONS 15454" refers to both ANSI and ETSI shelf assemblies.
Unless otherwise specified, "ONS 15454" refers to both ANSI and ETSI shelf assemblies.
Before You Begin
This section lists the procedures (NTPs) that you need to complete to turn up a DWDM node. Turn to a procedure for applicable tasks (DLPs).
Complete the procedures applicable to your site plan from the following chapters:
•![]() Chapter 1, "Install the Shelf and Common Control Cards"
Chapter 1, "Install the Shelf and Common Control Cards"
•![]() Chapter 2, "Connect the PC and Log into the GUI"
Chapter 2, "Connect the PC and Log into the GUI"
This section lists the chapter procedures (NTPs). Turn to a procedure for applicable tasks (DLPs).
1. ![]() G22 Verify Common Card Installation—Complete this procedure first.
G22 Verify Common Card Installation—Complete this procedure first.
2. ![]() G23 Create Users and Assign Security—Complete this procedure to create Cisco Transport Controller (CTC) users and assign their security levels.
G23 Create Users and Assign Security—Complete this procedure to create Cisco Transport Controller (CTC) users and assign their security levels.
3. ![]() G24 Set Up Name, Date, Time, and Contact Information—Continue with this procedure to set the node name, date, time, location, and contact information.
G24 Set Up Name, Date, Time, and Contact Information—Continue with this procedure to set the node name, date, time, location, and contact information.
4. ![]() G25 Set Power Monitor Thresholds—Continue with this procedure to set the node battery power thresholds.
G25 Set Power Monitor Thresholds—Continue with this procedure to set the node battery power thresholds.
5. ![]() G26 Set Up CTC Network Access—Continue with this procedure to provision the IP address, default router, subnet mask, and network configuration settings.
G26 Set Up CTC Network Access—Continue with this procedure to provision the IP address, default router, subnet mask, and network configuration settings.
6. ![]() G27 Set Up the ONS 15454 for Firewall Access—Continue with this procedure if the ONS 15454 will be accessed behind firewalls.
G27 Set Up the ONS 15454 for Firewall Access—Continue with this procedure if the ONS 15454 will be accessed behind firewalls.
7. ![]() G28 Set Up SNMP—Complete this procedure if simple network management protocol (SNMP) will be used for network monitoring.
G28 Set Up SNMP—Complete this procedure if simple network management protocol (SNMP) will be used for network monitoring.
8. ![]() G29 Preprovision a Slot—Complete this procedure to preprovision the ONS 15454 slots.
G29 Preprovision a Slot—Complete this procedure to preprovision the ONS 15454 slots.
9. ![]() G30 Install the DWDM Cards—Complete this procedure to install the DWDM cards, including optical units, muxponders, and transponders.
G30 Install the DWDM Cards—Complete this procedure to install the DWDM cards, including optical units, muxponders, and transponders.
10. ![]() G31 Install the DWDM Dispersion Compensating Units—Complete this procedure next.
G31 Install the DWDM Dispersion Compensating Units—Complete this procedure next.
11. ![]() G32 Install the Transponder and Muxponder Cards—Complete this procedure next.
G32 Install the Transponder and Muxponder Cards—Complete this procedure next.
12. ![]() G33 Create a Y-Cable Protection Group—Complete this procedure, as needed, for TXP and MXP cards that will be protected with Y-cable protection.
G33 Create a Y-Cable Protection Group—Complete this procedure, as needed, for TXP and MXP cards that will be protected with Y-cable protection.
13. ![]() G34 Install Fiber-Optic Cables on DWDM Cards—Complete this procedure, as needed, to install the fiber-optic cables on the DWDM cards.
G34 Install Fiber-Optic Cables on DWDM Cards—Complete this procedure, as needed, to install the fiber-optic cables on the DWDM cards.
14. ![]() G35 Route Fiber-Optic Cables—Complete this procedure, as needed, to route the fiber-optic cable.
G35 Route Fiber-Optic Cables—Complete this procedure, as needed, to route the fiber-optic cable.
15. ![]() G36 Calculate Cable Connections—Complete this procedure next.
G36 Calculate Cable Connections—Complete this procedure next.
16. ![]() G37 Run Automatic Node Setup—Complete this procedure next.
G37 Run Automatic Node Setup—Complete this procedure next.
17. ![]() G38 Provision Terminations and Ring ID—Complete this procedure next.
G38 Provision Terminations and Ring ID—Complete this procedure next.
18. ![]() G39 Verify OSCM and OSC-CSM Transmit Power—Complete this procedure next.
G39 Verify OSCM and OSC-CSM Transmit Power—Complete this procedure next.
19. ![]() G40 Replace the Front Door—Complete this procedure, as needed, to replace the ONS 15454 front door.
G40 Replace the Front Door—Complete this procedure, as needed, to replace the ONS 15454 front door.
NTP-G22 Verify Common Card Installation
Step 1 ![]() Verify that two TCC2 cards are installed in Slots 7 and 11.
Verify that two TCC2 cards are installed in Slots 7 and 11.
Step 2 ![]() Verify that the green ACT (active) LED is illuminated on one TCC2 and the amber STBY (standby) LED is illuminated on the second TCC2.
Verify that the green ACT (active) LED is illuminated on one TCC2 and the amber STBY (standby) LED is illuminated on the second TCC2.

Note ![]() If the TCC2 cards are not installed, or if their LEDs are not operating as described, do not continue. Repeat the "DLP-G33 Install the TCC2 Card" task on page 1-73 or refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 SONET and DWDM Troubleshooting Guide to resolve installation problems before proceeding to Step 3.
If the TCC2 cards are not installed, or if their LEDs are not operating as described, do not continue. Repeat the "DLP-G33 Install the TCC2 Card" task on page 1-73 or refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 SONET and DWDM Troubleshooting Guide to resolve installation problems before proceeding to Step 3.
Step 3 ![]() If your site plan requires an AIC or AIC-I card, verify that the AIC/AIC-I card is installed in Slot 9 and its ACT (active) LED displays a solid green light.
If your site plan requires an AIC or AIC-I card, verify that the AIC/AIC-I card is installed in Slot 9 and its ACT (active) LED displays a solid green light.
Step 4 ![]() Verify that the software release shown on the LCD matches the software release indicated in your site plan. If the release does not match, perform one of the following procedures:
Verify that the software release shown on the LCD matches the software release indicated in your site plan. If the release does not match, perform one of the following procedures:
•![]() Perform a software upgrade using a Cisco ONS 15454 software CD. Refer to the release-specific software upgrade document.
Perform a software upgrade using a Cisco ONS 15454 software CD. Refer to the release-specific software upgrade document.
•![]() Replace the TCC2 cards with cards containing the correct release.
Replace the TCC2 cards with cards containing the correct release.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-G23 Create Users and Assign Security
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-G46 Log into CTC" task on page 2-25 at the node where you need to create users. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the "DLP-G46 Log into CTC" task on page 2-25 at the node where you need to create users. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.

Note ![]() You must log in as a Superuser to create additional users. The CISCO15 user provided with each ONS 15454 can be used to set up other ONS 15454 users. You can add up to 500 users to one ONS 15454.
You must log in as a Superuser to create additional users. The CISCO15 user provided with each ONS 15454 can be used to set up other ONS 15454 users. You can add up to 500 users to one ONS 15454.
Step 2 ![]() Complete the "DLP-G54 Create a New User—Single Node" task or the "DLP-G55 Create a New User—Multiple Nodes" task as needed.
Complete the "DLP-G54 Create a New User—Single Node" task or the "DLP-G55 Create a New User—Multiple Nodes" task as needed.

Note ![]() You must add the same user name and password to each node a user will access.
You must add the same user name and password to each node a user will access.
Step 3 ![]() If you want to modify the security policy settings, including password aging and idle user timeout policies, complete the "NTP-G88 Modify Users and Change Security" procedure on page 9-34.
If you want to modify the security policy settings, including password aging and idle user timeout policies, complete the "NTP-G88 Modify Users and Change Security" procedure on page 9-34.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-G54 Create a New User—Single Node
Purpose |
This task creates a new user for one ONS 15454. |
Tools/Equipment |
None |
Prerequisite Procedures |
|
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite or remote |
Security Level |
Superuser only |
Step 1 ![]() In node view, click the Provisioning > Security > Users tabs.
In node view, click the Provisioning > Security > Users tabs.
Step 2 ![]() In the Users window, click Create.
In the Users window, click Create.
Step 3 ![]() In the Create User dialog box, enter the following:
In the Create User dialog box, enter the following:
•![]() Name—Type the user name. The name must be a minimum of six and a maximum of 20 alphanumeric (a-z, A-Z, 0-9) characters. For TL1 compatibility, the user name must be 6 to 10 characters.
Name—Type the user name. The name must be a minimum of six and a maximum of 20 alphanumeric (a-z, A-Z, 0-9) characters. For TL1 compatibility, the user name must be 6 to 10 characters.
•![]() Password—Type the user password. The password must be a minimum of six and a maximum of 20 alphanumeric (a-z, A-Z, 0-9) and special (+, #,%) characters, where at least two characters are non alphabetic and at least one character is a special character. For TL1 compatibility, the password must be 6 to 10 characters. The password must not contain the user name.
Password—Type the user password. The password must be a minimum of six and a maximum of 20 alphanumeric (a-z, A-Z, 0-9) and special (+, #,%) characters, where at least two characters are non alphabetic and at least one character is a special character. For TL1 compatibility, the password must be 6 to 10 characters. The password must not contain the user name.
•![]() Confirm Password—Type the password again to confirm it.
Confirm Password—Type the password again to confirm it.
•![]() Security Level—Choose a security level for the user: RETRIEVE, MAINTENANCE, PROVISIONING, or SUPERUSER. See the "18.1 Users and Security" section on page 18-1for information about the capabilities provided with each level.
Security Level—Choose a security level for the user: RETRIEVE, MAINTENANCE, PROVISIONING, or SUPERUSER. See the "18.1 Users and Security" section on page 18-1for information about the capabilities provided with each level.

Note ![]() Each security level has a different idle time. The idle time is the length of time that CTC can remain idle before the password must be reentered. The defaults are: Retrieve user = unlimited, Maintenance user = 60 minutes, Provisioning user = 30 minutes, and Superuser = 15 minutes. To change the idle times, refer to the "NTP-G88 Modify Users and Change Security" procedure on page 9-34.
Each security level has a different idle time. The idle time is the length of time that CTC can remain idle before the password must be reentered. The defaults are: Retrieve user = unlimited, Maintenance user = 60 minutes, Provisioning user = 30 minutes, and Superuser = 15 minutes. To change the idle times, refer to the "NTP-G88 Modify Users and Change Security" procedure on page 9-34.
Step 4 ![]() Click OK.
Click OK.
Step 5 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G55 Create a New User—Multiple Nodes
Purpose |
This task adds a new user to multiple ONS 15454s. |
Tools/Equipment |
None |
Prerequisite Procedures |
|
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite or remote |
Security Level |
Superuser |

Note ![]() All nodes where you want to add users must be accessible in network view.
All nodes where you want to add users must be accessible in network view.
Step 1 ![]() From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Provisioning > Security > Users tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Security > Users tabs.
Step 3 ![]() In the Users window, click Create.
In the Users window, click Create.
Step 4 ![]() In the Create User dialog box, enter the following:
In the Create User dialog box, enter the following:
•![]() Name—Type the user name. The name must be a minimum of six and a maximum of 20 alphanumeric (a-z, A-Z, 0-9) characters. For TL1 compatibility, the user name must 6 to 10 characters.
Name—Type the user name. The name must be a minimum of six and a maximum of 20 alphanumeric (a-z, A-Z, 0-9) characters. For TL1 compatibility, the user name must 6 to 10 characters.
•![]() Password—Type the user password. The password must be a minimum of six and a maximum of 20 alphanumeric (a-z, A-Z, 0-9) and special (+, #, %) characters, where at least two characters are non alphabetic and at least one character is a special character. For TL1 compatibility, the password must be 6 to 10 characters. The password must not contain the user name.
Password—Type the user password. The password must be a minimum of six and a maximum of 20 alphanumeric (a-z, A-Z, 0-9) and special (+, #, %) characters, where at least two characters are non alphabetic and at least one character is a special character. For TL1 compatibility, the password must be 6 to 10 characters. The password must not contain the user name.
•![]() Confirm Password—Type the password again to confirm it.
Confirm Password—Type the password again to confirm it.
•![]() Security Level—Choose a security level for the user: RETRIEVE, MAINTENANCE, PROVISIONING, or SUPERUSER. Refer to the "18.1 Users and Security" section on page 18-1 for information about the capabilities provided with each level.
Security Level—Choose a security level for the user: RETRIEVE, MAINTENANCE, PROVISIONING, or SUPERUSER. Refer to the "18.1 Users and Security" section on page 18-1 for information about the capabilities provided with each level.

Note ![]() Each security level has a different idle time. The idle time is the length of time that CTC can remain idle before it locks up and the password must be reentered. The defaults are: Retrieve user = unlimited, Maintenance user = 60 minutes, Provisioning user = 30 minutes, and Superuser = 15 minutes. To change the idle times, refer to the "NTP-G88 Modify Users and Change Security" procedure on page 9-34.
Each security level has a different idle time. The idle time is the length of time that CTC can remain idle before it locks up and the password must be reentered. The defaults are: Retrieve user = unlimited, Maintenance user = 60 minutes, Provisioning user = 30 minutes, and Superuser = 15 minutes. To change the idle times, refer to the "NTP-G88 Modify Users and Change Security" procedure on page 9-34.
Step 5 ![]() Under "Select applicable nodes," deselect any nodes where you do not want to add the user (all network nodes are selected by default).
Under "Select applicable nodes," deselect any nodes where you do not want to add the user (all network nodes are selected by default).
Step 6 ![]() Click OK.
Click OK.
Step 7 ![]() In the User Creation Results dialog box, verify that the user was added to all the nodes chosen in Step 5. If not, click OK and repeat Steps 2 through 6. If the user was added to all nodes, click OK and continue with the next step.
In the User Creation Results dialog box, verify that the user was added to all the nodes chosen in Step 5. If not, click OK and repeat Steps 2 through 6. If the user was added to all nodes, click OK and continue with the next step.
Step 8 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-G24 Set Up Name, Date, Time, and Contact Information
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-G46 Log into CTC" task on page 2-25 for the node you will turn up. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the "DLP-G46 Log into CTC" task on page 2-25 for the node you will turn up. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Provisioning > General tabs.
Click the Provisioning > General tabs.
Step 3 ![]() Enter the following information in the fields listed:
Enter the following information in the fields listed:
•![]() Node Name—Type a name for the node. For TL1 compliance, names must begin with an alpha character and have no more than 20 alphanumeric (a-z, A-Z, 0-9) characters.
Node Name—Type a name for the node. For TL1 compliance, names must begin with an alpha character and have no more than 20 alphanumeric (a-z, A-Z, 0-9) characters.

Note ![]() To avoid errors when you import the Cisco MetroPlanner configuration file in the "DLP-G74 Import a Cisco MetroPlanner Configuration File" task, the CTC node name and the MetroPlanner site name should be the same or at least easy to identify.
To avoid errors when you import the Cisco MetroPlanner configuration file in the "DLP-G74 Import a Cisco MetroPlanner Configuration File" task, the CTC node name and the MetroPlanner site name should be the same or at least easy to identify.
•![]() Contact—Type the name of the node contact person and the phone number, up to 255 characters (optional).
Contact—Type the name of the node contact person and the phone number, up to 255 characters (optional).
•![]() Latitude—Enter the node latitude: N (north) or S (south), degrees, and minutes (optional).
Latitude—Enter the node latitude: N (north) or S (south), degrees, and minutes (optional).
•![]() Longitude—Enter the node longitude: E (east) or W (west), degrees, and minutes (optional).
Longitude—Enter the node longitude: E (east) or W (west), degrees, and minutes (optional).
CTC uses the latitude and longitude to position ONS 15454 icons on the network view map. To convert a coordinate in degrees to degrees and minutes, multiply the number after the decimal by 60. For example, the latitude 38.250739 converts to 38 degrees, 15 minutes (0.250739 x 60 = 15.0443, rounded to the nearest whole number).
•![]() Description—Type a description of the node. The description can be a maximum of 255 characters.
Description—Type a description of the node. The description can be a maximum of 255 characters.
•![]() Use NTP/SNTP Server—When checked, CTC uses a Network Time Protocol (NTP) or Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) server to set the date and time of the node.
Use NTP/SNTP Server—When checked, CTC uses a Network Time Protocol (NTP) or Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) server to set the date and time of the node.
If you do not use an SNTP or NTP server, complete the Date and Time fields. The ONS 15454 will use these fields for alarm dates and times. (CTC displays all alarms in the login node's time zone for cross network consistency.)

Note ![]() Using an NTP or SNTP server ensures that all ONS 15454 network nodes use the same date and time reference. The server synchronizes the node's time after power outages or software upgrades.
Using an NTP or SNTP server ensures that all ONS 15454 network nodes use the same date and time reference. The server synchronizes the node's time after power outages or software upgrades.
If you check the Use NTP/SNTP Server check box, type the IP address of one of the following:
–![]() an NTP/SNTP server connected to the ONS 15454
an NTP/SNTP server connected to the ONS 15454
–![]() Another ONS 15454 with NTP/SNTP enabled that is connected to the ONS 15454
Another ONS 15454 with NTP/SNTP enabled that is connected to the ONS 15454
If you check gateway network element (GNE) for the ONS 15454 proxy server (see "DLP-G56 Provision IP Settings" task), external ONS 15454s must reference the gateway ONS 15454 for NTP/SNTP timing. For more information about the ONS 15454 gateway settings, see Chapter 19, "CTC Connectivity Reference."

•![]() Date—If Use NTP/SNTP Server is not checked, type the current date in the format m/d/yyyy, for example, September 24, 2002 is 9/24/2002.
Date—If Use NTP/SNTP Server is not checked, type the current date in the format m/d/yyyy, for example, September 24, 2002 is 9/24/2002.
•![]() Time—If Use NTP/SNTP Server is not checked, type the current time in the format hh:mm:ss, for example, 11:24:58. The ONS 15454 uses a 24-hour clock, so 10:00 PM is entered as 22:00:00.
Time—If Use NTP/SNTP Server is not checked, type the current time in the format hh:mm:ss, for example, 11:24:58. The ONS 15454 uses a 24-hour clock, so 10:00 PM is entered as 22:00:00.
•![]() Time Zone—Click the field and choose a city within your time zone from the drop-down list. The menu displays the 80 World Time Zones from -11 through 0 (GMT) to +14. Continental United States time zones are GMT-05:00 (Eastern), GMT-06:00 (Central), GMT-07:00 (Mountain), and GMT-08:00 (Pacific).
Time Zone—Click the field and choose a city within your time zone from the drop-down list. The menu displays the 80 World Time Zones from -11 through 0 (GMT) to +14. Continental United States time zones are GMT-05:00 (Eastern), GMT-06:00 (Central), GMT-07:00 (Mountain), and GMT-08:00 (Pacific).
•![]() Use Daylight Savings Time—Check this check box if the time zone that you chose is using Daylight Savings Time.
Use Daylight Savings Time—Check this check box if the time zone that you chose is using Daylight Savings Time.
•![]() Insert AIS-V on STS-1 SD-P—Not used in DWDM networks.
Insert AIS-V on STS-1 SD-P—Not used in DWDM networks.
•![]() SD-P BER—Not used in DWDM networks.
SD-P BER—Not used in DWDM networks.
Step 4 ![]() Click Apply.
Click Apply.
Step 5 ![]() In the confirmation dialog box, click Yes.
In the confirmation dialog box, click Yes.
Step 6 ![]() Review the node information. If you need to make corrections, repeat Steps 3 through 5 to enter the corrections. If the information is correct, continue with the "G25 Set Power Monitor Thresholds" procedure.
Review the node information. If you need to make corrections, repeat Steps 3 through 5 to enter the corrections. If the information is correct, continue with the "G25 Set Power Monitor Thresholds" procedure.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-G25 Set Power Monitor Thresholds
Purpose |
This procedure provisions extreme high, extreme low, and low input battery power thresholds within a -48 volts direct current (VDC) environment. When the thresholds are crossed, the TCC2 generates warning alarms in CTC. For ONS 15454 power specifications, see Appendix B, "Hardware Specifications." |
Tools/Equipment |
None |
Prerequisite Procedures |
|
Required/As Needed |
Required |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite or remote |
Security Level |
Provisioning or higher |
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-G46 Log into CTC" task on page 2-25 for the node you will set up. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the "DLP-G46 Log into CTC" task on page 2-25 for the node you will set up. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2 ![]() In node view, click the Provisioning > General > Power Monitor tabs.
In node view, click the Provisioning > General > Power Monitor tabs.
Step 3 ![]() To change the extreme low battery voltage threshold in 0.5 VDC increments, choose a voltage from the ELWBATVGVdc drop-down list.
To change the extreme low battery voltage threshold in 0.5 VDC increments, choose a voltage from the ELWBATVGVdc drop-down list.
Step 4 ![]() To change the low battery voltage threshold in 0.5 VDC increments, choose a voltage from the LWBATVGVdc drop-down list.
To change the low battery voltage threshold in 0.5 VDC increments, choose a voltage from the LWBATVGVdc drop-down list.
Step 5 ![]() To change the high battery voltage threshold in 0.5 VDC increments, choose a voltage from the HIBATVGVdc drop-down list.
To change the high battery voltage threshold in 0.5 VDC increments, choose a voltage from the HIBATVGVdc drop-down list.
Step 6 ![]() To change the extreme high battery voltage threshold in 0.5 VDC increments, choose a voltage from the EHIBATVGVdc drop-down list.
To change the extreme high battery voltage threshold in 0.5 VDC increments, choose a voltage from the EHIBATVGVdc drop-down list.
Step 7 ![]() Click Apply.
Click Apply.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-G26 Set Up CTC Network Access
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-G46 Log into CTC" task on page 2-25. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the "DLP-G46 Log into CTC" task on page 2-25. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2 ![]() Complete the "DLP-G56 Provision IP Settings" task to provision the ONS 15454 IP address, subnet mask, default router, DHCP server, IIOP listener port, and proxy server settings.
Complete the "DLP-G56 Provision IP Settings" task to provision the ONS 15454 IP address, subnet mask, default router, DHCP server, IIOP listener port, and proxy server settings.

Tip ![]() If you cannot log into the node, you can change its IP address, default router, and network mask by using the LCD on the ONS 15454 fan-tray assembly (unless LCD provisioning is suppressed). See the "DLP-G57 Set the IP Address, Default Router, and Network Mask Using the LCD" task for instructions. However, you cannot use the LCD to provision any other network settings.
If you cannot log into the node, you can change its IP address, default router, and network mask by using the LCD on the ONS 15454 fan-tray assembly (unless LCD provisioning is suppressed). See the "DLP-G57 Set the IP Address, Default Router, and Network Mask Using the LCD" task for instructions. However, you cannot use the LCD to provision any other network settings.
Step 3 ![]() If static routes are needed, complete the "DLP-G58 Create a Static Route" task. For more information about static routes, see Chapter 19, "CTC Connectivity Reference."
If static routes are needed, complete the "DLP-G58 Create a Static Route" task. For more information about static routes, see Chapter 19, "CTC Connectivity Reference."
Step 4 ![]() If the ONS 15454 is connected to a LAN or WAN that uses OSPF, complete the "DLP-G59 Set Up or Change Open Shortest Path First Protocol" task.
If the ONS 15454 is connected to a LAN or WAN that uses OSPF, complete the "DLP-G59 Set Up or Change Open Shortest Path First Protocol" task.
Step 5 ![]() If the ONS 15454 is connected to a LAN or WAN that uses RIP, complete the "DLP-G60 Set Up or Change Routing Information Protocol" task.
If the ONS 15454 is connected to a LAN or WAN that uses RIP, complete the "DLP-G60 Set Up or Change Routing Information Protocol" task.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-G56 Provision IP Settings

Step 1 ![]() In node view, click the Provisioning > Network tabs.
In node view, click the Provisioning > Network tabs.
Step 2 ![]() Complete the following information in the fields listed:
Complete the following information in the fields listed:
•![]() IP Address—Type the IP address assigned to the ONS 15454 node.
IP Address—Type the IP address assigned to the ONS 15454 node.
•![]() Suppress CTC IP Display—Check this check box if you want to prevent the node IP address from being displayed in CTC to users with Provisioner, Maintenance, or Retrieve security levels. (The IP address suppression is not applied to users with Superuser security level.)
Suppress CTC IP Display—Check this check box if you want to prevent the node IP address from being displayed in CTC to users with Provisioner, Maintenance, or Retrieve security levels. (The IP address suppression is not applied to users with Superuser security level.)
•![]() LCD IP Display—Choose one of the following:
LCD IP Display—Choose one of the following:
–![]() Allow Configuration—Displays the node IP address on the LCD and allows users to change the IP settings using the LCD. This option enables the "DLP-G57 Set the IP Address, Default Router, and Network Mask Using the LCD" task.
Allow Configuration—Displays the node IP address on the LCD and allows users to change the IP settings using the LCD. This option enables the "DLP-G57 Set the IP Address, Default Router, and Network Mask Using the LCD" task.
–![]() Display Only—Displays the node IP address on the LCD but does not allow users to change the IP address using the LCD.
Display Only—Displays the node IP address on the LCD but does not allow users to change the IP address using the LCD.
–![]() Suppress Display—Suppresses the node IP address display on the LCD.
Suppress Display—Suppresses the node IP address display on the LCD.
•![]() Default Router—If the ONS 15454 must communicate with a device on a network that the ONS 15454 is not directly connected to, the ONS 15454 can forward the packets to the default router. Type the IP address of the router in this field.
Default Router—If the ONS 15454 must communicate with a device on a network that the ONS 15454 is not directly connected to, the ONS 15454 can forward the packets to the default router. Type the IP address of the router in this field.

Note ![]() This field is ignored if the node is not connected to a LAN, or if you enable any of the gateway settings to implement the ONS 15454 proxy server feature.
This field is ignored if the node is not connected to a LAN, or if you enable any of the gateway settings to implement the ONS 15454 proxy server feature.
•![]() Forward DHCP Request To—Check this check box to enable DHCP. Also, enter the DHCP server IP address in the Request To field. Unchecked is the default. If you will enable any of the gateway settings to implement the ONS 15454 proxy server features, leave this field blank.
Forward DHCP Request To—Check this check box to enable DHCP. Also, enter the DHCP server IP address in the Request To field. Unchecked is the default. If you will enable any of the gateway settings to implement the ONS 15454 proxy server features, leave this field blank.

Note ![]() If you enable DHCP, computers connected to an ONS 15454 node can obtain temporary IP addresses from an external DHCP server. The ONS 15454 only forwards DHCP requests; it does not act as a DHCP server.
If you enable DHCP, computers connected to an ONS 15454 node can obtain temporary IP addresses from an external DHCP server. The ONS 15454 only forwards DHCP requests; it does not act as a DHCP server.
•![]() MAC Address—(Display only.) Displays the ONS 15454 IEEE 802 MAC address.
MAC Address—(Display only.) Displays the ONS 15454 IEEE 802 MAC address.
•![]() Net/Subnet Mask Length—Type the subnet mask length (decimal number representing the subnet mask length in bits) or click the arrows to adjust the subnet mask length. The subnet mask length is the same for all ONS 15454s in the same subnet.
Net/Subnet Mask Length—Type the subnet mask length (decimal number representing the subnet mask length in bits) or click the arrows to adjust the subnet mask length. The subnet mask length is the same for all ONS 15454s in the same subnet.
•![]() TCC CORBA (IIOP) Listener Port—Provisions the ONS 15454 IIOP listener port. This listener port enables communication with the ONS 15454 through firewalls. See the "G27 Set Up the ONS 15454 for Firewall Access" procedure for more information.
TCC CORBA (IIOP) Listener Port—Provisions the ONS 15454 IIOP listener port. This listener port enables communication with the ONS 15454 through firewalls. See the "G27 Set Up the ONS 15454 for Firewall Access" procedure for more information.
•![]() Gateway Settings—Provides options that enable the ONS 15454 proxy server features. In proxy server networks, the ONS 15454 is either an end network element (ENE), gateway network element (GNE), or proxy-only server. GNEs and ENEs manage their craft Ethernet ports differently. A GNE will connect to an entire intranet or internet through its craft Ethernet port. An ENE will only communicate with the hosts that have connected to it, such as a CTC computer or other ONS 15454 ENE. Provisioning must be consistent for each NE type. For more information, see the "19.2.7 Scenario 7: Provisioning the ONS 15454 Proxy Server" section on page 19-11.
Gateway Settings—Provides options that enable the ONS 15454 proxy server features. In proxy server networks, the ONS 15454 is either an end network element (ENE), gateway network element (GNE), or proxy-only server. GNEs and ENEs manage their craft Ethernet ports differently. A GNE will connect to an entire intranet or internet through its craft Ethernet port. An ENE will only communicate with the hosts that have connected to it, such as a CTC computer or other ONS 15454 ENE. Provisioning must be consistent for each NE type. For more information, see the "19.2.7 Scenario 7: Provisioning the ONS 15454 Proxy Server" section on page 19-11.
•![]() Enable proxy server on port—If checked, the ONS 15454 serves as a proxy for connections between CTC clients and ONS 15454s that are DCC-connected to the proxy ONS 15454. The CTC client establishes connections to data communications channel (DCC)-connected nodes through the proxy node. The CTC client does not require IP connectivity to the DCC-connected nodes, only to the proxy ONS 15454. If Enable proxy server on port is off, the node does not proxy for any CTC clients, although any established proxy connections continue until the CTC client exits. When this box is checked, you can set the node as an ENE or a GNE:
Enable proxy server on port—If checked, the ONS 15454 serves as a proxy for connections between CTC clients and ONS 15454s that are DCC-connected to the proxy ONS 15454. The CTC client establishes connections to data communications channel (DCC)-connected nodes through the proxy node. The CTC client does not require IP connectivity to the DCC-connected nodes, only to the proxy ONS 15454. If Enable proxy server on port is off, the node does not proxy for any CTC clients, although any established proxy connections continue until the CTC client exits. When this box is checked, you can set the node as an ENE or a GNE:
–![]() End Network Element (ENE)—If selected, the CTC computer is only visible to the ONS 15454 to which the CTC computer is connected. The computer is not visible to other DCC-connected nodes. In addition, firewall is enabled, which means that the node prevents IP traffic from being routed between the DCC and the LAN port.
End Network Element (ENE)—If selected, the CTC computer is only visible to the ONS 15454 to which the CTC computer is connected. The computer is not visible to other DCC-connected nodes. In addition, firewall is enabled, which means that the node prevents IP traffic from being routed between the DCC and the LAN port.
–![]() Gateway Network Element (GNE)—If selected, the CTC computer is visible to other DCC-connected nodes. The node prevents IP traffic from being routed between the DCC and the LAN port.
Gateway Network Element (GNE)—If selected, the CTC computer is visible to other DCC-connected nodes. The node prevents IP traffic from being routed between the DCC and the LAN port.
–![]() Proxy-only—If selected, the ONS 15454 responds to CTC requests with a list of DCC-connected nodes for which the node serves as a proxy. The CTC computer is visible to other DCC-connected nodes. The node does not prevent traffic from being routed between the DCC and LAN port.
Proxy-only—If selected, the ONS 15454 responds to CTC requests with a list of DCC-connected nodes for which the node serves as a proxy. The CTC computer is visible to other DCC-connected nodes. The node does not prevent traffic from being routed between the DCC and LAN port.
Step 3 ![]() Click Apply.
Click Apply.
Step 4 ![]() Click Yes in the confirmation dialog box.
Click Yes in the confirmation dialog box.
Both TCC2 cards reboot, one at a time. During this time (approximately 5 minutes), the active and standby TCC2 card LEDs go through the cycle shown in Table 3-1. Eventually, a "Lost node connection, switching to network view" message appears.
Step 5 ![]() Click OK. The network view appears. The node icon appears in gray, during which time you cannot access the node.
Click OK. The network view appears. The node icon appears in gray, during which time you cannot access the node.
Step 6 ![]() Double-click the node icon when it becomes green.
Double-click the node icon when it becomes green.
Step 7 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G57 Set the IP Address, Default Router, and Network Mask Using the LCD

Note ![]() You cannot perform this task if the LCD IP Display on the node view Provisioning > Network tab is set to Display Only or Suppress Display. See "DLP-G56 Provision IP Settings" task to view or change the LCD IP Display field.
You cannot perform this task if the LCD IP Display on the node view Provisioning > Network tab is set to Display Only or Suppress Display. See "DLP-G56 Provision IP Settings" task to view or change the LCD IP Display field.

Note ![]() The LCD reverts to normal display mode after 5 seconds of button inactivity.
The LCD reverts to normal display mode after 5 seconds of button inactivity.
Step 1 ![]() On the ONS 15454 front panel, repeatedly press the Slot button until Node appears on the LCD.
On the ONS 15454 front panel, repeatedly press the Slot button until Node appears on the LCD.
Step 2 ![]() Repeatedly press the Port button until the following displays:
Repeatedly press the Port button until the following displays:
•![]() To change the node IP address, Status=IpAddress (Figure 3-1)
To change the node IP address, Status=IpAddress (Figure 3-1)
•![]() To change the node network mask, Status=Net Mask
To change the node network mask, Status=Net Mask
•![]() To change the default router IP address, Status=Default Rtr
To change the default router IP address, Status=Default Rtr
Figure 3-1 Selecting the IP Address Option
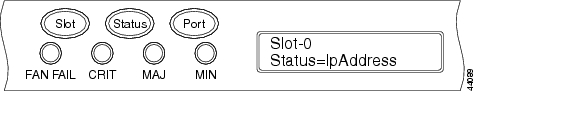
Step 3 ![]() Press the Status button to display the node IP address (Figure 3-2), the node subnet mask length, or the default router IP address.
Press the Status button to display the node IP address (Figure 3-2), the node subnet mask length, or the default router IP address.
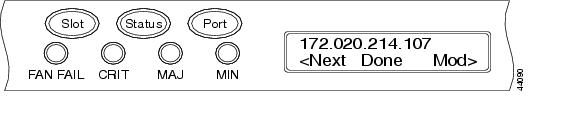
Figure 3-2 Changing the IP Address
Step 4 ![]() Push the Slot button to move to the IP address or subnet mask digit you need to change. The selected digit flashes.
Push the Slot button to move to the IP address or subnet mask digit you need to change. The selected digit flashes.

Tip ![]() The Slot, Status, and Port button positions correspond to the command position on the LCD. For example, in Figure 3-2, you press the Slot button to invoke the Next command and the Port button to invoke the Done command.
The Slot, Status, and Port button positions correspond to the command position on the LCD. For example, in Figure 3-2, you press the Slot button to invoke the Next command and the Port button to invoke the Done command.
Step 5 ![]() Press the Port button to cycle the IP address or subnet mask to the correct digit.
Press the Port button to cycle the IP address or subnet mask to the correct digit.
Step 6 ![]() When the change is complete, press the Status button to return to the Node menu.
When the change is complete, press the Status button to return to the Node menu.
Step 7 ![]() Repeatedly press the Port button until the Save Configuration option appears (Figure 3-3).
Repeatedly press the Port button until the Save Configuration option appears (Figure 3-3).
Figure 3-3 Selecting the Save Configuration Option

Step 8 ![]() Press the Status button to choose the Save Configuration option.
Press the Status button to choose the Save Configuration option.
A Save and REBOOT message appears (Figure 3-4).
Figure 3-4 Saving and Rebooting the TCC2/TCC2P

Step 9 ![]() Press the Slot button to apply the new IP address configuration or press Port to cancel the configuration.
Press the Slot button to apply the new IP address configuration or press Port to cancel the configuration.
Saving the new configuration causes the TCC2 cards to reboot. During the reboot, a "Saving Changes - TCC Reset" message displays on the LCD. The LCD returns to the normal alternating display after the TCC2 reboot is complete.

Note ![]() The IP address and default router must be on the same subnet. If not, you cannot apply the configuration.
The IP address and default router must be on the same subnet. If not, you cannot apply the configuration.
Step 10 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G58 Create a Static Route
Step 1 ![]() In node view, click the Provisioning > Network tabs.
In node view, click the Provisioning > Network tabs.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Static Routing tab. Click Create.
Click the Static Routing tab. Click Create.
Step 3 ![]() In the Create Static Route dialog box, enter the following:
In the Create Static Route dialog box, enter the following:
•![]() Destination—Enter the IP address of the computer running CTC. To limit access to one computer, enter the full IP address and a subnet mask of 255.255.255.255. To allow access to all computers on the 192.168.1.0 subnet, enter 192.168.1.0 and a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0. You can enter a destination of 0.0.0.0 to allow access to all CTC computers that connect to the router.
Destination—Enter the IP address of the computer running CTC. To limit access to one computer, enter the full IP address and a subnet mask of 255.255.255.255. To allow access to all computers on the 192.168.1.0 subnet, enter 192.168.1.0 and a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0. You can enter a destination of 0.0.0.0 to allow access to all CTC computers that connect to the router.
•![]() Mask—Enter a subnet mask. If the destination is a host route (that is, one CTC computer), enter a 32-bit subnet mask (255.255.255.255). If the destination is a subnet, adjust the subnet mask accordingly, for example, 255.255.255.0. If the destination is 0.0.0.0, CTC automatically enters a subnet mask of 0.0.0.0 to provide access to all CTC computers. You cannot change this value.
Mask—Enter a subnet mask. If the destination is a host route (that is, one CTC computer), enter a 32-bit subnet mask (255.255.255.255). If the destination is a subnet, adjust the subnet mask accordingly, for example, 255.255.255.0. If the destination is 0.0.0.0, CTC automatically enters a subnet mask of 0.0.0.0 to provide access to all CTC computers. You cannot change this value.
•![]() Next Hop—Enter the IP address of the router port or the node IP address if the CTC computer is connected to the node directly.
Next Hop—Enter the IP address of the router port or the node IP address if the CTC computer is connected to the node directly.
•![]() Cost—Enter the number of hops between the ONS 15454 and the computer.
Cost—Enter the number of hops between the ONS 15454 and the computer.
Step 4 ![]() Click OK. Verify that the static route appears in the Static Route window.
Click OK. Verify that the static route appears in the Static Route window.

Note ![]() Static route networking examples are provided in Chapter 19, "CTC Connectivity Reference."
Static route networking examples are provided in Chapter 19, "CTC Connectivity Reference."
Step 5 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G59 Set Up or Change Open Shortest Path First Protocol
Purpose |
This task enables the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol on the ONS 15454. Perform this task if you want to include the ONS 15454 in OSPF-enabled networks. |
Tools/Equipment |
None |
Prerequisite Procedures |
DLP-G46 Log into CTC, page 2-25 You will need the OSPF Area ID, Hello and Dead intervals, and authentication key (if OSPF authentication is enabled) provisioned on the router to which the ONS 15454 is connected. |
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite or remote |
Security Level |
Provisioning or higher |
Step 1 ![]() In node view, click the Provisioning > Network > OSPF tabs.
In node view, click the Provisioning > Network > OSPF tabs.
Step 2 ![]() On the top left side of the OSPF pane, complete the following:
On the top left side of the OSPF pane, complete the following:
•![]() DCC/GCC OSPF Area ID Table—In dotted decimal format, enter the number that identifies the ONS 15454s as a unique OSPF area ID. The Area ID can be any number between 000.000.000.000 and 255.255.255.255, but must be unique to the LAN OSPF area.
DCC/GCC OSPF Area ID Table—In dotted decimal format, enter the number that identifies the ONS 15454s as a unique OSPF area ID. The Area ID can be any number between 000.000.000.000 and 255.255.255.255, but must be unique to the LAN OSPF area.
•![]() SDCC Metric—This value is normally unchanged. It sets a cost for sending packets across the Section DCC, which is used by OSPF routers to calculate the shortest path. This value should always be higher than the LAN metric. The default SDCC metric is 100.
SDCC Metric—This value is normally unchanged. It sets a cost for sending packets across the Section DCC, which is used by OSPF routers to calculate the shortest path. This value should always be higher than the LAN metric. The default SDCC metric is 100.
•![]() LDCC Metric—Sets a cost for sending packets across the Line DCC. This value should always be lower than the SDCC metric. The default LDCC metric is 33. It is usually not changed.
LDCC Metric—Sets a cost for sending packets across the Line DCC. This value should always be lower than the SDCC metric. The default LDCC metric is 33. It is usually not changed.
Step 3 ![]() In the OSPF on LAN area, complete the following:
In the OSPF on LAN area, complete the following:
•![]() OSPF active on LAN—When checked, enables the ONS 15454 OSPF topology to be advertised to OSPF routers on the LAN. Enable this field on ONS 15454s that directly connect to OSPF routers.
OSPF active on LAN—When checked, enables the ONS 15454 OSPF topology to be advertised to OSPF routers on the LAN. Enable this field on ONS 15454s that directly connect to OSPF routers.
•![]() LAN Port Area ID—Enter the OSPF area ID (dotted decimal format) for the router port where the ONS 15454 is connected. (This number is different from the DCC/GCC OSPF Area ID.)
LAN Port Area ID—Enter the OSPF area ID (dotted decimal format) for the router port where the ONS 15454 is connected. (This number is different from the DCC/GCC OSPF Area ID.)
Step 4 ![]() By default, OSPF is set to No Authentication. If the OSPF router requires authentication, complete the following steps. If not, continue with Step 5.
By default, OSPF is set to No Authentication. If the OSPF router requires authentication, complete the following steps. If not, continue with Step 5.
a. ![]() Click the No Authentication button.
Click the No Authentication button.
b. ![]() In the Edit Authentication Key dialog box, complete the following:
In the Edit Authentication Key dialog box, complete the following:
•![]() Type—Choose Simple Password.
Type—Choose Simple Password.
•![]() Enter Authentication Key—Enter the password.
Enter Authentication Key—Enter the password.
•![]() Confirm Authentication Key—Enter the same password to confirm it.
Confirm Authentication Key—Enter the same password to confirm it.
c. ![]() Click OK.
Click OK.
The authentication button label changes to Simple Password.
Step 5 ![]() Provision the OSPF priority and interval settings.
Provision the OSPF priority and interval settings.
The OSPF priority and interval defaults are ones most commonly used by OSPF routers. Verify that these defaults match the ones used by the OSPF router where the ONS 15454 is connected.
•![]() Router Priority—Selects the designated router for a subnet.
Router Priority—Selects the designated router for a subnet.
•![]() Hello Interval (sec)—Sets the number of seconds between OSPF hello packet advertisements sent by OSPF routers. Ten seconds is the default.
Hello Interval (sec)—Sets the number of seconds between OSPF hello packet advertisements sent by OSPF routers. Ten seconds is the default.
•![]() Dead Interval—Sets the number of seconds that will pass while an OSPF router's packets are not visible before its neighbors declare the router down. Forty seconds is the default.
Dead Interval—Sets the number of seconds that will pass while an OSPF router's packets are not visible before its neighbors declare the router down. Forty seconds is the default.
•![]() Transit Delay (sec)—Indicates the service speed. One second is the default.
Transit Delay (sec)—Indicates the service speed. One second is the default.
•![]() Retransmit Interval (sec)—Sets the time that will elapse before a packet is resent. Five seconds is the default.
Retransmit Interval (sec)—Sets the time that will elapse before a packet is resent. Five seconds is the default.
•![]() LAN Metric—Sets a cost for sending packets across the LAN. This value should always be lower than the SDCC metric. Ten is the default.
LAN Metric—Sets a cost for sending packets across the LAN. This value should always be lower than the SDCC metric. Ten is the default.
Step 6 ![]() Under OSPF Area Range Table, create an area range table if one is needed:
Under OSPF Area Range Table, create an area range table if one is needed:

Note ![]() Area range tables consolidate the information that is outside an OSPF area border. One ONS 15454 in the ONS 15454 OSPF area is connected to the OSPF router. An area range table on this node points the router to the other nodes that reside within the ONS 15454 OSPF area.
Area range tables consolidate the information that is outside an OSPF area border. One ONS 15454 in the ONS 15454 OSPF area is connected to the OSPF router. An area range table on this node points the router to the other nodes that reside within the ONS 15454 OSPF area.
a. ![]() Under OSPF Area Range Table, click Create.
Under OSPF Area Range Table, click Create.
b. ![]() In the Create Area Range dialog box, enter the following:
In the Create Area Range dialog box, enter the following:
•![]() Range Address—Enter the area IP address for the ONS 15454s that reside within the OSPF area. For example, if the ONS 15454 OSPF area includes nodes with IP addresses 10.10.20.100, 10.10.30.150, 10.10.40.200, and 10.10.50.250, the range address would be 10.10.0.0.
Range Address—Enter the area IP address for the ONS 15454s that reside within the OSPF area. For example, if the ONS 15454 OSPF area includes nodes with IP addresses 10.10.20.100, 10.10.30.150, 10.10.40.200, and 10.10.50.250, the range address would be 10.10.0.0.
•![]() Range Area ID—Enter the OSPF area ID for the ONS 15454s. This is either the ID in the DCC OSPF Area ID field or the ID in the Area ID for LAN Port field.
Range Area ID—Enter the OSPF area ID for the ONS 15454s. This is either the ID in the DCC OSPF Area ID field or the ID in the Area ID for LAN Port field.
•![]() Mask Length—Enter the subnet mask length. In the Range Address example, this is 16.
Mask Length—Enter the subnet mask length. In the Range Address example, this is 16.
•![]() Advertise—Check if you want to advertise the OSPF range table.
Advertise—Check if you want to advertise the OSPF range table.
c. ![]() Click OK.
Click OK.
Step 7 ![]() All OSPF areas must be connected to Area 0. If the ONS 15454 OSPF area is not physically connected to Area 0, use the following steps to create a virtual link table that will provide the disconnected area with a logical path to Area 0:
All OSPF areas must be connected to Area 0. If the ONS 15454 OSPF area is not physically connected to Area 0, use the following steps to create a virtual link table that will provide the disconnected area with a logical path to Area 0:
a. ![]() Under OSPF Virtual Link Table, click Create.
Under OSPF Virtual Link Table, click Create.
b. ![]() In the Create Virtual Link dialog box, complete the following fields. OSPF settings must match OSPF settings for the ONS 15454 OSPF area:
In the Create Virtual Link dialog box, complete the following fields. OSPF settings must match OSPF settings for the ONS 15454 OSPF area:
•![]() Neighbor—The router ID of the Area 0 router.
Neighbor—The router ID of the Area 0 router.
•![]() Transit Delay (sec)—The service speed. One second is the default.
Transit Delay (sec)—The service speed. One second is the default.
•![]() Hello Int (sec)—The number of seconds between OSPF hello packet advertisements sent by OSPF routers. Ten seconds is the default.
Hello Int (sec)—The number of seconds between OSPF hello packet advertisements sent by OSPF routers. Ten seconds is the default.
•![]() Auth Type—If the router where the ONS 15454 is connected uses authentication, choose Simple Password. Otherwise, choose No Authentication.
Auth Type—If the router where the ONS 15454 is connected uses authentication, choose Simple Password. Otherwise, choose No Authentication.
•![]() Retransmit Int (sec)—Sets the time that will elapse before a packet is resent. Five seconds is the default.
Retransmit Int (sec)—Sets the time that will elapse before a packet is resent. Five seconds is the default.
•![]() Dead Int (sec)—Sets the number of seconds that will pass while an OSPF router's packets are not visible before its neighbors declare the router down. Forty seconds is the default.
Dead Int (sec)—Sets the number of seconds that will pass while an OSPF router's packets are not visible before its neighbors declare the router down. Forty seconds is the default.
c. ![]() Click OK.
Click OK.
Step 8 ![]() After entering ONS 15454 OSPF area data, click Apply.
After entering ONS 15454 OSPF area data, click Apply.
If you changed the Area ID, the TCC2 cards reset, one at a time. The reset takes approximately 10 to 15 minutes. Table 3-1 shows the LED behavior during the TCC2 reset.
Step 9 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G60 Set Up or Change Routing Information Protocol
Purpose |
This task enables Routing Information Protocol (RIP) on the ONS 15454. Perform this task if you want to include the ONS 15454 in RIP-enabled networks. |
Tools/Equipment |
None |
Prerequisite Procedures |
DLP-G46 Log into CTC, page 2-25 You need to create a static route to the router adjacent to the ONS 15454 for the ONS 15454 to communicate its routing information to non-DCC-connected nodes. |
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite or remote |
Security Level |
Provisioning or higher |
Step 1 ![]() In node view, click the Provisioning > Network > RIP tabs.
In node view, click the Provisioning > Network > RIP tabs.
Step 2 ![]() Check the RIP Active check box if you are activating RIP.
Check the RIP Active check box if you are activating RIP.
Step 3 ![]() Choose either RIP Version 1 or RIP Version 2 from the drop-down list, depending on which version is supported in your network.
Choose either RIP Version 1 or RIP Version 2 from the drop-down list, depending on which version is supported in your network.
Step 4 ![]() Set the RIP metric. The RIP metric can be set to a number between 1 and 15 and represents the number of hops.
Set the RIP metric. The RIP metric can be set to a number between 1 and 15 and represents the number of hops.
Step 5 ![]() By default, RIP is set to No Authentication. If the router that the ONS 15454 is connected to requires authentication, complete the following steps. If not, continue with Step 6.
By default, RIP is set to No Authentication. If the router that the ONS 15454 is connected to requires authentication, complete the following steps. If not, continue with Step 6.
a. ![]() Click the No Authentication button.
Click the No Authentication button.
b. ![]() In the Edit Authentication Key dialog box, complete the following:
In the Edit Authentication Key dialog box, complete the following:
•![]() Type—Choose Simple Password.
Type—Choose Simple Password.
•![]() Enter Authentication Key—Enter the password,
Enter Authentication Key—Enter the password,
•![]() Confirm Authentication Key—Enter the same password to confirm it.
Confirm Authentication Key—Enter the same password to confirm it.
c. ![]() Click OK.
Click OK.
The authentication button label changes to Simple Password.
Step 6 ![]() If you want to complete an address summary, complete the following steps. If not, continue with Step 7. Complete the address summary only if the ONS 15454 is a gateway NE with multiple external ONS 15454 NEs attached with IP addresses in different subnets.
If you want to complete an address summary, complete the following steps. If not, continue with Step 7. Complete the address summary only if the ONS 15454 is a gateway NE with multiple external ONS 15454 NEs attached with IP addresses in different subnets.
a. ![]() In the RIP Address Summary area, click Create.
In the RIP Address Summary area, click Create.
b. ![]() In the Create Address Summary dialog box, complete the following:
In the Create Address Summary dialog box, complete the following:
•![]() Summary Address—Enter the summary IP address.
Summary Address—Enter the summary IP address.
•![]() Mask Length—Enter the subnet mask length using the up and down arrows.
Mask Length—Enter the subnet mask length using the up and down arrows.
•![]() Hops—Enter the number of hops. The smaller the number of hops, the higher the priority.
Hops—Enter the number of hops. The smaller the number of hops, the higher the priority.
c. ![]() Click OK.
Click OK.
Step 7 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-G27 Set Up the ONS 15454 for Firewall Access
Step 1 ![]() Log into a node that is behind the firewall. See the "DLP-G46 Log into CTC" task on page 2-25 for instructions. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Log into a node that is behind the firewall. See the "DLP-G46 Log into CTC" task on page 2-25 for instructions. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2 ![]() Complete the "DLP-G61 Provision the IIOP Listener Port on the ONS 15454" task.
Complete the "DLP-G61 Provision the IIOP Listener Port on the ONS 15454" task.
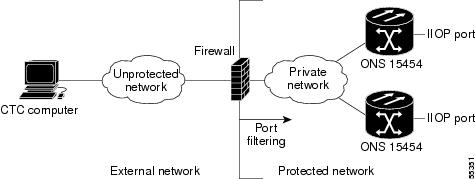
Figure 3-5 shows ONS 15454s in a protected network and the CTC computer in an external network. For the computer to access the ONS 15454s, you must provision the IIOP listener port specified by your firewall administrator on the ONS 15454.
Figure 3-5 Nodes Behind a Firewall
Step 3 ![]() If the CTC computer resides behind a firewall, complete the "DLP-G62 Provision the IIOP Listener Port on the CTC Computer" task.
If the CTC computer resides behind a firewall, complete the "DLP-G62 Provision the IIOP Listener Port on the CTC Computer" task.
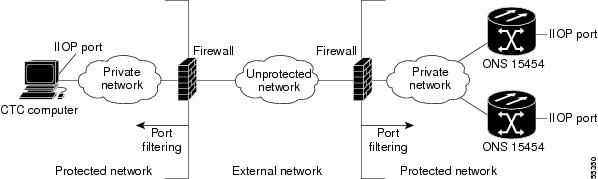
Figure 3-6 shows a CTC computer and ONS 15454 behind firewalls. For the computer to access the ONS 15454, you must provision the IIOP port on the CTC computer and on the ONS 15454.
Figure 3-6 CTC Computer and ONS 15454s Residing Behind Firewalls
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-G61 Provision the IIOP Listener Port on the ONS 15454

Note ![]() If the Enable Proxy Server on port 1080 check box is checked, CTC will use port 1080 and ignore the configured IIOP port setting. If Enable Proxy Server is subsequently unchecked, the configured IIOP listener port will be used.
If the Enable Proxy Server on port 1080 check box is checked, CTC will use port 1080 and ignore the configured IIOP port setting. If Enable Proxy Server is subsequently unchecked, the configured IIOP listener port will be used.
Step 1 ![]() In node view, click the Provisioning > Network > General tabs.
In node view, click the Provisioning > Network > General tabs.
Step 2 ![]() In the TCC CORBA (IIOP) Listener Port area, choose a listener port option:
In the TCC CORBA (IIOP) Listener Port area, choose a listener port option:
•![]() Default - TCC Fixed—Uses Port 57790 to connect to ONS 15454s on the same side of the firewall or if no firewall is used (default). This option can be used for access through a firewall if Port 57790 is open.
Default - TCC Fixed—Uses Port 57790 to connect to ONS 15454s on the same side of the firewall or if no firewall is used (default). This option can be used for access through a firewall if Port 57790 is open.
•![]() Standard Constant—Uses Port 683, the CORBA default port number.
Standard Constant—Uses Port 683, the CORBA default port number.
•![]() Other Constant—If Port 683 is not used, type the IIOP port specified by your firewall administrator. The port cannot use any of the ports shown in Table 3-2.
Other Constant—If Port 683 is not used, type the IIOP port specified by your firewall administrator. The port cannot use any of the ports shown in Table 3-2.
Step 3 ![]() Click Apply.
Click Apply.
Step 4 ![]() When the Change Network Configuration message appears, click Yes.
When the Change Network Configuration message appears, click Yes.
Both ONS 15454 TCC2/TCC2Ps reboot, one at a time. The reboot takes approximately 15 minutes.
Step 5 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G62 Provision the IIOP Listener Port on the CTC Computer
Purpose |
This task selects the IIOP listener port on CTC. |
Tools/Equipment |
IIOP listener port number from LAN or firewall administrator. |
Prerequisite Procedures |
G22 Verify Common Card Installation |
Required/As Needed |
Required only if the computer running CTC resides behind a firewall. |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite or remote |
Security Level |
Provisioning or higher |
Step 1 ![]() From the Edit menu, choose Preferences.
From the Edit menu, choose Preferences.
Step 2 ![]() In the Preferences dialog box, click the Firewall tab.
In the Preferences dialog box, click the Firewall tab.
Step 3 ![]() In the CTC CORBA (IIOP) Listener Port area, choose a listener port option:
In the CTC CORBA (IIOP) Listener Port area, choose a listener port option:
•![]() Default - Variable—Use to connect to ONS 15454s from within a firewall or if no firewall is used (default).
Default - Variable—Use to connect to ONS 15454s from within a firewall or if no firewall is used (default).
•![]() Standard Constant—Use Port 683, the CORBA default port number.
Standard Constant—Use Port 683, the CORBA default port number.
•![]() Other Constant—If Port 683 is not used, enter the IIOP port defined by your administrator.
Other Constant—If Port 683 is not used, enter the IIOP port defined by your administrator.
Step 4 ![]() Click Apply. A warning appears telling you that the port change will apply during the next CTC login.
Click Apply. A warning appears telling you that the port change will apply during the next CTC login.
Step 5 ![]() Click OK.
Click OK.
Step 6 ![]() In the Preferences dialog box, click OK.
In the Preferences dialog box, click OK.
Step 7 ![]() To access the ONS 15454 using the IIOP port, log out of CTC then log back in. (To log out, choose Exit from the File menu).
To access the ONS 15454 using the IIOP port, log out of CTC then log back in. (To log out, choose Exit from the File menu).
Step 8 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-G28 Set Up SNMP
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-G46 Log into CTC" task on page 2-25 at the node where you want to set up SNMP. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the "DLP-G46 Log into CTC" task on page 2-25 at the node where you want to set up SNMP. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2 ![]() In node view, click the Provisioning > SNMP tabs.
In node view, click the Provisioning > SNMP tabs.
Step 3 ![]() In the Trap Destinations area, click Create.
In the Trap Destinations area, click Create.
Step 4 ![]() Complete the following in the Create SNMP Trap Destination dialog box (Figure 3-7):
Complete the following in the Create SNMP Trap Destination dialog box (Figure 3-7):
•![]() Destination IP Address—Type the IP address of your network management system. If the node you are logged into is an ENE, set the destination address to the GNE.
Destination IP Address—Type the IP address of your network management system. If the node you are logged into is an ENE, set the destination address to the GNE.
•![]() Community—Type the SNMP community name. For a description of SNMP community names, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 SONET and DWDM Troubleshooting Guide.
Community—Type the SNMP community name. For a description of SNMP community names, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 SONET and DWDM Troubleshooting Guide.

Note ![]() The community name is a form of authentication and access control. The community name assigned to the ONS 15454 is case-sensitive and must match the community name of the network management system (NMS).
The community name is a form of authentication and access control. The community name assigned to the ONS 15454 is case-sensitive and must match the community name of the network management system (NMS).
•![]() UDP Port—The default User Datagram Protocol (UDP) port for SNMP is 162. If the node is an ENE in a proxy server network, the UDP port must be set to the GNE's SNMP relay port, which is 391.
UDP Port—The default User Datagram Protocol (UDP) port for SNMP is 162. If the node is an ENE in a proxy server network, the UDP port must be set to the GNE's SNMP relay port, which is 391.
•![]() Trap Version—Choose either SNMPv1 or SNMPv2. Refer to your NMS documentation to determine whether to use SNMP v1 or v2.
Trap Version—Choose either SNMPv1 or SNMPv2. Refer to your NMS documentation to determine whether to use SNMP v1 or v2.
Figure 3-7 Creating an SNMP Trap
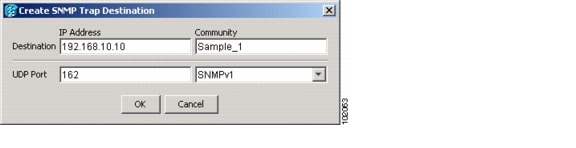
Step 5 ![]() Click OK. The node IP address of the node where you provisioned the new trap destination appears in the Trap Destinations area.
Click OK. The node IP address of the node where you provisioned the new trap destination appears in the Trap Destinations area.
Step 6 ![]() Click the node IP address in the Trap Destinations area. Verify the SNMP information that appears in the Selected Destination list.
Click the node IP address in the Trap Destinations area. Verify the SNMP information that appears in the Selected Destination list.
Step 7 ![]() If you want the SNMP agent to accept SNMP SET requests on certain MIBs, click the Allow SNMP Sets check box. If this box is not checked, SET requests are rejected.
If you want the SNMP agent to accept SNMP SET requests on certain MIBs, click the Allow SNMP Sets check box. If this box is not checked, SET requests are rejected.
Step 8 ![]() If you want to set up the SNMP proxy feature to allow network management, message reporting, and performance statistic retrieval across ONS firewalls, click the Enable SNMP Proxy check box located on the SNMP tab.
If you want to set up the SNMP proxy feature to allow network management, message reporting, and performance statistic retrieval across ONS firewalls, click the Enable SNMP Proxy check box located on the SNMP tab.

Note ![]() The ONS firewall proxy feature only operates on nodes running Software Release 4.6 or later. Using this feature effectively breaches the ONS firewall to exchange management information.
The ONS firewall proxy feature only operates on nodes running Software Release 4.6 or later. Using this feature effectively breaches the ONS firewall to exchange management information.
For more information about the SNMP proxy feature, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 SONET and DWDM Troubleshooting Guide.
Step 9 ![]() Click Apply.
Click Apply.
Step 10 ![]() If you are setting up SNMP proxies, for each trap destination address you can set up to three relays that send SNMP trap error counts back to NE:
If you are setting up SNMP proxies, for each trap destination address you can set up to three relays that send SNMP trap error counts back to NE:
a. ![]() Click the first trap destination IP address. The address and its community name appear in the Destination fields.
Click the first trap destination IP address. The address and its community name appear in the Destination fields.
b. ![]() Enter up to three SNMP Proxy relay addresses and community names in the fields for Relay A, Relay B, and Relay C.
Enter up to three SNMP Proxy relay addresses and community names in the fields for Relay A, Relay B, and Relay C.

Note ![]() The community names specified for each relay node must match one of the provisioned SNMP community names in the NE.
The community names specified for each relay node must match one of the provisioned SNMP community names in the NE.

Note ![]() The SNMP proxy directs SNMP traps from this node through IpA to IpB to IpC to the trap destination. Ensure that you enter the IP addresses in the correct order so that this sequence runs correctly.
The SNMP proxy directs SNMP traps from this node through IpA to IpB to IpC to the trap destination. Ensure that you enter the IP addresses in the correct order so that this sequence runs correctly.
Step 11 ![]() Click Apply.
Click Apply.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-G29 Preprovision a Slot
Purpose |
This procedure preprovisions the card slots in CTC based upon the network plan that was calculated for your site by Cisco MetroPlanner. (If you do not have Cisco MetroPlanner, you must enter the DWDM provisioning manually with a customized design.) Preprovisioning the slots ensures that the physical cards are installed in the slots anticipated by the automatic node setup parameters that will be imported from Cisco MetroPlanner. |
Tools/Equipment |
None |
Prerequisite Procedures |
Chapter 2, "Connect the PC and Log into the GUI" One of the following: • • |
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite or remote |
Security Level |
Provisioning or higher |
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-G46 Log into CTC" task on page 2-25 at the node where you want to preprovision the slots. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the "DLP-G46 Log into CTC" task on page 2-25 at the node where you want to preprovision the slots. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2 ![]() If you have Cisco MetroPlanner R2.5, launch the application and continue with Step 4. If you do not have Cisco MetroPlanner, you must have a print out of the node layout prepared by Cisco MetroPlanner. R2.5. If so, continue with Step 6. Do not continue if a node layout prepared by Cisco MetroPlanner is not available.
If you have Cisco MetroPlanner R2.5, launch the application and continue with Step 4. If you do not have Cisco MetroPlanner, you must have a print out of the node layout prepared by Cisco MetroPlanner. R2.5. If so, continue with Step 6. Do not continue if a node layout prepared by Cisco MetroPlanner is not available.
Step 3 ![]() In Cisco MetroPlanner, load the network plan for your installation. (For information about using Cisco MetroPlanner, refer to the Cisco MetroPlanner DWDM Operations Guide.)
In Cisco MetroPlanner, load the network plan for your installation. (For information about using Cisco MetroPlanner, refer to the Cisco MetroPlanner DWDM Operations Guide.)
Step 4 ![]() In Cisco MetroPlanner, display the Site Dialog window for the node you are provisioning. A site installation example is shown in Figure 3-8.
In Cisco MetroPlanner, display the Site Dialog window for the node you are provisioning. A site installation example is shown in Figure 3-8.
Figure 3-8 Cisco MetroPlanner Site Dialog Window
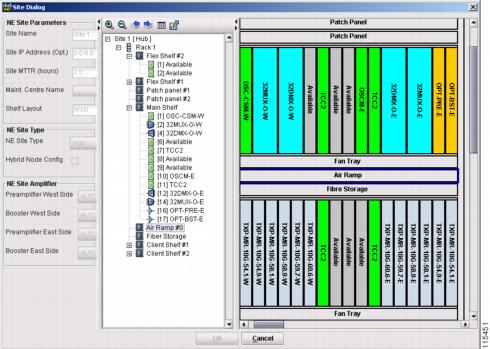
Step 5 ![]() Arrange the CTC and the Cisco MetroPlanner windows so you can view both windows simultaneously.
Arrange the CTC and the Cisco MetroPlanner windows so you can view both windows simultaneously.
Step 6 ![]() In CTC node view, right-click an empty slot where you will install a card.
In CTC node view, right-click an empty slot where you will install a card.
Step 7 ![]() From the Add Card popup menu, choose the card type that will be installed based on the Cisco MetroPlanner Site Dialog window. Only cards that can be installed in the slot appear in the Add Card popup menu.
From the Add Card popup menu, choose the card type that will be installed based on the Cisco MetroPlanner Site Dialog window. Only cards that can be installed in the slot appear in the Add Card popup menu.

Note ![]() When you preprovision a slot, the card appears purple in the CTC shelf graphic, rather than white when a card is installed in the slot. NP (not present) on the card graphic indicates that the card is not physically installed.
When you preprovision a slot, the card appears purple in the CTC shelf graphic, rather than white when a card is installed in the slot. NP (not present) on the card graphic indicates that the card is not physically installed.
Step 8 ![]() Repeat Step 7 until all the cards shown in the Cisco MetroPlanner the Site Dialog window are provisioned in CTC.
Repeat Step 7 until all the cards shown in the Cisco MetroPlanner the Site Dialog window are provisioned in CTC.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-G30 Install the DWDM Cards

Warning ![]() During this procedure, wear grounding wrist straps to avoid damaging the card. Do not directly touch the backplane with your hand or any metal tool due to electrical hazard.
During this procedure, wear grounding wrist straps to avoid damaging the card. Do not directly touch the backplane with your hand or any metal tool due to electrical hazard.

Warning ![]() Complies with 21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11 except for deviations pursuant to Laser Notice No. 50, dated July 26, 2001.
Complies with 21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11 except for deviations pursuant to Laser Notice No. 50, dated July 26, 2001.

Warning ![]() Class 1M Laser Product.
Class 1M Laser Product.

Warning ![]() Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the end of the unterminated fiber cable or connector. Do not stare into the beam or view directly with optical instruments. Viewing the laser output with certain optical instruments (for example, eye loupes, magnifiers, and microscopes) within a distance of 100 mm may pose an eye hazard. Use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures other than those specified may result in hazardous radiation exposure.
Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the end of the unterminated fiber cable or connector. Do not stare into the beam or view directly with optical instruments. Viewing the laser output with certain optical instruments (for example, eye loupes, magnifiers, and microscopes) within a distance of 100 mm may pose an eye hazard. Use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures other than those specified may result in hazardous radiation exposure.


Note ![]() If protective clips are installed on the backplane connectors of the cards, remove the clips before installing the cards.
If protective clips are installed on the backplane connectors of the cards, remove the clips before installing the cards.

Note ![]() If you install a card incorrectly, the FAIL LED flashes continuously.
If you install a card incorrectly, the FAIL LED flashes continuously.
Step 1 ![]() Display the card installation plan for the node using one of the following sources:
Display the card installation plan for the node using one of the following sources:
•![]() The Cisco MetroPlanner Site Dialog window (Figure 3-8) for the node you are provisioning.
The Cisco MetroPlanner Site Dialog window (Figure 3-8) for the node you are provisioning.
•![]() CTC node view with slots preprovisioned based on the Cisco MetroPlanner Site Dialog window.
CTC node view with slots preprovisioned based on the Cisco MetroPlanner Site Dialog window.
•![]() Written slot plan. The plan must be based on the Cisco MetroPlanner Site Dialog window for your installation.
Written slot plan. The plan must be based on the Cisco MetroPlanner Site Dialog window for your installation.
Step 2 ![]() Double check that the card placement fits within the following installation guidelines:
Double check that the card placement fits within the following installation guidelines:
•![]() OPT-BST—Any open east and west pair of slots but usually installed in Slots 1 and 17
OPT-BST—Any open east and west pair of slots but usually installed in Slots 1 and 17
•![]() OPT-PRE—Any open east and west pair of slots but usually installed in Slots 2 and 16
OPT-PRE—Any open east and west pair of slots but usually installed in Slots 2 and 16
•![]() OSCM—Slots 8 and 10
OSCM—Slots 8 and 10
•![]() OSC-CSM—Any open east and west pair of slots
OSC-CSM—Any open east and west pair of slots
•![]() 32MUX-O, 32DMX-O, 32DMX, 32WSS—Double-slot card; any two open slots.
32MUX-O, 32DMX-O, 32DMX, 32WSS—Double-slot card; any two open slots.
•![]() AD-xB-xx.x, AD-xC-xx.x, and 4MD-xx.x—Any open slots
AD-xB-xx.x, AD-xC-xx.x, and 4MD-xx.x—Any open slots
Step 3 ![]() Remove the DWDM card from its packaging, then remove the protective caps from the backplane connectors.
Remove the DWDM card from its packaging, then remove the protective caps from the backplane connectors.
Step 4 ![]() Open the card latches/ejectors.
Open the card latches/ejectors.
Step 5 ![]() Use the latches/ejectors to firmly slide the card along the slot guide rails until the card plugs into the receptacle at the back of the slot.
Use the latches/ejectors to firmly slide the card along the slot guide rails until the card plugs into the receptacle at the back of the slot.
Step 6 ![]() Verify that the card is inserted correctly and close the latches/ejectors on the card.
Verify that the card is inserted correctly and close the latches/ejectors on the card.

Note ![]() It is possible to close the latches/ejectors when the card is not completely plugged into the backplane. Ensure that you cannot insert the card any further.
It is possible to close the latches/ejectors when the card is not completely plugged into the backplane. Ensure that you cannot insert the card any further.
Step 7 ![]() Verify the LED activity:
Verify the LED activity:
•![]() The FAIL LED turns on for approximately 35 seconds.
The FAIL LED turns on for approximately 35 seconds.
•![]() The FAIL LED blinks for approximately 40 seconds.
The FAIL LED blinks for approximately 40 seconds.
•![]() All LEDs turn on and then turn off within 5 seconds.
All LEDs turn on and then turn off within 5 seconds.
•![]() If new software is being downloaded to the card, the ACT and SF LEDs blink for 20 seconds to 3.5 minutes, depending on the card type.
If new software is being downloaded to the card, the ACT and SF LEDs blink for 20 seconds to 3.5 minutes, depending on the card type.
•![]() The ACT LED turns on.
The ACT LED turns on.
•![]() The signal fail (SF) LED stays on until all card ports connect to their far-end counterparts and a signal is present.
The signal fail (SF) LED stays on until all card ports connect to their far-end counterparts and a signal is present.
Step 8 ![]() If the card does not boot up properly, or the LED activity does not mimic Step 7, check the following:
If the card does not boot up properly, or the LED activity does not mimic Step 7, check the following:
•![]() When a physical card type does not match the type of card provisioned for that slot in CTC, the card might not boot. If a DWDM card does not boot, open CTC and ensure that the slot is not provisioned for a different card type before assuming that the card is faulty.
When a physical card type does not match the type of card provisioned for that slot in CTC, the card might not boot. If a DWDM card does not boot, open CTC and ensure that the slot is not provisioned for a different card type before assuming that the card is faulty.
•![]() If the red FAIL LED does not turn on, check the power.
If the red FAIL LED does not turn on, check the power.
•![]() If you insert a card into a slot provisioned for a different card, all LEDs turn off.
If you insert a card into a slot provisioned for a different card, all LEDs turn off.
•![]() If the red FAIL LED is on continuously or the LEDs behave erratically, the card is not installed. Remove the card and repeat Steps 3 to 7. If the card does not boot up properly the second time, it may be defective. Contact your next level of support.
If the red FAIL LED is on continuously or the LEDs behave erratically, the card is not installed. Remove the card and repeat Steps 3 to 7. If the card does not boot up properly the second time, it may be defective. Contact your next level of support.

Note ![]() The DWDM node type is determined by the cards that are installed. For example, if two 32DMX-O and two 32MUX-O cards are installed but no AD-xC or AD-xB cards are installed, CTC considers the node a hub node. However, if one 32DMX-O and one 32MUX-O card are installed with no AD-xC or AD-xB cards, CTC considers the node a terminal node. For more information, refer to Chapter 14, "Card Reference."
The DWDM node type is determined by the cards that are installed. For example, if two 32DMX-O and two 32MUX-O cards are installed but no AD-xC or AD-xB cards are installed, CTC considers the node a hub node. However, if one 32DMX-O and one 32MUX-O card are installed with no AD-xC or AD-xB cards, CTC considers the node a terminal node. For more information, refer to Chapter 14, "Card Reference."
Step 9 ![]() Repeat Steps 3 through 8 until all the DWDM cards are installed in the node.
Repeat Steps 3 through 8 until all the DWDM cards are installed in the node.
Step 10 ![]() If you installed OPT-PRE cards, complete one of the following based upon your MetroPlanner site plan. If an OPT-PRE card is not installed, continue with Step 11.
If you installed OPT-PRE cards, complete one of the following based upon your MetroPlanner site plan. If an OPT-PRE card is not installed, continue with Step 11.
•![]() If the site plan includes DCUs, complete the "G31 Install the DWDM Dispersion Compensating Units" procedure.
If the site plan includes DCUs, complete the "G31 Install the DWDM Dispersion Compensating Units" procedure.
•![]() If the site plan does not include DCUs, install a 5 dB attenuator between the OPT-PRE DC TX and RX ports.
If the site plan does not include DCUs, install a 5 dB attenuator between the OPT-PRE DC TX and RX ports.
Step 11 ![]() Continue with the "G32 Install the Transponder and Muxponder Cards" procedure.
Continue with the "G32 Install the Transponder and Muxponder Cards" procedure.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-G31 Install the DWDM Dispersion Compensating Units
Purpose |
This procedure describes how to install the dispersion compensating units (DCU-xx.x) for DWDM shelves and is required if OPT-PRE cards are installed. |
Tools/Equipment |
DCU-xx.x cards |
Prerequisite Procedures |
NTP-G15 Install the Common Control Cards, page 1-72 |
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite |
Security Level |
Provisioning or higher |

Warning ![]() Complies with 21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11 except for deviations pursuant to Laser Notice No. 50, dated July 26, 2001.
Complies with 21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11 except for deviations pursuant to Laser Notice No. 50, dated July 26, 2001.

Warning ![]() Class 1M laser product.
Class 1M laser product.

Warning ![]() Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the end of the unterminated fiber cable or connector. Do not stare into the beam or view directly with optical instruments. Viewing the laser output with certain optical instruments (for example, eye loupes, magnifiers, and microscopes) within a distance of 100 mm may pose an eye hazard. Use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures other than those specified may result in hazardous radiation exposure.
Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the end of the unterminated fiber cable or connector. Do not stare into the beam or view directly with optical instruments. Viewing the laser output with certain optical instruments (for example, eye loupes, magnifiers, and microscopes) within a distance of 100 mm may pose an eye hazard. Use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures other than those specified may result in hazardous radiation exposure.


Note ![]() If protective clips are installed on the backplane connectors of the DCUs, remove the clips before installing the units.
If protective clips are installed on the backplane connectors of the DCUs, remove the clips before installing the units.

Note ![]() If a DCU is not installed and OPT-PRE cards are installed, insert a 5 dB attenuator between the OPT-PRE DC TX and RX ports.
If a DCU is not installed and OPT-PRE cards are installed, insert a 5 dB attenuator between the OPT-PRE DC TX and RX ports.
Step 1 ![]() Pull the DCU latch inward with your finger.
Pull the DCU latch inward with your finger.
Step 2 ![]() Firmly slide the DCU along the guide rails until the card plugs into the receptacle at the back of the horizontal dispersion compensating card slot at the top of the shelf.
Firmly slide the DCU along the guide rails until the card plugs into the receptacle at the back of the horizontal dispersion compensating card slot at the top of the shelf.

Note ![]() The west DCU is commonly installed on the left side and the east DCU is commonly installed on the right side.
The west DCU is commonly installed on the left side and the east DCU is commonly installed on the right side.

Note ![]() If you install the wrong DCU in a slot, remove the DCU and install the correct one.
If you install the wrong DCU in a slot, remove the DCU and install the correct one.
Step 3 ![]() Release the finger latch.
Release the finger latch.

Note ![]() It is possible to close the latch when the DCU is not completely plugged into the backplane. Ensure that you cannot insert the DCU any further.
It is possible to close the latch when the DCU is not completely plugged into the backplane. Ensure that you cannot insert the DCU any further.
Step 4 ![]() Verify that the DCU is engaged with the backplane by grasping and gently pulling the card handle. If the card does not move, it is fully installed. If it moves, repeat 2 and 3.
Verify that the DCU is engaged with the backplane by grasping and gently pulling the card handle. If the card does not move, it is fully installed. If it moves, repeat 2 and 3.
Step 5 ![]() Continue with the "G32 Install the Transponder and Muxponder Cards" procedure.
Continue with the "G32 Install the Transponder and Muxponder Cards" procedure.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-G32 Install the Transponder and Muxponder Cards

Warning ![]() During this procedure, wear grounding wrist straps to avoid ESD damage to the card. Do not directly touch the backplane with your hand or any metal tool due to electrical hazard.
During this procedure, wear grounding wrist straps to avoid ESD damage to the card. Do not directly touch the backplane with your hand or any metal tool due to electrical hazard.

Warning ![]() Class 1 Laser Product.
Class 1 Laser Product.

Warning ![]() Complies with 21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11 except for deviations pursuant to Laser Notice No. 50, dated July 26, 2001.
Complies with 21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11 except for deviations pursuant to Laser Notice No. 50, dated July 26, 2001.

Warning ![]() Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the end of the unterminated fiber cable or connector. Do not stare into the beam or view directly with optical instruments. Viewing the laser output with certain optical instruments (for example, eye loupes, magnifiers, and microscopes) within a distance of 100 mm may pose an eye hazard. Use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures other than those specified may result in hazardous radiation exposure.
Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the end of the unterminated fiber cable or connector. Do not stare into the beam or view directly with optical instruments. Viewing the laser output with certain optical instruments (for example, eye loupes, magnifiers, and microscopes) within a distance of 100 mm may pose an eye hazard. Use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures other than those specified may result in hazardous radiation exposure.


Note ![]() If protective clips are installed on the backplane connectors of the cards, remove the clips before installing the cards.
If protective clips are installed on the backplane connectors of the cards, remove the clips before installing the cards.

Note ![]() If you install a card incorrectly, the FAIL LED flashes continuously.
If you install a card incorrectly, the FAIL LED flashes continuously.
Step 1 ![]() Display card installation plan for the node using one of the following sources:
Display card installation plan for the node using one of the following sources:
•![]() The Cisco MetroPlanner Site Dialog window for the node you are provisioning.
The Cisco MetroPlanner Site Dialog window for the node you are provisioning.
•![]() CTC node view with slots preprovisioned based on the Cisco MetroPlanner Site Dialog window.
CTC node view with slots preprovisioned based on the Cisco MetroPlanner Site Dialog window.
•![]() Written slot plan. The plan must be based on the Cisco MetroPlanner Site Dialog window for your installation.
Written slot plan. The plan must be based on the Cisco MetroPlanner Site Dialog window for your installation.
Step 2 ![]() Remove the TXP or MXP card from its packaging, then remove the protective clips from the backplane connectors.
Remove the TXP or MXP card from its packaging, then remove the protective clips from the backplane connectors.
Step 3 ![]() Open the card latches/ejectors.
Open the card latches/ejectors.
Step 4 ![]() Use the latches/ejectors to firmly slide the TXP or MXP card along the guide rails until the card plugs into the receptacle at the back of the slot.
Use the latches/ejectors to firmly slide the TXP or MXP card along the guide rails until the card plugs into the receptacle at the back of the slot.

Note ![]() If you install the wrong card in a slot, complete the "NTP-G107 Remove and Replace DWDM Cards" procedure on page 11-12.
If you install the wrong card in a slot, complete the "NTP-G107 Remove and Replace DWDM Cards" procedure on page 11-12.
Step 5 ![]() Verify that the card is inserted correctly and close the latches/ejectors on the card.
Verify that the card is inserted correctly and close the latches/ejectors on the card.

Note ![]() It is possible to close the latches and ejectors when the card is not completely plugged into the backplane. Ensure that you cannot insert the card any further.
It is possible to close the latches and ejectors when the card is not completely plugged into the backplane. Ensure that you cannot insert the card any further.
Step 6 ![]() Verify the LED activity:
Verify the LED activity:
•![]() The red FAIL LED turns on for 20 to 30 seconds.
The red FAIL LED turns on for 20 to 30 seconds.
•![]() The red FAIL LED blinks for 35 to 45 seconds.
The red FAIL LED blinks for 35 to 45 seconds.
•![]() All LEDs blink once and turn off for 5 to 10 seconds.
All LEDs blink once and turn off for 5 to 10 seconds.
•![]() The ACT or ACT/STBY LED turns on. The SF LED can persist until all card ports connect to their far-end counterparts and a signal is present.
The ACT or ACT/STBY LED turns on. The SF LED can persist until all card ports connect to their far-end counterparts and a signal is present.
Step 7 ![]() If the card does not boot up properly, or the LED activity does not mirror Step 6, check the following:
If the card does not boot up properly, or the LED activity does not mirror Step 6, check the following:
•![]() When a physical card type does not match the type of card provisioned for that slot in CTC, the card might not boot. If a TXP or MXP card does not boot, open CTC and ensure that the slot is not provisioned for a different card type before assuming that the card is faulty.
When a physical card type does not match the type of card provisioned for that slot in CTC, the card might not boot. If a TXP or MXP card does not boot, open CTC and ensure that the slot is not provisioned for a different card type before assuming that the card is faulty.
•![]() If the red FAIL LED does not turn on, check the power.
If the red FAIL LED does not turn on, check the power.
•![]() If you insert a card into a slot provisioned for a different card, all LEDs turn off.
If you insert a card into a slot provisioned for a different card, all LEDs turn off.
•![]() If the red FAIL LED is on continuously or the LEDs behave erratically, the card is not installed properly. Remove the card and repeat Steps 3 to 6.
If the red FAIL LED is on continuously or the LEDs behave erratically, the card is not installed properly. Remove the card and repeat Steps 3 to 6.
Step 8 ![]() If the TXP or MXP requires a small-form pluggable (SFP), complete the "DLP-G63 Install an SFP" task. To remove an SFP, complete the "DLP-G64 Remove an SFP" task.
If the TXP or MXP requires a small-form pluggable (SFP), complete the "DLP-G63 Install an SFP" task. To remove an SFP, complete the "DLP-G64 Remove an SFP" task.

Note ![]() SFPs must be provisioned in CTC. You will be directed to the "NTP-G94 Provision Pluggable Port Modules" procedure on page 10-29 during network turn up. For more information about SFPs, see the "14.13 SFP Modules" section on page 14-123.
SFPs must be provisioned in CTC. You will be directed to the "NTP-G94 Provision Pluggable Port Modules" procedure on page 10-29 during network turn up. For more information about SFPs, see the "14.13 SFP Modules" section on page 14-123.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-G63 Install an SFP
Purpose |
This task installs SFPs into TXP and MXP cards. |
Tools/Equipment |
None |
Prerequisite Procedures |
|
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite or remote |
Security Level |
Provisioning or higher |
Step 1 ![]() Verify that the SFP is correct for your network and TXP or MXP card (see Table 14-67 on page 14-123). Check that you are installing compatible SFPs, for example, SX to SX or LX/LH to LX/LH.
Verify that the SFP is correct for your network and TXP or MXP card (see Table 14-67 on page 14-123). Check that you are installing compatible SFPs, for example, SX to SX or LX/LH to LX/LH.
Step 2 ![]() Install the SFP:
Install the SFP:
•![]() For a mylar tab SFP: slide the SFP into the slot.
For a mylar tab SFP: slide the SFP into the slot.
•![]() For an actuator/button SFP: slide the SFP all the way into the slot until you hear a click.
For an actuator/button SFP: slide the SFP all the way into the slot until you hear a click.
•![]() For a bail clasp SFP: latch (flip upwards) the bail clasp before inserting into the slot then slide into the slot.
For a bail clasp SFP: latch (flip upwards) the bail clasp before inserting into the slot then slide into the slot.

Note ![]() SFPs are keyed to prevent incorrect installation.
SFPs are keyed to prevent incorrect installation.
Step 3 ![]() Do not remove the protective caps from the SFP until you are ready to attach the network fiber-optic cable.
Do not remove the protective caps from the SFP until you are ready to attach the network fiber-optic cable.

Note ![]() SFPs must be provisioned in CTC. You will be directed to the "NTP-G94 Provision Pluggable Port Modules" procedure on page 10-29 during network turn up. For more information about SFPs, see the "14.13 SFP Modules" section on page 14-123.
SFPs must be provisioned in CTC. You will be directed to the "NTP-G94 Provision Pluggable Port Modules" procedure on page 10-29 during network turn up. For more information about SFPs, see the "14.13 SFP Modules" section on page 14-123.
Step 4 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G64 Remove an SFP
Purpose |
This task removes SFPs from TXP and MXP cards. |
Tools/Equipment |
None |
Prerequisite Procedures |
|
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite or remote |
Security Level |
Provisioning or higher |
Step 1 ![]() Disconnect the network fiber cable from the GBIC SC-type connector or SFP/XFP LC-type connector.
Disconnect the network fiber cable from the GBIC SC-type connector or SFP/XFP LC-type connector.
Step 2 ![]() Release the SFP from the slot by performing one of the following actions (depending which latch is on the SFP):
Release the SFP from the slot by performing one of the following actions (depending which latch is on the SFP):
•![]() For a mylar tab SFP: pull out the mylar tab.
For a mylar tab SFP: pull out the mylar tab.
•![]() For an actuator/button SFP: press the actuator/button.
For an actuator/button SFP: press the actuator/button.
•![]() For a bail clasp SFP: unlatching the bail clasp and swing it downward.
For a bail clasp SFP: unlatching the bail clasp and swing it downward.
Step 3 ![]() Slide the SFP out of the slot.
Slide the SFP out of the slot.
Step 4 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-G33 Create a Y-Cable Protection Group

Note ![]() Loss of Pointer Path (LOP-P) alarms can occur on a split signal if the ports are not in a Y-cable protection group.
Loss of Pointer Path (LOP-P) alarms can occur on a split signal if the ports are not in a Y-cable protection group.
Step 1 ![]() Verify that the TXP or MXP cards are installed according to the Y-cable requirements specified in Table 3-3. This table describes the protection types available in the ONS 15454 for DWDM client cards.
Verify that the TXP or MXP cards are installed according to the Y-cable requirements specified in Table 3-3. This table describes the protection types available in the ONS 15454 for DWDM client cards.
Step 2 ![]() Verify that pluggable port modules (PPM) are provisioned for the same payload and payload rate on the TXP and MXP cards where you will create the Y-cable protection group. You can use either of the following methods:
Verify that pluggable port modules (PPM) are provisioned for the same payload and payload rate on the TXP and MXP cards where you will create the Y-cable protection group. You can use either of the following methods:
•![]() In node view, move your mouse over the TXP or MXP client port. If a PPM is provisioned, two dots appear in the port graphic, and the port and PPM payload and rate appear when you move the mouse over the port.
In node view, move your mouse over the TXP or MXP client port. If a PPM is provisioned, two dots appear in the port graphic, and the port and PPM payload and rate appear when you move the mouse over the port.
•![]() Display the TXP or MXP card in card view. Click the Provisioning > Pluggable Port Module tabs. Verify that a PPM is provisioned in the Pluggable Port Module area, and the payload type and rate is provisioned for it in the Selected PPM area.
Display the TXP or MXP card in card view. Click the Provisioning > Pluggable Port Module tabs. Verify that a PPM is provisioned in the Pluggable Port Module area, and the payload type and rate is provisioned for it in the Selected PPM area.
The PPM payload and payload rate must be the same for both TXP or MXP cards.
Step 3 ![]() In node view, click the Provisioning > Protection tabs.
In node view, click the Provisioning > Protection tabs.
Step 4 ![]() In the Protection Groups area, click Create.
In the Protection Groups area, click Create.
Step 5 ![]() In the Create Protection Group dialog box, enter the following:
In the Create Protection Group dialog box, enter the following:
•![]() Name—Type a name for the protection group. The name can have up to 32 alphanumeric (a-z, A-Z, 0-9) characters. Special characters are permitted. For TL1 compatibility, do not use question mark (?), backslash (\), or double quote (") characters.
Name—Type a name for the protection group. The name can have up to 32 alphanumeric (a-z, A-Z, 0-9) characters. Special characters are permitted. For TL1 compatibility, do not use question mark (?), backslash (\), or double quote (") characters.
•![]() Type—Choose Y Cable from the drop-down list.
Type—Choose Y Cable from the drop-down list.
•![]() Protect Port—Choose the protect port from the drop-down list. The menu displays the available transponder or muxponder ports. If transponder or muxponder cards are not installed, no ports appear in the drop-down list.
Protect Port—Choose the protect port from the drop-down list. The menu displays the available transponder or muxponder ports. If transponder or muxponder cards are not installed, no ports appear in the drop-down list.
After you choose the protect port, a list of ports available for protection appear in the Available Ports list, as shown in Figure 3-9. If no cards are available, no ports appear. If this occurs, you can not complete this task until you install the physical cards or preprovision the ONS 15454 slots using the "G29 Preprovision a Slot" procedure.
Figure 3-9 Creating a Y-Cable Protection Group
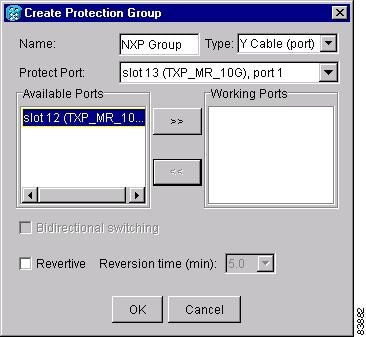
Step 6 ![]() From the Available Ports list, choose the port that will be protected by the port you selected in Protect Ports. Click the top arrow button to move each port to the Working Ports list.
From the Available Ports list, choose the port that will be protected by the port you selected in Protect Ports. Click the top arrow button to move each port to the Working Ports list.
Step 7 ![]() Complete the remaining fields:
Complete the remaining fields:
•![]() Revertive—Check this check box if you want traffic to revert to the working port after failure conditions remain corrected for the amount of time entered in the Reversion Time field.
Revertive—Check this check box if you want traffic to revert to the working port after failure conditions remain corrected for the amount of time entered in the Reversion Time field.
•![]() Reversion time—If Revertive is checked, select a reversion time from the drop-down list. The range is 0.5 to 12.0 minutes. The default is 5.0 minutes. Reversion time is the amount of time that will elapse before the traffic reverts to the working card. Traffic can revert when conditions causing the switch are cleared.
Reversion time—If Revertive is checked, select a reversion time from the drop-down list. The range is 0.5 to 12.0 minutes. The default is 5.0 minutes. Reversion time is the amount of time that will elapse before the traffic reverts to the working card. Traffic can revert when conditions causing the switch are cleared.
Step 8 ![]() Click OK.
Click OK.
Step 9 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-G34 Install Fiber-Optic Cables on DWDM Cards
Purpose |
This procedure installs the fiber-optic cables to DWDM cards and dispersion compensating cards. |
Tools/Equipment |
Fiber-optic cables |
Prerequisite Procedures |
G31 Install the DWDM Dispersion Compensating Units (as applicable) |
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite |
Security Level |
None |

Warning ![]() Complies with 21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11 except for deviations pursuant to Laser Notice No. 50, dated July 26, 2001.
Complies with 21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11 except for deviations pursuant to Laser Notice No. 50, dated July 26, 2001.

Warning ![]() Class 1M laser product.
Class 1M laser product.

Note ![]() In this procedure, you will generally connect fibers in an east-to-west or west-to-east pattern. "West" refers to cards and ports in Slots 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 8. "East" refers to cards and ports installed in Slots 10, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, and 17.
In this procedure, you will generally connect fibers in an east-to-west or west-to-east pattern. "West" refers to cards and ports in Slots 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 8. "East" refers to cards and ports installed in Slots 10, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, and 17.
Step 1 ![]() Display your site plan in Cisco MetroPlanner, or refer to a printed copy of the MetroPlanner internal connections table. For information about Cisco MetroPlanner, refer to the Cisco MetroPlanner DWDM Operations Guide.
Display your site plan in Cisco MetroPlanner, or refer to a printed copy of the MetroPlanner internal connections table. For information about Cisco MetroPlanner, refer to the Cisco MetroPlanner DWDM Operations Guide.
Step 2 ![]() Navigate to the Internal Connections table for the node you are provisioning (Figure 3-10).The internal connections table identifies the patch cord that you must cable by their end points. Position 1 identifies the fiber start point; Position 2 indicates the fiber end point. The patch cord end points are identified by site, slot, and port. Information provided by the Cisco MetroPlanner internal connections table includes:
Navigate to the Internal Connections table for the node you are provisioning (Figure 3-10).The internal connections table identifies the patch cord that you must cable by their end points. Position 1 identifies the fiber start point; Position 2 indicates the fiber end point. The patch cord end points are identified by site, slot, and port. Information provided by the Cisco MetroPlanner internal connections table includes:
•![]() Site—The DWDM network site number for the node where you are provisioning the internal connections.
Site—The DWDM network site number for the node where you are provisioning the internal connections.
•![]() IP Address—The node IP address.
IP Address—The node IP address.
•![]() Position-1—The first position rack, shelf, and slot. For example, Rack#1.Main Shelf.02 refers to Slot 2 in the Main Shelf of Rack #1. Refer to the Cisco MetroPlanner Site Dialog window for rack and shelf names and locations.
Position-1—The first position rack, shelf, and slot. For example, Rack#1.Main Shelf.02 refers to Slot 2 in the Main Shelf of Rack #1. Refer to the Cisco MetroPlanner Site Dialog window for rack and shelf names and locations.
•![]() Unit-1—The ONS 15454 DWDM card (unit) that is installed in the first position slot.
Unit-1—The ONS 15454 DWDM card (unit) that is installed in the first position slot.
•![]() Port#-1—The port identifier shown in the CTC for the first Position-1 connection.
Port#-1—The port identifier shown in the CTC for the first Position-1 connection.
•![]() Port ID-1—The port identifier shown in TL1 for the Position-1 connection.
Port ID-1—The port identifier shown in TL1 for the Position-1 connection.
•![]() Port Label-1—The name of the physical port printed on the card's front plate and shown in CTC card view for the Position-1 connection.
Port Label-1—The name of the physical port printed on the card's front plate and shown in CTC card view for the Position-1 connection.
•![]() Attenuator—Indicates whether attenuation is required.
Attenuator—Indicates whether attenuation is required.
•![]() Patchcord Type—Indicates the level of attenuation that is required, if needed.
Patchcord Type—Indicates the level of attenuation that is required, if needed.
•![]() Position-2—The second position rack, shelf, and slot. For example, Rack#1.Main Shelf.02 refers to Slot 2 in the Main Shelf of Rack #1. Refer to the Cisco MetroPlanner Site Dialog window for rack and shelf names and locations.
Position-2—The second position rack, shelf, and slot. For example, Rack#1.Main Shelf.02 refers to Slot 2 in the Main Shelf of Rack #1. Refer to the Cisco MetroPlanner Site Dialog window for rack and shelf names and locations.
•![]() Unit-2—The ONS 15454 DWDM card (unit) that is installed in the Position-2 slot.
Unit-2—The ONS 15454 DWDM card (unit) that is installed in the Position-2 slot.
•![]() Port #2—The port identifier shown in CTC for the first Position-2 connection.
Port #2—The port identifier shown in CTC for the first Position-2 connection.
•![]() Port ID-2—The port identifier shown in TL1 for the Position-2 connection.
Port ID-2—The port identifier shown in TL1 for the Position-2 connection.
•![]() Port Label-2—The name of the physical port printed on the card's front plate and shown in CTC card view for the Position-2 connection.
Port Label-2—The name of the physical port printed on the card's front plate and shown in CTC card view for the Position-2 connection.
•![]() Manually Set—Indicates whether you must create the connection manually in CTC.
Manually Set—Indicates whether you must create the connection manually in CTC.
Figure 3-10 Cisco MetroPlanner Internal Connections Table
Step 3 ![]() Export the internal connections table:
Export the internal connections table:
a. ![]() Click Export.
Click Export.
b. ![]() Enter a file name in the File Name field of the Save Table dialog box.
Enter a file name in the File Name field of the Save Table dialog box.
c. ![]() In the Files of Type field, choose HTML (to save the file as an HTML file viewable in a web browser), or Tab Separated Values to save the file as a tab-separated text file, which you can import into a spreadsheet application.
In the Files of Type field, choose HTML (to save the file as an HTML file viewable in a web browser), or Tab Separated Values to save the file as a tab-separated text file, which you can import into a spreadsheet application.
d. ![]() Click Save.
Click Save.
Step 4 ![]() Open the exported Cisco MetroPlanner internal connections file in a web browser (or spreadsheet application), and then print the file.
Open the exported Cisco MetroPlanner internal connections file in a web browser (or spreadsheet application), and then print the file.
Step 5 ![]() Verify that fibers are available to complete the connections shown in the Cisco MetroPlanner internal connections table.
Verify that fibers are available to complete the connections shown in the Cisco MetroPlanner internal connections table.
Step 6 ![]() Complete the "NTP-G115 Clean Fiber Connectors" procedure on page 11-32 for all fiber connections, even new fiber. Dust particles can degrade performance. Put caps on any fiber connectors that are not used.
Complete the "NTP-G115 Clean Fiber Connectors" procedure on page 11-32 for all fiber connections, even new fiber. Dust particles can degrade performance. Put caps on any fiber connectors that are not used.
Step 7 ![]() Complete the "DLP-G65 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for OSC Link Terminations on All Nodes" task.
Complete the "DLP-G65 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for OSC Link Terminations on All Nodes" task.
Step 8 ![]() As required, complete the following tasks based on the DWDM node type:
As required, complete the following tasks based on the DWDM node type:
•![]() "DLP-G66 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for a Hub Node" task
"DLP-G66 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for a Hub Node" task
•![]() "DLP-G67 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for a Terminal Node" task.
"DLP-G67 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for a Terminal Node" task.
•![]() "DLP-G68 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for a Line Amplifier Node" task.
"DLP-G68 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for a Line Amplifier Node" task.
•![]() "DLP-G70 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for an Amplified or Passive OADM Node" task.
"DLP-G70 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for an Amplified or Passive OADM Node" task.
•![]() "DLP-G69 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for an OSC Regeneration Node" task
"DLP-G69 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for an OSC Regeneration Node" task
•![]() "DLP-G71 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for an ROADM Node" task
"DLP-G71 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for an ROADM Node" task
Step 9 ![]() Continue with the "G35 Route Fiber-Optic Cables" procedure.
Continue with the "G35 Route Fiber-Optic Cables" procedure.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-G65 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for OSC Link Terminations on All Nodes
Step 1 ![]() Refer to the Cisco MetroPlanner internal connections table for your site when completing OSC connections. Before you begin the OSC connections, read the following rules:
Refer to the Cisco MetroPlanner internal connections table for your site when completing OSC connections. Before you begin the OSC connections, read the following rules:
•![]() The OPT-BST and the OSC-CSM are the only cards that directly interface with the line (span) fiber.
The OPT-BST and the OSC-CSM are the only cards that directly interface with the line (span) fiber.
•![]() The OSCM only carries optical service channels, not DWDM channels.
The OSCM only carries optical service channels, not DWDM channels.
•![]() The OSCM and the OSC-CSM cannot both be installed on the same side of the shelf (east or west). You can have different cards on each side, for example an OSCM on the west side and an OSC-CSM on the east side.
The OSCM and the OSC-CSM cannot both be installed on the same side of the shelf (east or west). You can have different cards on each side, for example an OSCM on the west side and an OSC-CSM on the east side.
•![]() When an OPT-BST and an OSC-CSM are both used on the same side of the node, the OPT-BST combines the supervision channel with the DWDM channels and the OSC-CSM acts as an OSCM; it does not carry DWDM traffic.
When an OPT-BST and an OSC-CSM are both used on the same side of the node, the OPT-BST combines the supervision channel with the DWDM channels and the OSC-CSM acts as an OSCM; it does not carry DWDM traffic.
•![]() If an OPT-BST and OSCM card are installed on the east side, the east OPT-BST OSC RX port is connected to the east OSCM TX port, and the east OPT-BST OSC TX port is connected to the east OSCM RX port.
If an OPT-BST and OSCM card are installed on the east side, the east OPT-BST OSC RX port is connected to the east OSCM TX port, and the east OPT-BST OSC TX port is connected to the east OSCM RX port.
•![]() If you have an OPT-BST and OSC-CSM card are installed on the east side, the east OPT-BST OSC RX port is connected to the east OSC-CSM LINE TX port, and the east OPT-BST OSC TX port is connected to the east OSC-CSM LINE RX port.
If you have an OPT-BST and OSC-CSM card are installed on the east side, the east OPT-BST OSC RX port is connected to the east OSC-CSM LINE TX port, and the east OPT-BST OSC TX port is connected to the east OSC-CSM LINE RX port.
•![]() If an OPT-BST and OSCM card are installed on the west side, The west OPT-BST OSC TX port is connected to the west OSCM RX port, and the west OPT-BST OSC RX port is connected to the west OSCM TX port.
If an OPT-BST and OSCM card are installed on the west side, The west OPT-BST OSC TX port is connected to the west OSCM RX port, and the west OPT-BST OSC RX port is connected to the west OSCM TX port.
•![]() If you have an OPT-BST and OSC-CSM card are installed on the west side, the west OPT-BST OSC TX port is connected to the west OSC-CSM LINE RX port, and the west OPT-BST OSC RX port is connected to the west OSC-CSM LINE TX port.
If you have an OPT-BST and OSC-CSM card are installed on the west side, the west OPT-BST OSC TX port is connected to the west OSC-CSM LINE RX port, and the west OPT-BST OSC RX port is connected to the west OSC-CSM LINE TX port.
Figure 3-11 shows an example of OSC fibering for a hub node with OSCM cards installed.
Figure 3-11 Fibering OSC Terminations—Hub Node with OSCM Cards
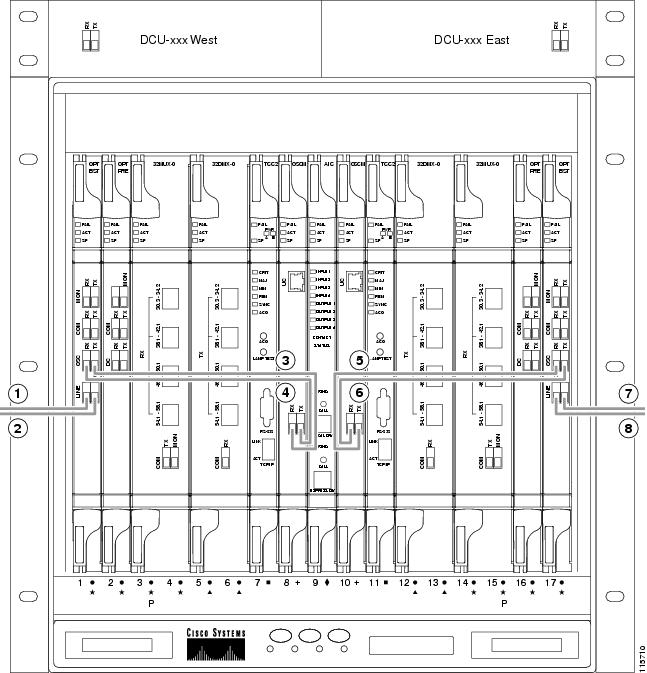
Step 2 ![]() Plug one end of a fiber into the west OPT-BST or OSC-CSM LINE TX connector and the other end into the adjacent node east OPT-BST or OSC-CSM LINE RX connector. Repeat in the other direction (east to west, TX to RX). Always connect the west line ports to the adjacent node east line ports.
Plug one end of a fiber into the west OPT-BST or OSC-CSM LINE TX connector and the other end into the adjacent node east OPT-BST or OSC-CSM LINE RX connector. Repeat in the other direction (east to west, TX to RX). Always connect the west line ports to the adjacent node east line ports.

Note ![]() Cards display an SF LED after the OSC terminations are created (see the "G38 Provision Terminations and Ring ID" procedure) and transmit and receive fibers are not connected correctly. For example, an RX port is connected to another RX port or a TX port is connected to another TX port.
Cards display an SF LED after the OSC terminations are created (see the "G38 Provision Terminations and Ring ID" procedure) and transmit and receive fibers are not connected correctly. For example, an RX port is connected to another RX port or a TX port is connected to another TX port.
Step 3 ![]() If OSCM cards are not installed, continue with Step 4. If OSCM cards are installed.
If OSCM cards are not installed, continue with Step 4. If OSCM cards are installed.
a. ![]() Plug one end of a fiber into the west OPT-BST OSC RX connector and the other end into west OSCM OSC TX connector.
Plug one end of a fiber into the west OPT-BST OSC RX connector and the other end into west OSCM OSC TX connector.
b. ![]() Plug another fiber into the west OSCM OSC RX connector and the other end to the west OPT-BST OSC TX connector.
Plug another fiber into the west OSCM OSC RX connector and the other end to the west OPT-BST OSC TX connector.
c. ![]() plug one end of a fiber into the east OPT-BST OSC RX connector and the other end into east OSCM TX connector.
plug one end of a fiber into the east OPT-BST OSC RX connector and the other end into east OSCM TX connector.
d. ![]() Plug another fiber into the east OSCM OSC RX connector and the other end to the east OPT-BST OSC TX connector.
Plug another fiber into the east OSCM OSC RX connector and the other end to the east OPT-BST OSC TX connector.
Step 4 ![]() Repeat Steps 2 and 3 at each node in the network.
Repeat Steps 2 and 3 at each node in the network.
Step 5 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G66 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for a Hub Node
Purpose |
This task installs fiber-optic cables on a hub node DWDM shelf. |
Tools |
Fiber-optic cables |
Prerequisite Procedures |
|
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite |
Security Level |
None |
Step 1 ![]() Refer to the Cisco MetroPlanner internal connections table for your site when completing connections. Before you begin hub node connections, read the following rules:
Refer to the Cisco MetroPlanner internal connections table for your site when completing connections. Before you begin hub node connections, read the following rules:
•![]() The west OPT-BST or OSC-CSM card common (COM) TX port is connected to the west OPT-PRE COM RX port or the west 32DMX-O COM RX port.
The west OPT-BST or OSC-CSM card common (COM) TX port is connected to the west OPT-PRE COM RX port or the west 32DMX-O COM RX port.
•![]() The west OPT-PRE COM TX port is connected to the west 32DMX-O COM RX port.
The west OPT-PRE COM TX port is connected to the west 32DMX-O COM RX port.
•![]() The west 32MUX-O COM TX port is connected to the west OPT-BST or west OSC-CSM COM RX port.
The west 32MUX-O COM TX port is connected to the west OPT-BST or west OSC-CSM COM RX port.
•![]() The east 32MUX-O COM TX port is connected to the east OPT-BST or east OSC-CSM COM RX port.
The east 32MUX-O COM TX port is connected to the east OPT-BST or east OSC-CSM COM RX port.
•![]() The east OPT-BST or east OSC-CSM COM TX port is connected to the east OPT-PRE COM RX port or the east 32DMX-O COM RX port.
The east OPT-BST or east OSC-CSM COM TX port is connected to the east OPT-PRE COM RX port or the east 32DMX-O COM RX port.
•![]() The east OPT-PRE COM TX port is connected to the east 32DMX-O COM RX port.
The east OPT-PRE COM TX port is connected to the east 32DMX-O COM RX port.
Figure 3-12 shows an example of a hub node with cabling. In the example, OSCM cards are installed. If OSC-CSM are installed, they are usually installed in Slots 1and 17.
Figure 3-12 Fibering a Hub Node
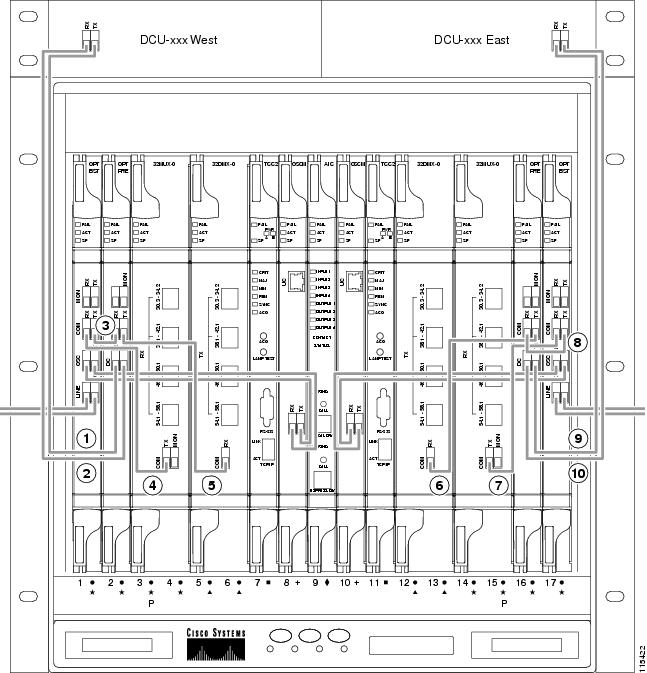
|
|
West DCU TX to west OPT-PRE DC RX1 |
|
|
West DCU RX to west OPT-PRE DC TX1 |
|
|
West OPT-BST COM TX to west OPT-PRE COM RX |
|
|
West OPT-BST COM RX to west 32MUX-O COM TX |
|
|
West OPT-PRE COM TX to west 32DMX-O COM RX |
|
|
East 32DMX-O COM RX to east OPT-PRE COM TX |
|
|
East 32MUX-O COM TX to east OPT-BST COM RX |
|
|
East OPT-PRE COM RX to east OPT-BST COM TX |
|
|
East DCU TX to east OPT-PRE DC RX1 |
|
|
East DCU RX to east OPT-PRE DC TX1 |
1 If a DCU is not installed, a 5 dB attenuator loop must be installed between the OPT-PRE DC ports. |
Step 2 ![]() Plug one end of the fiber cable into the desired RX port and other end into the desired TX port.
Plug one end of the fiber cable into the desired RX port and other end into the desired TX port.

Note ![]() Cards display an SF LED after the OSC terminations are created (see the "G38 Provision Terminations and Ring ID" procedure) and transmit and receive fibers are not connected correctly. For example, an RX port is connected to another RX port or a TX port is connected to another TX port.
Cards display an SF LED after the OSC terminations are created (see the "G38 Provision Terminations and Ring ID" procedure) and transmit and receive fibers are not connected correctly. For example, an RX port is connected to another RX port or a TX port is connected to another TX port.
Step 3 ![]() Repeat Step 2 until you have connected the nodes according to the site plan.
Repeat Step 2 until you have connected the nodes according to the site plan.
Step 4 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G67 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for a Terminal Node
Purpose |
This task installs fiber-optic cables on a terminal node DWDM shelf. |
Tools |
Fiber-optic cables |
Prerequisite Procedures |
|
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite |
Security Level |
None |
Step 1 ![]() Refer to the Cisco MetroPlanner internal connections table for your site when completing connections. Before you begin terminal node connections, read the following rules:
Refer to the Cisco MetroPlanner internal connections table for your site when completing connections. Before you begin terminal node connections, read the following rules:
•![]() A terminal site has only one side (as compared to a hub node, which has two sides). The terminal side can be either east or west.
A terminal site has only one side (as compared to a hub node, which has two sides). The terminal side can be either east or west.
•![]() The terminal side OPT-BST or OSC-CSM card common (COM) TX port is connected to the terminal side OPT-PRE COM RX port or the 32DMX-O COM RX port.
The terminal side OPT-BST or OSC-CSM card common (COM) TX port is connected to the terminal side OPT-PRE COM RX port or the 32DMX-O COM RX port.
•![]() The terminal side OPT-PRE COM TX port is connected to the terminal side 32DMX-O COM RX port.
The terminal side OPT-PRE COM TX port is connected to the terminal side 32DMX-O COM RX port.
•![]() The terminal side 32MUX-O COM TX port is connected to the terminal side OPT-BST or OSC-CSM COM RX port.
The terminal side 32MUX-O COM TX port is connected to the terminal side OPT-BST or OSC-CSM COM RX port.
Step 2 ![]() Plug one fiber cable end into the desired RX port and other end into the desired TX port.
Plug one fiber cable end into the desired RX port and other end into the desired TX port.

Note ![]() Cards display an SF LED after the OSC terminations are created (see the "G38 Provision Terminations and Ring ID" procedure) and transmit and receive fibers are not connected correctly. For example, an RX port is connected to another RX port or a TX port is connected to another TX port.
Cards display an SF LED after the OSC terminations are created (see the "G38 Provision Terminations and Ring ID" procedure) and transmit and receive fibers are not connected correctly. For example, an RX port is connected to another RX port or a TX port is connected to another TX port.
Step 3 ![]() Repeat Step 2 until you have connected the nodes according to the site plan.
Repeat Step 2 until you have connected the nodes according to the site plan.
Step 4 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G68 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for a Line Amplifier Node
Step 1 ![]() Refer to the Cisco MetroPlanner internal connections table for your site when completing connections.Before you begin the line amplifier node connections, read the following rules:
Refer to the Cisco MetroPlanner internal connections table for your site when completing connections.Before you begin the line amplifier node connections, read the following rules:
•![]() Line amplifier node layout allows all combinations of OPT-PRE and OPT-BST and allows you to use asymmetrical card choices in west-to-east and east-to-west configurations. For a given line direction, you can configure the four following possibilities:
Line amplifier node layout allows all combinations of OPT-PRE and OPT-BST and allows you to use asymmetrical card choices in west-to-east and east-to-west configurations. For a given line direction, you can configure the four following possibilities:
–![]() Only preamplification (OPT-PRE)
Only preamplification (OPT-PRE)
–![]() Only booster amplification (OPT-BST)
Only booster amplification (OPT-BST)
–![]() Both preamplification and booster amplification (where a line amplifier node has amplification in at least one direction)
Both preamplification and booster amplification (where a line amplifier node has amplification in at least one direction)
–![]() Neither preamplification nor booster amplification
Neither preamplification nor booster amplification
•![]() If a west OPT-PRE card is installed:
If a west OPT-PRE card is installed:
–![]() The west OSC-CSM or OPT-BST COM TX is connected to the west OPT-PRE COM RX port.
The west OSC-CSM or OPT-BST COM TX is connected to the west OPT-PRE COM RX port.
–![]() The west OPT-PRE COM TX port is connected to the east OSC-CSM or OPT-BST COM RX port.
The west OPT-PRE COM TX port is connected to the east OSC-CSM or OPT-BST COM RX port.
•![]() If a west OPT-PRE card is not installed, the west OSC-CSM or the OPT-BST COM TX port is connected to the east OSC-CSM or OPT-BST COM RX port.
If a west OPT-PRE card is not installed, the west OSC-CSM or the OPT-BST COM TX port is connected to the east OSC-CSM or OPT-BST COM RX port.
•![]() If an east OPT-PRE card is installed:
If an east OPT-PRE card is installed:
–![]() The east OSC-CSM or OPT-BST COM TX port is connected to the east OPT-PRE COM RX port.
The east OSC-CSM or OPT-BST COM TX port is connected to the east OPT-PRE COM RX port.
–![]() The east OPT-PRE COM TX port is connected to the west OSC-CSM or OPT-BST COM RX port.
The east OPT-PRE COM TX port is connected to the west OSC-CSM or OPT-BST COM RX port.
•![]() If an east OPT-PRE card is not installed, the east OSC-CSM or OPT-BST COM TX port is connected to the west OSC-CSM or OPT-BST COM RX port.
If an east OPT-PRE card is not installed, the east OSC-CSM or OPT-BST COM TX port is connected to the west OSC-CSM or OPT-BST COM RX port.
Figure 3-13 shows a sample line amplifier node with cabling.
Figure 3-13 Fibering a Line Amplifier Node
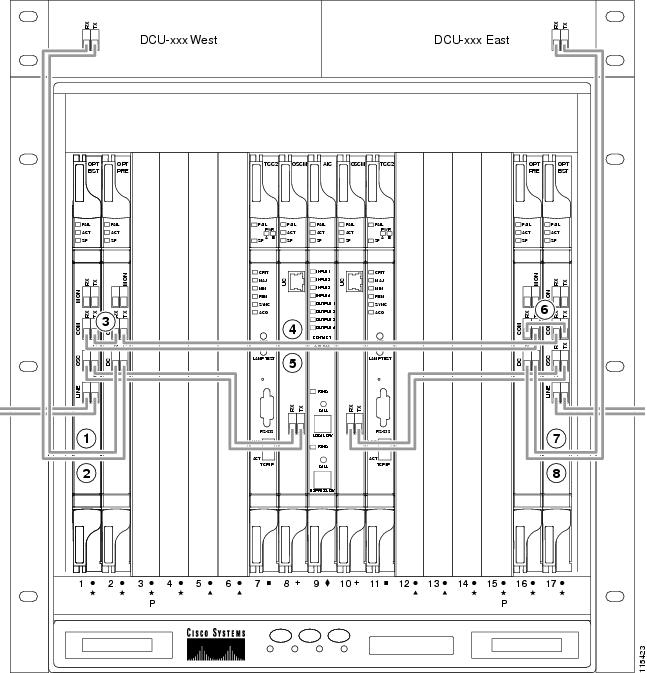
|
|
West DCU TX to west OPT-PRE DC RX1 |
|
West OPT-BST COM RX to east OPT-PRE COM TX |
|
|
West DCU RX to west OPT-PRE DC TX1 |
|
West OPT-BST COM RX to east OPT-PRE COM TX |
|
|
West OPT-BST COM TX to west OPT-PRE COM RX |
|
East DCU TX to east OPT-PRE DC RX1 |
|
|
West OPT-PRE COM TX to east OPT-BST COM RX |
|
East DCU RX to east OPT-PRE DC TX1 |
1 If a DCU is not installed, a 5 dB attenuator loop must be installed between the OPT-PRE DC ports. |
Step 2 ![]() Plug one end of the fiber cable into the desired RX port and other end into the desired TX port.
Plug one end of the fiber cable into the desired RX port and other end into the desired TX port.

Note ![]() Cards display an SF LED after the OSC terminations are created (see the "G38 Provision Terminations and Ring ID" procedure) and transmit and receive fibers are not connected correctly. For example, an RX port is connected to another RX port or a TX port is connected to another TX port.
Cards display an SF LED after the OSC terminations are created (see the "G38 Provision Terminations and Ring ID" procedure) and transmit and receive fibers are not connected correctly. For example, an RX port is connected to another RX port or a TX port is connected to another TX port.
Step 3 ![]() Repeat Step 2 until you have connected the nodes according to the site plan.
Repeat Step 2 until you have connected the nodes according to the site plan.
Step 4 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G69 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for an OSC Regeneration Node
Step 1 ![]() Refer to the Cisco MetroPlanner internal connections table for your site when completing connections. Before you begin OSC regeneration node connections, read the following rules:
Refer to the Cisco MetroPlanner internal connections table for your site when completing connections. Before you begin OSC regeneration node connections, read the following rules:
•![]() The west OSC-CSM COM TX port connects to the east OSC-CSM COM RX port.
The west OSC-CSM COM TX port connects to the east OSC-CSM COM RX port.
•![]() The west OSC-CSM COM RX port connects to the east OSC-CSM COM TX port.
The west OSC-CSM COM RX port connects to the east OSC-CSM COM TX port.
•![]() Slots 2 through 5 and 12 through 16 can be used for TXP/MXP cards.
Slots 2 through 5 and 12 through 16 can be used for TXP/MXP cards.
Figure 3-14 shows a sample OSC regeneration node with cabling.
Figure 3-14 Fibering an OSC Regeneration Node
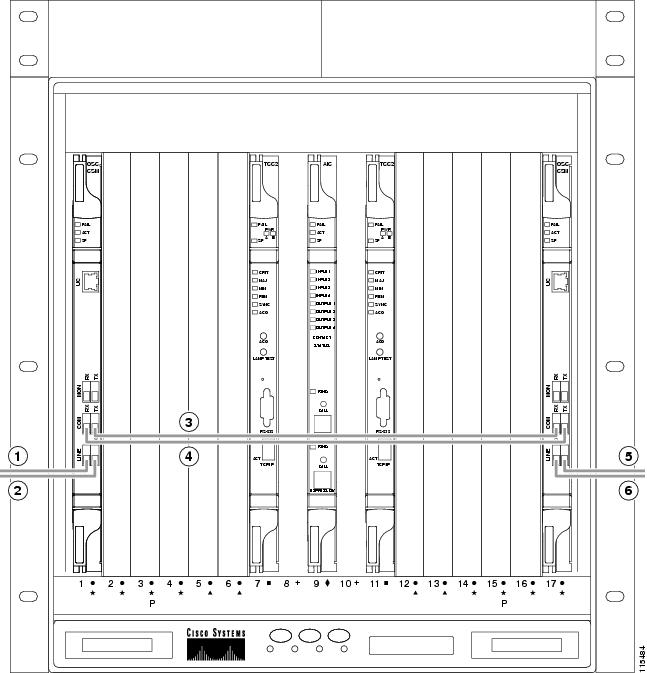
Step 2 ![]() Plug one end of the fiber cable into the desired RX port and other end into the desired TX port.
Plug one end of the fiber cable into the desired RX port and other end into the desired TX port.

Note ![]() Cards display an SF LED after the OSC terminations are created (see the "G38 Provision Terminations and Ring ID" procedure) and transmit and receive fibers are not connected correctly. For example, an RX port is connected to another RX port or a TX port is connected to another TX port.
Cards display an SF LED after the OSC terminations are created (see the "G38 Provision Terminations and Ring ID" procedure) and transmit and receive fibers are not connected correctly. For example, an RX port is connected to another RX port or a TX port is connected to another TX port.
Step 3 ![]() Repeat Step 2 until you have connected the nodes according to the site plan.
Repeat Step 2 until you have connected the nodes according to the site plan.
Step 4 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G70 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for an Amplified or Passive OADM Node

Note ![]() Amplified OADM nodes contain OPT-PRE cards and/or OPT-BST cards. Passive OADM nodes do not. Both contain add/drop channel or band cards.
Amplified OADM nodes contain OPT-PRE cards and/or OPT-BST cards. Passive OADM nodes do not. Both contain add/drop channel or band cards.
Step 1 ![]() Refer to the Cisco MetroPlanner internal connections table for your site when completing connections. Before you begin connecting fiber-optic cabling for amplified or passive OADM nodes, read the following rules for all OADM connections:
Refer to the Cisco MetroPlanner internal connections table for your site when completing connections. Before you begin connecting fiber-optic cabling for amplified or passive OADM nodes, read the following rules for all OADM connections:
•![]() The two sides of the OADM node do not need to be symmetrical. On each side, Cisco MetroPlanner can create one of the following four configurations:
The two sides of the OADM node do not need to be symmetrical. On each side, Cisco MetroPlanner can create one of the following four configurations:
–![]() OPT-BST and OPT-PRE
OPT-BST and OPT-PRE
–![]() OSC-CSM and OPT-PRE
OSC-CSM and OPT-PRE
–![]() Only OSC-CSM
Only OSC-CSM
–![]() Only OPT-BST
Only OPT-BST
Step 2 ![]() Consult the following rules for OADM node express path cabled connections:
Consult the following rules for OADM node express path cabled connections:
•![]() TX ports should only be connected to RX ports.
TX ports should only be connected to RX ports.
•![]() EXP ports are connected only to COM ports in between AD-xC or AD-xB cards that all belong to the east side (that is, they are daisy-chained).
EXP ports are connected only to COM ports in between AD-xC or AD-xB cards that all belong to the east side (that is, they are daisy-chained).
•![]() EXP ports are connected only to COM ports in between AD-xC or AD-xB cards that all belong to the west side (that is, they are daisy-chained).
EXP ports are connected only to COM ports in between AD-xC or AD-xB cards that all belong to the west side (that is, they are daisy-chained).
•![]() The EXP port of the last AD-xC or AD-xB card on the west side is connected to the EXP port of the first AD-xC or AD-xB card on the east side.
The EXP port of the last AD-xC or AD-xB card on the west side is connected to the EXP port of the first AD-xC or AD-xB card on the east side.
•![]() The OPT-BST COM RX port is connected to the nearest (in slot position) AD-xC or AD-xB COM TX port.
The OPT-BST COM RX port is connected to the nearest (in slot position) AD-xC or AD-xB COM TX port.
•![]() The OPT-PRE COM TX port is connected to the nearest (in slot position) AD-xC or AD-xB COM RX port.
The OPT-PRE COM TX port is connected to the nearest (in slot position) AD-xC or AD-xB COM RX port.
•![]() If OADM cards are located in adjacent slots, the TCC2 card assumes they are connected in a daisy-chain between the EXP ports and COM ports as noted previously.
If OADM cards are located in adjacent slots, the TCC2 card assumes they are connected in a daisy-chain between the EXP ports and COM ports as noted previously.
•![]() The first west AD-xC or AD-xB card COM RX port is connected to the west OPT-PRE or OSC-CSM COM TX port.
The first west AD-xC or AD-xB card COM RX port is connected to the west OPT-PRE or OSC-CSM COM TX port.
•![]() The first west AD-xC or AD-xB card COM TX port is connected to the west OPT-BST or OSC-CSM COM RX port.
The first west AD-xC or AD-xB card COM TX port is connected to the west OPT-BST or OSC-CSM COM RX port.
•![]() The first east AD-xC or AD-xB card COM RX port is connected to the east OPT-PRE or OSC-CSM COM TX port.
The first east AD-xC or AD-xB card COM RX port is connected to the east OPT-PRE or OSC-CSM COM TX port.
•![]() The first east AD-xC or AD-xB card COM TX port is connected to the east OPT-BST or OSC-CSM RX port.
The first east AD-xC or AD-xB card COM TX port is connected to the east OPT-BST or OSC-CSM RX port.
•![]() If a west OPT-PRE is present, the west OPT-BST or OSC-CSM COM TX port is connected to the west OPT-PRE COM RX port.
If a west OPT-PRE is present, the west OPT-BST or OSC-CSM COM TX port is connected to the west OPT-PRE COM RX port.
•![]() If an east OPT-PRE is present, the east OPT-BST or OSC-CSM COM TX port is connected to the east OPT-PRE COM RX port.
If an east OPT-PRE is present, the east OPT-BST or OSC-CSM COM TX port is connected to the east OPT-PRE COM RX port.
Step 3 ![]() Consult the following rules for OADM node add/drop path cabled connections:
Consult the following rules for OADM node add/drop path cabled connections:
•![]() AD-xB add/drop (RX or TX) ports are only connected to the following ports:
AD-xB add/drop (RX or TX) ports are only connected to the following ports:
–![]() 4MD COM TX or 4MD COM RX ports
4MD COM TX or 4MD COM RX ports
–![]() Another AD-xB add/drop port (a pass-through configuration)
Another AD-xB add/drop port (a pass-through configuration)
•![]() An AD-xB add/drop band port is only connected to a 4MD card belonging to the same band.
An AD-xB add/drop band port is only connected to a 4MD card belonging to the same band.
•![]() For each specific AD-xB, the add and drop ports for that band card are connected to the COM TX and COM RX ports of the same 4MD card.
For each specific AD-xB, the add and drop ports for that band card are connected to the COM TX and COM RX ports of the same 4MD card.
•![]() The AD-xB and 4MD cards are located in the same side (the connected ports will all have the same line direction).
The AD-xB and 4MD cards are located in the same side (the connected ports will all have the same line direction).
Step 4 ![]() Consult the following rules for OADM node pass-through path cabled connections:
Consult the following rules for OADM node pass-through path cabled connections:
•![]() Pass-through connections are only established between add and drop ports on the same band or channel and same line direction.
Pass-through connections are only established between add and drop ports on the same band or channel and same line direction.
•![]() Only connect AD-xC or AD-xB add/drop ports to other AD-xC or AD-xB add/drop ports (as pass-through configurations).
Only connect AD-xC or AD-xB add/drop ports to other AD-xC or AD-xB add/drop ports (as pass-through configurations).
•![]() An add (RX) port is only connected to a drop (TX) port.
An add (RX) port is only connected to a drop (TX) port.
•![]() Only connect 4MD client input/output ports to other 4MD client input/output ports.
Only connect 4MD client input/output ports to other 4MD client input/output ports.
•![]() A west AD-xB drop (TX) port is connected to the corresponding west 4MD COM RX port.
A west AD-xB drop (TX) port is connected to the corresponding west 4MD COM RX port.
•![]() A west AD-xB add (RX) port is connected to the corresponding west 4MD COM TX port.
A west AD-xB add (RX) port is connected to the corresponding west 4MD COM TX port.
•![]() An east AD-xB drop (TX) port is connected to the corresponding east 4MD COM RX port.
An east AD-xB drop (TX) port is connected to the corresponding east 4MD COM RX port.
•![]() An east AD-xB add (RX) port is connected to the corresponding east 4MD COM TX port.
An east AD-xB add (RX) port is connected to the corresponding east 4MD COM TX port.
Figure 3-15 shows a sample amplified OADM node with AD-1C-xx.x cards installed.
Figure 3-15 Fibering an Amplified OADM Node
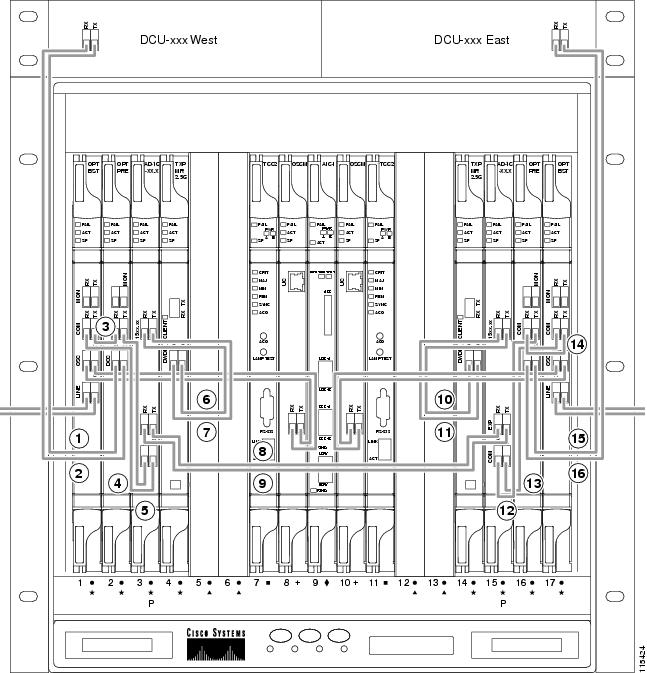
|
|
West DCU TX to west OPT-PRE DC RX1 |
|
|
West DCU RX to west OPT-PRE DC TX1 |
|
|
West OPT-BST COM TX to west OPT-PRE COM RX |
|
|
West OPT-BST COM RX to west AD-1C-xx.x COM TX |
|
|
West OPT-PRE COM TX to west AD-1C-xx.x COM RX |
|
|
West AD-1C-xx.x (15xx.xx) RX to west TXP_MR_2.5G DWDM TX |
|
|
West AD-1C-xx.x (15xx.xx) TX to west TXP_MR_2.5G DWDM RX |
|
|
West AD-1C-xx.x EXP TX to east AD-1C-xx.x EXP RX |
|
|
West AD-1C-xx.x EXP RX to east AD-1C-xx.x EXP TX |
|
|
East TXP_MR_2.5G DWDM RX to east AD-1C-xx.x (15xx.xx) TX |
|
|
East TXP_MR_2.5G DWDM TX to east AD-1C-xx.x (15xx.xx) RX |
|
|
East AD-1C-xx.x COM RX to OPT-PRE COM TX |
|
|
East AD-1C-xx.x COM TX to OPT-BST COM RX |
|
|
East OPT-PRE COM RX to east OPT-BST COM TX |
|
|
East DCU TX to east OPT-PRE DC RX1 |
|
|
East DCU RX to east OPT-PRE DC TX1 |
1 If a DCU is not installed, a 5 dB attenuator loop must be installed between the OPT-PRE DC ports. |
Figure 3-16 shows an example of a passive OADM node with two AD-1C-xx.x cards installed.
Figure 3-16 Fibering a Passive OADM Node
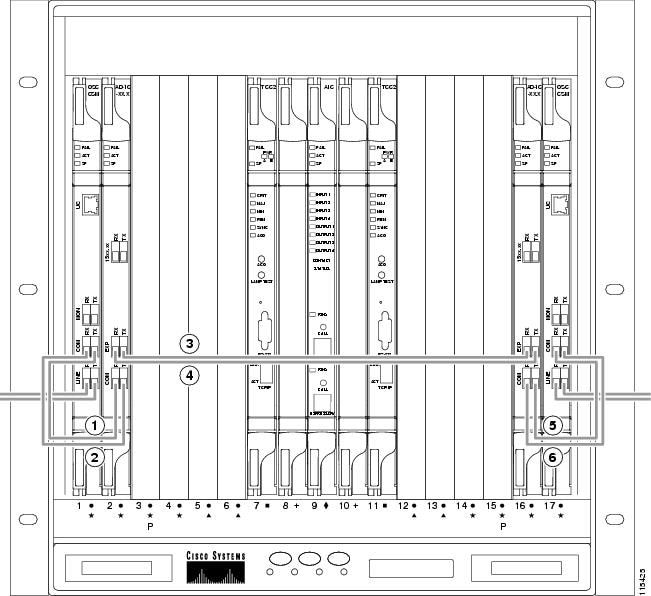
Step 5 ![]() Plug one end of the fiber cable into the desired RX port and other end into the desired TX port.
Plug one end of the fiber cable into the desired RX port and other end into the desired TX port.

Note ![]() Cards display an SF LED after the OSC terminations are created (see the "G38 Provision Terminations and Ring ID" procedure) and transmit and receive fibers are not connected correctly. For example, an RX port is connected to another RX port or a TX port is connected to another TX port.
Cards display an SF LED after the OSC terminations are created (see the "G38 Provision Terminations and Ring ID" procedure) and transmit and receive fibers are not connected correctly. For example, an RX port is connected to another RX port or a TX port is connected to another TX port.
Step 6 ![]() Repeat Step 5 until you have connected the nodes according to the site plan.
Repeat Step 5 until you have connected the nodes according to the site plan.
Step 7 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G71 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for an ROADM Node

Note ![]() To avoid error, connect fiber-optic cable so that the farthest slot to the right represents the east port, and the farthest slot to the left represents the west port. Fiber connected to an east port on one node must plug into the west port on an adjacent node.
To avoid error, connect fiber-optic cable so that the farthest slot to the right represents the east port, and the farthest slot to the left represents the west port. Fiber connected to an east port on one node must plug into the west port on an adjacent node.
Step 1 ![]() Refer to the Cisco MetroPlanner internal connections table for your site when completing connections. Before you begin connecting fiber-optic cabling for ROADM nodes, read the following rules:
Refer to the Cisco MetroPlanner internal connections table for your site when completing connections. Before you begin connecting fiber-optic cabling for ROADM nodes, read the following rules:
•![]() The west OPT-BST or OSC-CSM COM TX port is connected to the west OPT-PRE COM RX port.
The west OPT-BST or OSC-CSM COM TX port is connected to the west OPT-PRE COM RX port.
•![]() The west OPT-BST or OSC-CSM COM RX port is connected to the west 32WSS COM TX port.
The west OPT-BST or OSC-CSM COM RX port is connected to the west 32WSS COM TX port.
•![]() The west OPT-BST (if installed) OSC TX port is connected to the west OSCM RX port.
The west OPT-BST (if installed) OSC TX port is connected to the west OSCM RX port.
•![]() The west OPT-BST (if installed) OSC RX port is connected to the west OSCM TX port.
The west OPT-BST (if installed) OSC RX port is connected to the west OSCM TX port.
•![]() The west 32WSS EXP TX port is connected to the east 32WSS EXP RX port.
The west 32WSS EXP TX port is connected to the east 32WSS EXP RX port.
•![]() The west 32WSS EXP RX port is connected to the east 32WSS EXP TX port.
The west 32WSS EXP RX port is connected to the east 32WSS EXP TX port.
•![]() The west 32WSS DROP TX port is connected to the west 32DMX COM RX port.
The west 32WSS DROP TX port is connected to the west 32DMX COM RX port.
•![]() The east OPT-BST or OSC-CSM COM TX port is connected to the east OPT-PRE COM RX port.
The east OPT-BST or OSC-CSM COM TX port is connected to the east OPT-PRE COM RX port.
•![]() The east OPT-BST or OSC-CSM COM RX port is connected to the east 32WSS COM TX port.
The east OPT-BST or OSC-CSM COM RX port is connected to the east 32WSS COM TX port.
•![]() The east OPT-BST (if installed) OSC TX port is connected to the east OSCM RX port.
The east OPT-BST (if installed) OSC TX port is connected to the east OSCM RX port.
•![]() The east OPT-BST (if installed) OSC RX port is connected to the east OSCM TX port.
The east OPT-BST (if installed) OSC RX port is connected to the east OSCM TX port.
•![]() The east 32WSS DROP TX port is connected to the east 32DMX COM RX port.
The east 32WSS DROP TX port is connected to the east 32DMX COM RX port.
Figure 3-17 shows a sample amplified ROADM node with cabling.
Figure 3-17 Fibering an ROADM Node
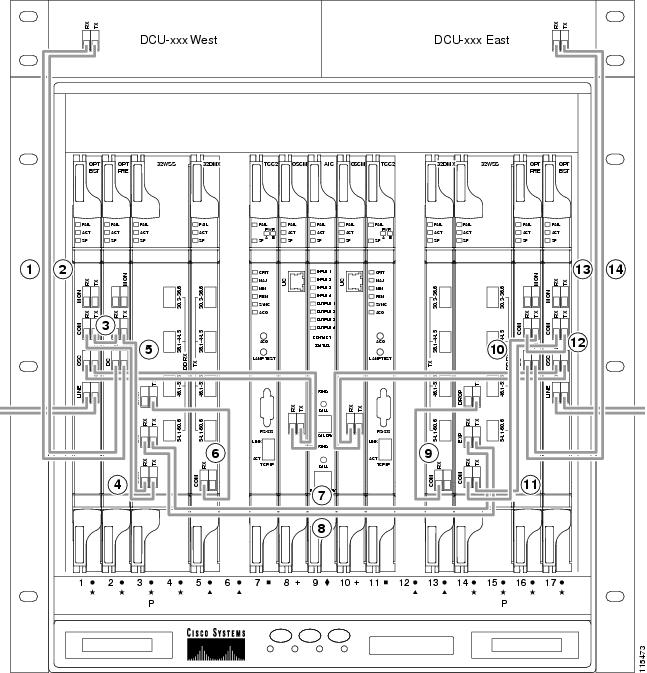
|
|
West DCU TX to west OPT-PRE DC RX1 |
|
|
West DCU RX to west OPT-PRE DC TX1 |
|
|
West OPT-BST COM TX to west OPT-PRE COM RX |
|
|
West 32WSS COM TX to west OPT-BST COM RX |
|
|
West 32WSS COM RX to west OPT-PRE COM TX |
|
|
West 32DMX COM RX to west 32WSS DROP TX |
|
|
West 32WSS EXP TX to east 32WSS EXP RX |
|
|
West 32WSS EXP RX to east 32WSS EXP TX |
|
|
East 32DMX COM RX to east 32WSS DROP TX |
|
|
East 32WSS COM RX to east OPT-PRE COM TX |
|
|
East 32WSS COM TX to east OPT-BST COM RX |
|
|
East OPT-BST COM TX to east OPT-PRE COM RX |
|
|
East DCU RX to east OPT-PRE DC TX1 |
|
|
East DCU TX to east OPT-PRE DC RX1 |
1 If a DCU is not installed, a 5 dB attenuator loop must be installed between the OPT-PRE DC ports. |

Note ![]() Cards display an SF LED after the OSC terminations are created (see the "G38 Provision Terminations and Ring ID" procedure) and transmit and receive fibers are not connected correctly. For example, an RX port is connected to another RX port or a TX port is connected to another TX port.
Cards display an SF LED after the OSC terminations are created (see the "G38 Provision Terminations and Ring ID" procedure) and transmit and receive fibers are not connected correctly. For example, an RX port is connected to another RX port or a TX port is connected to another TX port.
Step 2 ![]() Plug one end of the fiber into the desired RX port and the other into the correct TX port
Plug one end of the fiber into the desired RX port and the other into the correct TX port
Step 3 ![]() Repeat Step 2 until you have connected the nodes according to the site plan.
Repeat Step 2 until you have connected the nodes according to the site plan.
Step 4 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-G35 Route Fiber-Optic Cables
Purpose |
This procedure describes how to route fiber-optic cables. |
Tools/Equipment |
None |
Prerequisite Procedures |
|
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite |
Security Level |
None |
Step 1 ![]() Open the fold-down front door on the cable-management tray.
Open the fold-down front door on the cable-management tray.
Step 2 ![]() Route the fiber cable on the card faceplate through the fiber clip on the faceplate, if provided. Fiber clips are factory-attached to the faceplates of 32MUX-O, 32DMX-O, OSCM, OPT-PRE, and OPT-BST cards.
Route the fiber cable on the card faceplate through the fiber clip on the faceplate, if provided. Fiber clips are factory-attached to the faceplates of 32MUX-O, 32DMX-O, OSCM, OPT-PRE, and OPT-BST cards.
Step 3 ![]() Route the fiber cables into the cable-management tray.
Route the fiber cables into the cable-management tray.
Step 4 ![]() Route the fiber cables out either side of the cable-management tray through the cutouts on each side of the shelf assembly. Use the reversible fiber guides to route cables out the desired side.
Route the fiber cables out either side of the cable-management tray through the cutouts on each side of the shelf assembly. Use the reversible fiber guides to route cables out the desired side.
Step 5 ![]() Close the fold-down front door when all fiber cables in the front compartment are properly routed.
Close the fold-down front door when all fiber cables in the front compartment are properly routed.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-G36 Calculate Cable Connections
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-G46 Log into CTC" task on page 2-25 at the node where you want to provision the DWDM cable connections. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the "DLP-G46 Log into CTC" task on page 2-25 at the node where you want to provision the DWDM cable connections. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Alarms tab.
Click the Alarms tab.
a. ![]() Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-G128 Disable Alarm Filtering" task on page 7-32 as necessary.
Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-G128 Disable Alarm Filtering" task on page 7-32 as necessary.
b. ![]() Verify that no unexplained equipment alarms appear on the node. If alarms appear, investigate and resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 SONET and DWDM Troubleshooting Guide for procedures.
Verify that no unexplained equipment alarms appear on the node. If alarms appear, investigate and resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 SONET and DWDM Troubleshooting Guide for procedures.
Step 3 ![]() Click the Provisioning > WDM-ANS > Connections tabs.
Click the Provisioning > WDM-ANS > Connections tabs.
Step 4 ![]() Click the Calculate Connections button.
Click the Calculate Connections button.
CTC verifies that the cards installed in the ONS 15454 shelf are compatible and that all cards required for the DWDM node type are installed. If so, CTC calculates the fiber connections that should be provisioned. If the cards are not compatible or missing, for example, if an OPT-BST is installed but an OSCM card is not installed, the calculate connections function generates an error.

Note ![]() The connections calculation is not based on the Cisco MetroPlanner site plan. Calculations are based on the cards that are physically installed. If the site plan calls for a hub node but OADM cards are installed, CTC calculates connections based on the cards expected for an OADM node.
The connections calculation is not based on the Cisco MetroPlanner site plan. Calculations are based on the cards that are physically installed. If the site plan calls for a hub node but OADM cards are installed, CTC calculates connections based on the cards expected for an OADM node.
Step 5 ![]() If no errors were generated, continue with Step 6. If errors appear, verify that the cards installed in the shelf match the shelf plan calculated by Cisco MetroPlanner. If cards are installed incorrectly or are missing, remove the cards and install them in the correct slots following the "G30 Install the DWDM Cards" procedure.
If no errors were generated, continue with Step 6. If errors appear, verify that the cards installed in the shelf match the shelf plan calculated by Cisco MetroPlanner. If cards are installed incorrectly or are missing, remove the cards and install them in the correct slots following the "G30 Install the DWDM Cards" procedure.
Step 6 ![]() Verify that the connections in the CTC Connections tab match the connections in the Cisco MetroPlanner internal connections file. (The CTC Connections tab will not show OPT-PRE dispersion connections, span connections, or connections between TXP and MXP cards and the DWDM cards.)
Verify that the connections in the CTC Connections tab match the connections in the Cisco MetroPlanner internal connections file. (The CTC Connections tab will not show OPT-PRE dispersion connections, span connections, or connections between TXP and MXP cards and the DWDM cards.)
Step 7 ![]() Complete the "DLP-G72 Create a DWDM Connection" task for any connections that require manual provisioning. (Connections that require manual creation are indicated by a "Yes" in the Cisco MetroPlanner connections file Manually Set column.) If you need to delete a connection, complete the "DLP-G73 Delete a DWDM Connection" task
Complete the "DLP-G72 Create a DWDM Connection" task for any connections that require manual provisioning. (Connections that require manual creation are indicated by a "Yes" in the Cisco MetroPlanner connections file Manually Set column.) If you need to delete a connection, complete the "DLP-G73 Delete a DWDM Connection" task
Step 8 ![]() Continue with the "G37 Run Automatic Node Setup" procedure.
Continue with the "G37 Run Automatic Node Setup" procedure.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-G72 Create a DWDM Connection
Purpose |
This task creates a DWDM connection. |
Tools/Equipment |
None |
Prerequisite Procedures |
|
Required/As Needed |
Required |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite or remote |
Security Level |
Superuser |
Step 1 ![]() In node view, click the Provisioning > WDM-ANS > Connections tabs.
In node view, click the Provisioning > WDM-ANS > Connections tabs.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Create button.
Click the Create button.
Step 3 ![]() In the Create Optical Link dialog box, choose the From and To slots and ports from the drop-down lists.
In the Create Optical Link dialog box, choose the From and To slots and ports from the drop-down lists.
Step 4 ![]() If the connection is unidirectional, uncheck the bidirectional check box.
If the connection is unidirectional, uncheck the bidirectional check box.
Step 5 ![]() Click OK. The new connection appears in the Connections table, but its State is "Uncommitted."
Click OK. The new connection appears in the Connections table, but its State is "Uncommitted."
Step 6 ![]() If you need to create additional connections, repeat Steps 2 through 5 for each new connection.
If you need to create additional connections, repeat Steps 2 through 5 for each new connection.
Step 7 ![]() Click the new connection in the table. Click the Commit button. The connection state changes to "Connected."
Click the new connection in the table. Click the Commit button. The connection state changes to "Connected."
Step 8 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G73 Delete a DWDM Connection
Purpose |
This task deletes a DWDM connection. |
Tools/Equipment |
None |
Prerequisite Procedures |
|
Required/As Needed |
Required |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite or remote |
Security Level |
Superuser |
Step 1 ![]() In node view, click the Provisioning > WDM-ANS > Connection tabs.
In node view, click the Provisioning > WDM-ANS > Connection tabs.
Step 2 ![]() Click the connection you want to delete.
Click the connection you want to delete.
Step 3 ![]() Click Delete.
Click Delete.
Step 4 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-G37 Run Automatic Node Setup
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-G46 Log into CTC" task on page 2-25 at the node where you want to run automatic node setup. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the "DLP-G46 Log into CTC" task on page 2-25 at the node where you want to run automatic node setup. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Alarms tab.
Click the Alarms tab.
a. ![]() Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-G128 Disable Alarm Filtering" task on page 7-32 as necessary.
Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-G128 Disable Alarm Filtering" task on page 7-32 as necessary.
b. ![]() Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If alarms appear, investigate and resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 SONET and DWDM Troubleshooting Guide for procedures.
Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If alarms appear, investigate and resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 SONET and DWDM Troubleshooting Guide for procedures.
Step 3 ![]() Complete the "DLP-G74 Import a Cisco MetroPlanner Configuration File" task.
Complete the "DLP-G74 Import a Cisco MetroPlanner Configuration File" task.
Step 4 ![]() Click the Port Status tab. Click Launch ANS.
Click the Port Status tab. Click Launch ANS.
Step 5 ![]() In the Apply Launch ANS dialog box, click Yes. ANS adjusts the values of the VOAs to equalize the per-channel power at the amplifier level.
In the Apply Launch ANS dialog box, click Yes. ANS adjusts the values of the VOAs to equalize the per-channel power at the amplifier level.
Step 6 ![]() In the Launch ANS confirmation dialog box, click OK.
In the Launch ANS confirmation dialog box, click OK.
Step 7 ![]() Verify that one of the following statuses appears in the Link Status column for all ports. If so, continue with Step 8.
Verify that one of the following statuses appears in the Link Status column for all ports. If so, continue with Step 8.
•![]() Success - Changed—The parameter setpoint was recalculated successfully.
Success - Changed—The parameter setpoint was recalculated successfully.
•![]() Success - Unchanged—The parameter setpoint did not need recalculation.
Success - Unchanged—The parameter setpoint did not need recalculation.
•![]() Not Applicable—The parameter setpoint does not apply to this node type.
Not Applicable—The parameter setpoint does not apply to this node type.
If one of the following statuses is shown, complete the provided instructions:
•![]() Fail - Out of Range—The calculated setpoint is outside the expected range. Repeat the "G36 Calculate Cable Connections" procedure to verify that all connections have been provisioned correctly, paying attention to connections that require manual provisioning.
Fail - Out of Range—The calculated setpoint is outside the expected range. Repeat the "G36 Calculate Cable Connections" procedure to verify that all connections have been provisioned correctly, paying attention to connections that require manual provisioning.
•![]() Fail - Port in IS State—The parameter could not be calculated because the port is in-service. This status should normally not appear at this point in node turnup. If it does, display the card in card view, change the port admin state to OOS,DSLB (ANSI)/Locked,disabled (ETSI) and repeat Steps 4 through 7.
Fail - Port in IS State—The parameter could not be calculated because the port is in-service. This status should normally not appear at this point in node turnup. If it does, display the card in card view, change the port admin state to OOS,DSLB (ANSI)/Locked,disabled (ETSI) and repeat Steps 4 through 7.

Note ![]() After your network is completed before you create circuits, launch ANS again at each network node to ensure all ports are regulated according to the network values. Individual node values may change during installation
After your network is completed before you create circuits, launch ANS again at each network node to ensure all ports are regulated according to the network values. Individual node values may change during installation
Step 8 ![]() Continue with the "G39 Verify OSCM and OSC-CSM Transmit Power" procedure.
Continue with the "G39 Verify OSCM and OSC-CSM Transmit Power" procedure.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-G74 Import a Cisco MetroPlanner Configuration File

Step 1 ![]() Export the Installation Parameters for your node from Cisco MetroPlanner. Refer to the Cisco MetroPlanner DWDM Operations Guide for procedures. If the parameters file has been exported, continue with Step 2.
Export the Installation Parameters for your node from Cisco MetroPlanner. Refer to the Cisco MetroPlanner DWDM Operations Guide for procedures. If the parameters file has been exported, continue with Step 2.
a. ![]() In Cisco MetroPlanner, select Network > Install > Assisted Conf Setup.
In Cisco MetroPlanner, select Network > Install > Assisted Conf Setup.
b. ![]() In the dialog box, choose a location to save the Cisco MetroPlanner installation file.
In the dialog box, choose a location to save the Cisco MetroPlanner installation file.
Step 2 ![]() In CTC node view, click the Provisioning > WDM-ANS > Provisioning tabs.
In CTC node view, click the Provisioning > WDM-ANS > Provisioning tabs.
Step 3 ![]() Click Import. The Import NE Update From File dialog box opens.
Click Import. The Import NE Update From File dialog box opens.
Step 4 ![]() Enter the path to the configuration file, or click Browse and navigate to the configuration file using the Open dialog box.
Enter the path to the configuration file, or click Browse and navigate to the configuration file using the Open dialog box.
Step 5 ![]() Click OK. The Import NE Update From File dialog box closes.
Click OK. The Import NE Update From File dialog box closes.
The MetroPlanner configuration settings are imported and a pencil icon appears next to each parameter that will change.
Step 6 ![]() Verify that the imported parameters are correct according to the printout of the MetroPlanner parameters file, then click Apply.
Verify that the imported parameters are correct according to the printout of the MetroPlanner parameters file, then click Apply.
Step 7 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-G38 Provision Terminations and Ring ID
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-G46 Log into CTC" task on page 2-25 at the node where you want to provision the DWDM cable connections. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the "DLP-G46 Log into CTC" task on page 2-25 at the node where you want to provision the DWDM cable connections. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Alarms tab.
Click the Alarms tab.
a. ![]() Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-G128 Disable Alarm Filtering" task on page 7-32 as necessary.
Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-G128 Disable Alarm Filtering" task on page 7-32 as necessary.
b. ![]() Verify that no unexplained alarms appear. If alarms appear, investigate and resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 SONET and DWDM Troubleshooting Guide for procedures.
Verify that no unexplained alarms appear. If alarms appear, investigate and resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 SONET and DWDM Troubleshooting Guide for procedures.
Step 3 ![]() Complete the "DLP-G75 Create OSC Terminations" task.
Complete the "DLP-G75 Create OSC Terminations" task.
Step 4 ![]() If you are using TXP or MXP cards, complete the "DLP-G76 Provision GCC Terminations" task
If you are using TXP or MXP cards, complete the "DLP-G76 Provision GCC Terminations" task
Step 5 ![]() As needed, complete the "DLP-G77 Provision the Ring ID" task.
As needed, complete the "DLP-G77 Provision the Ring ID" task.
Step 6 ![]() Continue with the "G39 Verify OSCM and OSC-CSM Transmit Power" procedure.
Continue with the "G39 Verify OSCM and OSC-CSM Transmit Power" procedure.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-G75 Create OSC Terminations
Purpose |
This task creates the terminations required by OSC channels between network nodes. |
Tools/Equipment |
None |
Prerequisite Procedures |
G36 Calculate Cable Connections |
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite or remote |
Security Level |
Provisioning or higher |
Step 1 ![]() In node view, click the Provisioning > Comm Channels > OSC tabs.
In node view, click the Provisioning > Comm Channels > OSC tabs.
Step 2 ![]() In the OSC Terminations pane, click Create (Figure 3-18).
In the OSC Terminations pane, click Create (Figure 3-18).
Figure 3-18 OSC Terminations Pane
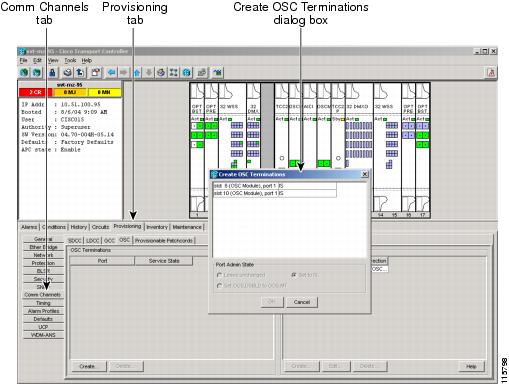
Step 3 ![]() In the Create OSC Terminations dialog box, choose the ports where you want to create the OSC termination. To select more than one port, press the Shift key (to select a range of ports) or the Ctrl key (to select multiple individual ports).
In the Create OSC Terminations dialog box, choose the ports where you want to create the OSC termination. To select more than one port, press the Shift key (to select a range of ports) or the Ctrl key (to select multiple individual ports).

Note ![]() OSC on the DWDM node uses a separate OC3/STM1 channel to transport the section data communications channel (SDCC), which is used for ONS 15454 DCC terminations.
OSC on the DWDM node uses a separate OC3/STM1 channel to transport the section data communications channel (SDCC), which is used for ONS 15454 DCC terminations.
Step 4 ![]() Click OK. Ports are automatically placed in service. Until all network OSC connections between nodes are created and the ports are in service, the following alarms might appear:
Click OK. Ports are automatically placed in service. Until all network OSC connections between nodes are created and the ports are in service, the following alarms might appear:
•![]() LOS-P (OSC termination failure)
LOS-P (OSC termination failure)
•![]() Power failure alarms on the OPT-BST and/or OSC-CSM
Power failure alarms on the OPT-BST and/or OSC-CSM

Note ![]() After the OSC termination is created, the line ports are placed in service and span power levels are checked. If power levels are low and/or the spans are not connected correctly, the OSC termination alarms appear.
After the OSC termination is created, the line ports are placed in service and span power levels are checked. If power levels are low and/or the spans are not connected correctly, the OSC termination alarms appear.
Step 5 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G76 Provision GCC Terminations
Step 1 ![]() In node view click the Provisioning > Comm Channels > GCC tabs.
In node view click the Provisioning > Comm Channels > GCC tabs.
Step 2 ![]() In the GCC Terminations pane, click Create.
In the GCC Terminations pane, click Create.
Step 3 ![]() In the Create optical transport network (OTN) GCC Terminations dialog box, click the ports where you want to create the GCC termination. To select more than one port, press the Shift key or the Ctrl key.
In the Create optical transport network (OTN) GCC Terminations dialog box, click the ports where you want to create the GCC termination. To select more than one port, press the Shift key or the Ctrl key.

Note ![]() GCC refers to the general communications channel, which is used for ONS 15454 transponders and muxponders in DWDM applications.
GCC refers to the general communications channel, which is used for ONS 15454 transponders and muxponders in DWDM applications.
Step 4 ![]() (Optional) From the GCC Rate drop-down list, choose from two options:
(Optional) From the GCC Rate drop-down list, choose from two options:
•![]() 192k is the line rate of Section DCC (SDCC)—This is the default option in Software R4.6.
192k is the line rate of Section DCC (SDCC)—This is the default option in Software R4.6.
•![]() 576k is the line rate of Line DCC (LDCC)—This option will be supported in a future software release.
576k is the line rate of Line DCC (LDCC)—This option will be supported in a future software release.
Step 5 ![]() Click Set to IS if you want to put ports in service.
Click Set to IS if you want to put ports in service.
Step 6 ![]() If the SDCC termination is to include a non-ONS node, check the Far End is Foreign check box. This automatically sets the far-end node IP address to 0.0.0.0, which means that any address can be specified by the far end. To change the default to a specific the IP address, see the "DLP-G184 Change a GCC Termination" task on page 9-28.
If the SDCC termination is to include a non-ONS node, check the Far End is Foreign check box. This automatically sets the far-end node IP address to 0.0.0.0, which means that any address can be specified by the far end. To change the default to a specific the IP address, see the "DLP-G184 Change a GCC Termination" task on page 9-28.
Step 7 ![]() Click OK. Until all network GCC terminations are created and the ports are in service, GCC-EOC alarms appear.
Click OK. Until all network GCC terminations are created and the ports are in service, GCC-EOC alarms appear.
Step 8 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G77 Provision the Ring ID
Purpose |
This task creates a DWDM ring ID. |
Tools/Equipment |
None |
Prerequisite Procedures |
|
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite or remote |
Security Level |
Provisioning or higher |
Step 1 ![]() In node view, click the Provisioning > Comm Channels > OSC tabs.
In node view, click the Provisioning > Comm Channels > OSC tabs.
Step 2 ![]() Click the OSC tab.
Click the OSC tab.
Step 3 ![]() In the DWDM Ring ID area, click Create.
In the DWDM Ring ID area, click Create.
Step 4 ![]() In the DWDM Ring ID dialog box, enter the following information:
In the DWDM Ring ID dialog box, enter the following information:
•![]() Ring ID—Enter the same ID for all nodes on the ring. Choose a number from 1 to 255.
Ring ID—Enter the same ID for all nodes on the ring. Choose a number from 1 to 255.
•![]() West Line—Select a card from the drop-down list. Selectable cards are OSCM or OSC-CSM. Slots 1 through 8 represent the west side of the node.
West Line—Select a card from the drop-down list. Selectable cards are OSCM or OSC-CSM. Slots 1 through 8 represent the west side of the node.
•![]() East Line—Select a card from the drop-down list. Selectable cards are OSCM or OSC-CSM. Slots 10 through 17 represent the east side of the node.
East Line—Select a card from the drop-down list. Selectable cards are OSCM or OSC-CSM. Slots 10 through 17 represent the east side of the node.
Step 5 ![]() Click OK.
Click OK.
Step 6 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-G39 Verify OSCM and OSC-CSM Transmit Power
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-G46 Log into CTC" task on page 2-25 at the node where you want to provision the DWDM cable connections. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the "DLP-G46 Log into CTC" task on page 2-25 at the node where you want to provision the DWDM cable connections. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2 ![]() In the node view shelf graphic, double-click the OSCM or OSC-CSM card.
In the node view shelf graphic, double-click the OSCM or OSC-CSM card.
Step 3 ![]() Click the Maintenance tab.
Click the Maintenance tab.
Step 4 ![]() From the ALS Mode drop-down list, choose Manual Start for Test. Click Apply.
From the ALS Mode drop-down list, choose Manual Start for Test. Click Apply.
Step 5 ![]() Click the Provisioning > Optical Line tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Optical Line tabs.
Step 6 ![]() For the TX (transmit) port entry, verify that the Power value is one of the following:
For the TX (transmit) port entry, verify that the Power value is one of the following:
•![]() If the OSC-CSM is connected to the span and OPT-BST cards are not installed, Power should be the Poutad value or -6.5, whichever is less.
If the OSC-CSM is connected to the span and OPT-BST cards are not installed, Power should be the Poutad value or -6.5, whichever is less.
•![]() If OSCM and OPT-BST cards are installed: -5 dBm if the OPT-PRE is set to Control Gain and the OPT-PRE is not provisioned or equipped; or -0.5 dBm (the maximum value) if it is set to Control Power. (Evaluate the power of the OPT-PRE that is installed on the same side as the OSCM card.)
If OSCM and OPT-BST cards are installed: -5 dBm if the OPT-PRE is set to Control Gain and the OPT-PRE is not provisioned or equipped; or -0.5 dBm (the maximum value) if it is set to Control Power. (Evaluate the power of the OPT-PRE that is installed on the same side as the OSCM card.)
•![]() If OSC-CSM and OPT-BST cards are installed and the OPT-PRE is not provisioned or equipped: -5 dBm if the OPT-PRE is set to Control Gain, or -1.5 dBm (the maximum value) if it is set to Control Power. (Evaluate the power of the OPT-PRE that is installed on the same side as the OSC-CSM.)
If OSC-CSM and OPT-BST cards are installed and the OPT-PRE is not provisioned or equipped: -5 dBm if the OPT-PRE is set to Control Gain, or -1.5 dBm (the maximum value) if it is set to Control Power. (Evaluate the power of the OPT-PRE that is installed on the same side as the OSC-CSM.)
Step 7 ![]() If the OSCM or OSC-CSM power levels are not within the ranges specified in Step 6, complete the following steps. Otherwise, continue with Step 8.
If the OSCM or OSC-CSM power levels are not within the ranges specified in Step 6, complete the following steps. Otherwise, continue with Step 8.
a. ![]() Click the Maintenance > ALS tabs. Verify that the ALS Command is set to OSRI off.
Click the Maintenance > ALS tabs. Verify that the ALS Command is set to OSRI off.
b. ![]() In the ALS Command area, choose Manual Restart and click Apply.
In the ALS Command area, choose Manual Restart and click Apply.
c. ![]() Clean the optical connections. See the "NTP-G115 Clean Fiber Connectors" procedure on page 11-32.
Clean the optical connections. See the "NTP-G115 Clean Fiber Connectors" procedure on page 11-32.
d. ![]() Verify the optical connections inside the unit.
Verify the optical connections inside the unit.
e. ![]() Relaunch ANS.
Relaunch ANS.
Step 8 ![]() Continue with the node acceptance test procedures in Chapter 4, "Perform Node Acceptance Tests".
Continue with the node acceptance test procedures in Chapter 4, "Perform Node Acceptance Tests".
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-G40 Replace the Front Door

Note ![]() Be careful not to crimp any fiber cables that are connected to the MXP/TXP cards or DWDM cards. Some might not have the fiber boot attached.
Be careful not to crimp any fiber cables that are connected to the MXP/TXP cards or DWDM cards. Some might not have the fiber boot attached.
Step 1 ![]() Insert the front door into the hinges on the shelf assembly.
Insert the front door into the hinges on the shelf assembly.
Step 2 ![]() Attach one end of the ground strap terminal lug (72-3622-01) to the male stud on the inside of the door. Attach and tighten the #6 Kepnut (49-0600-01) using the open-end wrench (Figure 3-19).
Attach one end of the ground strap terminal lug (72-3622-01) to the male stud on the inside of the door. Attach and tighten the #6 Kepnut (49-0600-01) using the open-end wrench (Figure 3-19).
Figure 3-19 Installing the Door Ground Strap Retrofit Kit
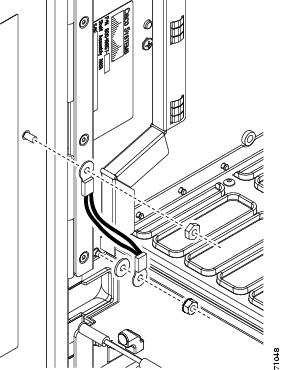
Step 3 ![]() Attach the other end of the ground strap to the longer screw on the fiber guide.
Attach the other end of the ground strap to the longer screw on the fiber guide.
a. ![]() Attach the lock washer.
Attach the lock washer.
b. ![]() Attach the terminal lug.
Attach the terminal lug.
c. ![]() Using the open-end wrench, attach and tighten the #4 Kepnut (49-0337-01) on the terminal lug.
Using the open-end wrench, attach and tighten the #4 Kepnut (49-0337-01) on the terminal lug.

Note ![]() To avoid interference with the traffic (line) card, make sure the ground strap is in a flat position when the door is open. To move the ground strap into a flat position, rotate the terminal lug counterclockwise before tightening the Kepnut.
To avoid interference with the traffic (line) card, make sure the ground strap is in a flat position when the door is open. To move the ground strap into a flat position, rotate the terminal lug counterclockwise before tightening the Kepnut.
Step 4 ![]() Replace the left cable-routing channel.
Replace the left cable-routing channel.
Step 5 ![]() Using a Phillips screwdriver, insert and tighten the screws for the cable-routing channel.
Using a Phillips screwdriver, insert and tighten the screws for the cable-routing channel.
Figure 3-20 shows the shelf assembly with the front door and ground strap installed.
Figure 3-20 Shelf Assembly with Door Ground Strap Retrofit Kit Installed
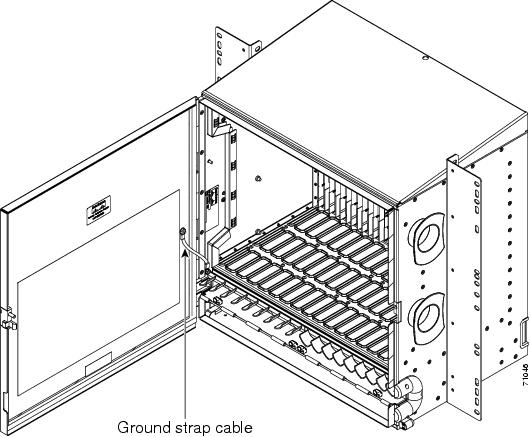
Step 6 ![]() Swing the door closed.
Swing the door closed.

Note ![]() The ONS 15454 comes with a pinned hex key tool for locking and unlocking the front door. Turn the key counterclockwise to unlock the door and clockwise to lock it.
The ONS 15454 comes with a pinned hex key tool for locking and unlocking the front door. Turn the key counterclockwise to unlock the door and clockwise to lock it.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
 Feedback
Feedback