- Securing User Services Overview
- Autosecure
-
-
-
- Configuring RADIUS
- AAA Dead-Server Detection
- ACL Default Direction
- Attribute Screening for Access Requests
- Enable Multilink PPP via RADIUS for Preauthentication User
- Enhanced Test Command
- Framed-Route in RADIUS Accounting
- Offload Server Accounting Enhancement
- Per VRF AAA
- RFC-2867 RADIUS Tunnel Accounting
- RADIUS Attribute Screening
- RADIUS Centralized Filter Management
- RADIUS Debug Enhancements
- RADIUS Logical Line ID
- RADIUS NAS-IP-Address Attribute Configurability
- RADIUS Route Download
- RADIUS Support of 56-Bit Acct Session-Id
- RADIUS Tunnel Preference for Load Balancing and Fail-Over
- RADIUS Server Reorder on Failure
- Tunnel Authentication via RADIUS on Tunnel Terminator
-
-
-
- RADIUS Attributes Overview and RADIUS IETF Attributes
- RADIUS Vendor-Proprietary Attributes
- Vendor-Specific Attributes (VSA) and RADIUS Disconnect-Cause Attribute Values
- Connect-Info RADIUS Attribute 77
- Encrypted Vendor Specific Attributes
- Local AAA Server
- Per-User QoS via AAA Policy Name
- RADIUS Attribute 5 (NAS-Port) Format Specified on a Per-Server Group Level
- RADIUS Attribute 8 (Framed-IP-Address) in Access Requests
- RADIUS Attribute 82: Tunnel Assignment ID
- RADIUS Attribute 104
- RADIUS Progress Codes
- RADIUS Timeout Set During Pre-Authentication
- RADIUS Tunnel Attribute Extensions
- V.92 Reporting Using RADIUS Attribute v.92-info
-
- Cisco IOS Login Enhancements (Login Block)
- Cisco IOS Resilient Configuration
- Image Verification
- IP Source Tracker
- Role-Based CLI Access
Cisco IOS Security Configuration Guide: Securing User Services, Release 12.4
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- Updated:
- March 30, 2011
Chapter: IP Traffic Export
IP Traffic Export
The IP Traffic Export feature allows users to configure their router to export IP packets that are received on multiple, simultaneous WAN or LAN interfaces. The unaltered IP packets are exported on a single LAN or VLAN interface, thereby, easing deployment of protocol analyzers and monitoring devices in the following ways:
•![]() Filter copied packets through an access control list (ACL)
Filter copied packets through an access control list (ACL)
•![]() Filter copied packets through sampling, which allows you to export one in every few packets in which you are interested. Use this option when it is not necessary to export all incoming traffic. Also, sampling is useful when a monitored ingress interface can send traffic faster than the egress interface can transmit it.
Filter copied packets through sampling, which allows you to export one in every few packets in which you are interested. Use this option when it is not necessary to export all incoming traffic. Also, sampling is useful when a monitored ingress interface can send traffic faster than the egress interface can transmit it.
•![]() Configure bidirectional traffic on an interface. (By default, only incoming traffic is exported.)
Configure bidirectional traffic on an interface. (By default, only incoming traffic is exported.)
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest feature information and caveats, see the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the "Feature Information for IP Traffic Export" section.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to http://www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Contents
•![]() Restrictions for IP Traffic Export
Restrictions for IP Traffic Export
•![]() Information About IP Traffic Export
Information About IP Traffic Export
•![]() Configuration Examples for IP Traffic Export
Configuration Examples for IP Traffic Export
•![]() Feature Information for IP Traffic Export
Feature Information for IP Traffic Export
Restrictions for IP Traffic Export
Platform Restriction
IP traffic export is intended only for software switching platforms; distributed architectures are not supported.
IP Packet Forwarding Performance Impact
When IP traffic export is enabled, a delay is incurred on the outbound interface when packets are captured and transmitted across the interface. Performance delays increase with the increased number of interfaces that are monitored and the increased number of destination hosts.
Exported Traffic Limitation
•![]() The MAC address of the device that is receiving the exported traffic must be on the same VLAN or directly connected to one of the router interfaces. (Use the show arp command to determine the MAC address of device that is directly connected to an interface.)
The MAC address of the device that is receiving the exported traffic must be on the same VLAN or directly connected to one of the router interfaces. (Use the show arp command to determine the MAC address of device that is directly connected to an interface.)
•![]() The outgoing interface for exported traffic must be Ethernet (10/100/1000). (Incoming (monitored) traffic can traverse any interface.)
The outgoing interface for exported traffic must be Ethernet (10/100/1000). (Incoming (monitored) traffic can traverse any interface.)
Information About IP Traffic Export
Simplified IDS Deployment
Without the ability to export IP traffic, the Intrusion Detection System (IDS) probe must be inline with the network device to monitor traffic flow. IP traffic export eliminates the probe placement limitation, allowing users to place an IDS probe in any location within their network or direct all exported traffic to a VLAN that is dedicated for network monitoring. Allowing users to choose the optimal location of their IDS probe reduces processing burdens.
Also, because packet processing that was once performed on the network device can now be performed away from the network device, the need to enable IDS with the Cisco IOS software can be eliminated.
IP Traffic Export Profiles
All packet export configurations are specified through IP traffic export profiles, which consist of IP-traffic-export-related command-line interfaces (CLIs) that control various attributes for both incoming and outgoing exported IP traffic. You can configure a router with multiple IP traffic export profiles. (Each profile must have a different name.) You can apply different profiles on different interfaces.
The two different IP traffic export profiles are as follows:
•![]() The global configuration profile, which is configured through the ip traffic-export profile command.
The global configuration profile, which is configured through the ip traffic-export profile command.
•![]() The IP traffic export submode configuration profile, which is configured through any of the following router IP Traffic Export (RITE) commands—bidirectional, incoming, interface, mac-address, and outgoing.
The IP traffic export submode configuration profile, which is configured through any of the following router IP Traffic Export (RITE) commands—bidirectional, incoming, interface, mac-address, and outgoing.
How to Use IP Traffic Export
•![]() Configuring IP Traffic Export
Configuring IP Traffic Export
•![]() Displaying IP Traffic Export Configuration Data
Displaying IP Traffic Export Configuration Data
Configuring IP Traffic Export
Use this task to configure IP traffic export profiles, which enable IP traffic to be exported on an ingress interface and allow you to specify profile attributes, such as the outgoing interface for exporting traffic.

Note ![]() Packet exporting is performed before packet switching or filtering.
Packet exporting is performed before packet switching or filtering.
SUMMARY STEPS
1. ![]() enable
enable
2. ![]() configure terminal
configure terminal
3. ![]() ip traffic-export profile profile-name
ip traffic-export profile profile-name
4. ![]() interface interface-name
interface interface-name
5. ![]() bidirectional
bidirectional
6. ![]() mac-address H.H.H
mac-address H.H.H
7. ![]() incoming {access-list {standard | extended | named} | sample one-in-every packet-number}
incoming {access-list {standard | extended | named} | sample one-in-every packet-number}
8. ![]() outgoing {access-list {standard | extended | named} | sample one-in-every packet-number}
outgoing {access-list {standard | extended | named} | sample one-in-every packet-number}
9. ![]() exit
exit
10. ![]() interface type number
interface type number
11. ![]() ip traffic-export apply profile-name
ip traffic-export apply profile-name
DETAILED STEPS
Troubleshooting Tips
Creating an IP Traffic Export Profile
The interface and mac-address commands are required to successfully create a profile. If these commands are not issued, then the following profile incomplete message is displayed in the show running config command output:
ip traffic-export profile newone
! No outgoing interface configured
! No destination mac-address configured
Applying an IP Traffic Export Profile to an interface
The following system logging messages should appear immediately after you activate and deactivate a profile from an interface (through the ip traffic-export apply profile command):
•![]() Activated profile:
Activated profile:
%RITE-5-ACTIVATE: Activated IP traffic export on interface FastEthernet 0/0.
•![]() Deactivated profile:
Deactivated profile:
%RITE-5-DEACTIVATE: Deactivated IP traffic export on interface FastEthernet 0/0.
If an incomplete profile is applied to an interface, the following message displays:
Router(config-if)# ip traffic-export apply newone
RITE: profile newone has missing outgoing interface
What to Do Next
After you have configured a profile and enabled the profile on an ingress interface, you can monitor IP traffic exporting events and verify your profile configurations. To complete these steps, refer to the following task ""Displaying IP Traffic Export Configuration Data" section."
Displaying IP Traffic Export Configuration Data
This task allows you to verify IP traffic export parameters such as the monitored ingress interface, which is where the IP traffic is exported, and outgoing and incoming IP packet information, such as configured ACLs. You can also use this task to monitor packets that are captured and then transmitted across an interface to a destination host. Use this optional task to help you troubleshoot any problems with your exported IP traffic configurations.
SUMMARY STEPS
1. ![]() enable
enable
2. ![]() debug ip traffic-export events
debug ip traffic-export events
3. ![]() show ip traffic-export [interface interface-name | profile profile-name]
show ip traffic-export [interface interface-name | profile profile-name]
DETAILED STEPS
Examples
The following sample output from the show ip traffic-export command is for the profile "one." This example is for a single, configured interface. If multiple interfaces are configured, the information shown below is displayed for each interface.
Router# show ip traffic-export
Router IP Traffic Export Parameters
Monitored Interface FastEthernet0/0
Export Interface FastEthernet0/1
Destination MAC address 0030.7131.abfc
bi-directional traffic export is off
Input IP Traffic Export Information Packets/Bytes Exported 0/0
Packets Dropped 0
Sampling Rate one-in-every 1 packets
No Access List configured
Profile one is Active
Configuration Examples for IP Traffic Export
•![]() Example: Exporting IP Traffic Configuration
Example: Exporting IP Traffic Configuration
Example: Exporting IP Traffic Configuration
Figure 1 and the following the show running-config command output describes how to configure Router 2 to export the incoming traffic from Router 1 to IDS.
Figure 1
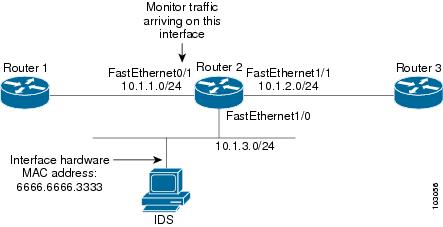
Router 2 exports the incoming traffic from Router 1 to IDS
Router2# show running-config
Building configuration...
Current configuration :2349 bytes
! Last configuration change at 20:35:39 UTC Wed Oct 8 2003
! NVRAM config last updated at 20:35:39 UTC Wed Oct 8 2003
!
version 12.3
service timestamps debug uptime
service timestamps log uptime
no service password-encryption
service internal
service udp-small-servers
!
hostname rite-3745
!
boot system flash:c3745-js-mz.123-1.8.PI2d
no logging console
enable password lab
!
no aaa new-model
ip subnet-zero
!
no ip domain lookup
!
ip cef
!
ip traffic-export profile my_rite
interface FastEthernet1/0
mac-address 6666.6666.3333
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 10.0.0.94 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
ip traffic-export apply my_rite
!
interface FastEthernet1/0
ip address 10.1.3.2 255.255.255.0
no ip redirects
no cdp enable
!
interface FastEthernet1/1
ip address 10.1.2.2 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
!
router ospf 100
log-adjacency-changes
network 10.1.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 0
!
ip http server
ip classless
!
snmp-server engineID local 0000000902000004C1C59140
snmp-server community public RO
snmp-server enable traps tty
!
control-plane
!
dial-peer cor custom
!
gateway
!
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
stopbits 1
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
password lab
login
!
ntp clock-period 17175608
ntp server 10.0.0.2
!
end
Additional References
Related Documents
|
|
|
|---|---|
Cisco IOS commands |
|
Configuring IDS |
"Configuring Cisco IOS Firewall Intrusion Detection System" feature module. |
Standards
|
|
|
|---|---|
None |
— |
MIBs
|
|
|
|---|---|
None |
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco software releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL: |
RFCs
|
|
|
|---|---|
None |
— |
Technical Assistance
Feature Information for IP Traffic Export
Table 1 lists the release history for this feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and software image support. Cisco Feature Navigator enables you to determine which software images support a specific software release, feature set, or platform. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to http://www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.

Note ![]() Table 1 lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Table 1 lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
 Feedback
Feedback