Cisco APIC M1/M2/M3/M4/L1/L2/L3/L4 to APIC-G5 Cluster Migration, Release 6.1(4)
Available Languages
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- US/Canada 800-553-2447
- Worldwide Support Phone Numbers
- All Tools
 Feedback
Feedback
Guidelines and Limitations for Migrating Cisco APIC Servers
Replacing the In-service Cisco APIC Servers
Replacing APIC Servers with APIC Servers Running a Different Software Release
Commissioning APIC Servers Without CIMC Connections
Decommissioning the Standby Cisco APIC Servers to be Replaced by a Normal Cluster
This document provides details on how to perform an in-service replacement of older generation Cisco APIC servers with the APIC-G5 model. As announced on cisco.com[1], the Cisco APIC L1/M1 and L2/M2 servers have reached their end-of-sale and end-of-life date and the Cisco APIC M3/L3 has reached end-of-sale date. At the time of this writing, the suggested Cisco APIC server replacement is Cisco APIC-G5 for ACI fabrics running software release 6.1(4) or later.
The Cisco APIC-G5 requires the Cisco APIC software 6.1(4) release or later. Cisco APIC servers forming a cluster must all run the same software release. You cannot have different software releases inside one cluster; doing so will result in the cluster not converging. There is one exception to this rule: during a software upgrade process, there will be a temporary divergence in software releases within the cluster. This means that before you attempt to replace the existing Cisco APIC M1/L1, M2/L2, M3/L3, or M4/L4 server with a Cisco APIC-G5 server, you must bring the running cluster to a supported release.
You can mix Cisco APIC M2/L2, M3/L3, M4/L4 and APIC-G5 using any possible combination. There are no restrictions other than the minimum software release mentioned in the Software Release Requirements. APIC M1/L1 servers are not supported on ACI release 6.1(4); however, upgrading to release 6.1(4) is not blocked. Upgrading APIC M1/L1 servers to ACI release 6.1(4) should only be done for the purpose of migrating to a supported APIC model.
Table 1. Supported APIC combinations on ACI release 6.1(4) and later.
|
|
APIC-M1/L1 |
APIC-M2/L2 |
APIC-M3/L3 |
APIC-M4/L4 |
APIC-G5 |
| APIC-M1/L1 |
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
Only when migrating to APIC-G5
|
| APIC-M2/L2 |
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
| APIC-M3/L3 |
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
| APIC-M4/L4 |
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
| APIC-G5 |
Only when migrating to APIC-G5
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
When a cluster has a mix of hardware models, its performance aligns to the lowest common denominator. For example, a Cisco APIC-M2 cluster scales up to 1000 edge ports while an APIC-M3 cluster increases that number to 1200[2]. There is no medium version for the APIC-G5 server. Mixing any medium APIC model in a cluster with APIC-G5 severs will align the cluster scale to the medium server scale.
Guidelines and Limitations for Migrating Cisco APIC Servers
The Cisco APIC L1/M1 server is no longer supported. However, you can still use the procedures in this document to migrate Cisco APIC L1/M1 servers to a newer server model.
When you decommission a Cisco APIC, the APIC loses all fault, event, and audit log history that was stored in it. If you replace all Cisco APICs, you lose all log history. Before you migrate a Cisco APIC, we recommend that you manually backup the log history.
Do not decommission more than one Cisco APIC at a time.
Wait until the cluster reaches the fully fit state before proceeding with a new replacement.
Do not leave a decommissioned Cisco APIC powered on.
Replacing the In-service Cisco APIC Servers
This section describes how to replace a Cisco APIC cluster on every existing M1/L1, M2/L2, M3/L3, or M4/L4 server with an APIC-G5 server model in service with no impact to the data plane nor the control plane. The procedure is fully supported by Cisco. This procedure focuses on a 3-node Cisco APIC cluster and the process is similar for larger clusters.
Procedure
Step 1. Validate that the existing cluster is fully-fit.
Ensure your existing cluster is fully fit before attempting this procedure. You must not upgrade or modify a Cisco APIC cluster that is not fully fit. To verify that your existing cluster is fully fit:
a. In the menu bar, choose System > Controllers.
b. In the Navigation pane, expand Controllers and choose any Cisco APIC.
c. Expand the Cisco APIC and choose Cluster as seen by node.
Figure 1
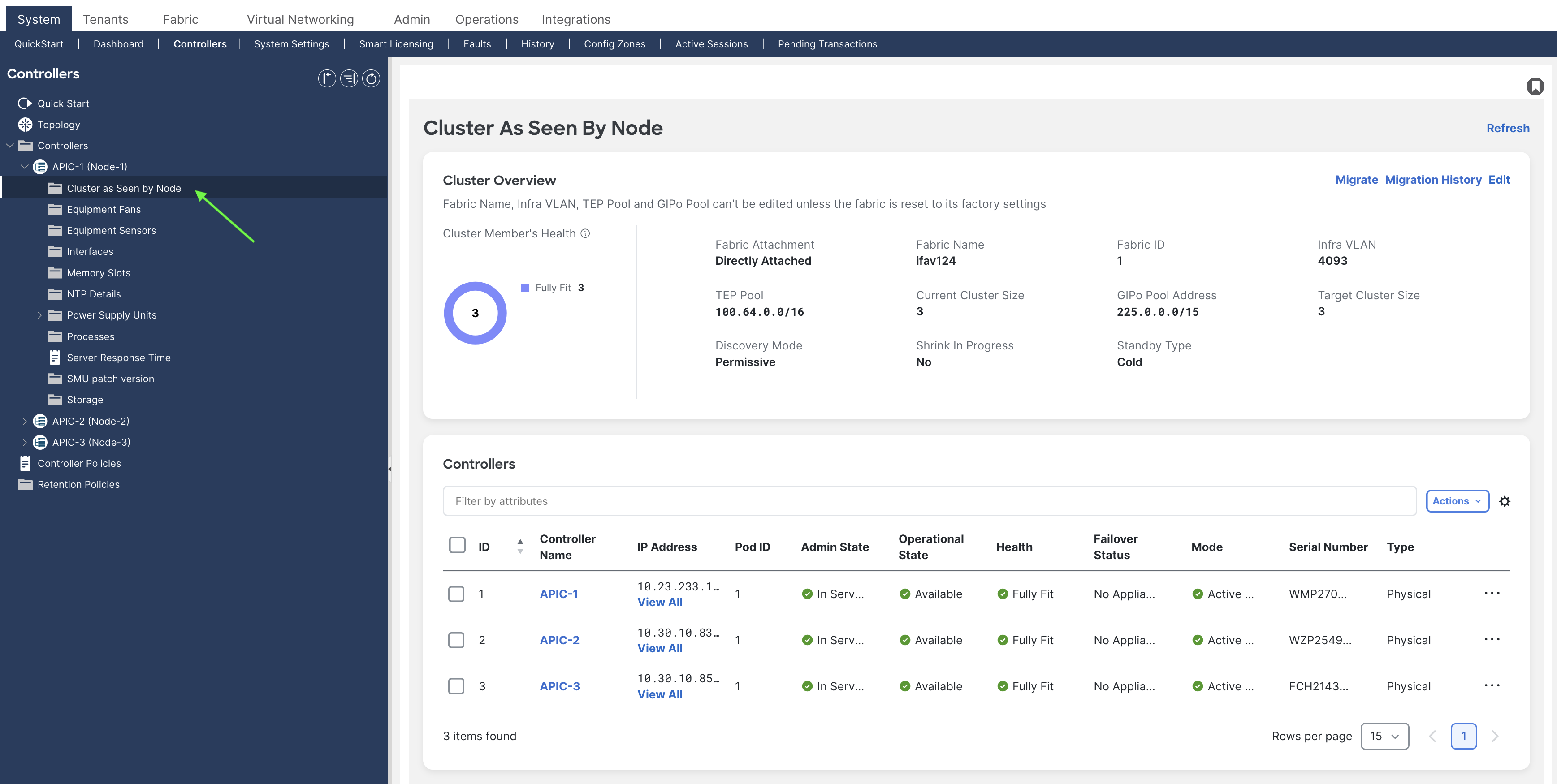
d. Check the operational state of all nodes. The nodes must be "Available" and the health state must be "Fully Fit."
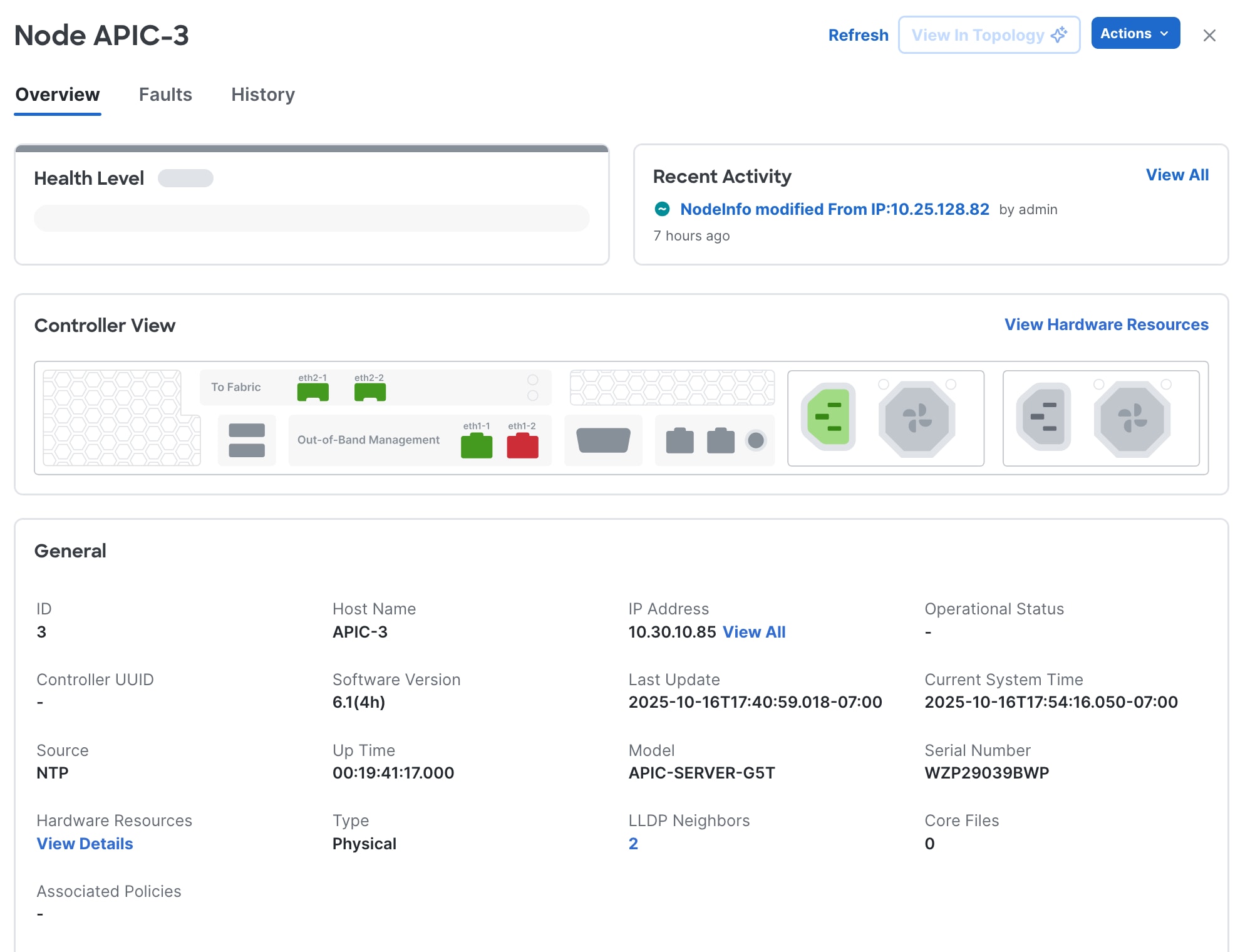
e. You can check the APIC hardware model by selecting the APIC and navigating to General > Hardware as shown in figure 2. In this example, we will be migrating an APIC-M3 server to the APIC-G5.
Figure 2
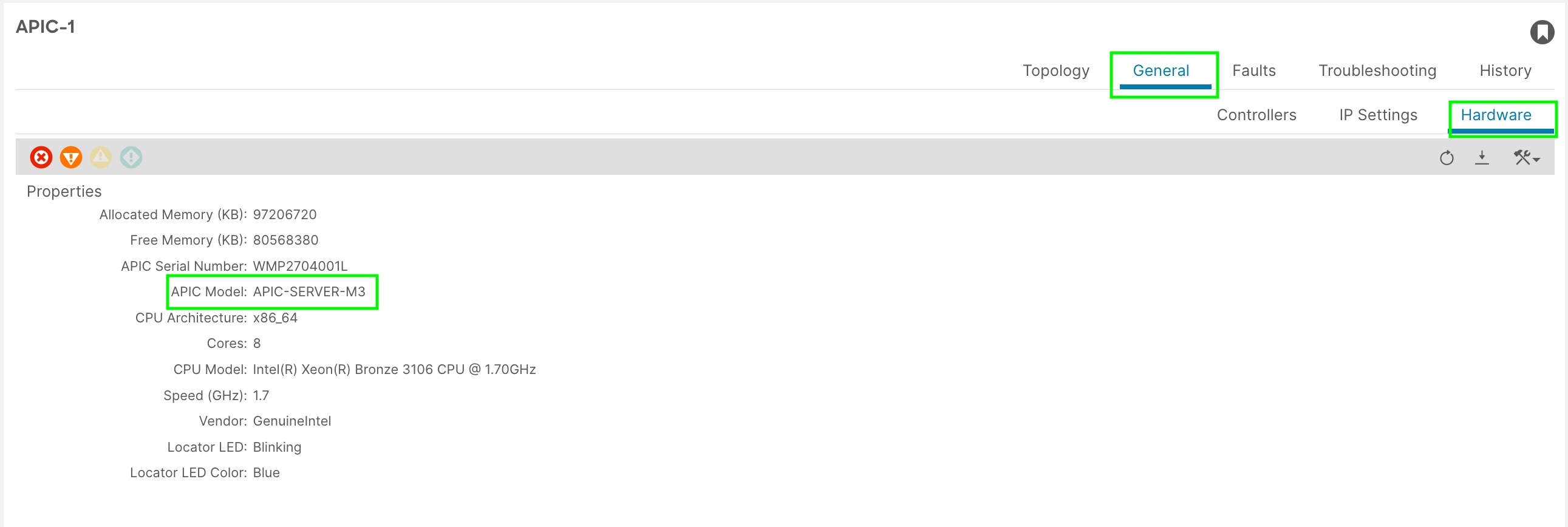
Step 2. Cable the replacement Cisco APIC-G5 servers.
In this scenario, you are replacing all three Cisco APIC servers with Cisco APIC-G5 servers. The process is the same as when replacing four, five, six, or seven servers. Physically install the replacement servers in the data center and cable them to the existing Cisco ACI fabric as you would with any server. Cable the Out-of-band (OOB) management connection. There is no need to set aside new IP addresses for the replacement Cisco APIC servers, because each Cisco APIC will simply take over the IP address of the server it is replacing.
Alternatively, you can replace existing APICs one at time. Rack and connect an APIC-G5 server in the same physical location as the one it is replacing using the same switch connections.
Step 3. Power up the Cisco APIC-G5 server that will replace an existing Cisco APIC server.
Bring up a Serial over LAN (SoL), vKVM console connection, or physical VGA connection so you can monitor their boot process. After a few minutes, you will be prompted to press any key to continue. You do not need to perform any configuration from the console. This step is just to verify that the APIC server is ready to be commissioned as a new APIC.
Figure 3
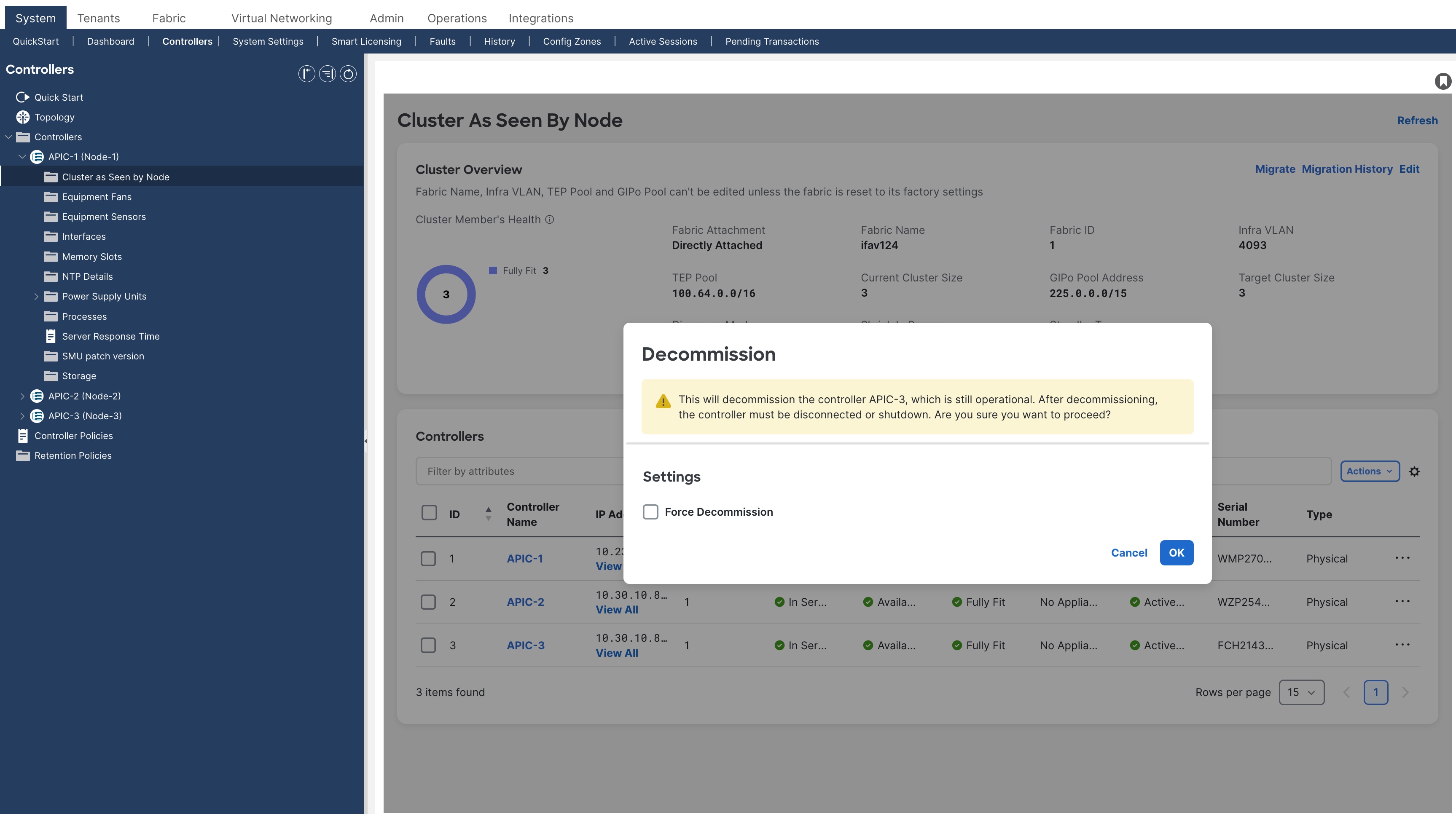
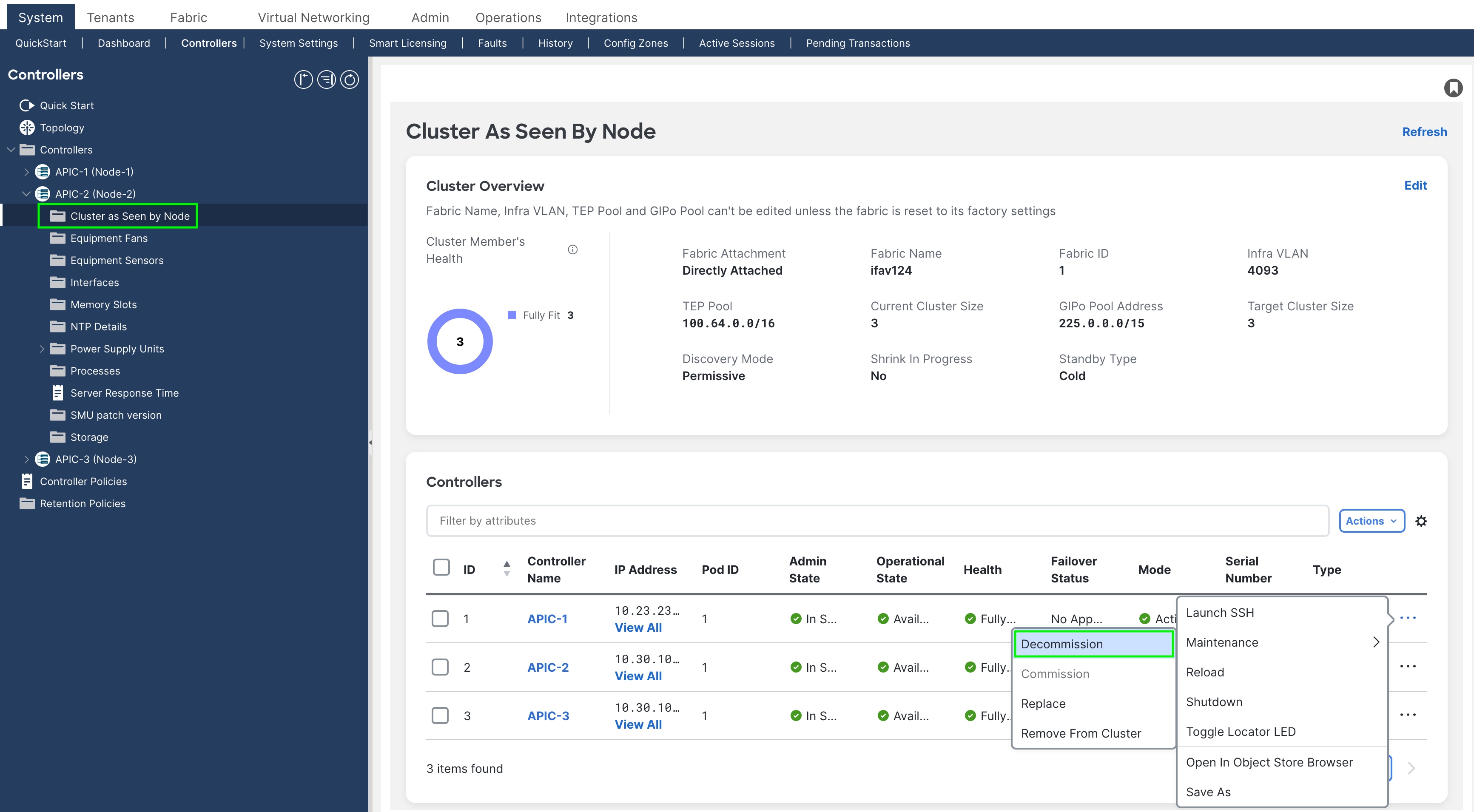
Step 4. Decommission Cisco APIC 3 (or the highest number APIC in the cluster).
From Cisco APIC number 1 or 2, within the "cluster as seen by node" view (Figure 4), decommission the last Cisco APIC by right-clicking on that Cisco APIC and choosing MaintenanceàDecommission.
Figure 4
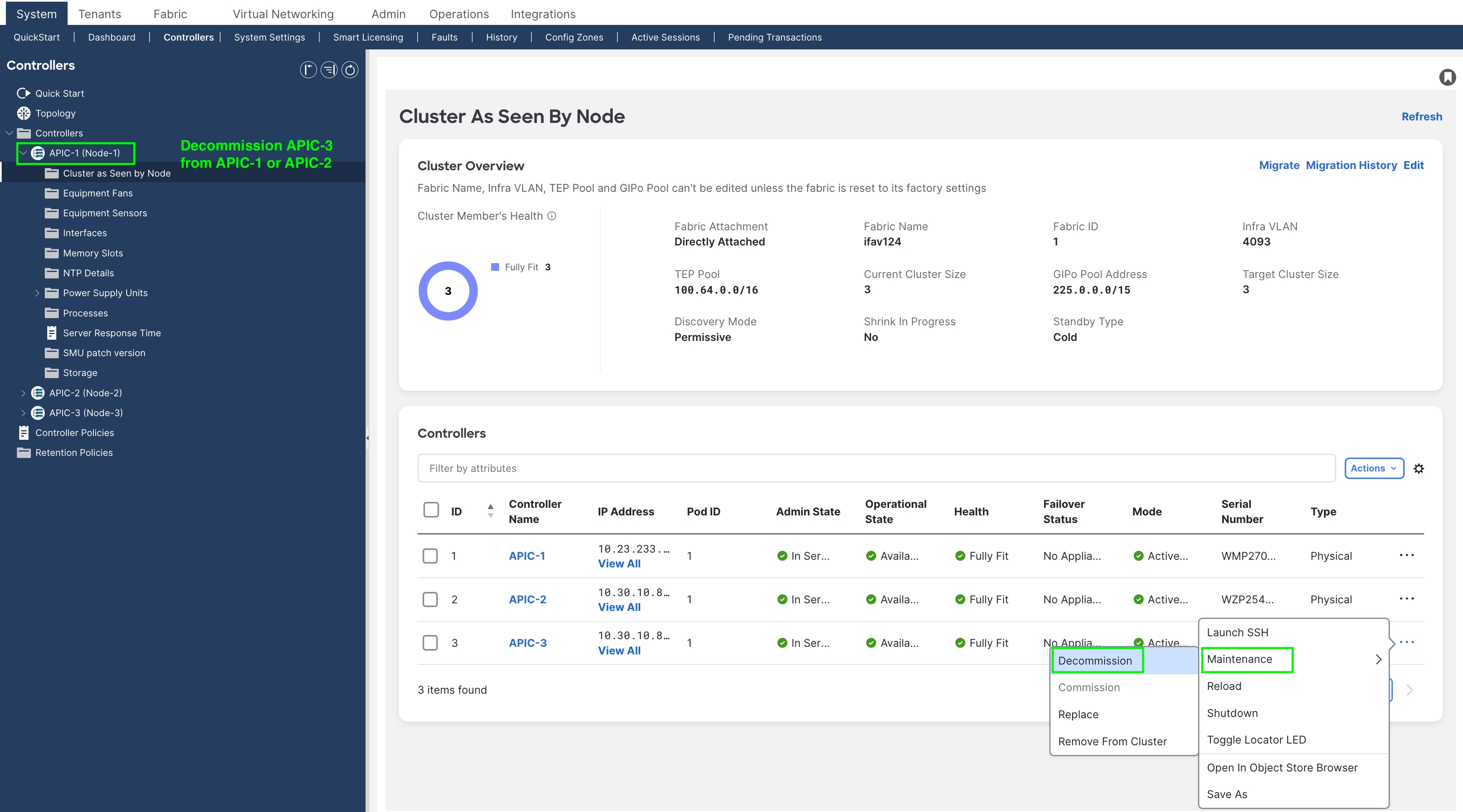
After choosing Decommission, you are prompted to confirm the selection. A message displays instructing you to disconnect or power down the APIC after decommissioning it.
Figure 5
After decommissioning the APIC, the GUI shows the APIC as "Out of Service" and "Unregistered."
Figure 6
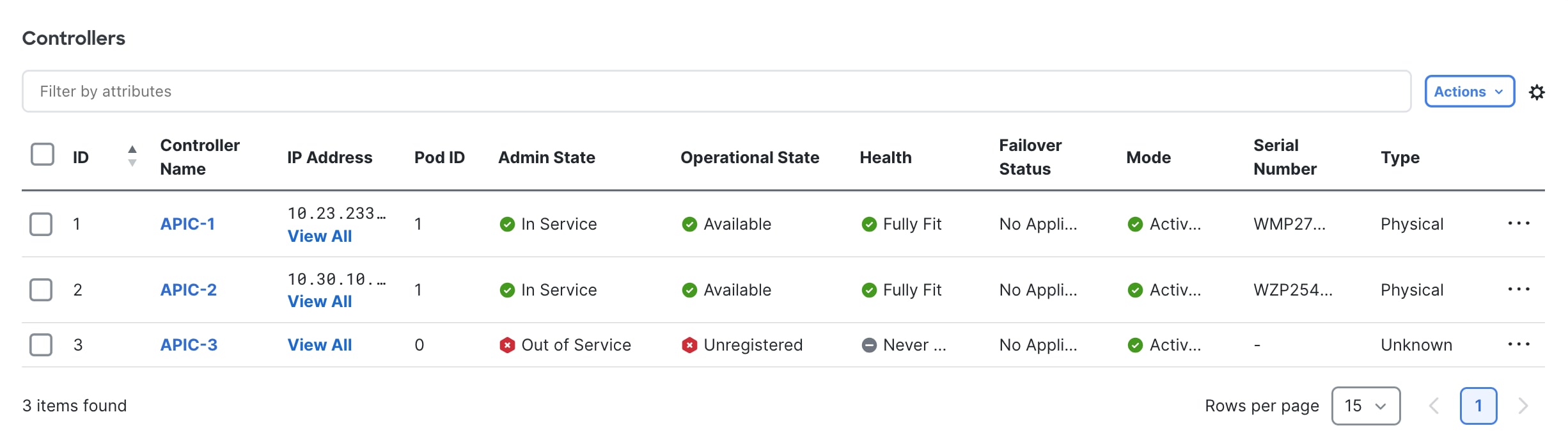
Wait roughly 5 minutes, then log into that Cisco APIC's CIMC to initiate a power off sequence or use the server power off button to power off the server after having decommissioned the Cisco APIC server.
You can power off the Cisco APIC from the CIMC GUI or CLI.
Step 5. Register the new Cisco APIC for the cluster membership.
Cisco APIC release 6.0(3) and later allows you to replace a Cisco APIC server directly from the GUI, if the APIC has access to the replacement APIC server's CIMC or out-of-band management IP address. If the APIC-G5 servers have CIMC connections, it is not necessary to perform any configuration on the APIC server console. Commissioning of the APIC will be done via the CIMC. If CIMC connections are not used, you will be required to configure an out-of-band management IP on the replacement APICs.
The following steps are for APICs with CIMC connections.
The commission step bootstraps the replacement APIC-G5 with the following settings:
· CIMC Address
· CIMC username
· CIMC password
· APIC Name (this will be pre-populated when doing commission)
· Admin Password: (cluster password)
· Controller ID: (this will be pre-populated when doing commission)
· Pod-ID
· Serial Number: (will be discovered automatically when APIC connects to CIMC)
· Out-of-Band Address
· Out-of-Band gateway
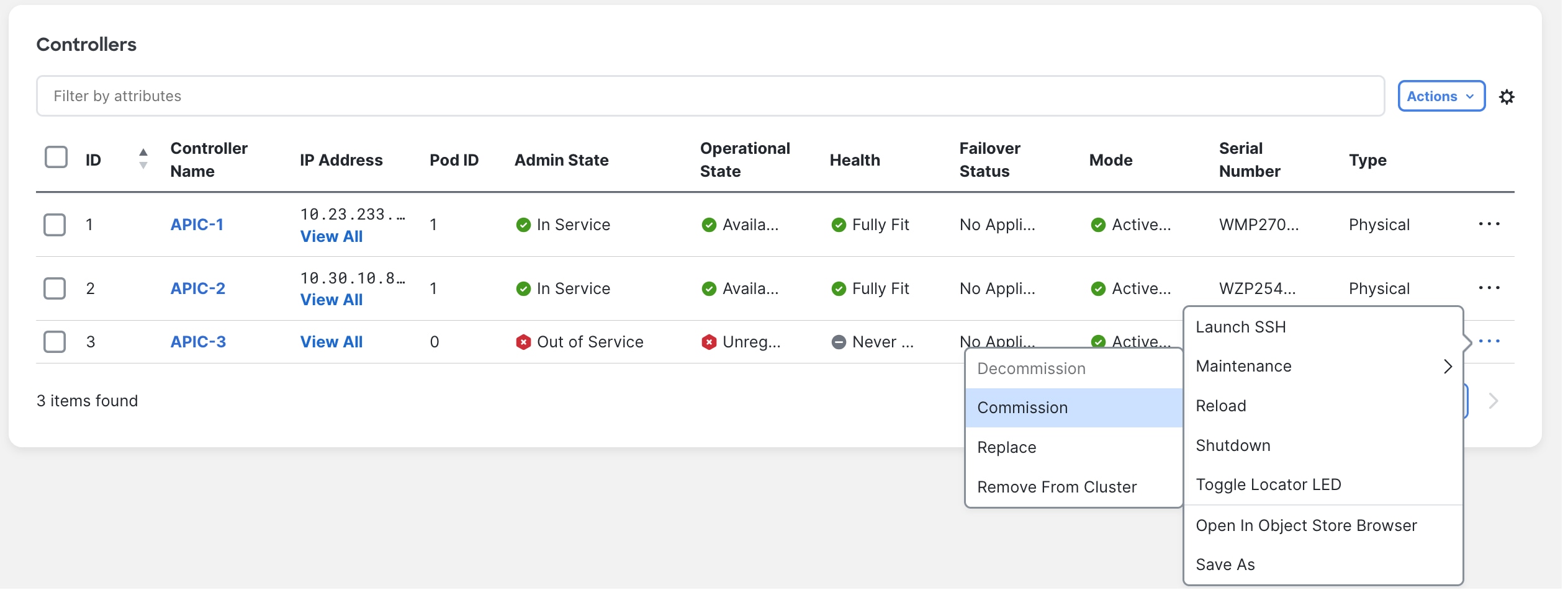
On the APIC server that was decommissioned, Right-click on the server and select commission.
Figure 7
Step 6. Enter the APIC-G5 CIMC address and login credentials and click Validate:
Figure 8
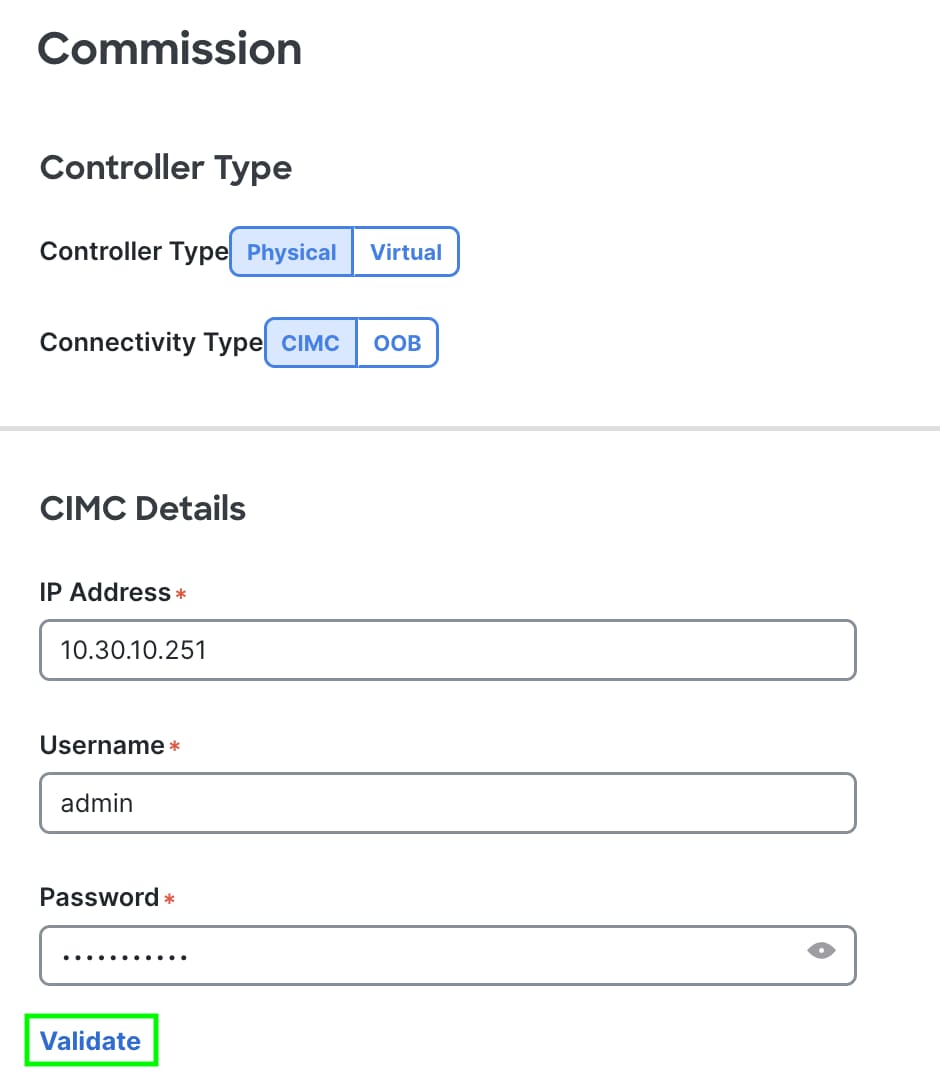
Figure 9
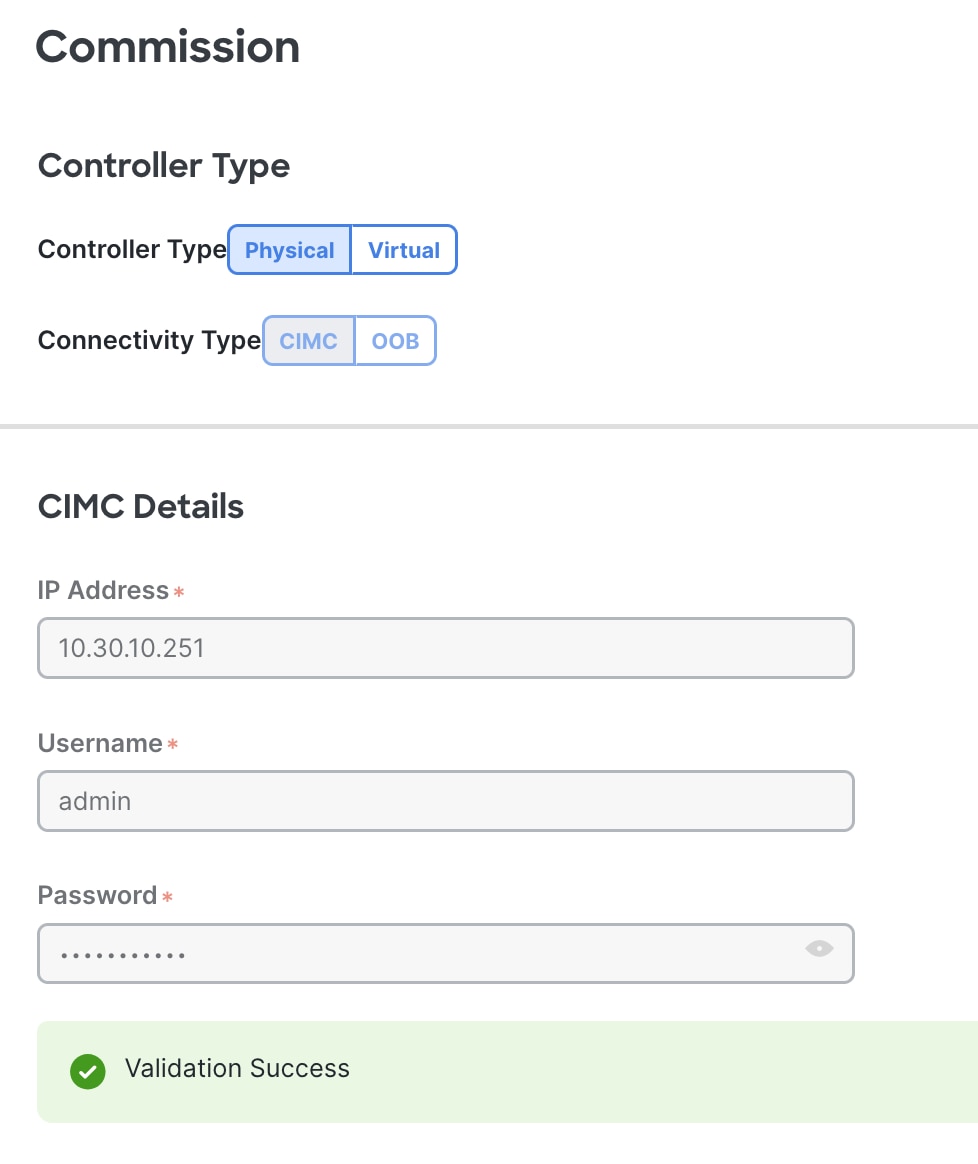
Enter the cluster password, pod-id where the APIC is located, and out-of-band management address. The out-of-band management address should be the same as the decommissioned APIC.
Figure 10
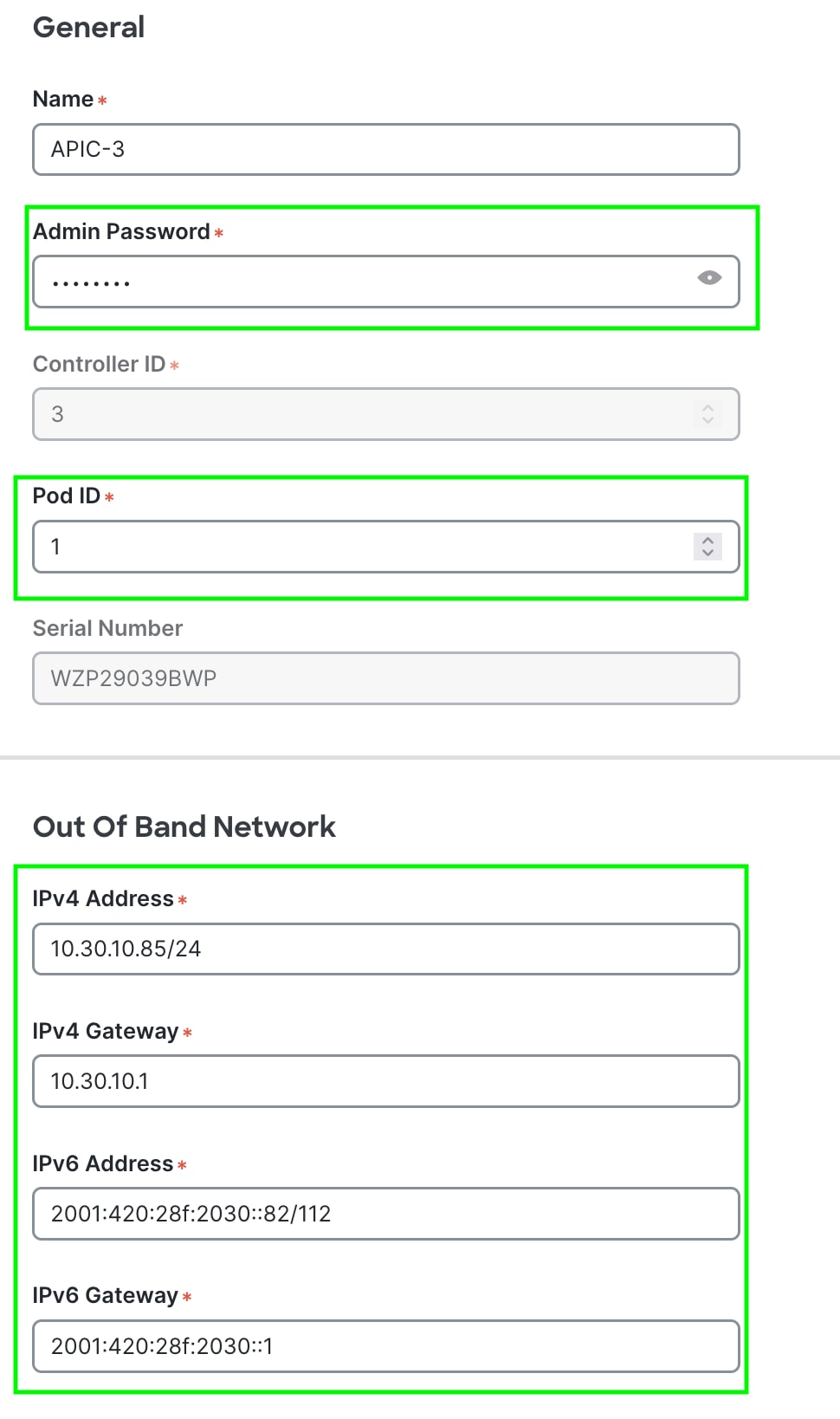
Step 7. Verify cluster membership.
After approximately 5 minutes, you will observe transitions in the operational state and health status. First, you may see the infra IP address configured on the new server. The new server serial number will be populated.
Figure 11
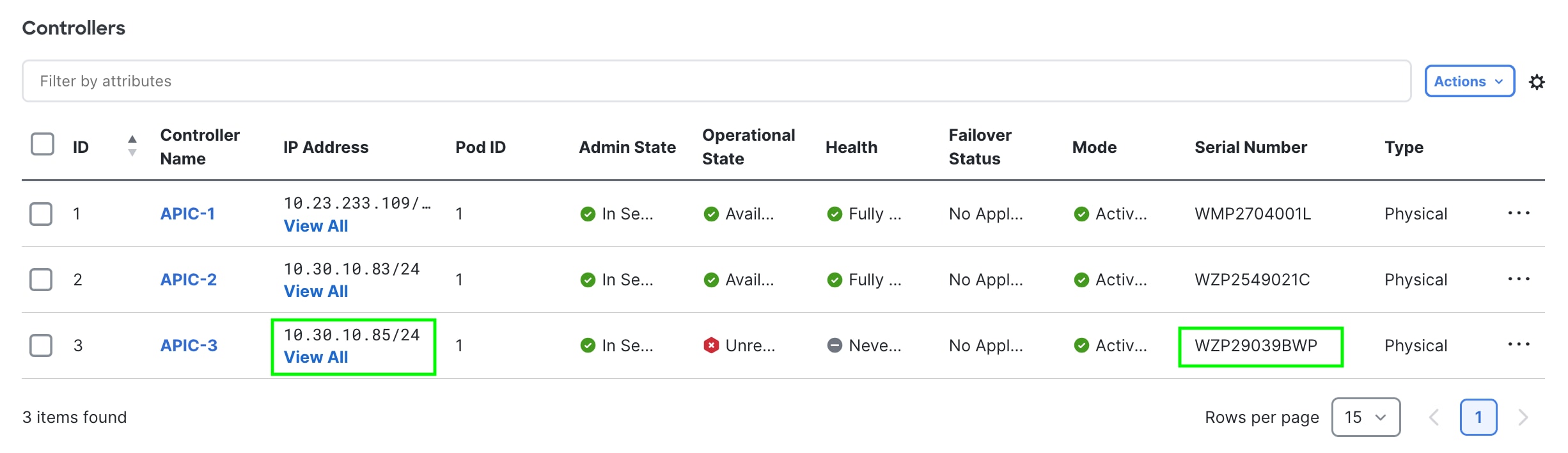
During commissioning of the APIC, the Health state may display “Diverged” and/or “Data Layer Partially Diverged”. Wait until the Health status show “Fully Fit” before decommissioning the next APIC.
Figure 12
If you check the new server's properties, you will show the APIC-G5 model with a new serial number:
Figure 13
Step 8. Decommission another server.
To decommission another server, repeat steps 4 through 7. Remember that to decommission a server, you need to perform the operation from another server. If you are logged into APIC-1 for example, do not decommission APIC-1. Log into APIC-2, go to the "Cluster As Seen By Node" view for APIC-2 and decommission APIC-1. This is shown below:
Figure 14
Do not forget to power off the server that you decommissioned before attempting to bring in a replacement.
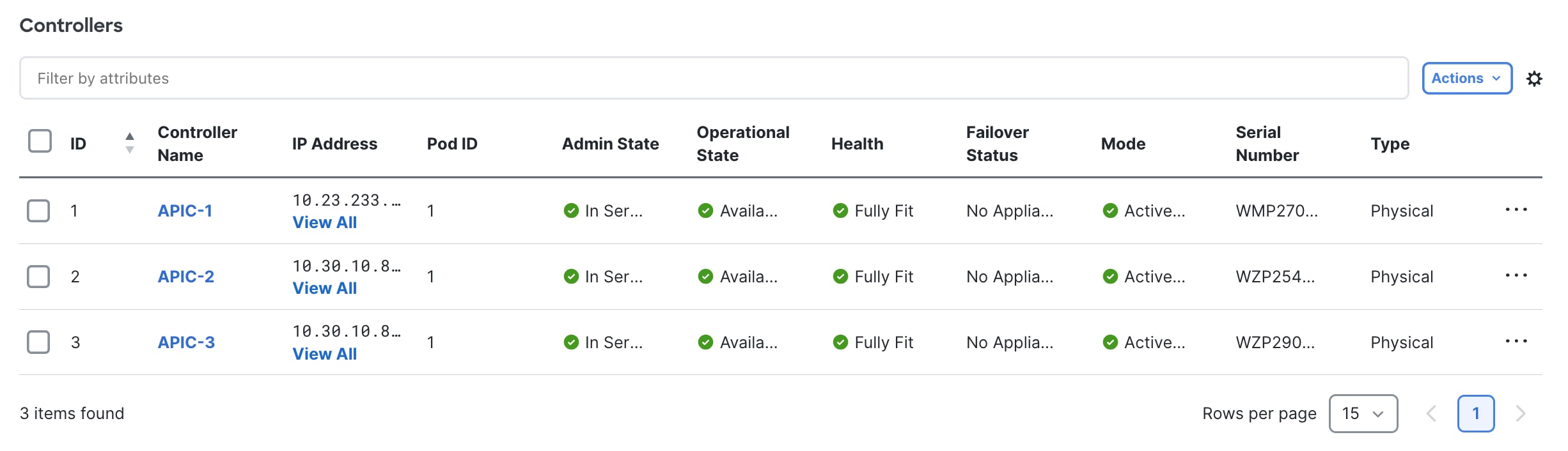
Step 9. Verify the entire cluster.
After replacing all APICs with APIC-G5s, validate that the entire cluster is fully fit:
Figure 15
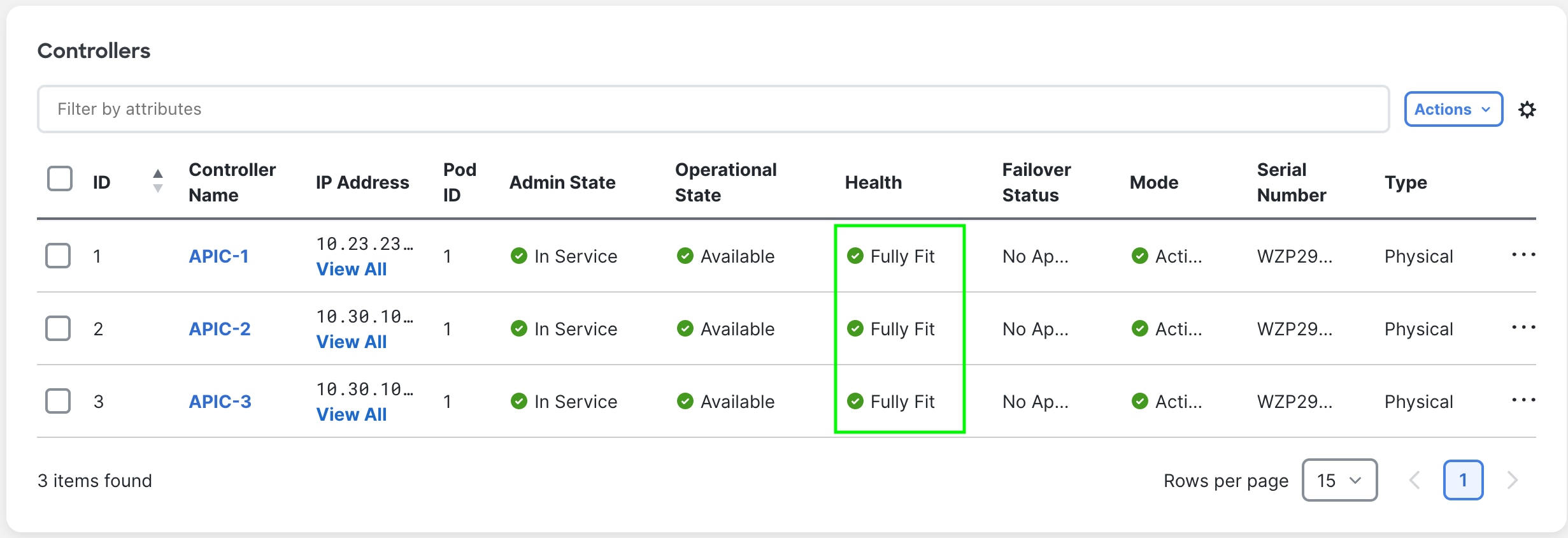
At this point, you have a fully operational, fully-fit Cisco APIC cluster with new hardware.
Replacing APIC Servers with APIC Servers Running a Different Software Release
Beginning with Cisco APIC release 6.0(2), APIC servers being commissioned to the cluster can be running a different software release than the cluster. The replacement procedure described in the previous section is the same when the replacement APIC server is running a different software release. You must download the APIC ISO image for the currently installed release to the APIC cluster prior to executing the migration procedure. In the example below in figure 16, the APIC is running release 6.1(4h)
Figure 16
When executing the APIC server migration with APICs running a different software release, it will take longer for the commission step to execute. This step can take more than 30 minutes to be executed. During this time, the APIC cluster state will not update, and the replacement server out-of-band management IP address will be unavailable.
Commissioning APIC Servers Without CIMC Connections
When the APIC servers are using CIMC connections, the APICs can be commissioned or added to the cluster from the CIMC address. This method does not require any configuration done on the APIC console and simplifies the APIC commissioning process. If APICs are not deployed with CIMC connections, it will be required to first configure the out-of-band management address for the APIC from the console. This can be done from the KVM SoL (serial over LAN) connection or directly on the server.
When configuring the out-of-band management address on the APIC it is only required to configure the APIC password and out-of-band management address and gateway. All other configurations will be done during the commission step.
Example of out-of-band management configuration from serial over LAN console connection.
CISCO Serial Over LAN:
Close Network Connection to Exit
Enter the password for admin [None]:
Reenter the password for admin [None]:
Out-of-band management configuration ...
Enter the IP Address [192.168.10.1/24]: 10.1.1.1/24
Enter the IP Address of default gateway [192.168.10.254]: 10.1.1.254
Would you like to edit the configuration? (y/n) [n]:
When commissioning the APIC select the OOB connectivity type.
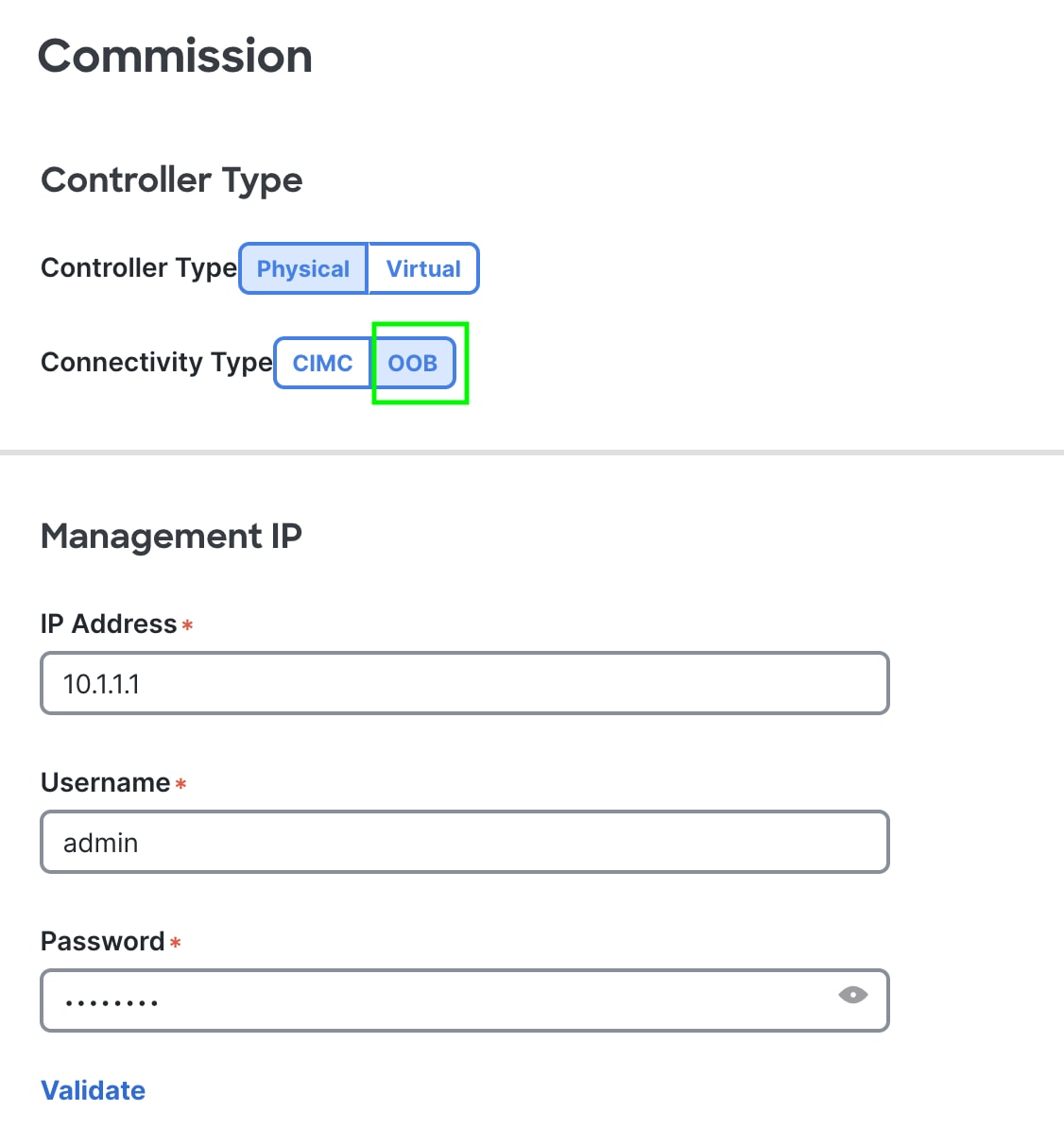
Decommissioning the Standby Cisco APIC Servers to be Replaced by a Normal Cluster
If your cluster contains standby Cisco APIC servers, the same process applies. When you bring your existing cluster to a supported release, the standby Cisco APIC servers are automatically upgraded.
Starting in ACI release 6.1(2), standby APICs can be setup as Warm Standby as opposed to Cold Standby APICs which was the only option prior to the 6.1(2) release. Warm Standby APICs will synchronize all data from the active APIC cluster. The Warm Standby APIC can be used to replace a single APIC node (same as Cold Standby) or recover the entire cluster if three or more active APICs fail. See the 6.1(2) and later APIC Getting Started guide for more details on Warm Standby APIC.
The procedure for replacing a standby APIC does not differ between Cold and Warm Standby APICs.
Procedure
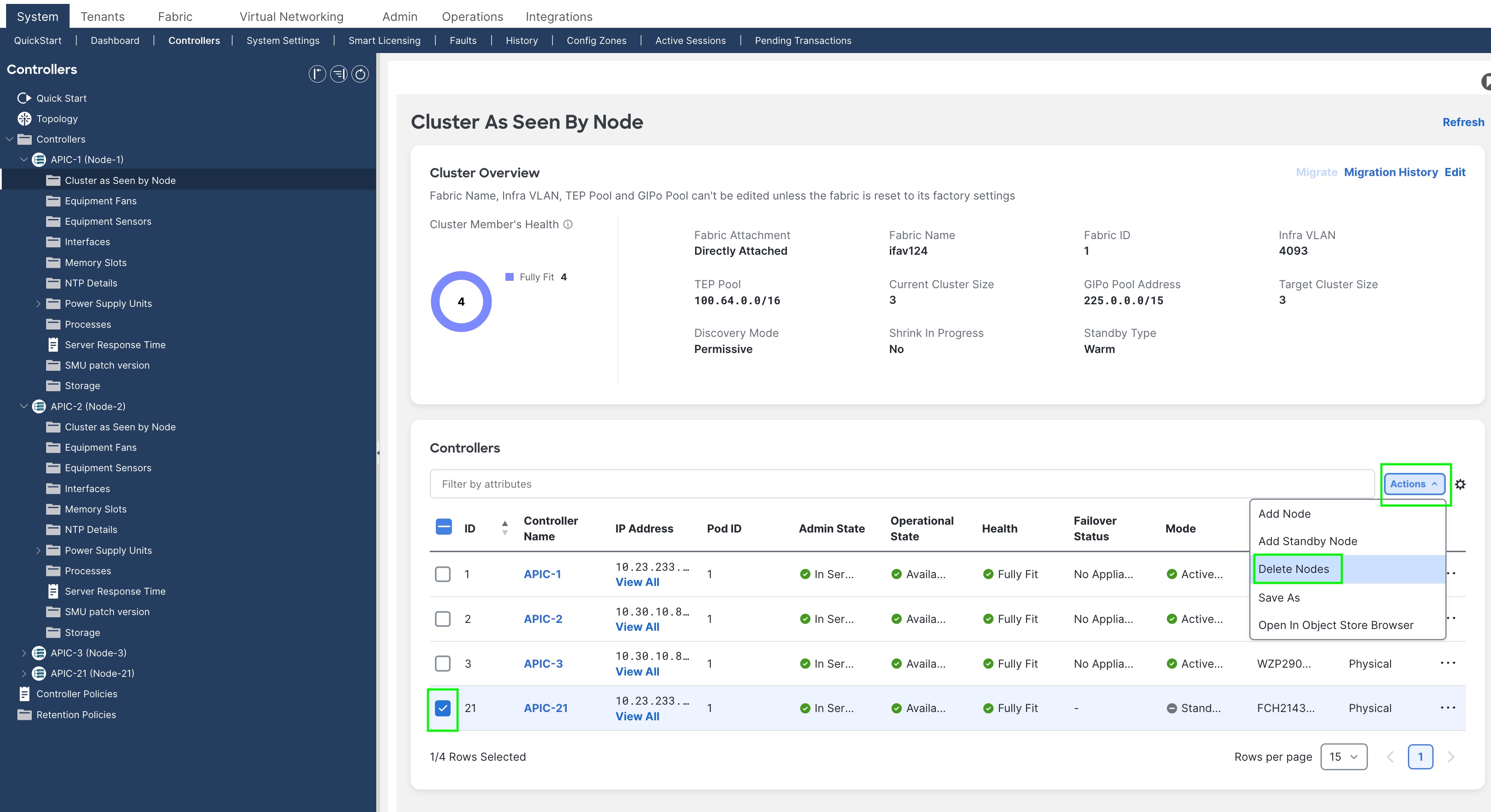
Step 1. From the GUI of any active APIC, delete the standby APIC node. Select the checkbox next to the Standby Node and select Delete Nodes under the Actions menu.
Figure 18
Step 2. Power down the standby controller
Step 3. 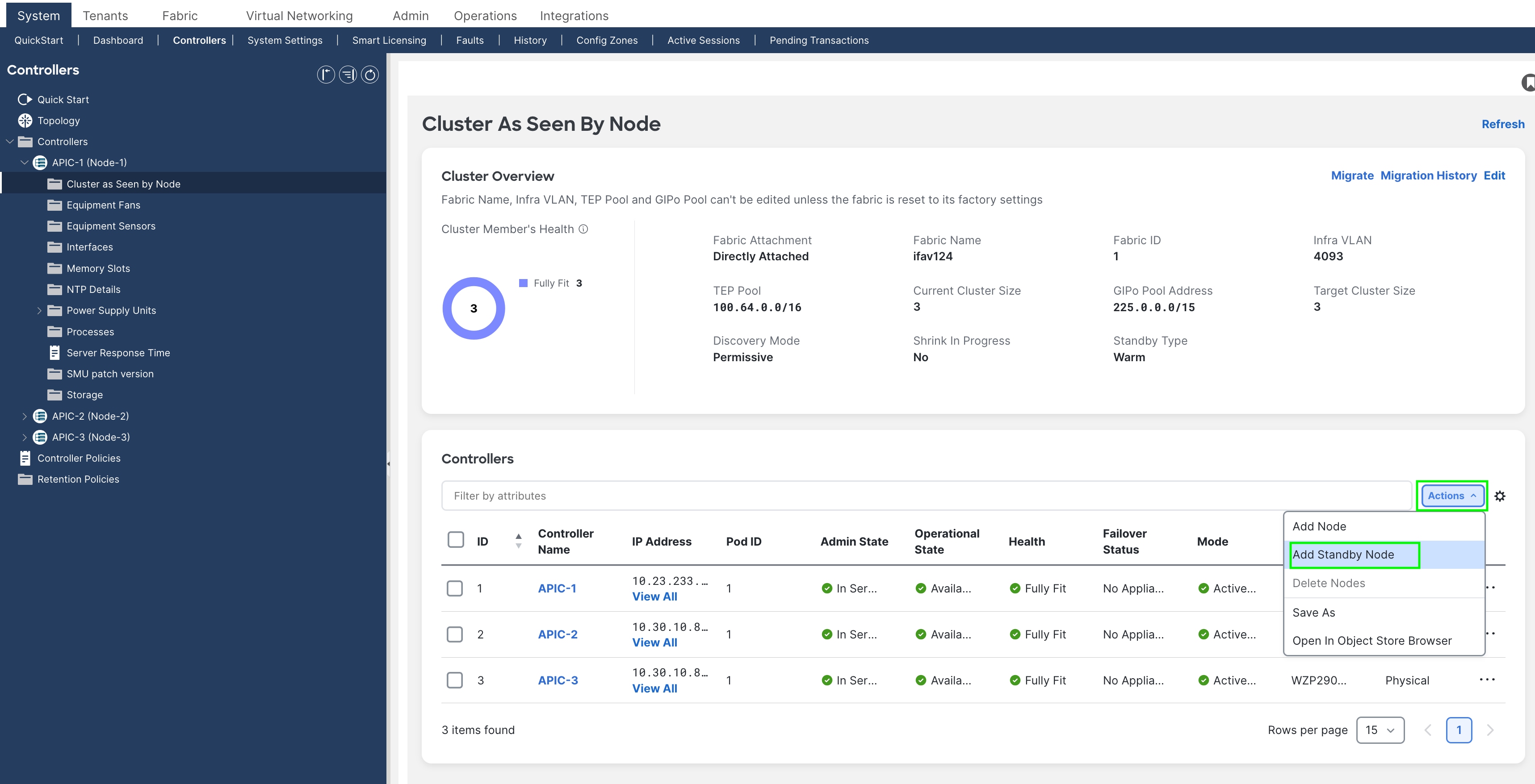
Add the new APIC-G Standby controller. The process is similar to adding active controllers. Select Add Standby Node from the Actions menu.
Figure 19
Step 4. Use the CIMC or OOB connectivity type.
Figure 20
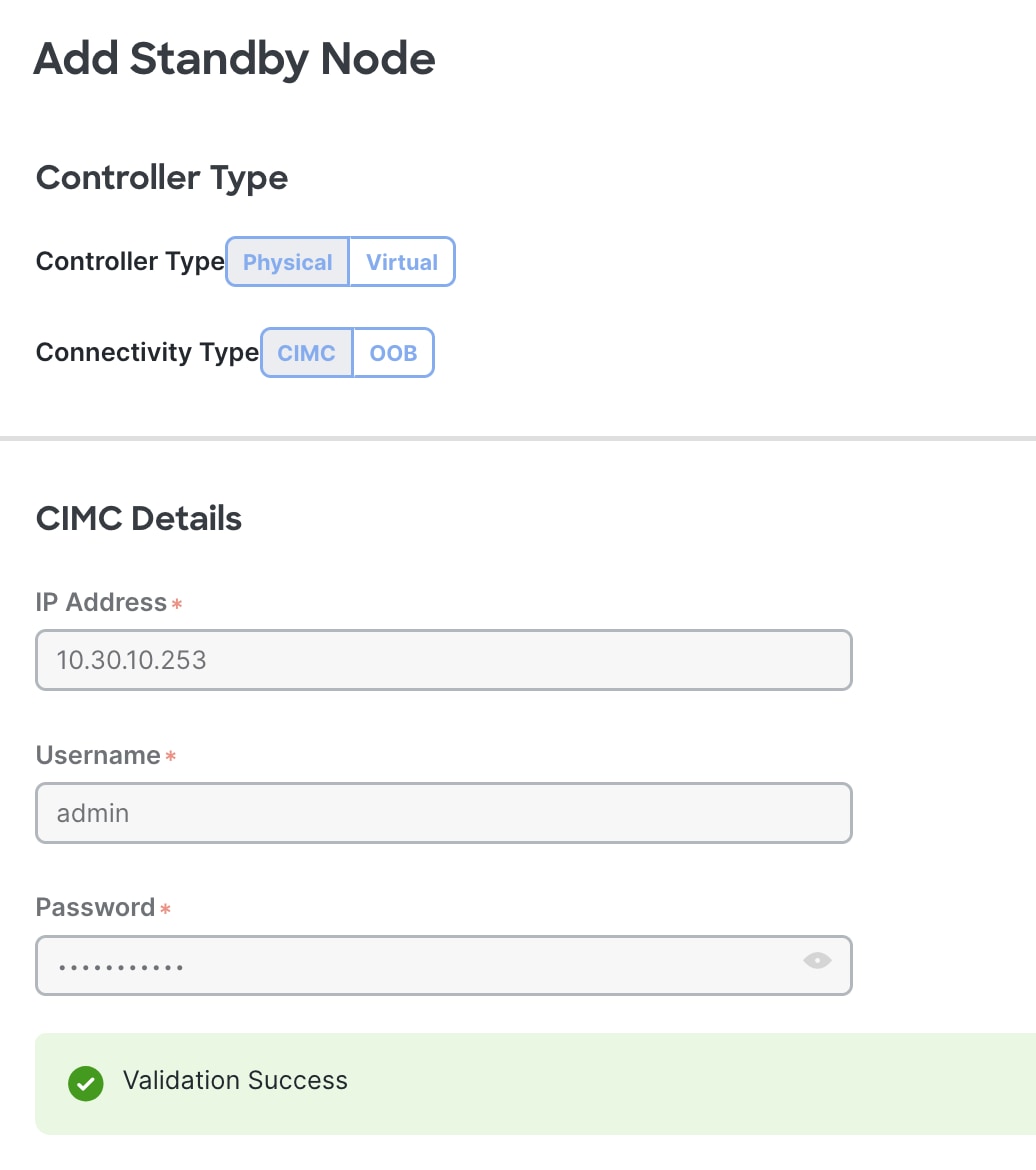
Step 5. Enter the APIC name, ID, pod, and management addresses for the Standby Node. When adding a Standby Node in the UI the node id must be between 21 and 29.
Figure 21
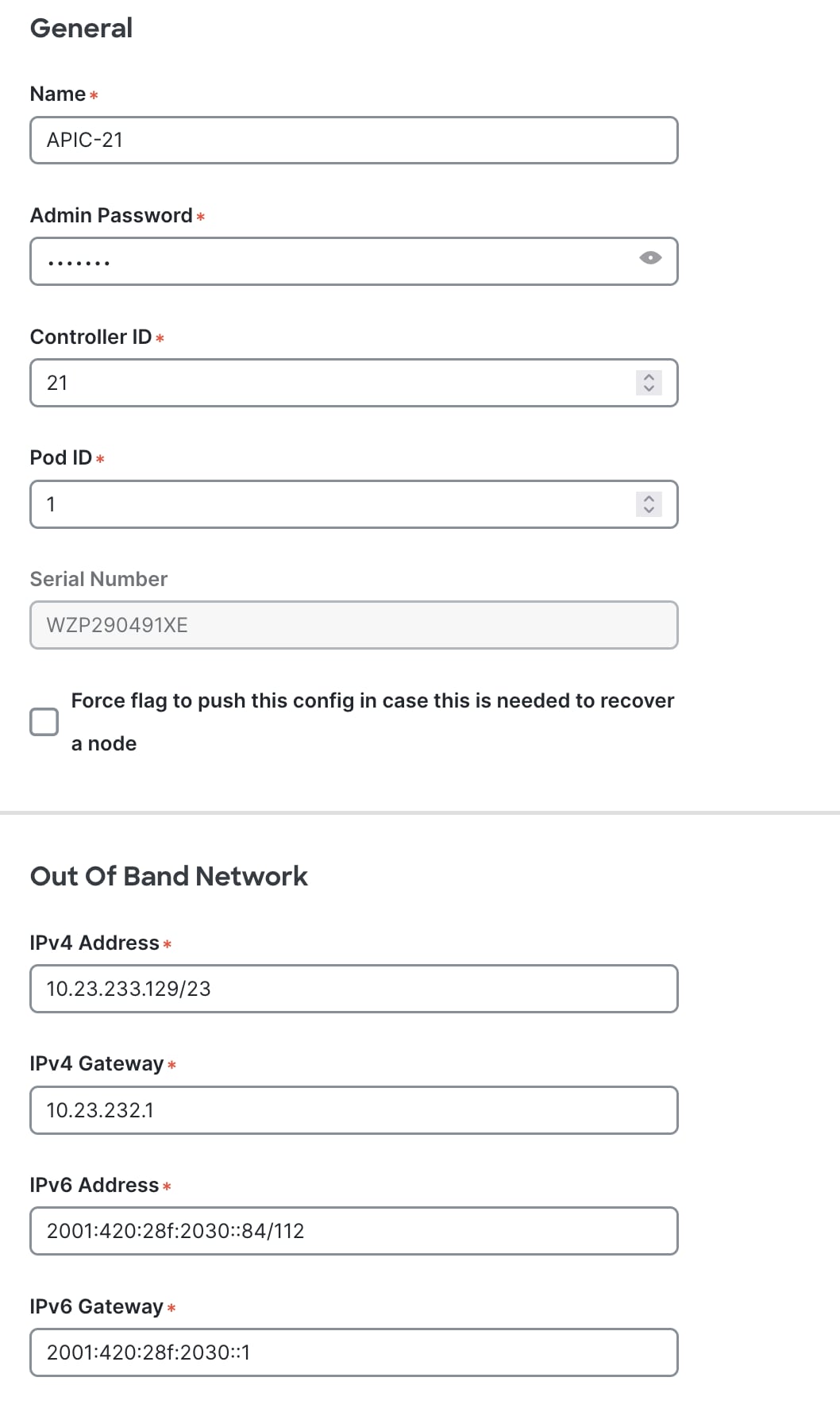
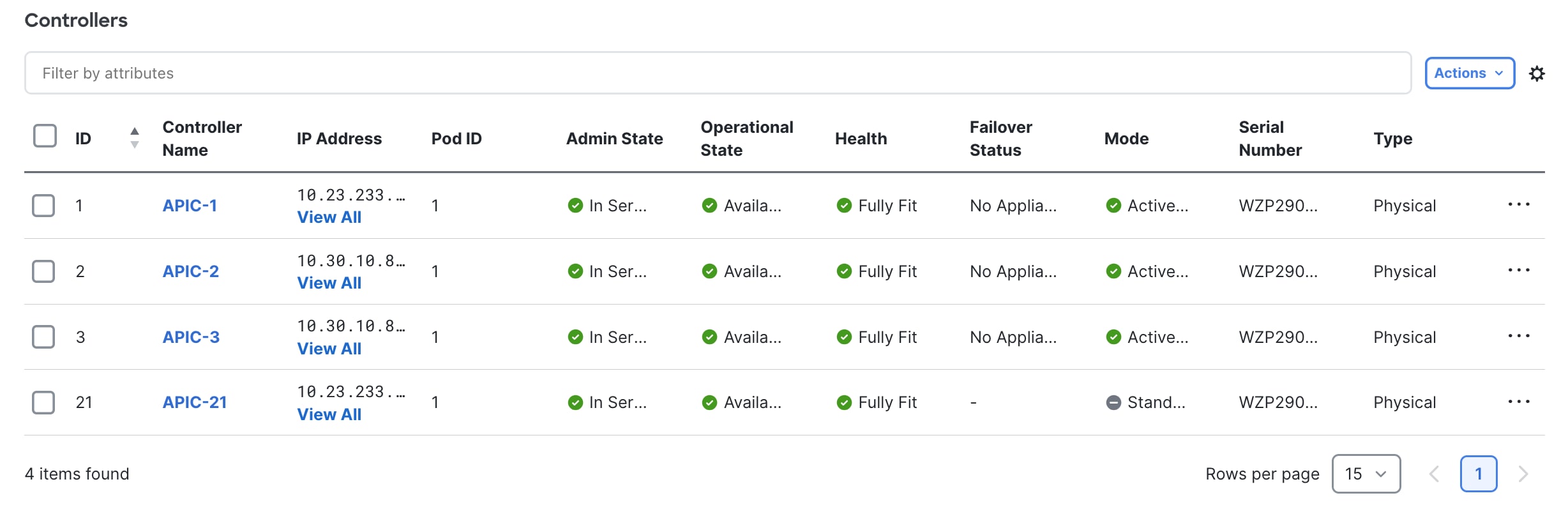
Step 6. Verify the Standby APIC successfully connects to cluster in Fully Fit Heath.
Figure 22
 Feedback
Feedback