Introduction to Crosswork Data Gateway
Crosswork Data Gateway, also referred to as Data Gateway, is a secure, common collection platform for gathering network data from multivendor devices that:
-
operates as an on-premises application deployed close to network devices,
-
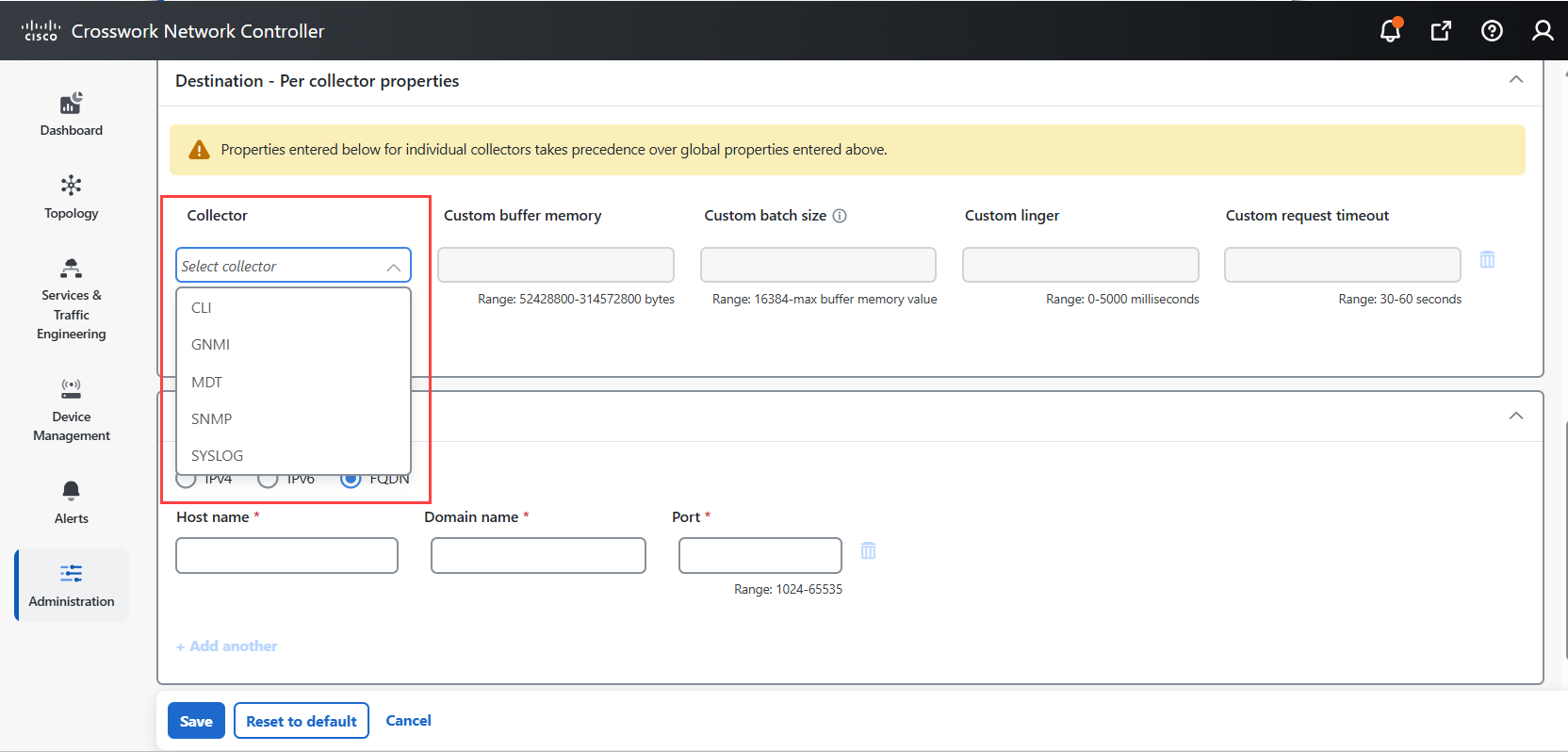
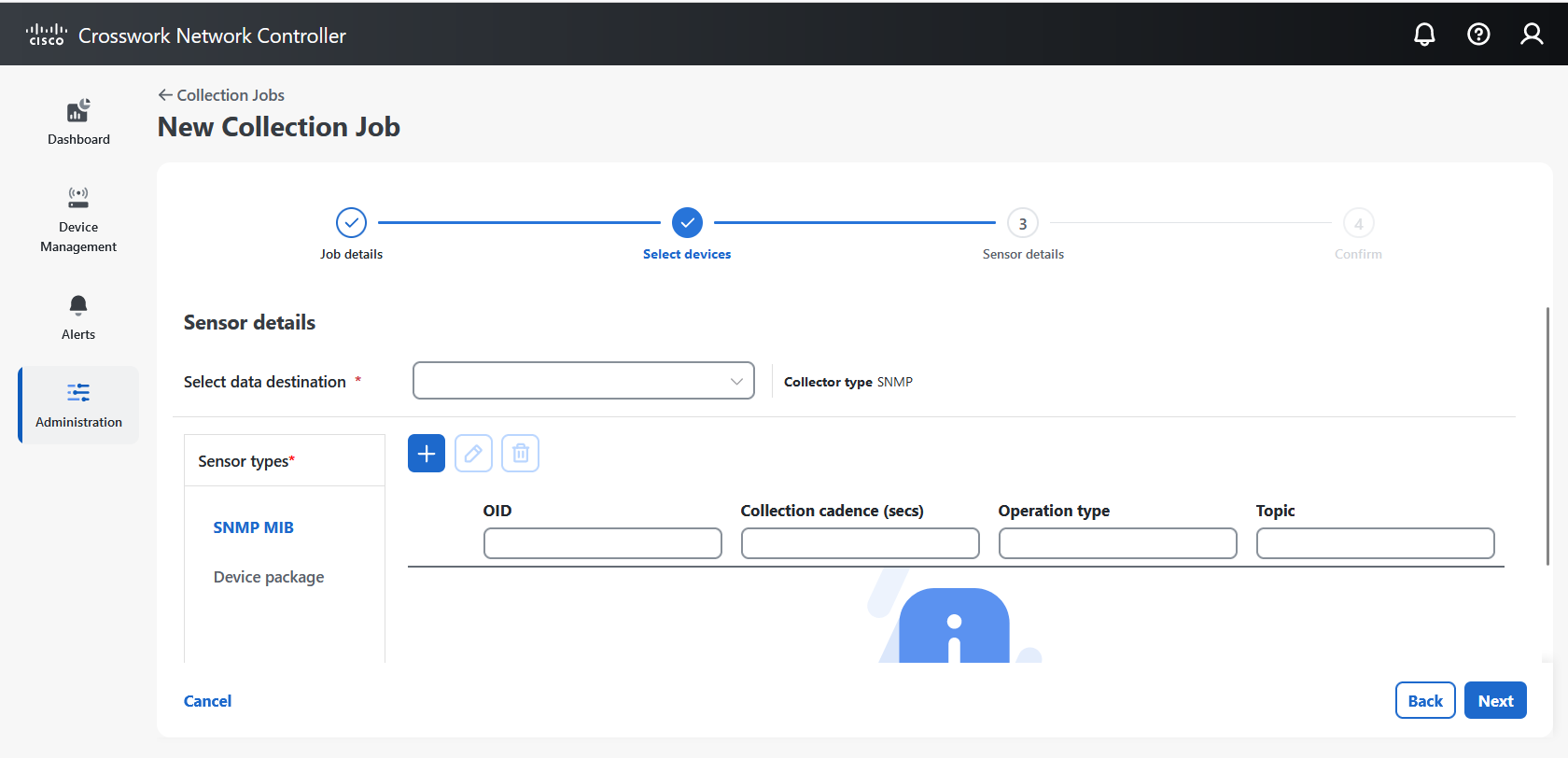
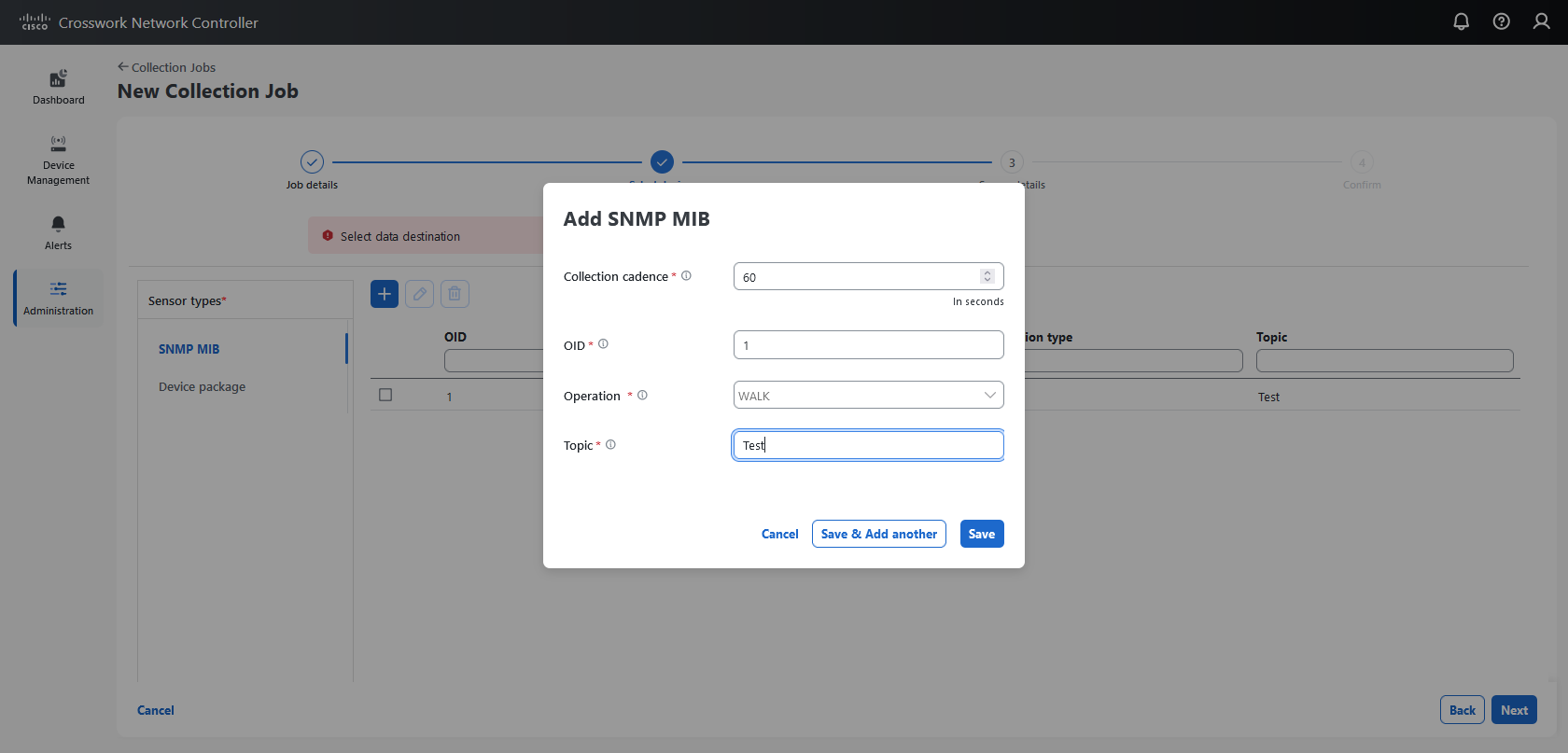
supports multiple data collection protocols such as MDT, SNMP, CLI, gNMI, and Syslog, and
-
enables consistent data collection across heterogeneous device environments.
 Note |
The terms Crosswork Data Gateway and Data Gateway are used interchangeably in this documentation and refer to the same component. This naming is consistent with the terminology in the product user interface. |
Core components of Data Gateway
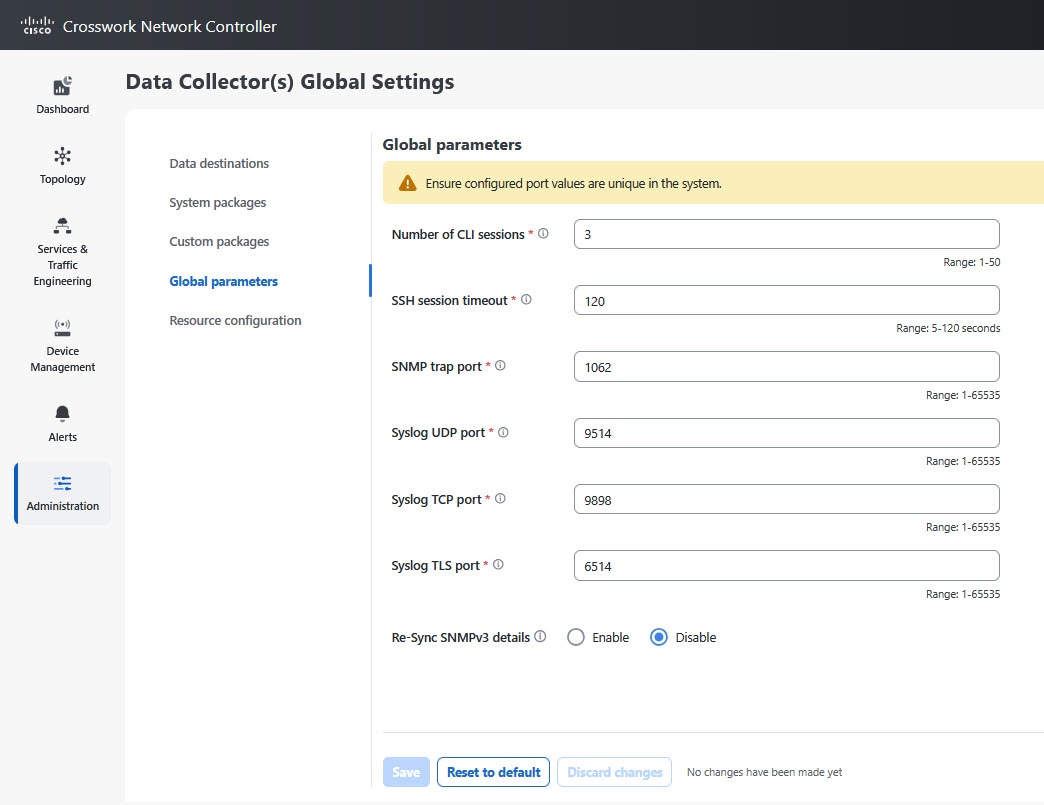
Data Gateway uses these concepts:
-
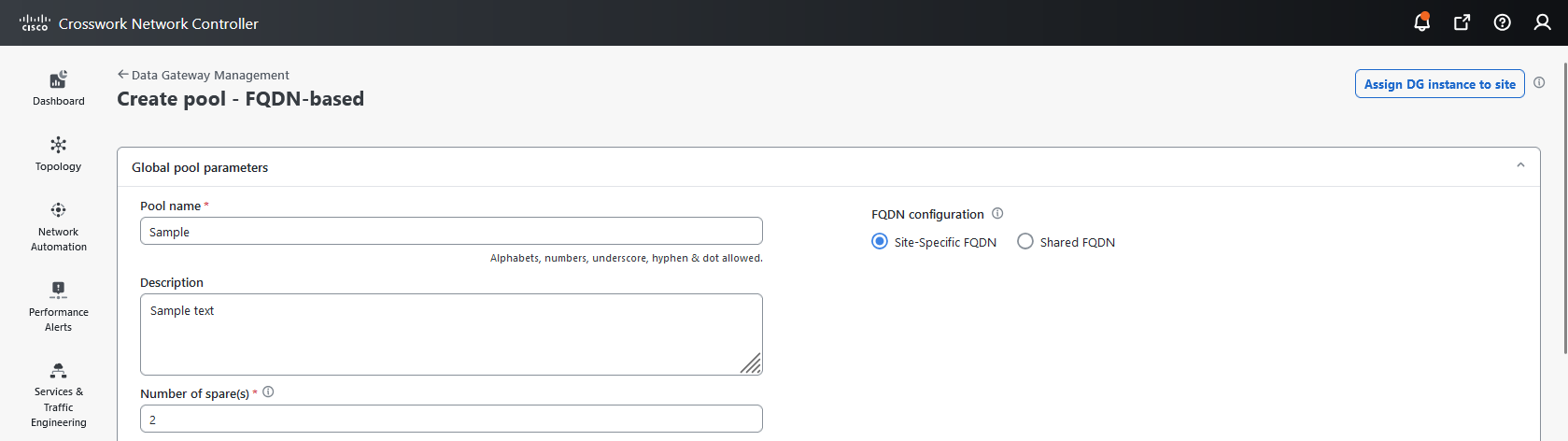
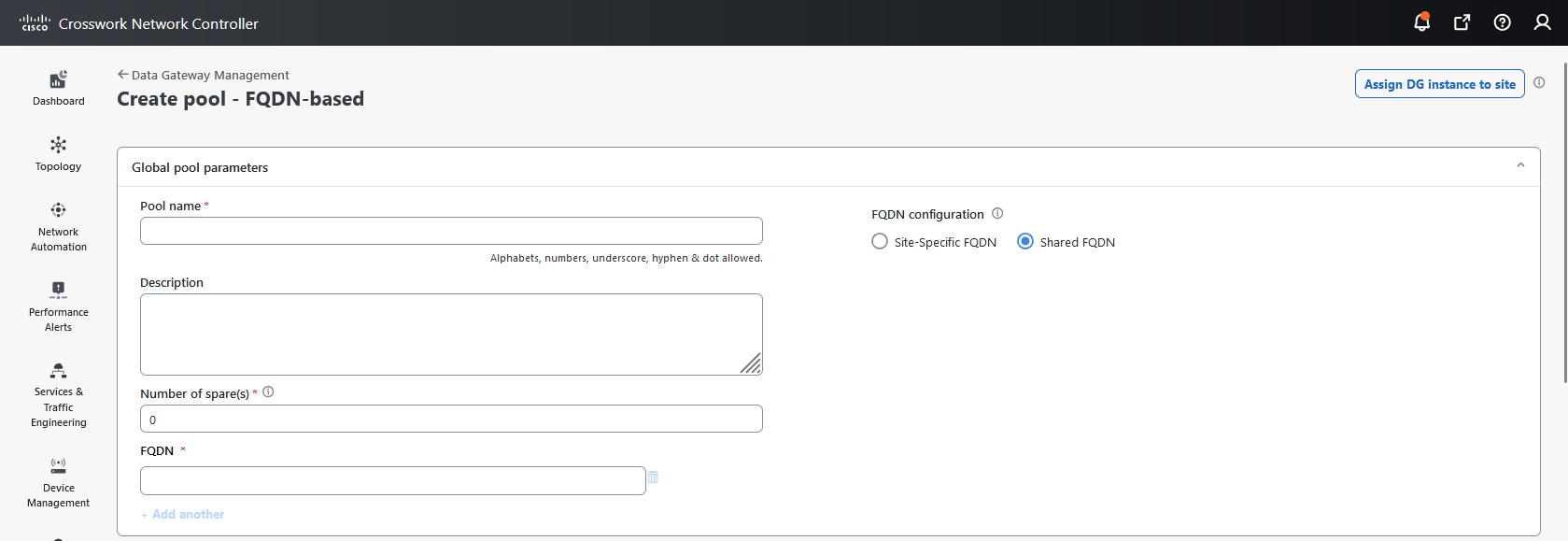
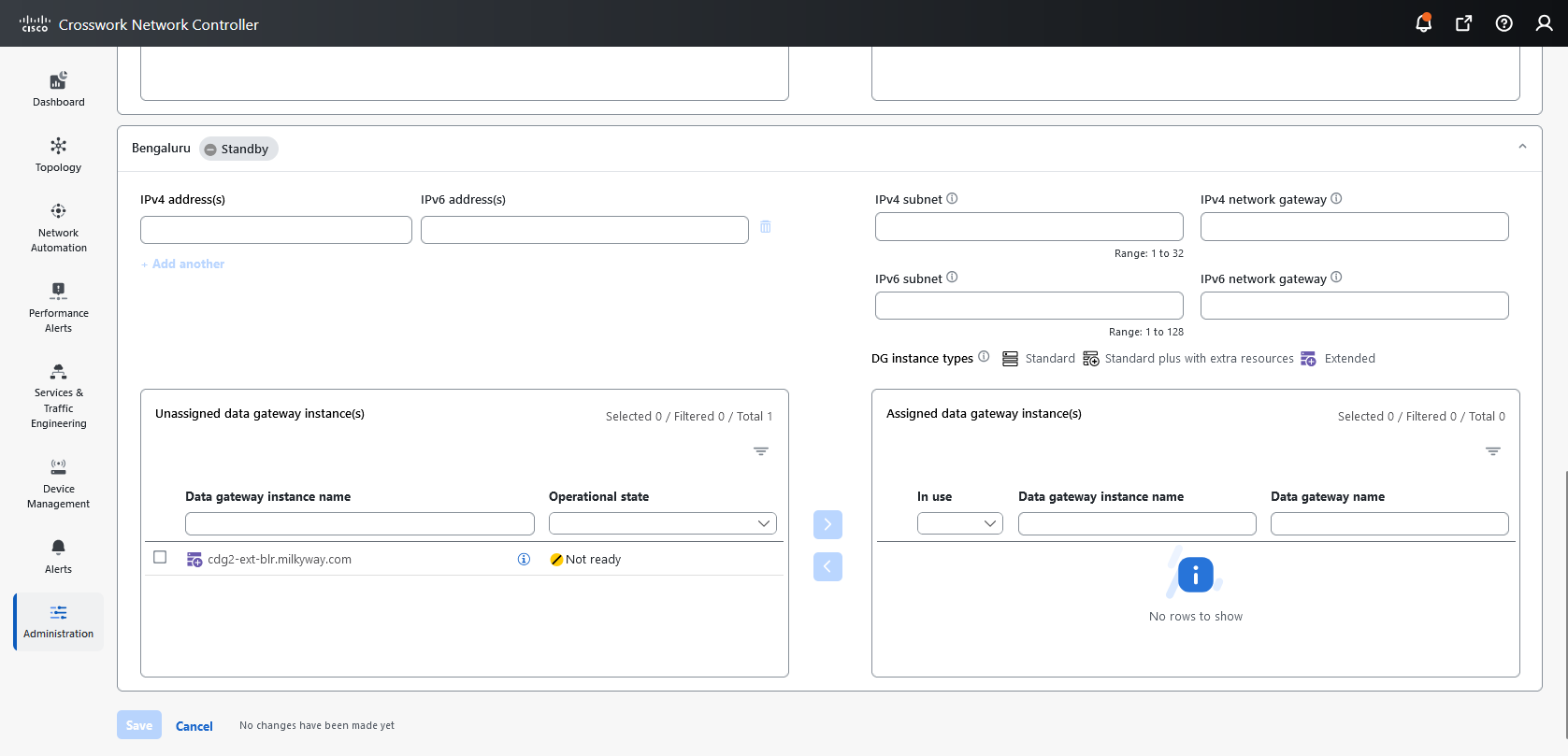
Crosswork Data Gateway: Refers to a Data Gateway instance that you install. It can either be associated with the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of a Network Load Balancer (NLB) or assigned a virtual IP address when added to a pool.
- Profile: Data gateway supports the following deployment profiles:
-
Standard: for use with all Crosswork applications, except Crosswork Health Insights, and Crosswork Service Health (Automated Assurance).
-
Extended: for use with Crosswork Health Insights and Crosswork Service Health (Automated Assurance).

Attention
The Standard with Extra Resources profile is available as a limited-availability feature and must not be used while deploying a Data Gateway in your data center.
-
-
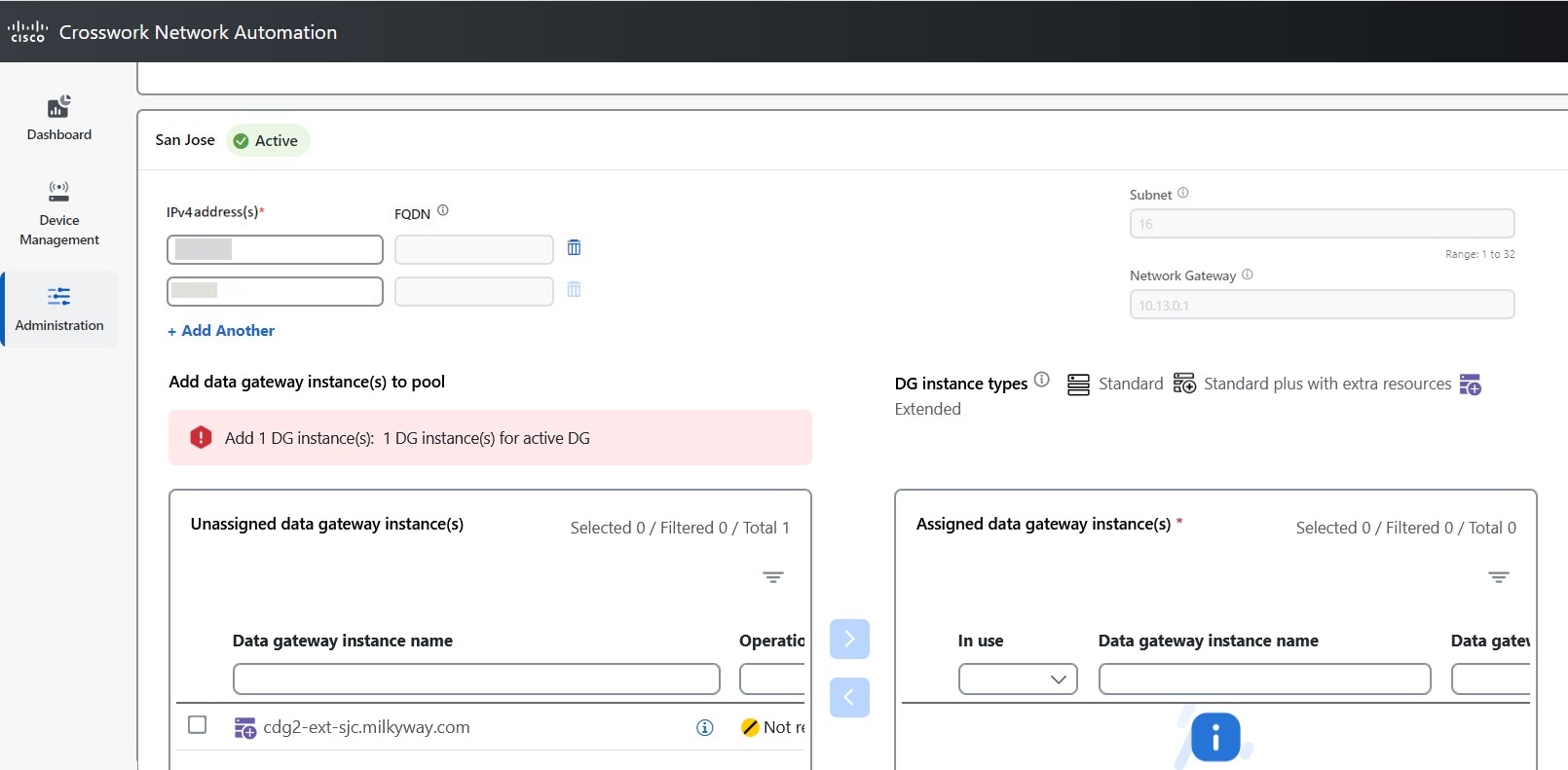
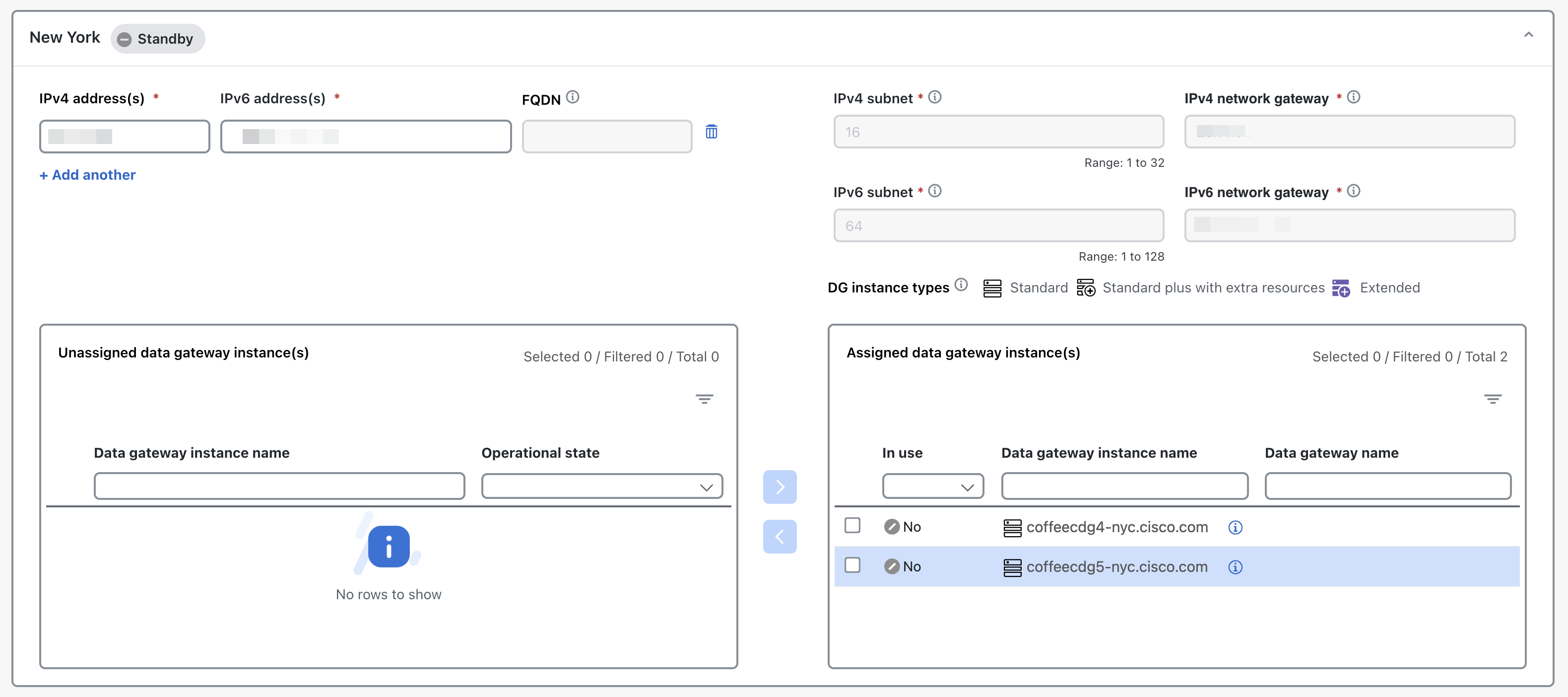
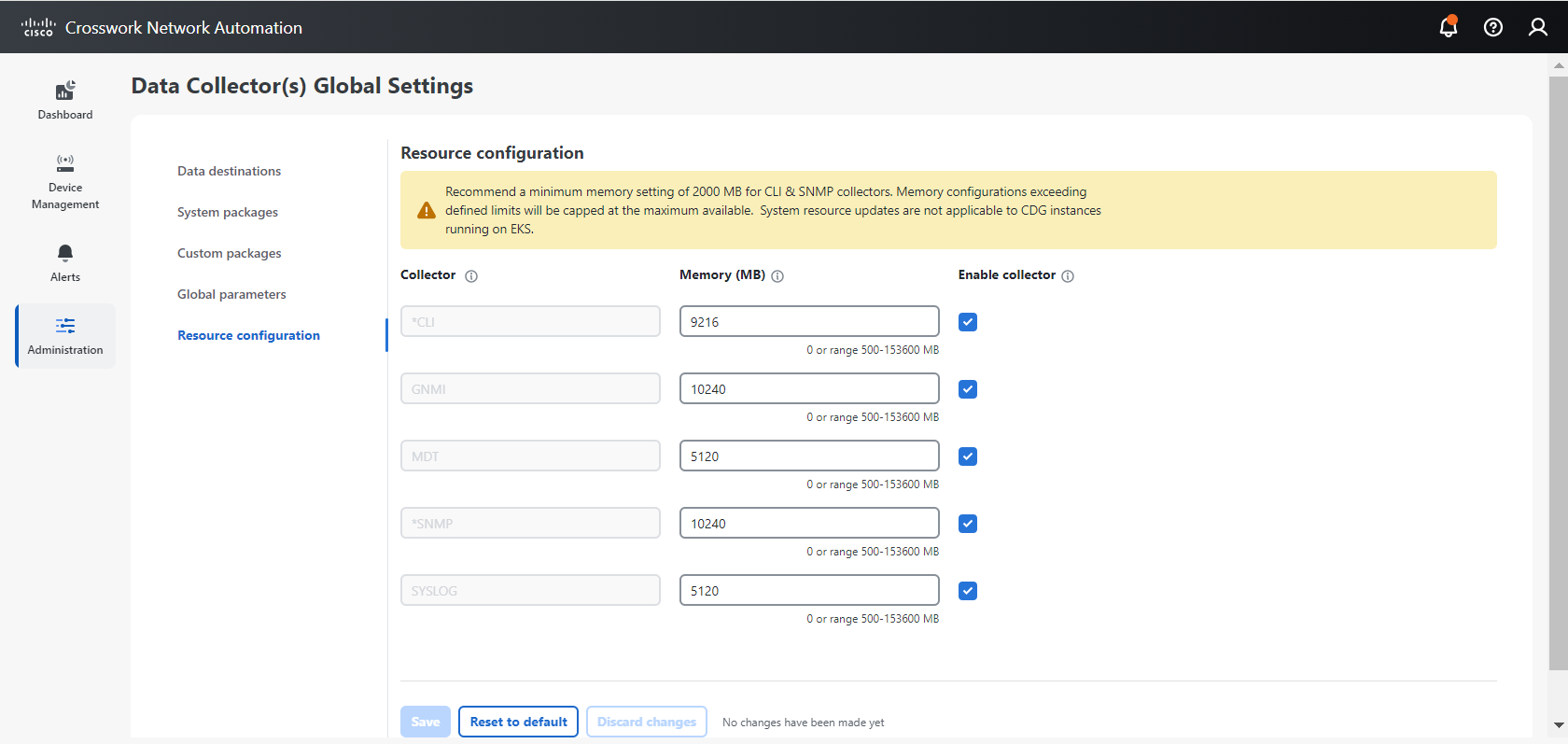
Crosswork Data Gateway pool: A logical unit of one or more Data Gateway instances with an option to enable high availability. When a Data Gateway instance goes down, Cisco Crosswork automatically replaces the instance with a spare instance from the pool to ensure that data collections have minimal disruption.
-
Data destination: Internal or external recipients of data that are collected by Data Gateway. By default, Cisco Crosswork is defined as a data destination. Other destinations (external users) can be defined using the Cisco Crosswork UI or APIs.
-
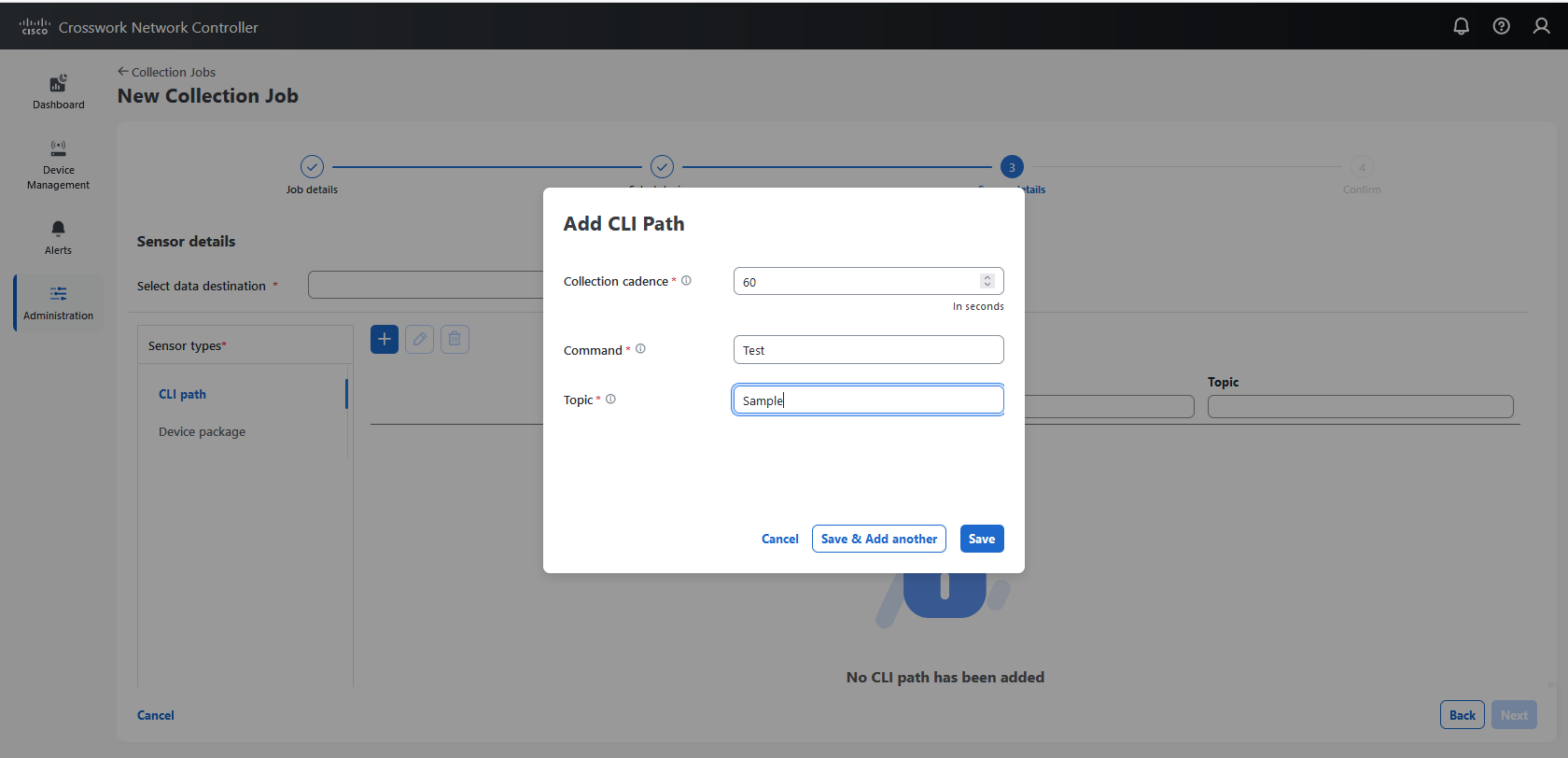
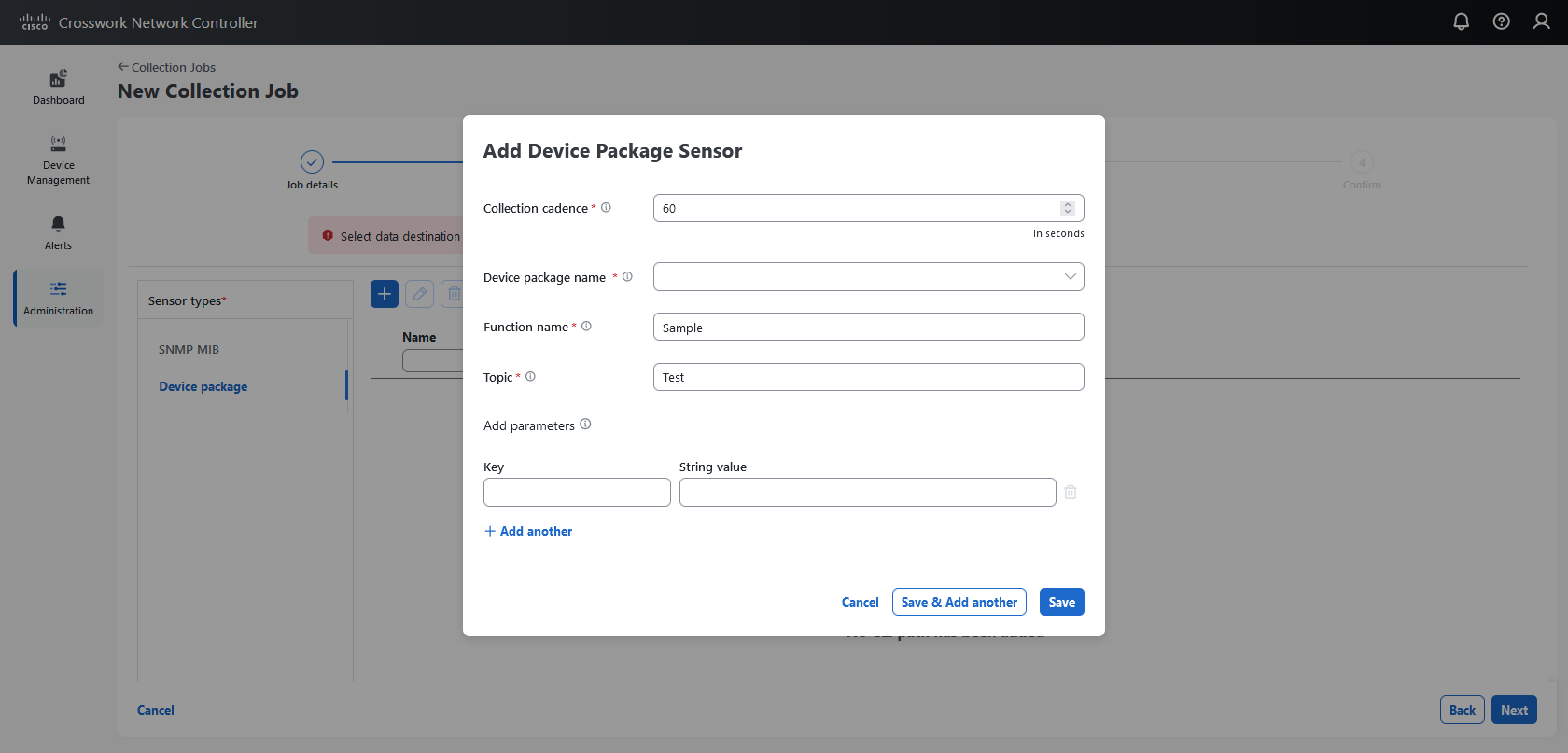
Collection job: A task that Data Gateway has to complete to collect data. Crosswork applications create collection jobs to check device reachability, collect telemetry data that is needed to determine network and service health. The Cisco Crosswork UI and API lets you configure the collection jobs for non-Crosswork applications.
-
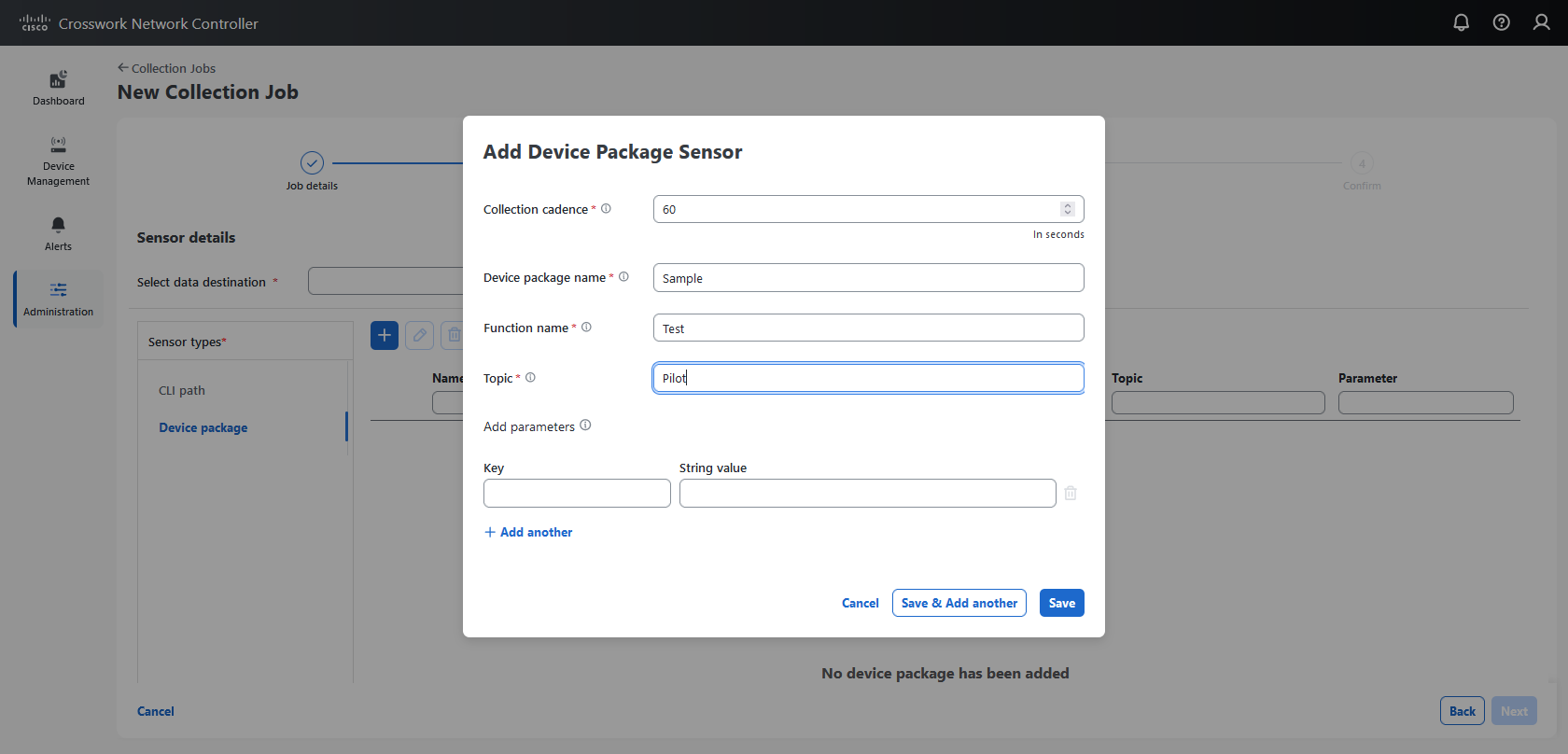
Custom software packages: Files and device model definitions to extend device coverage and support data collection from currently unsupported devices.
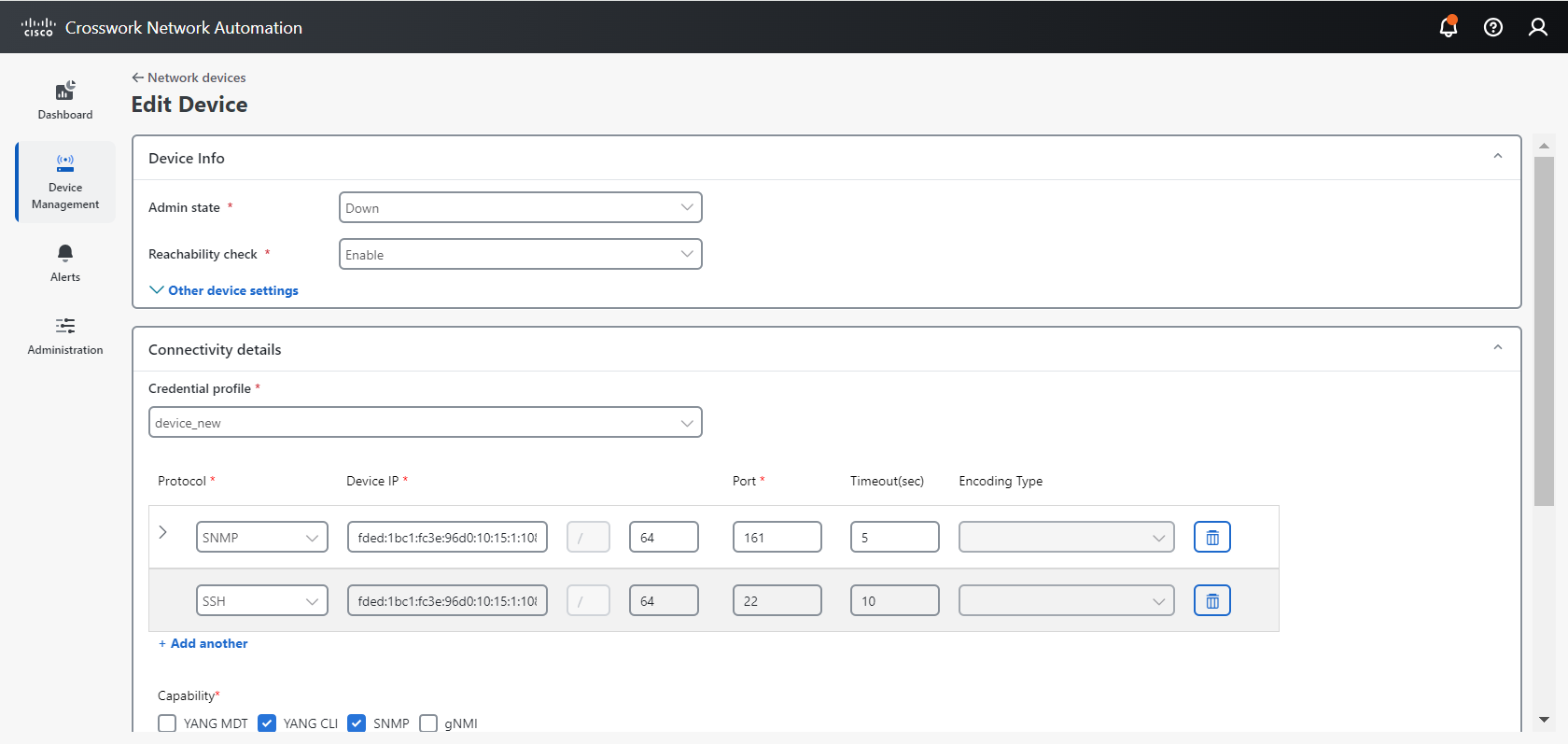
Access the Data Gateway user interface
The Data Gateway user interface provides administrators with tools to monitor, filter, and manage pools efficiently.
Follow these steps to access and use the Data Gateway user interface.
Before you begin
Ensure that you are familiar with the Crosswork Network Controller user interface.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Log in to Cisco Crosswork Network Controller. |
|
Step 2 |
Navigate to Administration > Data Gateway Management using the left navigation bar. |
|
Step 3 |
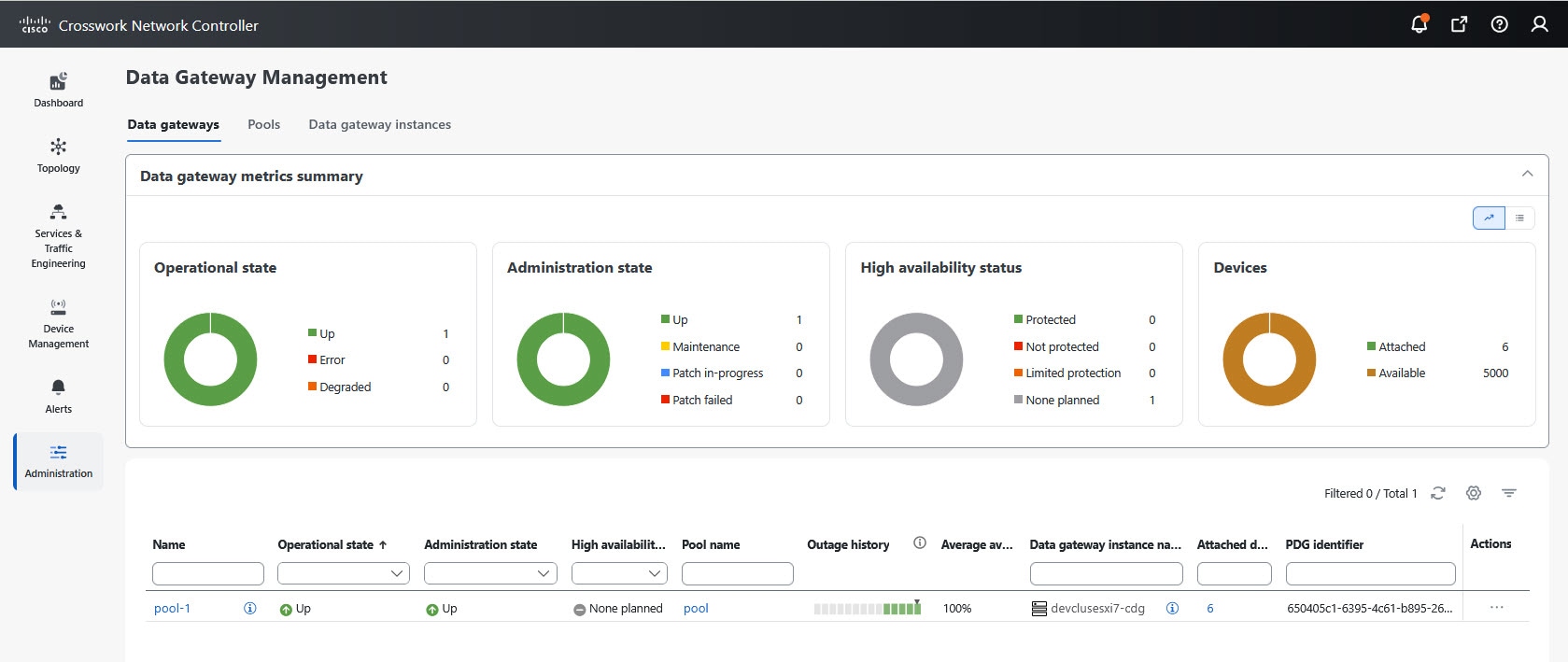
Use the donut chart legends to filter tables: 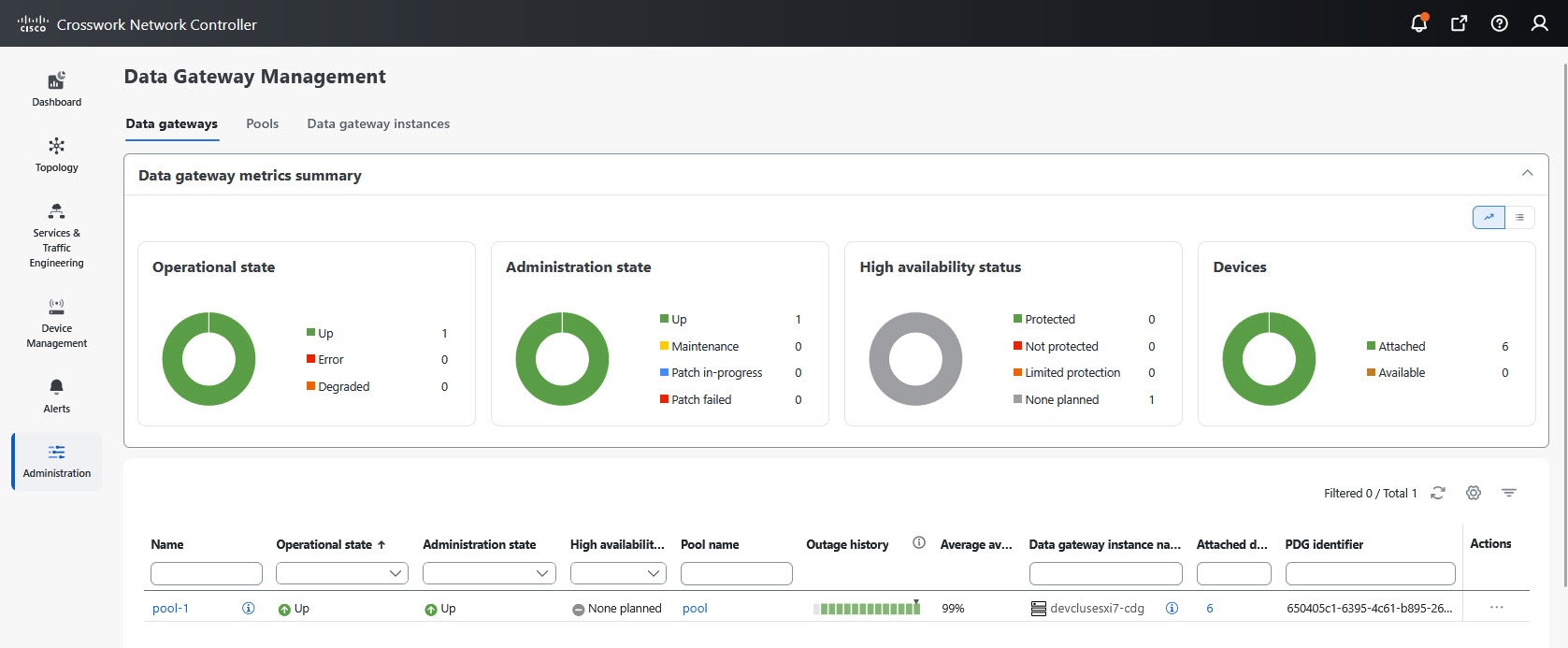
To view pools with the administration state Up, click the Up icon next to the chart. |
|
Step 4 |
Adjust table column visibility:
|
|
Step 5 |
Select multiple items from the tables:
|
You can monitor and manage pools using the filtering, column customization, and multiselection features of the Data Gateway user interface.
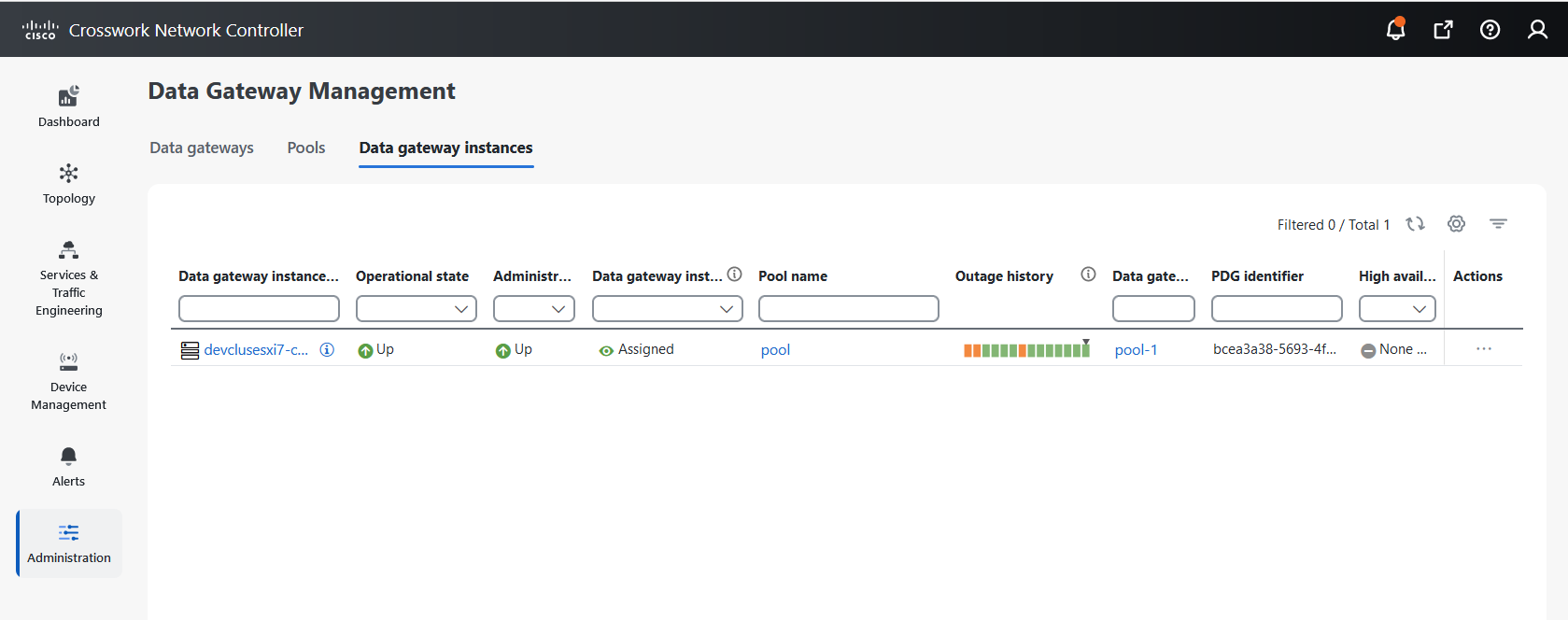
Data Gateway user interface components
The Data Gateway Management page has three tabs:
-
Data gateways: Displays details of the virtual Data Gateway instances in the network. You can attach or detach devices to the Data Gateway from this tab.
-
Pools: Manages the Data Gateway pools.
-
Data gateways instances: Manages virtual the Data Gateway instances.
This table explains the various columns in the Data Gateway Management page.
|
Column |
Description |
||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Operational State |
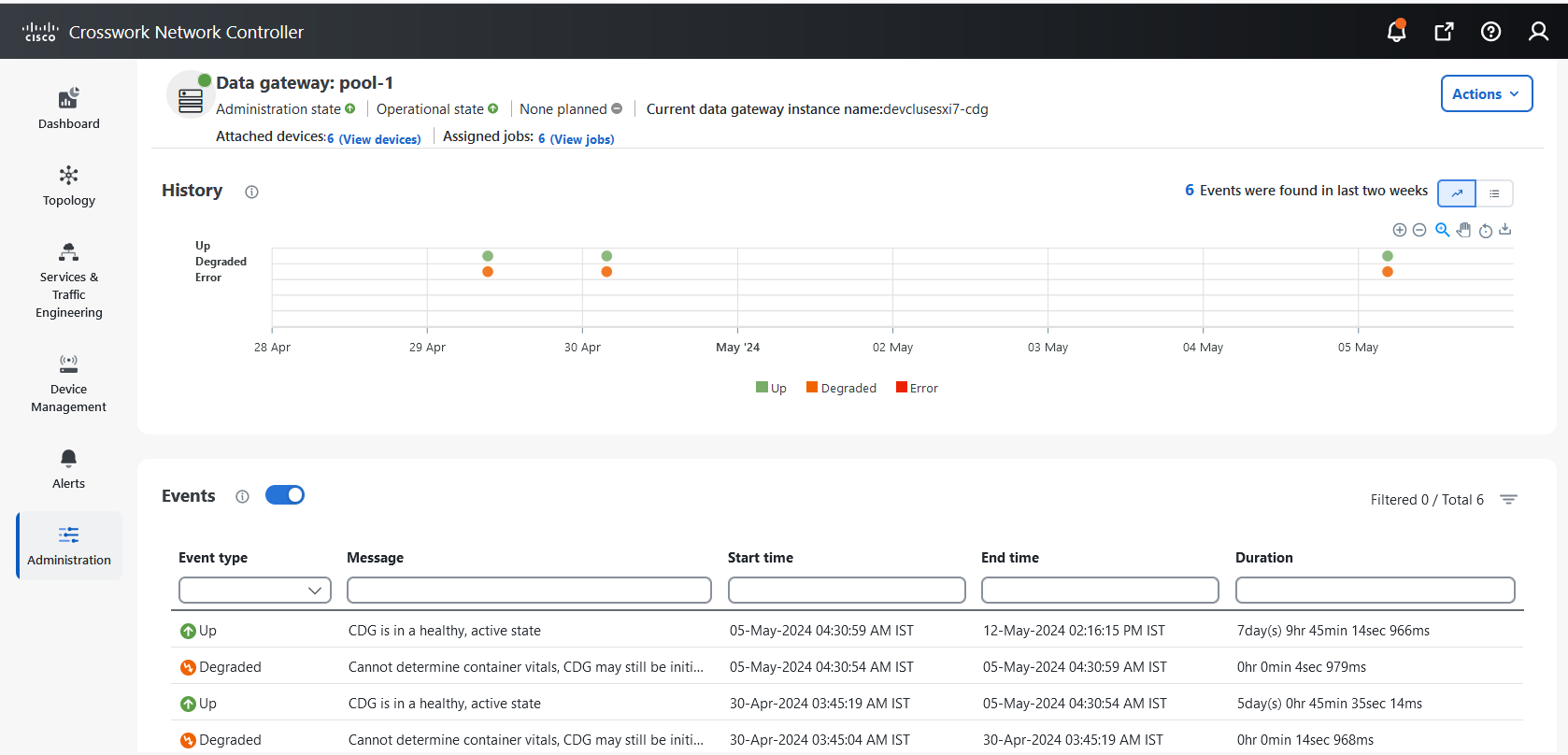
Operational state of the Data Gateway instance. A Data Gateway has the following operational states:
|
||
|
Administration state |
Administration state of the Data Gateway instance. The state could be any of the following:
|
||
|
High availability status |
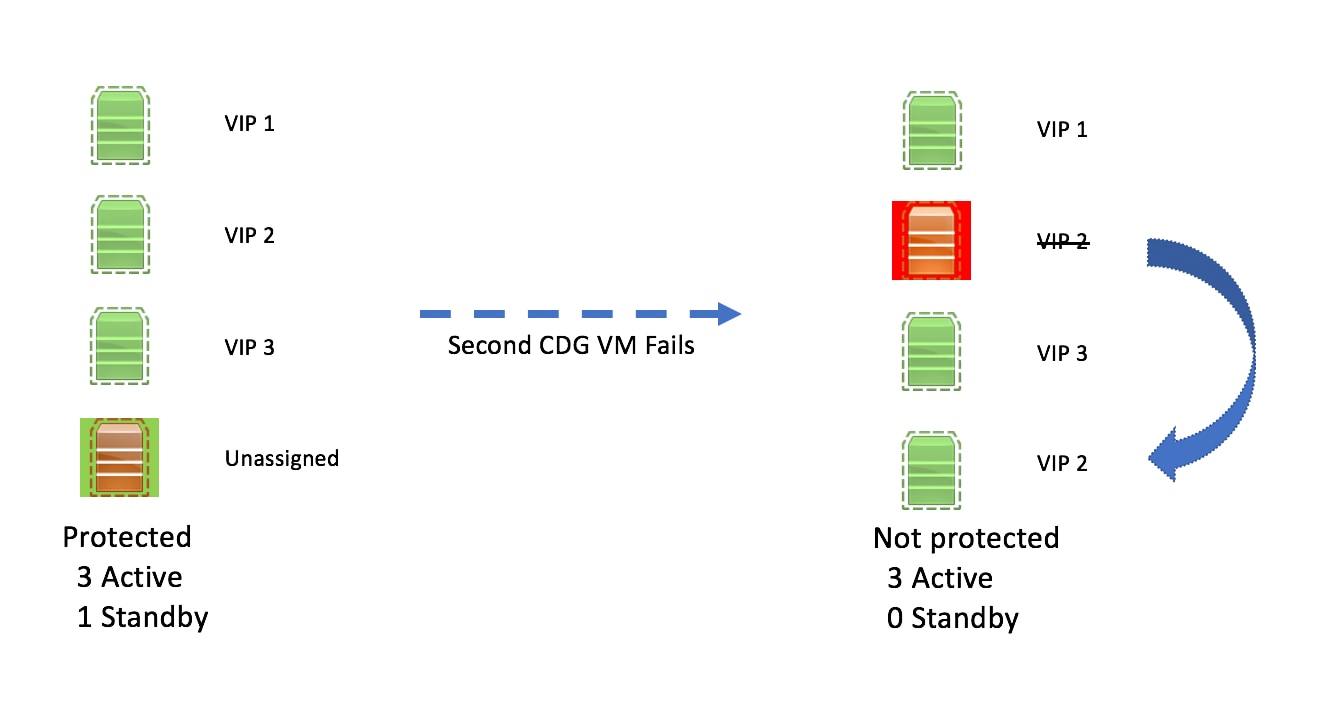
High availability status of a Data Gateway could be either:
|
||
|
Devices |
Number of devices that are attached to the Data Gateway pool. |
||
|
Name |
Name of the Data Gateway instance. Clicking the
Click the instance name to open the Data Gateway vitals page. The page displays the operations and health summary of a Data Gateway. |
||
|
Pool name |
Name of the Data Gateway pool. On clicking the pool name, the Data Gateway vitals page opens. |
||
|
Site name |
Site to which the Data Gateway instance is assigned.
|
||
|
Data gateway instance role |
Indicates the current role of the Data Gateway instance. The role could be any of the following:
|
||
|
Outage history |
Outage history of the Data Gateway instance over a period of 14 days. State aggregation for a day is done in the order of precedence as Error, Degraded, Up, Unknown and Not Ready. For example, if the Data Gateway instance went Unknown to Degraded to Up, the color is displayed as Degraded (orange) for that day as Degraded takes precedence over Up and Unknown. If the Data Gateway was in Error state at any time during that day, the tile is Red. If the Data Gateway was not in Error but in Degraded State anytime of the day, the tile is Orange. If the Data Gateway was not in Error or Degraded state and was only Up, then the tile is Green. |
||
|
Average availability |
Value indicating the health of the Data Gateway instance. This percentage is calculated as the total time (in milliseconds) a Data Gateway was in the UP state over the time between start time of first event and end time of last event.
|
||
|
Data gateway instance name |
Name of the Data Gateway that is created automatically when you add a Data Gateway instance to a pool. Clicking the
The Additional interface role information describes the interface roles available in Data Gateway. |
||
|
Attached device count |
Indicates the number of the devices that are attached to the Data Gateway pool. |
||
|
PDG identifier |
Unique identifier of the physical Data Gateway instance. |
||
|
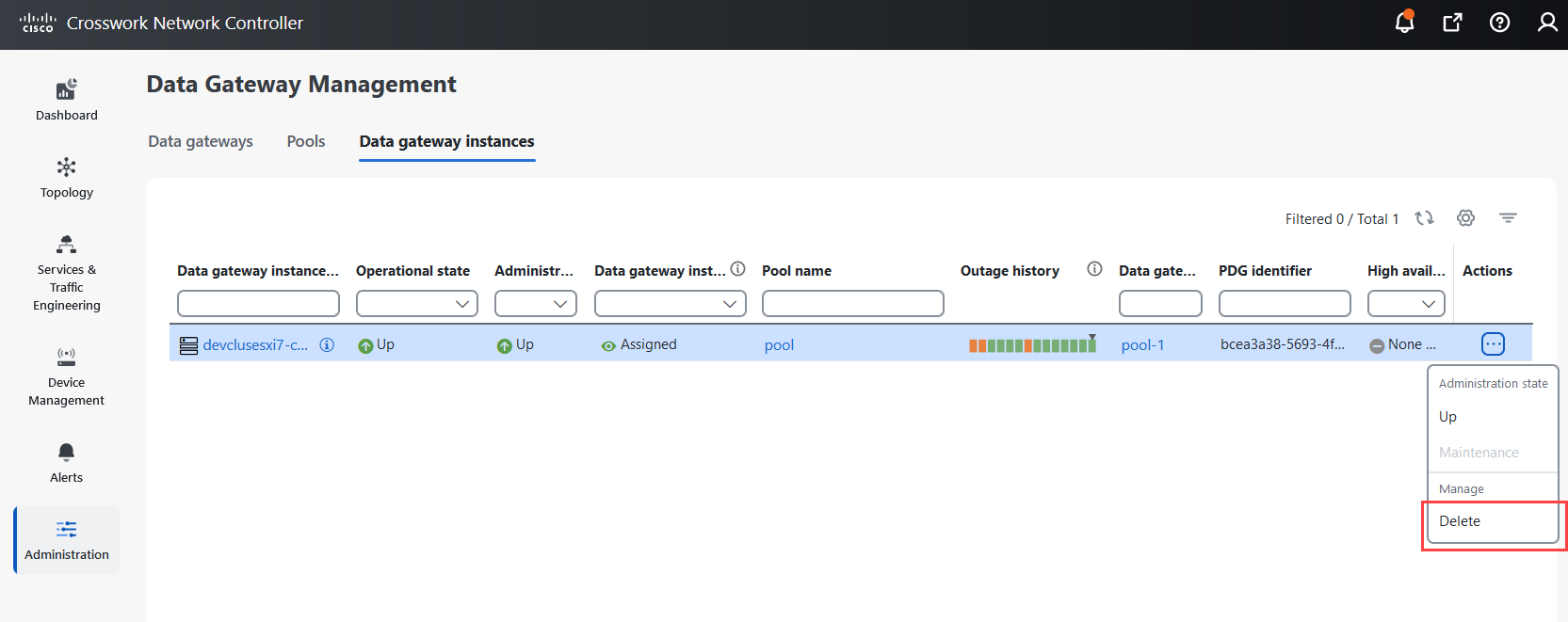
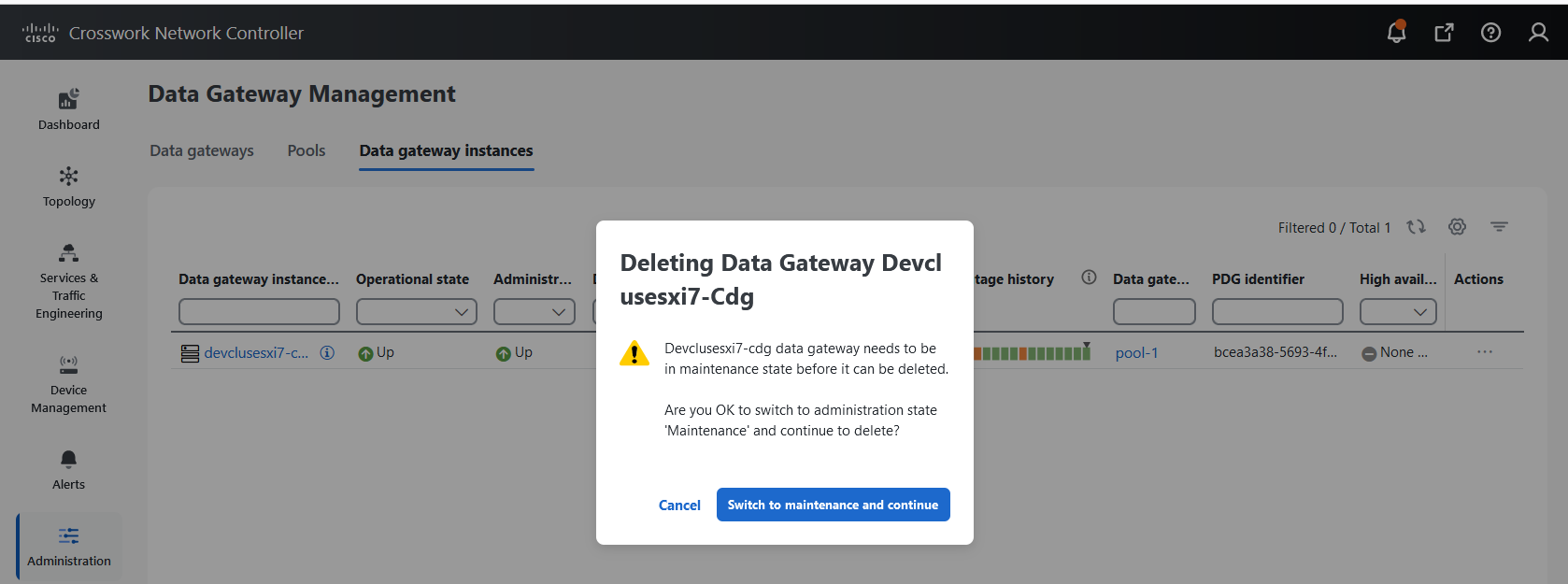
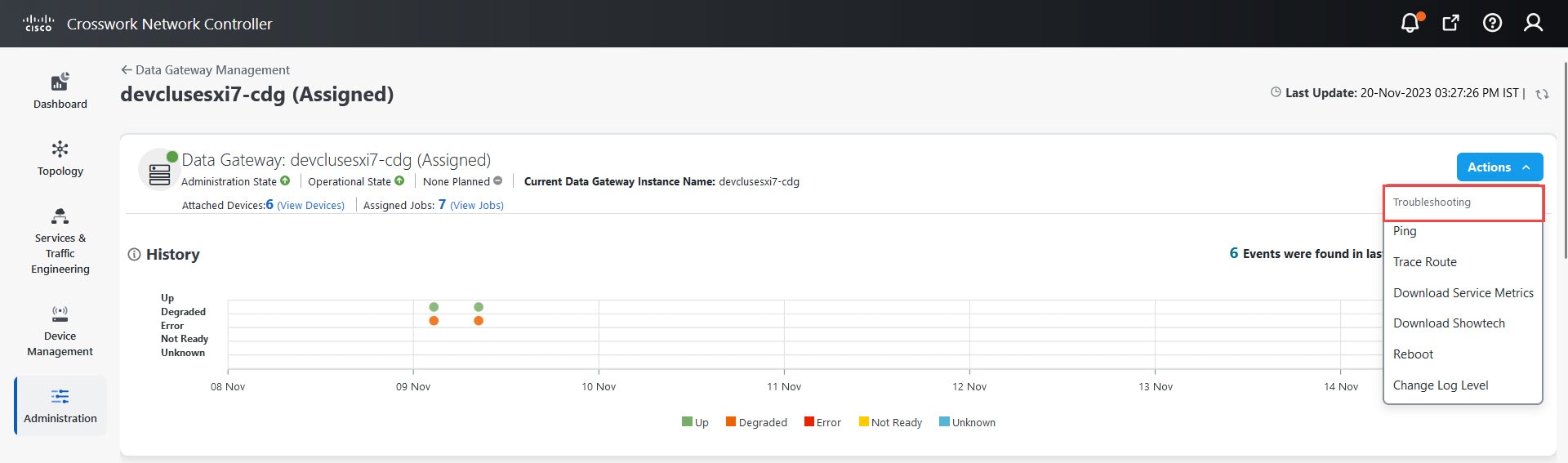
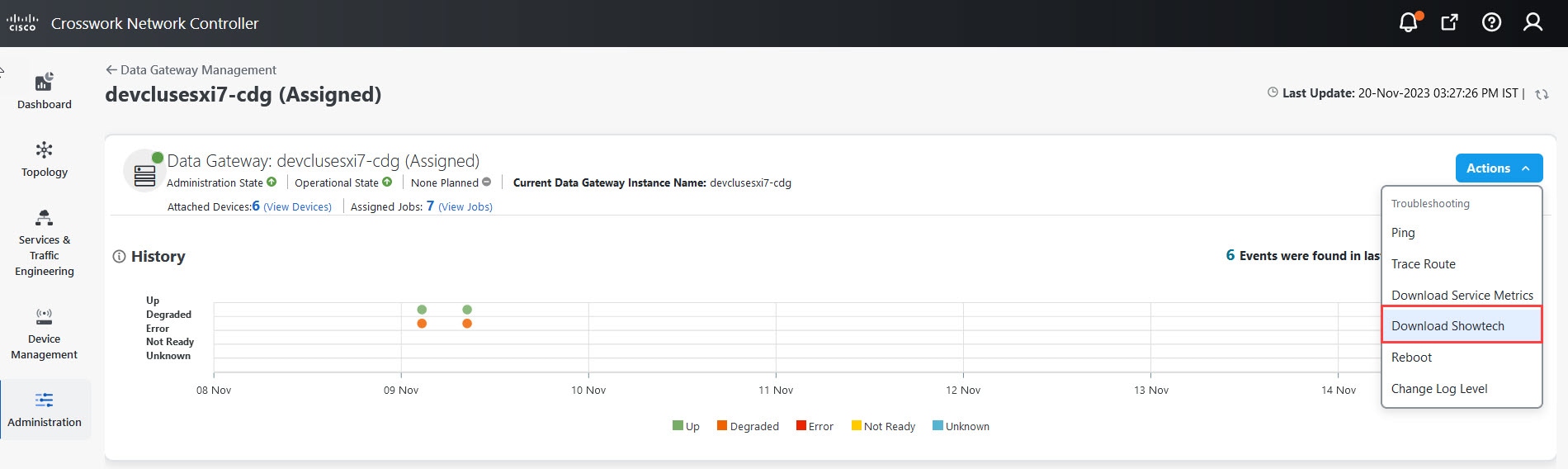
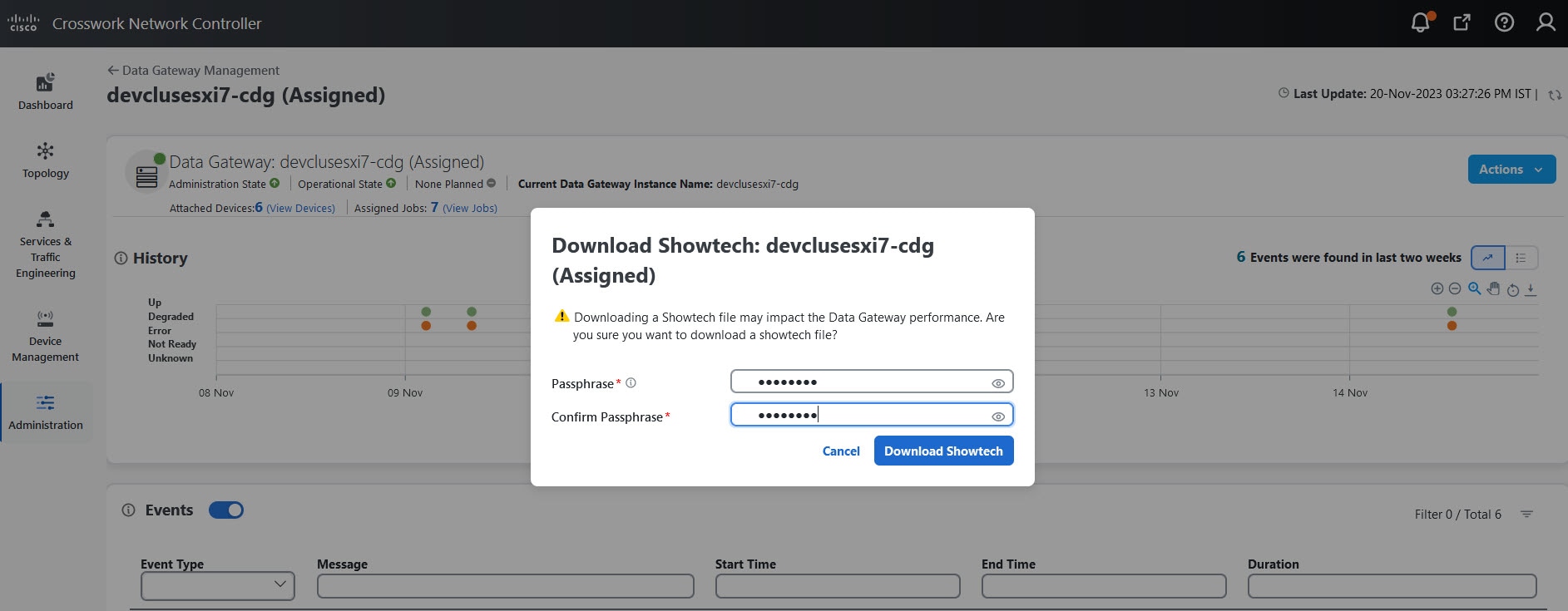
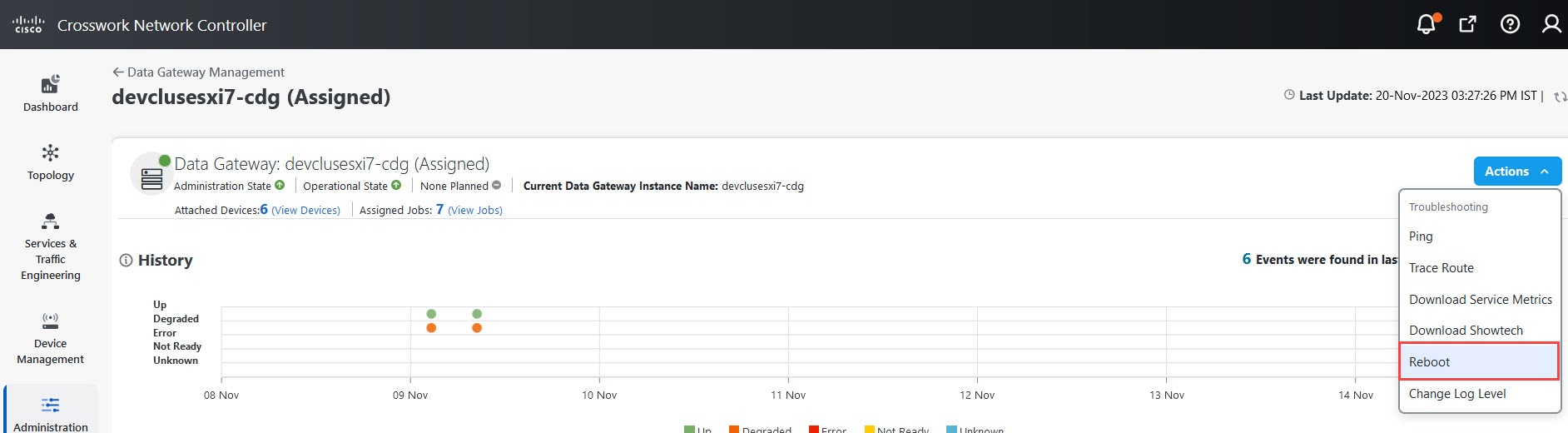
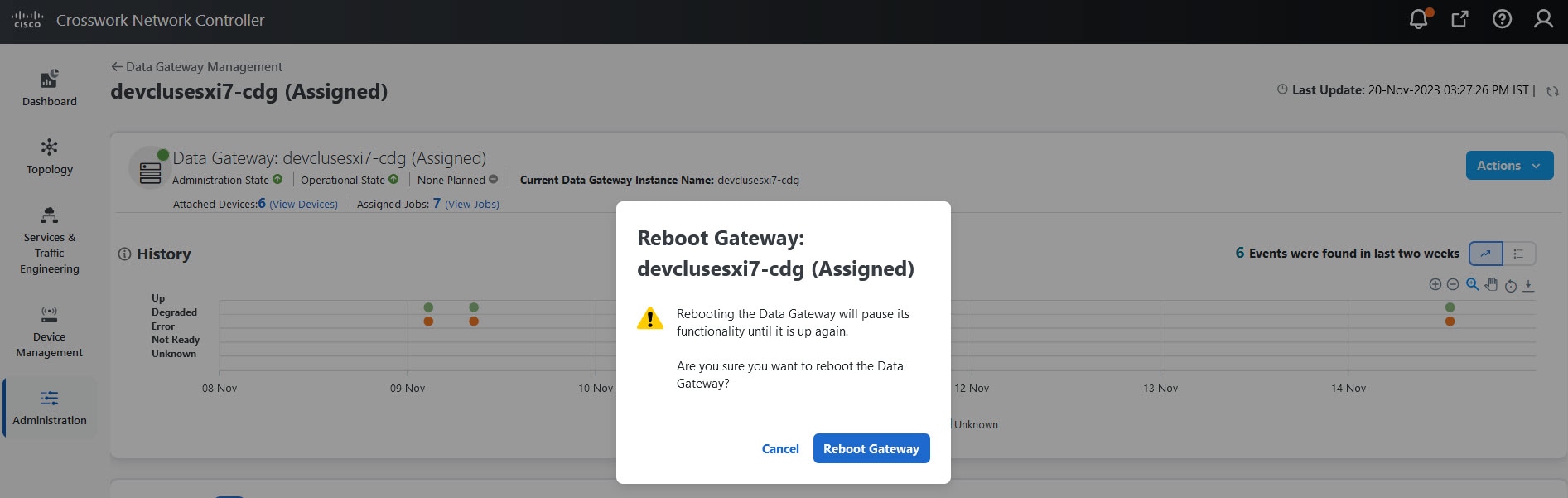
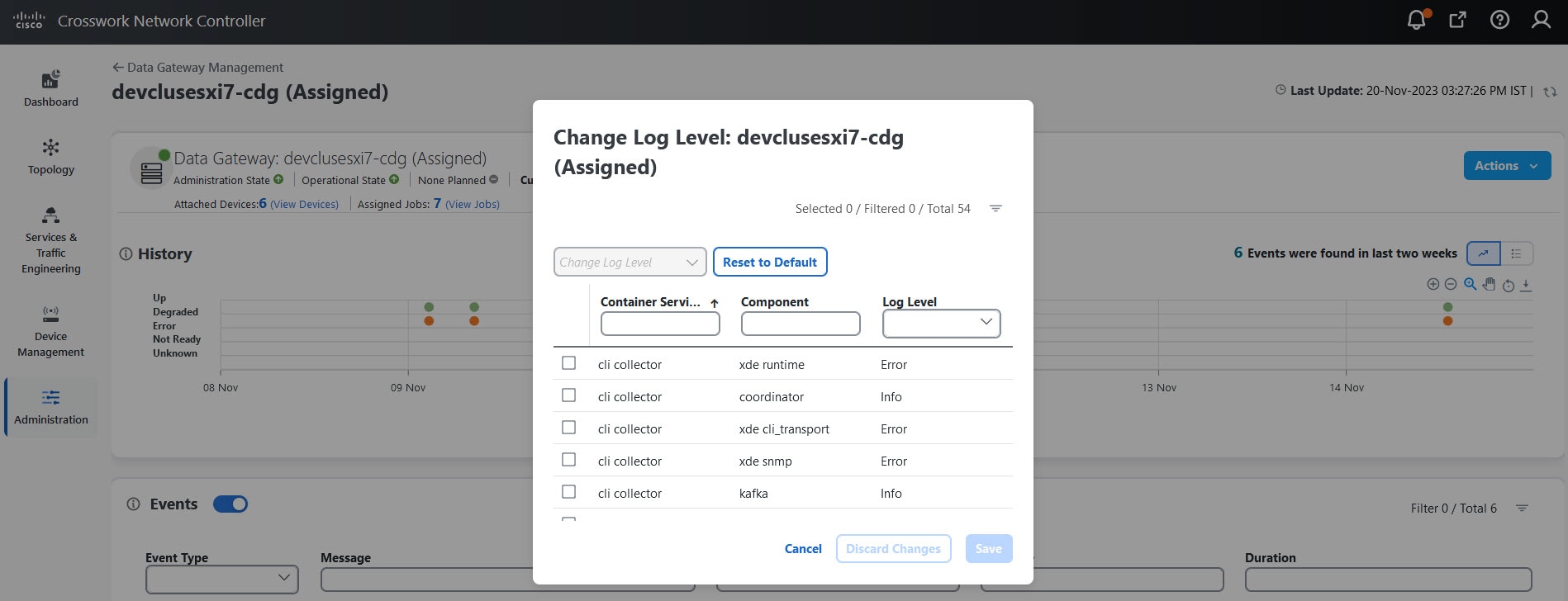
Actions |
Click
|
Deprecated NETCONF protocol
 Caution |
Starting from the Crosswork Network Controller 6.0 release, NETCONF data collection is no longer supported. Avoid using NETCONF for data collection, and transition to the supported protocols such as MDT, SNMP, CLI, gNMI, and Syslog to ensure compatibility. |
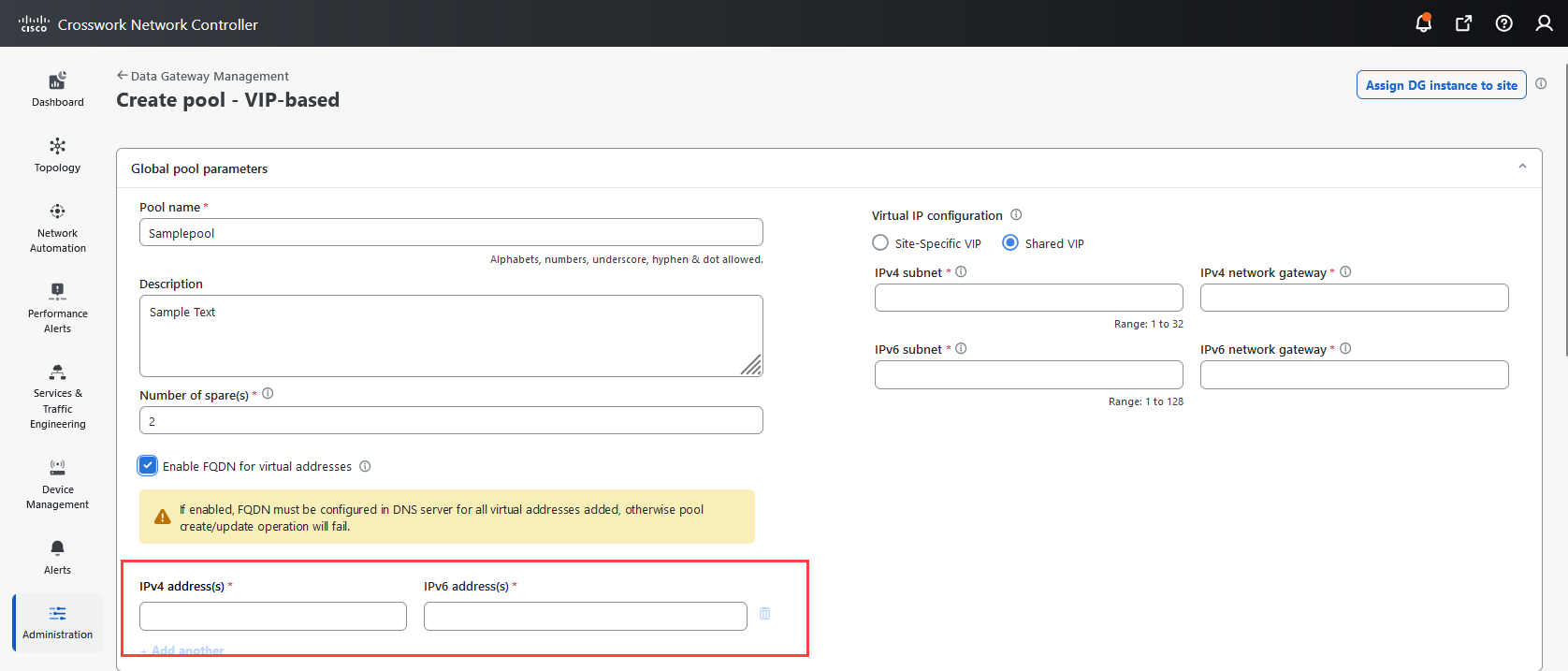

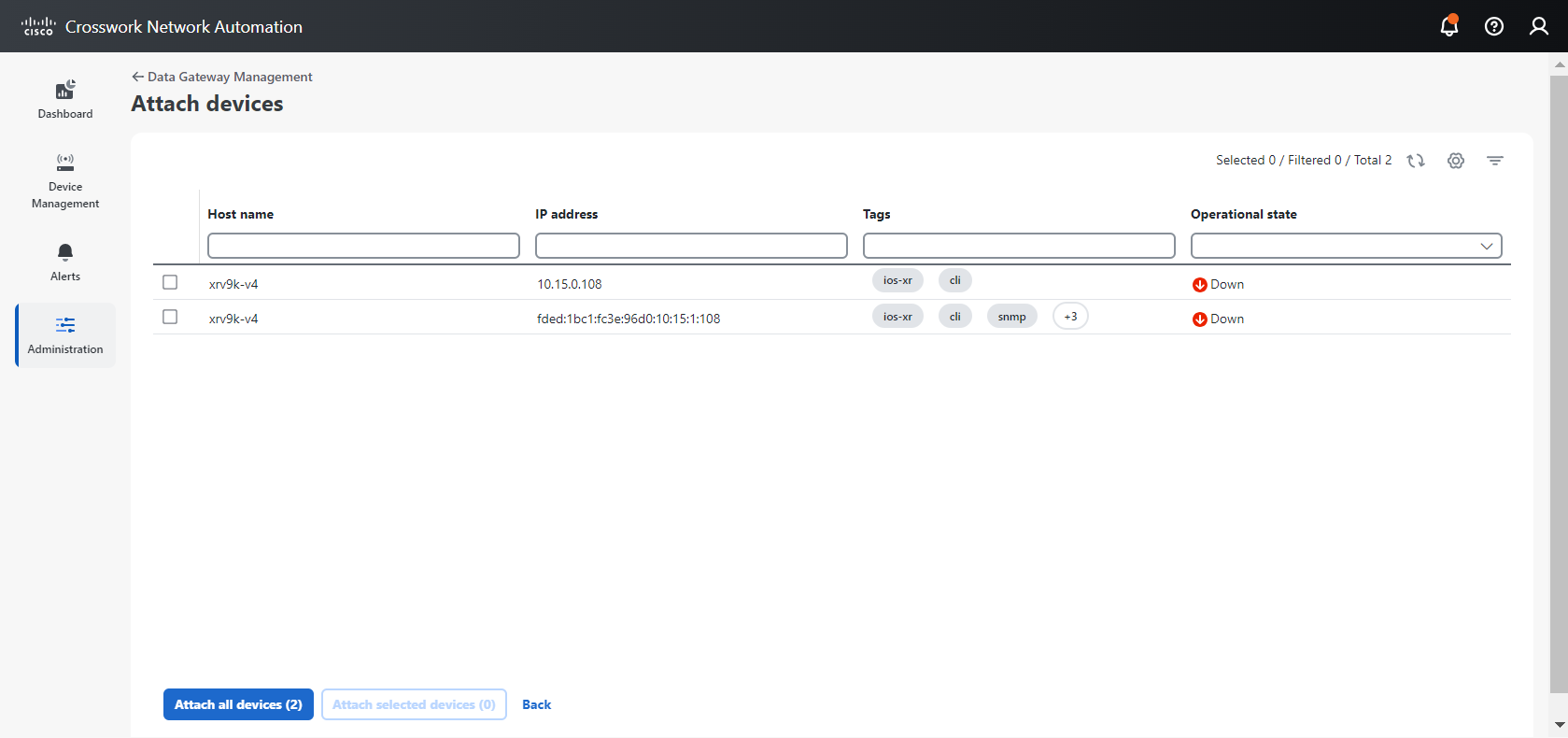

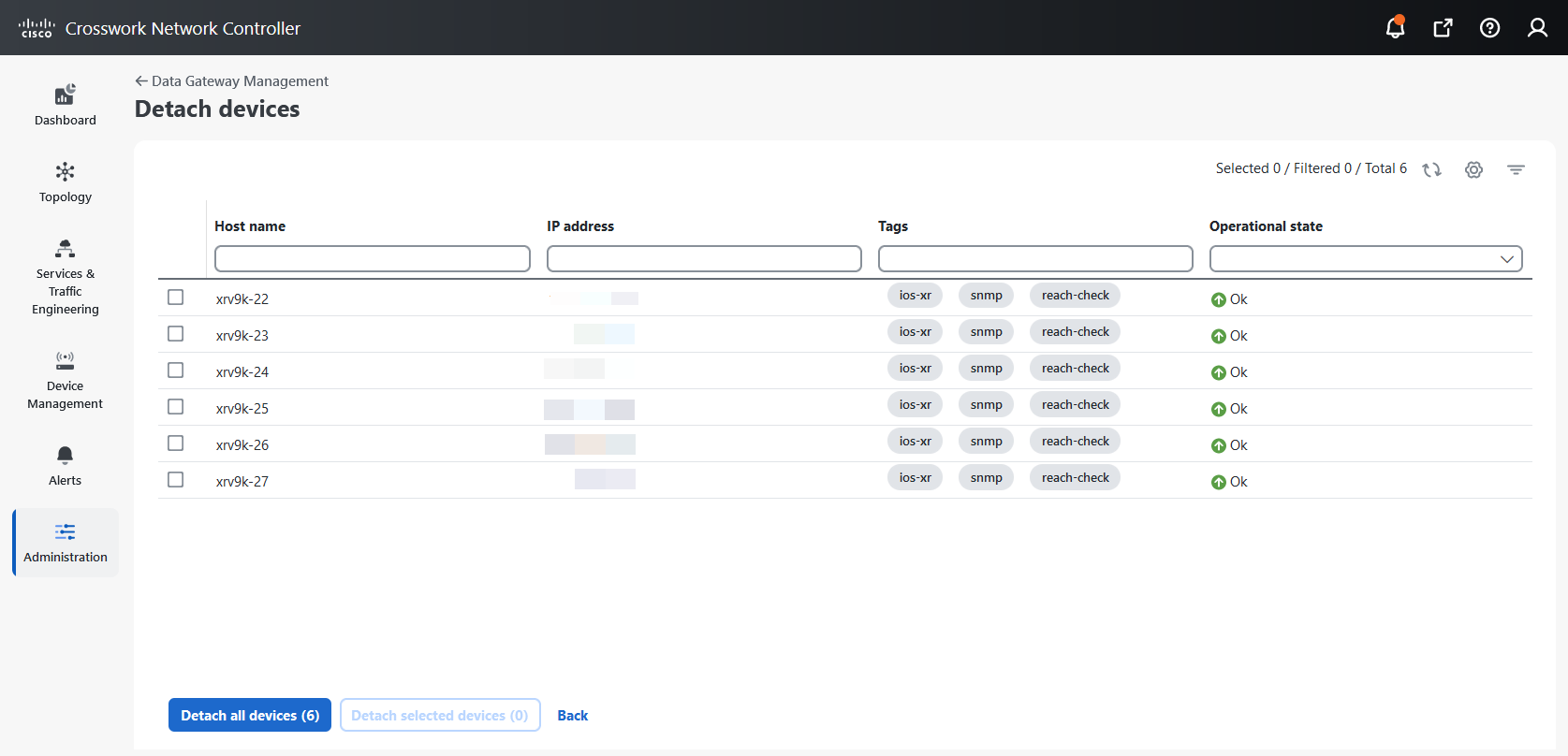
 icon next to the attached device count to see the list of devices attached to the selected Data Gateway.
icon next to the attached device count to see the list of devices attached to the selected Data Gateway.

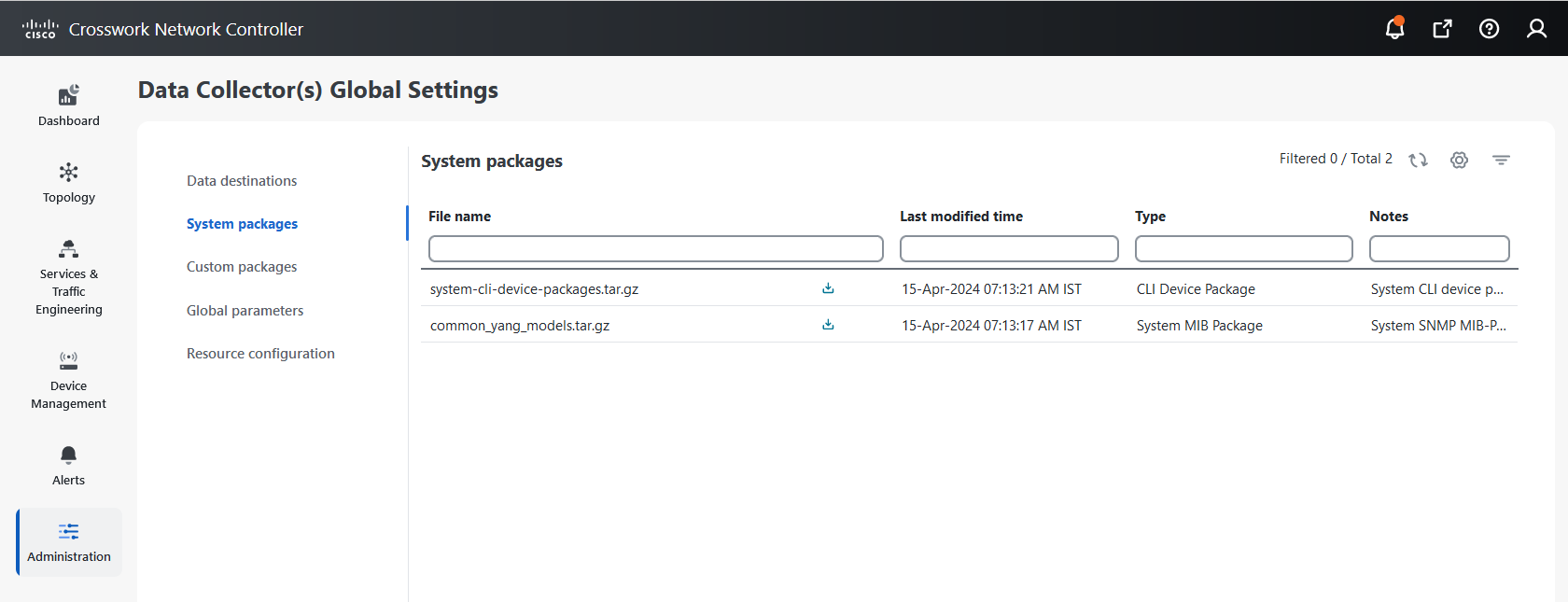
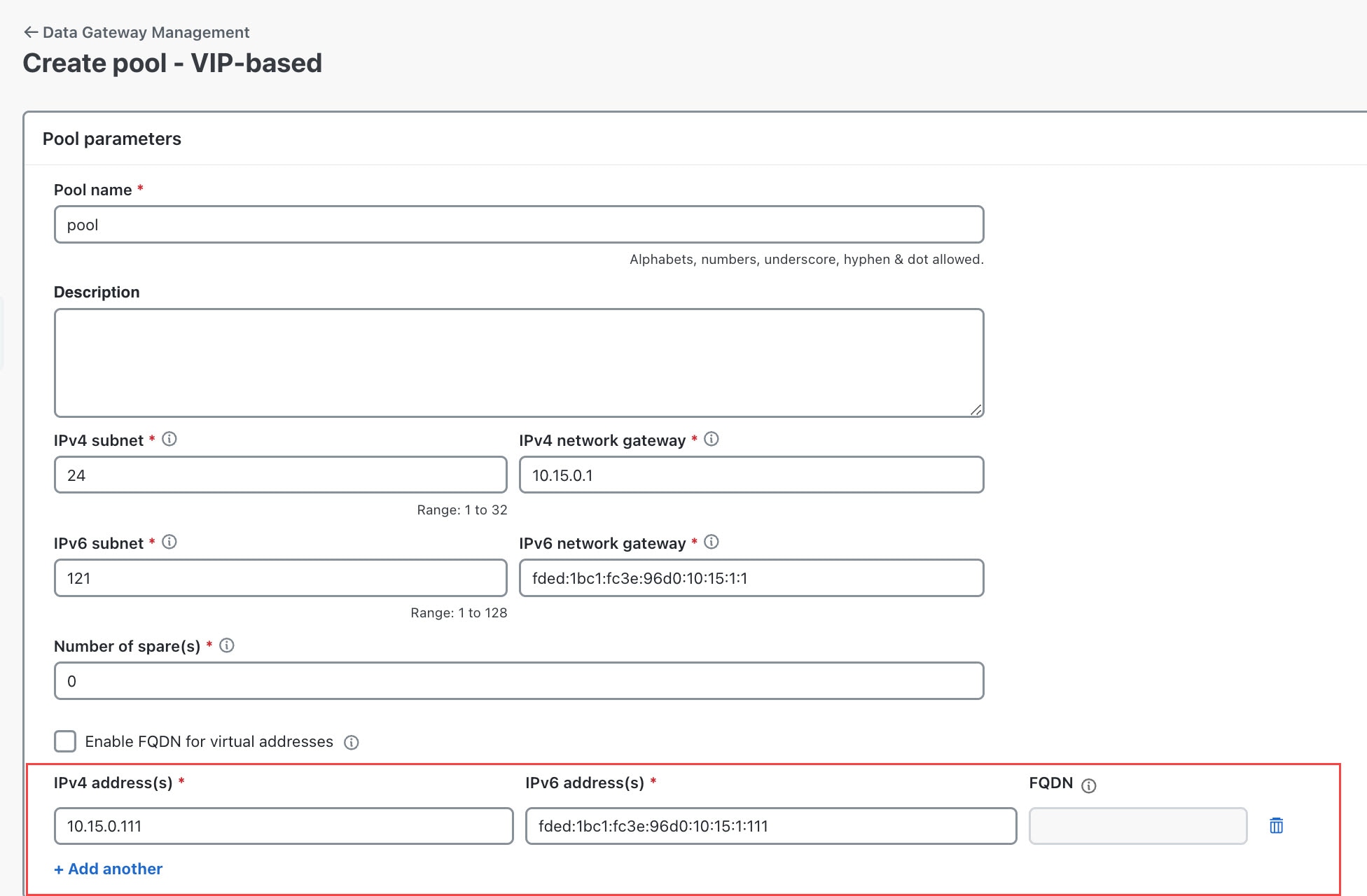
 button next to its name in the File name column.
button next to its name in the File name column.

 Feedback
Feedback