Introduction
This document describes how to troubleshoot non-browser applications in Cisco Umbrella.
Prerequisites
Requirements
There are no specific requirements for this document.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on Cisco Umbrella.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Overview
This article explains best practices and troubleshooting steps for configuring Non-Browser applications to function with Umbrella Secure Web Gateway. In most cases, no configuration changes are required. However, certain applications do not work well with security/inspection functions (such as SSL Decryption) and exceptions must be added to make the application function with a web proxy. This applies to Umbrella SWG as well as other web proxy solutions.
This is useful in circumstances where the website/browser version of an application works, but the desktop/mobile version of the application does not.
Compatibility Problems
Applications can be incompatible for these reasons:
|
Umbrella Root CA Installation
|
The Cisco Umbrella Root CA must always be trusted for errorless TLS connections.
- Solution: For Non-Web applications ensure the Cisco Umbrella Root CA is trusted in the System / Local Machine certificate store.
|
|
Certificate Pinning
|
Certificate Pinning (PKP) is when the application expects to receive a precise leaf (or CA certificate) to validate the TLS handshake. The application cannot accept a certificate generated by a web proxy and is not compatible with SSL Decryption functions.
More details about Applications known to be affected by certificate pinning are available here: Understand Public Key Pinning and Certificate Pinning
|
|
TLS Version Support
|
The application can use an older TLS Version / Cipher which is not supported by SWG for security reasons.
- Solution: Bypass the traffic from being sent to Umbrella using the External Domains feature (PAC / AnyConnect) or VPN exclusions (Tunnel) (see Warning after table).
|
|
Non-Web Protocol
|
Some applications use non-http(s) protocols but still send this data over common web ports that are intercepted by SWG. SWG cannot understand this traffic.
- Solution: Consult the Application Vendor to determine the destination addresses / IP ranges used by the software. This software needs to be excluded from SWG using External Domains (PAC / AnyConnect) or VPN Exclusions (Tunnel) (see Warning after table).
|
|
SAML Authentication
|
Most non-browser applications are unable to perform SAML authentication. Umbrella does not challenge non-browser applications for SAML and therefore User/Group based filtering policies cannot match.
- Solution: Enable the IP Surrogates feature so user information can be cached for use with Non-Browser applications.
- Alternative: Allow the Application/Domain in a web rule based on Network or Tunnel Identities (not users/groups).
|
|
HTTP Range Requests
|
Some applications use HTTP “Byte-Range” requests when downloading data; meaning only a small chunk of the file is downloaded at a time. These requests are disabled for security reasons in SWG because this technique can also be used to bypass Anti-Virus detection.
- Solution (HTTPS): Bypass the Application or Domain from SSL Decryption* in Umbrella using Selective Decryption Lists.
- Solution (HTTP): Bypass the Application or Domain from Anti-Virus scanning* using a web rule with the Override Security option.
- Alternative: Contact Umbrella support if you wish to have Range requests enabled by default* for your organization.
|
|
Explicit Proxy Compatibility
|
Some applications do not respect system proxy settings (eg. PAC files) and are generally not compatible with explicit web proxies. These applications do not route through Umbrella SWG in a PAC file deployment.
- Solution: The application must be allowed via the local network firewall. Consult the application vendor for details on destinations/ports to be allowed.
|

Warning: Creating these exceptions can disable security inspection functions including Anti-Virus scanning, DLP scanning, Tenant Controls, File Type Control and URL inspection. Only do this if you are happy to trust the source of these files. The business need for the application must be weighed against the security impact of disabling these features.
Microsoft 365 Applications
The Microsoft 365 Compatibility feature automatically excludes a number of Microsoft domains from SSL Decryption and policy enforcement functions. This feature can be enabled to resolve problems with the Desktop version of Microsoft apps. For more information see Manage Global Settings.

Note: The Microsoft 365 Compatibility feature does not exclude all Microsoft domains. Umbrella uses Microsoft's recommendations for the list of domains which must be excluded from filtering. For more information see New Office365 Endpoint Categories.
Certificate Pinning Bypass
Certificate Pinning (PKP) is a common cause of app compatibility issues. Cisco provide a comprehensive list of named Applications that can be configured to bypass SSL Decryption to workaround. The selective decryption can be configured in Policies > Selective Decryption Lists.
In most cases, the administrator can resolve certificate pinning issues simply by excluding the application by its name. This means that these issues can be resolved without having to learn or maintain lists of domains.
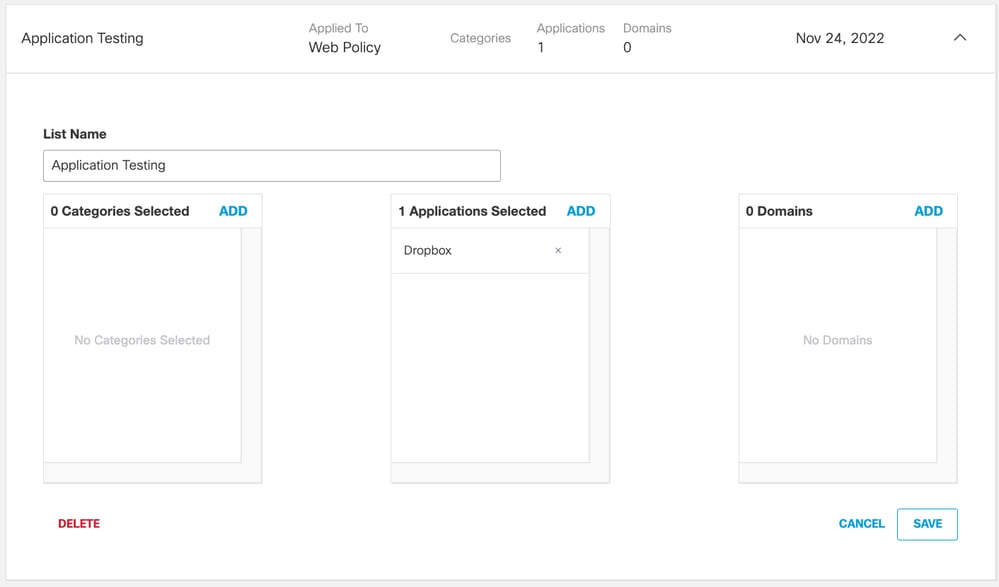
Alternatively, applications can be bypassed based on destination domain/IP address. Contact the application vendor to determine the applicable list of domains/IPs or see Identify exclusions for certificate pinning.
TLS Compatibility Bypass
Legacy or custom TLS versions are a common cause of app compatibility issues. These problems can be solved by excluding the traffic from Umbrella in Deployments > Domain Management > External Domains & IPs. In a tunnel deployment the traffic can only be excluded by adding exceptions in your VPN configuration.
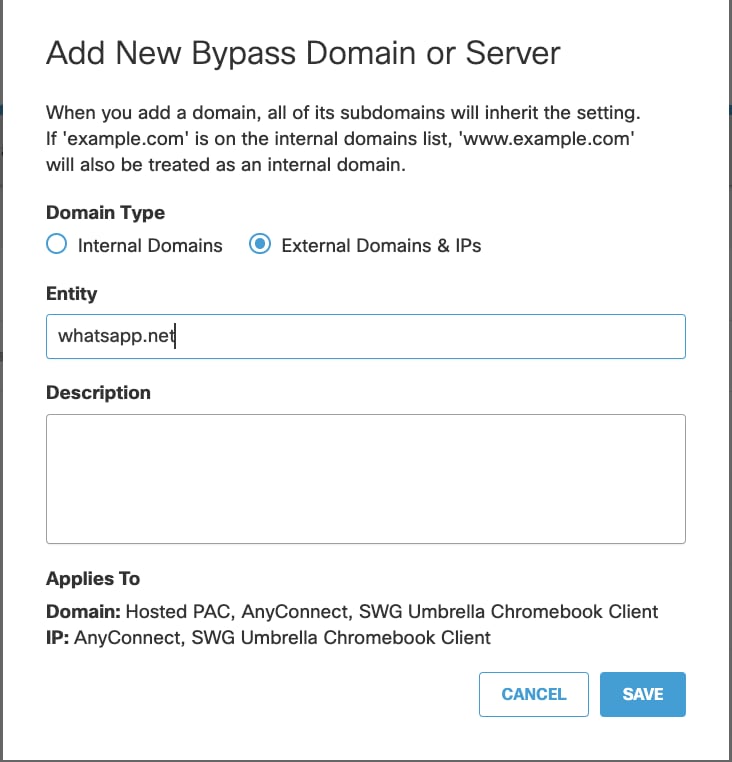
Contact the application vendor to determine the applicable list of domains/IPs to exclude or see "Identify Exclusions for Incompatible TLS Versions" (later in this article).
Troubleshooting (Advanced)
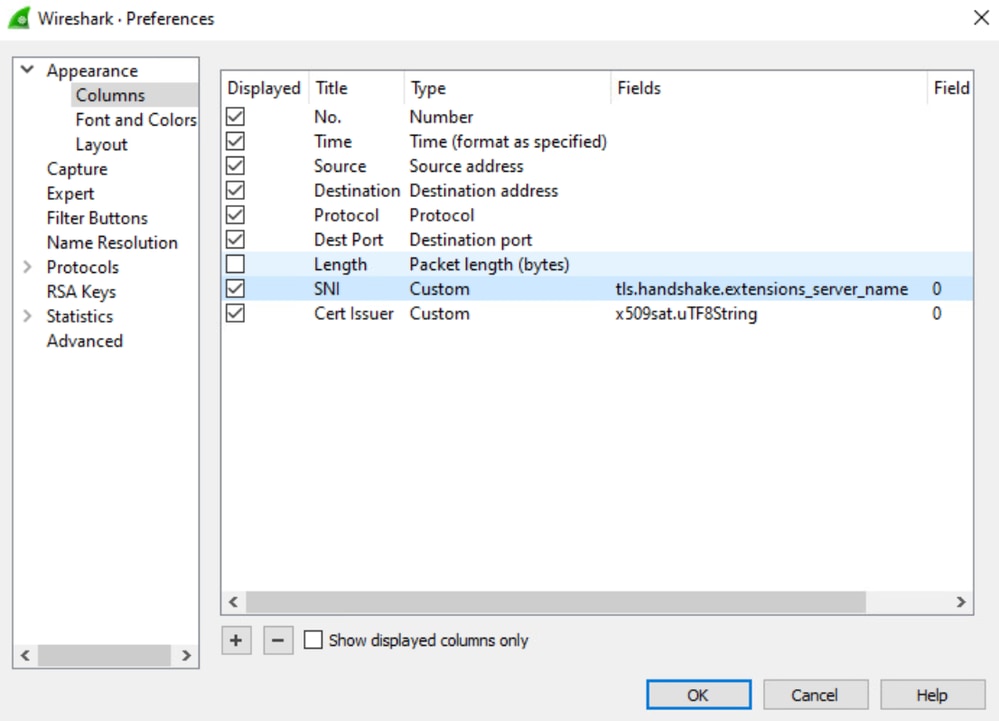
The remaining instructions in this article use Wireshark (www.wireshark.org) packet captures for troubleshooting purposes. Wireshark can help to identify which domains are used by applications for help with implementing custom exclusions. Before starting, add these custom columns in Wireshark:
1. Download Wireshark from www.wireshark.org.
2. Go to Edit > Preferences > Columns.
3. Create columns of type Custom with these fields:
http.host
tls.handshake.extensions_server_name
x509sat.uTF8String
To perform a packet capture, complete these instructions or see Capture Network Traffic with Wireshark.
1. Run Wireshark as an Administrator.
2. Select the relevant network interfaces in Capture > Options.
- For PAC / Tunnel Deployments, capture on your normal LAN network interface.
- For AnyConnect Deployments, capture on your LAN network interface and the loopback interface.
3. Close down all other applications except the problem application.
4. Flush your DNS cache: ipconfig /flushdns
5. Start the Wireshark capture.
6. Quickly replicate the issue and stop the Wireshark capture.
Identify Exclusions for Certificate Pinning
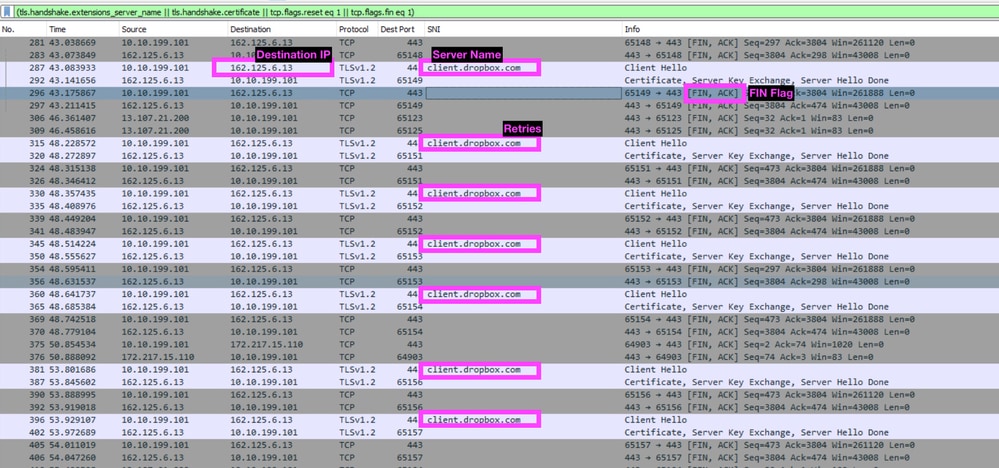
Certificate pinning is enforced on the client, meaning that the exact behavior and resolution steps differs for every application. In the capture output, look for telltale signs that a TLS connection is failing:
- A TLS connection is being quickly closed or reset (RST or FIN).
- A TLS connection is being repeatedly retried.
- The certificate for the TLS connection is being issued by Cisco Umbrella and is therefore being decrypted.
These example Wireshark filters can help to view the important details of TLS connections.
Tunnel / AnyConnec
tcp.port eq 443 && (tls.handshake.extensions_server_name || tls.handshake.certificate || tcp.flags.reset eq 1 || tcp.flags.fin eq 1)
PAC / Proxy Chaining
tcp.port eq 443 && (http.request.method eq CONNECT || tcp.flags.reset eq 1)
In this example, the DropBox desktop application is affected by certificate pinning when attempting to connect to client.dropbox.com.

Note: After adding the necessary exclusion(s), you can repeat these steps multiple times to identify all the destinations used by the application.
Identify Exclusions for Incompatible TLS Versions
Look for SSL/TLS connections that do not use the mandatory TLS1.2+ protocols supported by Umbrella SWG. This can include legacy protocols (TLS1.0 or earlier) or bespoke custom-protocols implemented by an application.
This example filter shows you initial TLS handshake packets along with DNS queries.
Tunnel / AnyConnect
dns || (tls && tcp.seq eq 1 && tcp.ack eq 1)
PAC / Proxy Chaining
dns || http.request.method eq CONNECT
In this example, the Spotify desktop application is attempting to connect to ap-gew4.spotify.com using a non-standard or legacy "SSL" protocol which cannot be sent via SWG.


Note: After adding the necessary exclusion(s), you can repeat these steps multiple times to identify all the destinations used by the application.








 Feedback
Feedback