Introduction
This document describes how to change static IP or DNS settings on a device with the Umbrella roaming client installed.
Overview
The Umbrella Roaming Client modifies the DNS settings on the computers' Network Interface (NIC). This means you must take extra care wherever you attempt to change settings on the interface, such as assigning a static IP address.

Note: This article only applies to the standalone Roaming Client and not the AnyConnect Roaming Security Module.
Basics
The Roaming Client replaces the DNS server assigned to the network interface with the loopback address (127.0.0.1). It is normal to see this value (127.0.0.1) assigned as DNS server when the client is running.
When making a change to the Network Interface you MUST also replace the 127.0.0.1 DNS server value with the correct DNS server value for your network. Do not use the default value of 127.0.0.1.

Caution: When switching from a DHCP IP address to a static IP configuration, you MUST also supply a static DNS server. If this is not done it can cause the DNS resolution to fail.
Examples
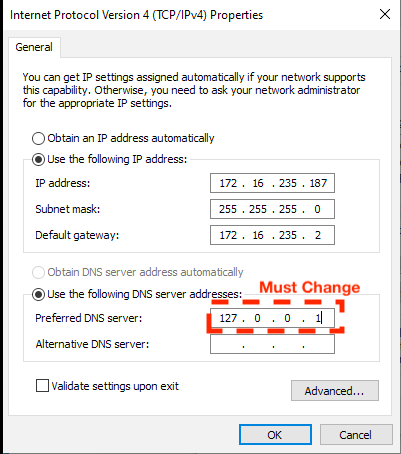
This screenshot shows an example of the DNS setting which must be updated when setting the static IP address:
 360041282071
360041282071
Remove the 127.0.0.1 setting.
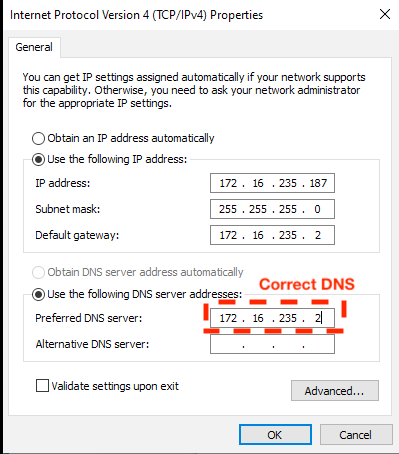
This screenshot shows an example of a correctly set DNS server:
 360041282111
360041282111
It is now safe to click OK and save the new Network interface settings.

Note: After saving the NIC settings the Roaming Client again replaces the DNS server with 127.0.0.1. This is normal and expected behaviour.
More Information
The computer is configured to send all DNS traffic through the Roaming Client on 127.0.0.1:53. However, the Roaming Client remembers the list of DNS servers that you assign to the network interface and uses them for handling DNS traffic:
- If a DNS query is for an Internal Domain it is sent to the saved DNS servers from the network interface
- All other DNS queries are sent directly to Umbrella DNS resolvers in the cloud
When switching to a static IP configuration the DHCP DNS server address is lost which triggers a known limitation in the Roaming Client. The Roaming Client does not configure DNS protection on a network interface with no DNS server, leading to a scenario where the network interface has no DNS configured.





 Feedback
Feedback