Introduction
This document describes a technical overview of IS-IS microloops, the conditions under which they occur, and mechanisms used to prevent them.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have basic knowledge of Intermediate System to Intermediate System (ISIS) Segment Routing (SR) version 6.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on Device: Network Convergence System (NCS) 540, NCS 5500.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Microloop Overview
IS-IS is a widely deployed link-state routing protocol used in large-scale Service Provider networks due to its fast convergence and scalability. However, during topology changes such as link or node failures, transient forwarding consistenc, commonly known as microloops, can occur while routers update their forwarding information bases (FIBs) at different times. These microloops lead to temporary packet loss, increased latency, or traffic blackholing, which can negatively impact real-time and latency-sensitive applications.
IS-IS routing protocol leverage Segment Routing (SR and SRv6) microloop avoidance mechanisms in order to prevent such transient forwarding loops during network convergence. These mechanisms ensure loop-free forwarding even while the network is transitioning to a new steady state.
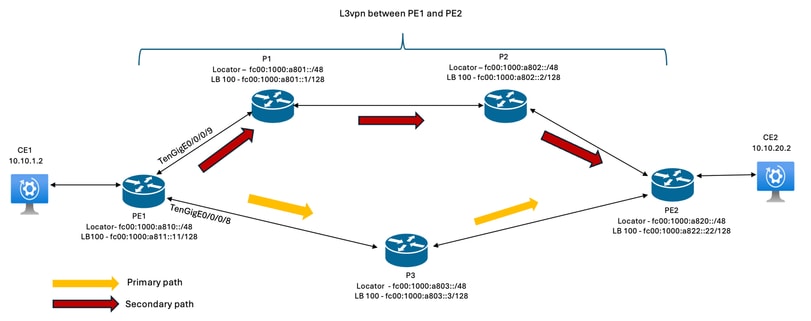
Figure 1. Network Topology Diagram
Generic Configuration
interface Loopback100
ipv6 address <>
interface <>
ipv6 enable
router isis <>
is-type level-2-only
net <>
address-family ipv6 unicast
metric-style wide
microloop avoidance segment-routing ## enables Microloop avoidance mechanism
microloop avoidance rib-update-delay <> ## specify the time in ms
router-id Loopback100
segment-routing srv6
locator <>
interface Loopback100
address-family ipv6 unicast
interface <>
point-to-point
address-family ipv6 unicast
fast-reroute per-prefix
fast-reroute per-prefix ti-lfa ## enables topology-independent loop-free alternates (TI-LFA)
segment-routing
srv6
encapsulation
source-address <>
!
locators
locator <>
micro-segment behavior unode psp-usd ## enables SRv6 Micro-SIDs (uSIDs) the PSP-USD (Penultimate Segment Pop - Ultimate Segment Pop) flavor
prefix <configure the locator >
router bgp <>
vrf <>
address-family <> unicast
segment-routing srv6 ## steering the packet using SRv6 uSID
locator <>
In Steady-State
When there is no change in the network, 10.10.1.0/24 network is advertised by Provider Edge 1 (PE1) via Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to Provider Edge 2 (PE2), 10.10.20.0/24 network is advertised by PE2 to PE1.
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:PE1#show bgp vrf mobility 10.10.1.0/24 detail
BGP routing table entry for 10.10.1.0/24, Route Distinguisher: 10.10.11.11:0
SRv6-VPN SID: fc00:1000:a810:e003::/64
Local
0.0.0.0 from 0.0.0.0 (10.10.11.11), if-handle 0x3c000090
Origin incomplete, metric 0, localpref 100, weight 32768, valid, redistributed, best, group-best, import-candidate
Received Path ID 0, Local Path ID 1, version 8
Extended community:

Note: fc00:1000:a810:e003::/64 >> fc00:1000:a810 ## locator of PE1, e003 ## function.
RP/0/RP0/CPU0: PE1#show bgp vrf mobility 10.10.20.0/24 detail
Local
fc00:1000:a822::22 (metric 2000) from fc00:1000:a822::22 (10.10.22.22), if-handle 0x00000000
Received Label 0xe0030
Origin incomplete, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal, best, group-best, import-candidate, imported
Received Path ID 0, Local Path ID 1, version 714
Extended community:
PSID-Type:L3, SubTLV Count:1, R:0x00,
SubTLV:
T:1(Sid information), Sid:fc00:1000:a820::, F:0x00, R2:0x00, Behavior:63, R3:0x00, SS-TLV Count:1
SubSubTLV:
T:1(Sid structure):
Length [Loc-blk,Loc-node,Func,Arg]:[32,16,16,0], Tpose-len:16, Tpose-offset:48
Source AFI: VPNv4 Unicast, Source VRF: default, Source Route Distinguisher: 10.10.22.22:2

Note: This 10.10.20.0/24 is received from PE2 on PE1 with the locator sid fc00:1000:a820:: and function e0030.
RP/0/RP0/CPU0: PE1#show route vrf mobility 10.10.20.0/24 detail
Known via "bgp 100", distance 200, metric 0, type internal
Routing Descriptor Blocks
fc00:1000:a822::22, from fc00:1000:a822::22
<snip>
SRv6 Headend: H.Encaps.Red [f3216], SID-list {fc00:1000:a820:e003::}

Note: In steady state the packets destined to Cusctomer Edge 2 (CE2) are sent to PE2 with Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) header destination address fc00:1000:a820:e003::.
Packet sent by PE1 in steady state.
Frame 2: 136 bytes on wire (1088 bits), 136 bytes captured (1088 bits)
Ethernet II, Src: Cisco_a7:8a:0d (c4:b2:39:a7:8a:0d), Dst: Cisco_ff:d4:16 (a0:b4:39:ff:d4:16)
Destination: Cisco_ff:d4:16 (a0:b4:39:ff:d4:16)
Source: Cisco_a7:8a:0d (c4:b2:39:a7:8a:0d)
Type: IPv6 (0x86dd)
Internet Protocol Version 6, Src: fc00:1000:a811::11, Dst: fc00:1000:a820:e003::
0110 .... = Version: 6
<0110 .... = Version: 6 [This field makes the filter match on "ip.version == 6" possible]>
.... 0000 0000 .... .... .... .... .... = Traffic Class: 0x00 (DSCP: CS0, ECN: Not-ECT)
.... 0000 0000 0000 1110 1111 = Flow Label: 0x000ef
Payload Length: 82
Next Header: IPIP (4)
Hop Limit: 254
Source Address: fc00:1000:a811::11
<Source or Destination Address: fc00:1000:a811::11>
<[Source Host: fc00:1000:a811::11]>
<[Source or Destination Host: fc00:1000:a811::11]>
Destination Address: fc00:1000:a820:e003::
<Source or Destination Address: fc00:1000:a820:e003::>
<[Destination Host: fc00:1000:a820:e003::]>
<[Source or Destination Host: fc00:1000:a820:e003::]>
Internet Protocol Version 4, Src: 10.10.1.2, Dst: 10.10.20.2
0100 .... = Version: 4
.... 0101 = Header Length: 20 bytes (5)
Differentiated Services Field: 0x00 (DSCP: CS0, ECN: Not-ECT)

Note:
- Src: fc00:1000:a811::11 >> loopback 100 of PE1 used as the source address.
- Dst : fc00:1000:a820:e003:: >> locator of PE2: function.
- the IPv6 transport header, next is the IPv4 payload.
Per-computed primary and back-up path via Topology-Independent - Loop-Free Alternate (TI-LFA):
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:PE1#show cef ipv6 fc00:1000:a820::
via fe80::a2b4:39ff:feff:d416/128, TenGigE0/0/0/9, 11 dependencies, weight 0, class 0, backup (TI-LFA) [flags 0xb00]
path-idx 0 NHID 0x0 [0x8ef0f2b0 0x0]
next hop fe80::a2b4:39ff:feff:d416/128, Repair Node(s): fc00:1000:a802::2
local adjacency
SRv6 H.Insert.Red SID-list {fc00:1000:a802::}
via fe80::9ee1:76ff:feca:e8a8/128, TenGigE0/0/0/8, 4 dependencies, weight 0, class 0, protected [flags 0x400]
path-idx 1 bkup-idx 0 NHID 0x0 [0x8f2db710 0x0]
next hop fe80::9ee1:76ff:feca:e8a8/128
Sequency of Events when the Interface TenGigE0/0/0/8 (Primary Path) on PE1 Goes Down
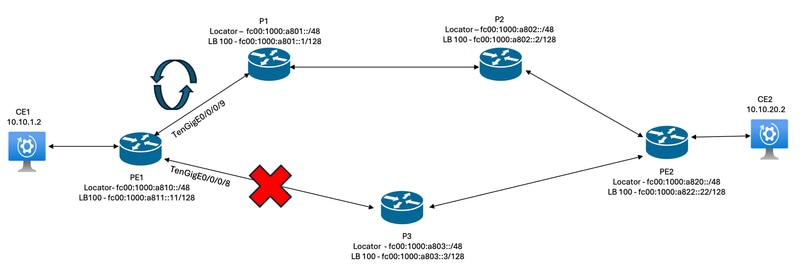
Figure 2. microloop Occurrence
On PE1 when the link tengig 0/0/8 goes down, on the backup path between PE1 and P1, a microloop is suspected which in turn triggers microloop avoidance (MLA) mechanism on PE1.
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:PE1#show logging
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:Mar 21 08:30:10.244 UTC: ifmgr[307]: %PKT_INFRA-LINK-5-CHANGED : Interface TenGigE0/0/0/8, changed state to Administratively Down
When the interface TenGigE0/0/0/8 when down, first there is an Fast Reroute (FRR) event, that is, traffic is sent on the TI-LFA path.
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:PE1#show cef trace
Mar 21 08:30:10.244 fib/common/frr 0/RP0/CPU0 43# t5991 Common: FRR-ITF-EVENT: proto=3 type=0 ifh=0x3c0000a0
Mar 21 08:30:10.244 fib/common/frr 0/RP0/CPU0 13# t5991 IPv6: FRR-LOOKUP-DONE: evt=0, ifh=0x3c0000a0, main_ifh=0, proto=1
Mar 21 08:30:10.244 fib/common/frr 0/RP0/CPU0 12# t5991 IPv6: FRR-ITF-EVENT: Global Active; handle:0x3c0000a0[0x0]
Mar 21 08:30:10.244 fib/common/frr 0/RP0/CPU0 13# t5991 IPv6: FRR-ITF-EVENT: FRR Active; handle:0x3c0000a0[0x0]
Mar 21 08:30:10.244 fib/common/frr 0/RP0/CPU0 1# t5991 IPv6: FRR-EVENT: evt=0, notify protocol=1, ifh=0x0, switched=111768 ns
Mar 21 08:30:10.244 fib/common/fast 0/RP0/CPU0 20# t5991 Common: PLAT-UPD-FAST: Proto=common, Obj[FIB_DATA_TYPE2_ALL]=0, flags=0 Acttype=FRR_EOD
At 08:30:10:307, there is an IS-IS delete adjacency.
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:PE1#show isis lsp last 20
08:30:10:307 1 Te0/0/0/8 DELADJ
At 08:30:10:358, Label Switched Path (LSP) was received, Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP) was calculated, and uloop was activated.
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:PE1#show isis spf-log detail
08:30:10:358 FSPF 2 5 2 PE1.00-00 DELADJ LINKBAD
Delay: 50ms (since first trigger)
46257ms (since end of last calculation)
Trigger Link: P3.00
Trigger Next Hop: P3
New LSP Arrivals: 0
SR uloop: Link Down
Seeing these events more in detail in IS-IS trace, in this case, the configured Routing Information Base (RIB) update delay time is: 65535 ms ~ 65 sec.
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:PE1#show isis trace all
Mar 21 08:30:10.308 isis/Mring_2801/std 0/RP0/CPU0 t8712 isis_roca_event_schedule_result_debug:329 SPF_TRIGGER_PRIMARY L2 IPv6 Unicast
Mar 21 08:30:10.308 isis/Mring_2801/spf 0/RP0/CPU0 t8712 isis_roca_spf_linkchanged_trigger:2609 SPF_TRIGGER_LINKCHANGED_ADD L2 IPv6 Unicast 0370.0011.0011.00
Mar 21 08:30:10.358 isis/Mring_2801/std 0/RP0/CPU0 6669# t8712 isis_roca_event_start:1541 SPF_ROCA_START L2 IPv6 Unicast SPF Type: Full >>>>>>>>. SPF was trigger
Mar 21 08:30:10.358 isis/Mring_2801/sr_ 0/RP0/CPU0 t8712 isis_roca_sr_uloop_prep:3069 SR_ULOOP_SPF_PREP_START L2 IPv6 Unicast SPF Type: Full>>>>>>>> uloop activated and uloop path installed
Mar 21 08:30:10.358 isis/Mring_2801/sr_ 0/RP0/CPU0 8451# t8712 isis_roca_uloop_install_exp_path:3915 SR_ULOOP_DETAIL_ADD_EXP_PATH L2 IPv6 Unicast SPF Type: Full
Mar 21 08:30:10.358 isis/Mring_2801/sr_ 0/RP0/CPU0 t8712 isis_roca_prefix_update_run:1040 SR_ULOOP_SPF_START_DELAYED_UPD_TIMER_8 L2 IPv6 Unicast SPF Type: Full 65535 >>>>>> the MLA timer has began
Mar 21 08:30:10.864 isis/Mring_2801/std 0/RP0/CPU0 t8712 isis_roca_frr_run:1538 SPF_FRR_DEFERRED_ULOOP L2 IPv6 Unicast
Mar 21 08:31:15.893 isis/Mring_2801/sr_ 0/RP0/CPU0 t8712 isis_ip_rib_worker_delayed_update_run:2344 SR_ULOOP_EVENT_DELAYED_UPDATE L2 IPv6 Unicast >> after 65 seconds the rib is updated and MLA is deactivated
RIB status at the time when MLA is active.
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:PE1#show route ipv6 fc00:1000:a820:: detail
Routing entry for fc00:1000:a820::/48
Routing Descriptor Blocks
fe80::a2b4:39ff:feff:d416, from fc00:1000:a822::22, via TenGigE0/0/0/9
Route metric is 6000
<snip>
SRv6 Headend: H.Insert.Red [f3216], SID-list {fc00:1000:a802::} ##this locator of P2 is inserted before the SRH
Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF) status at the time when MLA is active.
RP/0/RP0/CPU0: PE1#show cef ipv6 fc00:1000:a820:: detail
local adjacency to TenGigE0/0/0/9
<snip>
via fe80::a2b4:39ff:feff:d416/128, TenGigE0/0/0/9, 10 dependencies, weight 0, class 0 [flags 0x0]
SRv6 H.Insert.Red SID-list {fc00:1000:a802::} ## P node (locator of P2)sid is inserted into the packet
Load distribution: 0 (refcount 9)
Hash OK Interface Address
0 Y TenGigE0/0/0/9 fe80::a2b4:39ff:feff:d416
A packet originating from PE1 is forwarded via P1 with P2s Micro-Segment Identifier (uSID) as the first active destination. When the packet reaches P2, the SRv6 behavior associated with the uSID triggers Segment Routing Header (SRH) decapsulation, after which the original packet is forwarded to PE2 under MLA forwarding.
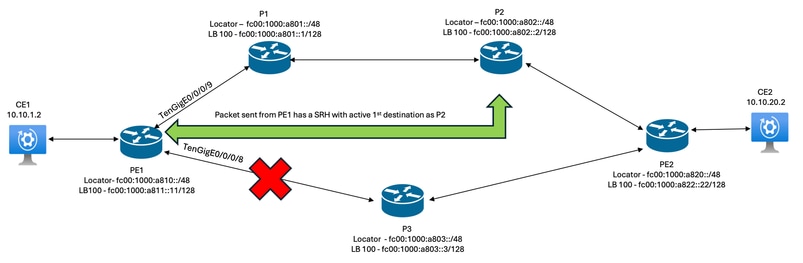
Figure 3. The Path Taken During MLA
Packet forwarded by PE1 and P1 during MLA.
Frame 1: 160 bytes on wire (1280 bits), 160 bytes captured (1280 bits)
Ethernet II, Src: Cisco_a7:8a:0d (c4:b2:39:a7:8a:0d), Dst: Cisco_ff:d4:16 (a0:b4:39:ff:d4:16)
Internet Protocol Version 6, Src: fc00:1000:a811::11, Dst: fc00:1000:a802:: >> during MLA the 1st active destination locator is of P2
0110 .... = Version: 6
<0110 .... = Version: 6 [This field makes the filter match on "ip.version == 6" possible]>
.... 0000 0000 .... .... .... .... .... = Traffic Class: 0x00 (DSCP: CS0, ECN: Not-ECT)
.... 0000 0000 0000 1110 1111 = Flow Label: 0x000ef
Payload Length: 106
Next Header: Routing Header for IPv6 (43) >> indicates the next header is a SRH
Hop Limit: 254
Source Address: fc00:1000:a811::11
<Source or Destination Address: fc00:1000:a811::11>
<[Source Host: fc00:1000:a811::11]>
<[Source or Destination Host: fc00:1000:a811::11]>
Destination Address: fc00:1000:a802::
<Source or Destination Address: fc00:1000:a802::>
<[Destination Host: fc00:1000:a802::]>
<[Source or Destination Host: fc00:1000:a802::]>
Routing Header for IPv6 (Segment Routing) >>>>>>>>> SRH header which contains the orginal PE2 locator
Next Header: IPIP (4)
Length: 2
[Length: 24 bytes]
Type: Segment Routing (4)
Segments Left: 1
Last Entry: 0
Flags: 0x00
Tag: 0000
Address[0]: fc00:1000:a820:e003:: >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> PE2 locator : function
Internet Protocol Version 4, Src: 10.10.1.2, Dst: 10.10.20.2
0100 .... = Version: 4
.... 0101 = Header Length: 20 bytes (5)
After decapsulation, the orginal packet is sent by P2 and the SRH is removed by P2 during MLA.
Frame 1: 136 bytes on wire (1088 bits), 136 bytes captured (1088 bits)
Ethernet II, Src: Cisco_87:d8:58 (b0:a6:51:87:d8:58), Dst: Cisco_af:48:01 (c8:47:09:af:48:01)
Internet Protocol Version 6, Src: fc00:1000:a811::11, Dst: fc00:1000:a820:e003::
0110 .... = Version: 6
<0110 .... = Version: 6 [This field makes the filter match on "ip.version == 6" possible]>
.... 0000 0000 .... .... .... .... .... = Traffic Class: 0x00 (DSCP: CS0, ECN: Not-ECT)
.... 0000 0000 0000 1110 1111 = Flow Label: 0x000ef
Payload Length: 82
Next Header: IPIP (4)
Hop Limit: 252
Source Address: fc00:1000:a811::11
<Source or Destination Address: fc00:1000:a811::11>
<[Source Host: fc00:1000:a811::11]>
<[Source or Destination Host: fc00:1000:a811::11]>
Destination Address: fc00:1000:a820:e003::
<Source or Destination Address: fc00:1000:a820:e003::>
<[Destination Host: fc00:1000:a820:e003::]>
<[Source or Destination Host: fc00:1000:a820:e003::]>
Internet Protocol Version 4, Src: 10.10.1.2, Dst: 10.10.20.2
Data (62 bytes)
After convergency (after RIB update delay timer), the SRH inserted is removed and the packet is sent on the converged best Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) path.
RP/0/RP0/CPU0: PE1#show cef ipv6 fc00:1000:a822::22/128
local adjacency to TenGigE0/0/0/9
Prefix Len 128, traffic index 0, precedence n/a, priority 1
via fe80::a2b4:39ff:feff:d416/128, TenGigE0/0/0/9, 9 dependencies, weight 0, class 0 [flags 0x0]
path-idx 0 NHID 0x0 [0x8ef0f2b0 0x0]
next hop fe80::a2b4:39ff:feff:d416/128
local adjacency
Timeline Summary
|
Time
|
Action
|
Mechanism
|
|
08:30:10.244
|
Link failure, traffic shift to backup path
|
TI-LFA
|
|
08:30:10:307
|
LSP received, new Shortest Path First (SPF) calculated
|
MLA (triggered)
|
|
08:30:10.358
|
RIB update is delayed, traffic is using MLA tunnel
|
MLA (active)
|
|
08:31:15.893
|
Delay timer expiries, final path installed in FIB
|
Full convergency
|
Conclusion
This document detailed how IS-IS–advertised SRv6 uSID paths support MLA during network convergence. By encoding ordered topological intent directly into the uSID list, traffic is steered through a deterministic sequence of nodes, ensuring loop-free forwarding even while IS-IS SPF calculations are temporarily inconsistent across the network.
During convergence, packets egressing from ingress PEs takes the precomputed uSID sequence, traversing intermediate P nodes without relying on transient IGP next-hop decisions. The decapsulation behavior at the designated uSID endpoint ensures clean transition back to native forwarding once the protected segment is completed. This tightly coupled interaction between IS-IS control-plane updates and SRv6 uSID data-plane behaviors enables fast and deterministic rerouting.
IS-IS uSID–based MLA provides a scalable, topology-aware, and operationally simple solution for microloop-free convergence, making it well suited for large SRv6-enabled networks where fast reroute and deterministic traffic steering are critical.
Commands
- #show isis instance <> ipv6 microloop avoidance <prefix> detail
- #show isis





 Feedback
Feedback