|
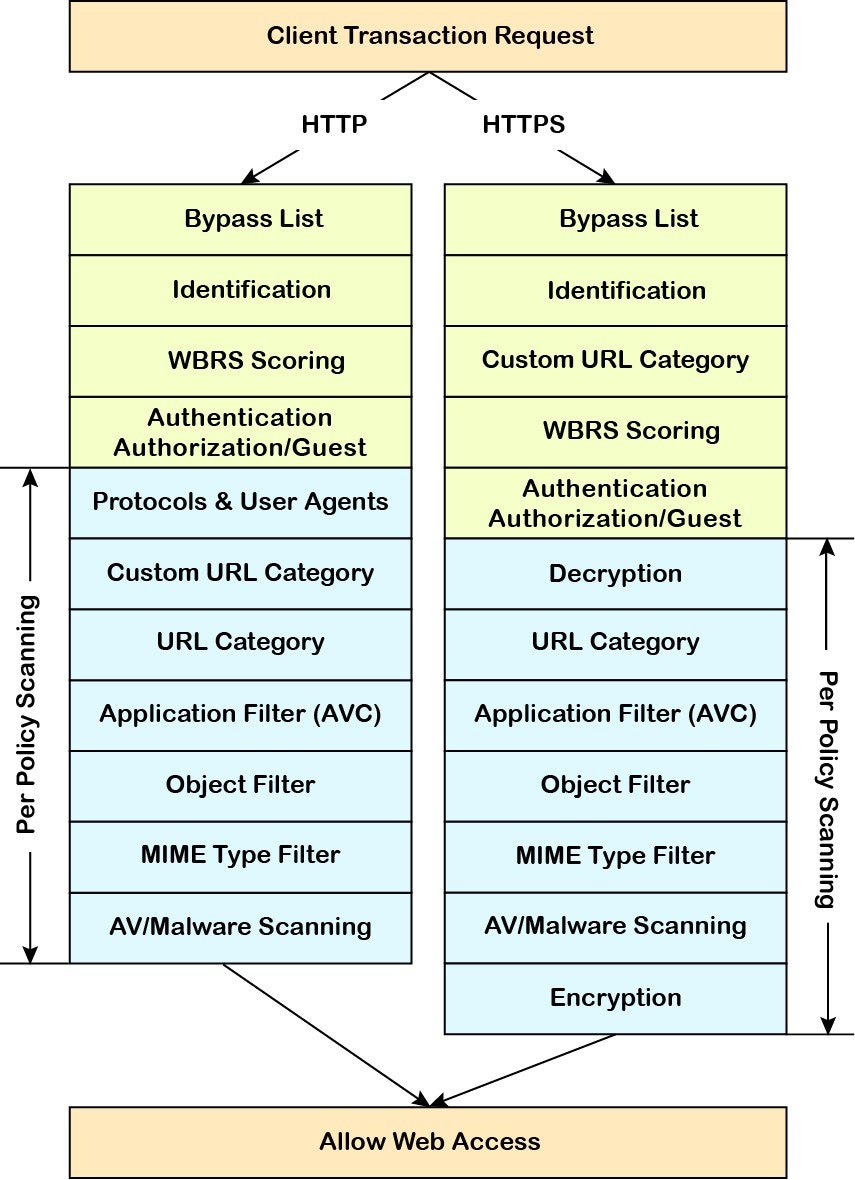
Protocols
and User Agents
|
Used to
control policy access to protocols and configure blocking for particular client
applications, such as instant messaging clients, web browsers, and Internet
phone services. You can also configure the appliance to tunnel HTTP CONNECT
requests on specific ports. With tunneling enabled, the appliance passes HTTP
traffic through specified ports without evaluating it.
|
|
URL
Filtering
|
AsyncOS for
Web allows you to configure how the appliance handles a transaction based on
the URL category of a particular HTTP or HTTPS request. Using a predefined
category list, you can choose to block, monitor, warn, or set quota-based or
time-based filters.
You can
also create custom URL categories and then choose to block, redirect, allow,
monitor, warn, or apply quota-based or time-based filters for Websites in the
custom categories. See
カスタム URL カテゴリの作成および編集
for information about creating custom URL categories.
In
addition, you can add exceptions to blocking of embedded or referred content.
|
|
Applications
|
The AVC or ADC engine is an acceptable use policy component which inspects web traffic to gain deeper understanding and control
of web traffic used for applications. You can configure the web proxy to be configured to block or allow application based
on the application types, and by individual applications.
Starting with AsyncOS 15.0, you can use either AVC or ADC engine to monitor web traffic. By default, AVC is enabled.
While the AVC engine operates the same as ADC, the AVC engine supports a limited number of applications. In AVC you can also
apply controls to particular application behaviors, such as, file transfer within a particular application. See Web アプリケーションへのアクセスの管理 for configuration information
|
Note
|
In the post-configuration of ADC activities, the ADC application engine searches or evalutes for the activity information
for a particular traffic.
|
Due to the ADC signature database update, even if the entire category is set to Block, any new applications added will be set to Monitor by default.
|
|
Objects
|
These
options let you configure the Web Proxy to block file downloads based on file
characteristics, such as file size,
file type, and MIME type. An
object is, generally, any item that can be individually selected, uploaded,
downloaded and manipulated. See
アクセス ポリシー:オブジェクトのブロッキング
for information about specifying blocked objects.
|
|
Anti-Malware and Reputation
|
Web reputation filters allow for a web-based reputation score to be assigned to a URL to determine the probability of it
containing URL-based malware. Anti-malware scanning identifies and stops web-based malware threats. Secure Endpoint identifies malware in downloaded files.
The
Anti-Malware and Reputation policy inherits global settings respective to each
component. Within
Security Services >
Anti-Malware and Reputation, malware categories can
be customized to monitor or block based on malware scanning verdicts and web
reputation score thresholds can be customized. Malware categories can be
further customized within a policy. There are also global settings for file
reputation and analysis services.
For more information, see アクセス ポリシーにおけるマルウェア対策およびレピュテーションの設定 and Configuring File Reputation and Analysis Features.
|
|
HTTP ReWrite Profile
|
You can configure custom header profiles for HTTP requests and can create multiple headers under a header rewrite profile.
The header rewrite profile feature enables the appliance to pass the user and group information to another upstream device
after successful authentication. The upstream proxy considers the user as authenticated, bypasses further authentication,
and provides access to the user based on the defined access policies.
See ポリシーごとの Web プロキシ カスタム ヘッダー.
|
|
Clone Policy
|
If an existing policy has most of the settings that you want in a new policy, you can save time by cloning the existing policy
and then modifying it. Although the cloned policy shares the same grouping attributes, it has its own unique identity, such
as the display name, IP address, host, and domain name.
The following policies with cloning option in Secure Web Appliance can also be managed by Cisco Secure Email and Web Manager
(SMA).
|
Note
|
You can clone only one policy at an instance.
|
|
|
Delete
|
Deletes the created policy.
|

 フィードバック
フィードバック