Information about Software-Defined Access Wireless
The Enterprise Fabric provides end-to-end enterprise-wide segmentation, flexible subnet addressing, and controller-based networking with uniform enterprise-wide policy and mobility. It moves the enterprise network from current VLAN-centric architecture to a user group-based enterprise architecture, with flexible Layer 2 extensions within and across sites.
Enterprise fabric is a network topology where traffic is passed through inter-connected switches, while providing the abstraction of a single Layer 2 or Layer 3 device. This provides seamless connectivity, with policy application and enforcement at the edge of the fabric. Fabric uses IP overlay, which makes the network appear as a single virtual entity without using clustering technologies.
The following definitions are used for fabric nodes:
-
Enterprise Fabric: A network topology where traffic is passed through inter-connected switches, while providing the abstraction of a single Layer 2 or Layer 3 device.
-
Fabric Domain: An independent operation part of the network. It is administered independent of other fabric domains.
-
End Points: Hosts or devices that connect to the fabric edge node are known as end points (EPs). They directly connect to the fabric edge node or through a Layer 2 network.
The SD-Access solution combines the Cisco Catalyst Center software and fabric wireless controller funtionality. In an SD-Access solution, a fabric site is composed of an independent set of fabric control plane nodes, edge nodes, intermediate (transport only) nodes, and border nodes.
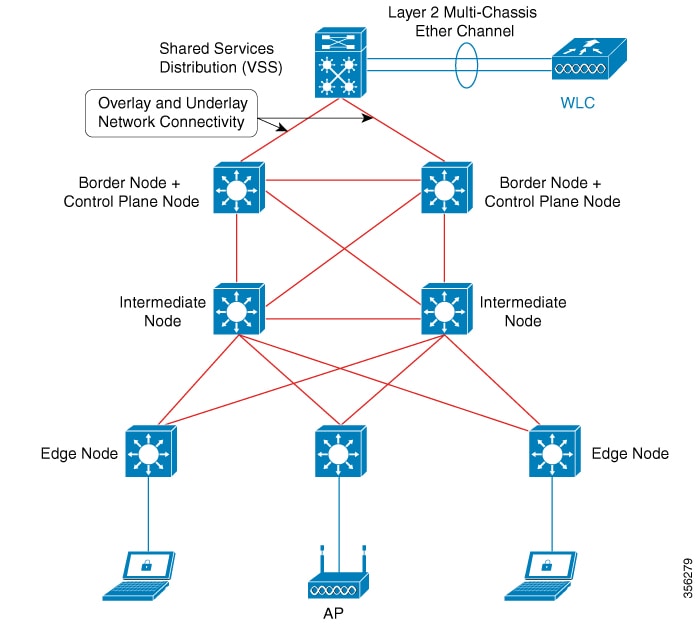
The following figure shows the components of a typical SD-Access Wireless. It consists of Fabric Border Nodes (BN), Fabric Intermediate Nodes (IN), Fabric Edge Nodes (EN), Wireless Controller, Cisco Catalyst Center, and Host Tracking Database (HDB).
This figure covers the following concepts:
-
Cisco Catalyst Center: Is an open, software-driven architecture built on a set of design principles with the objective of configuring and managing Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controllers.
-
Wireless Controller (WLCs): The controller provides AP image and configuration management, client session management and mobility. Additionally, it registers the mac address of wireless clients in the host tracking database at the time of client join, as well as updates the location at the time of client roam.
-
Shared Services Distribution (VSS): WLCs typically connect to a shared services distribution block that is part of the underlay. The preferred distribution block has chassis redundancy and also the capability to support L2 multichassis EtherChannel connections for link and platform redundancy to the WLCs.
-
Underlay Network: The underlay network is defined by the physical switches used to deploy the SD-Access network. The underlay implementation for SD-Access uses a well-designed Layer 3 foundation inclusive of the campus edge switches to ensure performance, scalability, and high availability of the network.
-
Overlay Network: An overlay network is created on top of the underlay to create a virtualized network. Multiple overlay networks can run across the same underlay network to support multitenancy through virtualization. Each overlay network appears as a virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) instance for connectivity to external networks.
-
Border Node: These nodes connect traditional Layer 3 networks or different fabric domains to the enterprise fabric domain. If there are multiple fabric domains, these nodes connect a fabric domain to one or more fabric domains, which could be of the same or different type. These nodes are responsible for translation of context from one fabric domain to another. When the encapsulation is the same across different fabric domains, the translation of fabric context is generally 1:1. The fabric control planes of two domains exchange reachability and policy information through this device.
-
Control Plane Node: This allows the network to determine the location of a device or user. When the EP ID of a host is learnt, other end points can query the database about the location of the host. The flexibility of tracking subnets helps in summarization across domains and improves the scalability of the database.
-
Intermediate Node: Are part of the Layer 3 network used to interconnect the edge nodes to the border nodes. Intermediate nodes route and transport IP traffic in fabric.
-
Edge Node: These nodes are responsible for admitting, encapsulating or decapsulating, and forwarding of traffic from the EPs. They lie at the perimeter of the fabric and are the first points of attachment of the policy. EPs could be directly or indirectly attached to a fabric edge node using an intermediate Layer 2 network that lies outside the fabric domain. Traditional Layer 2 networks, wireless access points, or end hosts are connected to fabric edge nodes.
-
Access Points: AP applies all the wireless media specific features. For example, radio and SSID policies, webauth punt, peer-to-peer blocking, and so on. It establishes CAPWAP control and data tunnel to controller. It converts 802.11 data traffic from wireless clients to 802.3 and sends it to the access switch with VXLAN encapsulation.
In this deployment scenario, the wireless controllers are connected to the border nodes using the Shared Services Distribution (VSS). Here, VSS refers to the modular configuration switch. The fabric deployment covers border nodes, intermediate nodes, and edge nodes. All the nodes are interconnected to each other using Layer 3 connections. The laptops and access points receive the data traffic (IP connectivity) using Layer 2 connections.
 Note |
The RED lines are all Layer 3 connections. The BLUE lines connected to laptops and access points are Layer 2 connections. |
The SDA allows to simplify:
-
Addressing in wireless networks
-
Mobility in wireless networks
-
Guest access and move towards multi-tenancy
-
Leverage Sub-net extension (stretched subnet) in wireless network
-
Provide consistent wireless policies
Platform Support
|
Platforms |
Support |
|---|---|
|
Catalyst 9300 |
Yes |
|
Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller for Cloud |
Yes |
|
Cisco Catalyst 9800-40 Series Wireless Controller |
Yes |
|
Cisco Catalyst 9800-80 Series Wireless Controller |
Yes |
|
Multi-instance |
Support |
|---|---|
|
Multiple LISP sessions |
Yes |
|
Emulated database support |
Yes |
|
Client roaming between WNCd instances |
Yes |
|
Feature |
Support |
|---|---|
|
Inter-WLC roam for IRCM |
Only L2 mobility is supported as VLAN is stretched across the fabric. |
|
DNS-IPv4-ACL |
|
|
IPv6 ACL for clients |
Yes. Open, 802.11x, WebAuth, PSK WLANs, IPv6 address visibility are also supported. |
|
Location tracking/Hyperlocation |
Yes |
|
Multicast Video-Stream (IPv4) |
Yes |
|
Smart Licensing |
Yes |
|
AP |
Support |
|---|---|
|
1542 |
Yes |
|
1560 |
Yes |
 Feedback
Feedback