Introduction to Wi-Fi Alliance Agile Multiband
The Wi-Fi Alliance Agile Multiband (MBO) feature enables better use of Wi-Fi network resources. This feature is built on the fundamental premise that both Wi-Fi networks and client devices have information that can enable better roaming decisions and improve the overall performance of Wi-Fi networks and user experience.
 Note |
This feature applies to MBO certified clients only. |
This feature certifies the interoperability of a bundle of features that are defined by the IEEE standard amendments 802.11k, 802.11v, and 802.11u, as well as the Wi-Fi-Alliance defined specifications. These technologies are used to exchange access points (AP), band, and channel preferences, link quality, and status information between AP and client device.
MBO focuses on the following:
-
Interactions between the wireless clients and APs
-
Exchange of AP and client knowledge about the wireless medium (such as RF neighbors)
-
Allow clients to work with APs and take intelligent decisions on the connection and improve the quality of service.
Wi-Fi Alliance Agile Multiband Topology
Multiple components form a Wi-Fi Agile Multiband wireless infrastructure network, which may vary based on the wireless network deployment.
The following figure depicts the system topology for connecting Wi-Fi Agile Multiband devices.
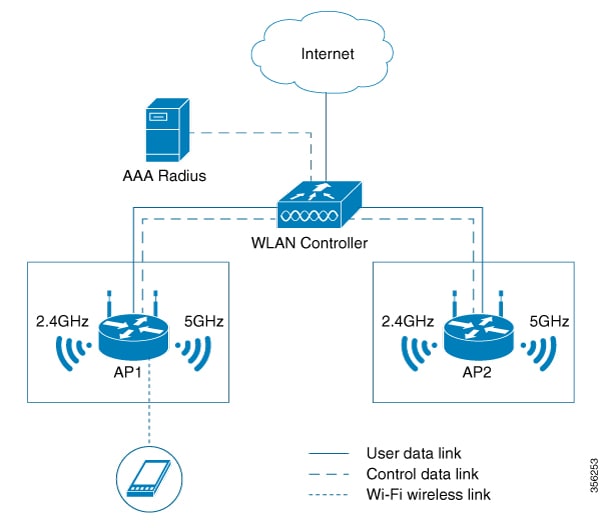
The following components form a Wi-Fi Agile Multiband wireless infrastructure network:
-
Access Point (AP): A Wi-Fi Agile Multiband wireless infrastructure network contains one or more Wi-Fi Agile Multiband APs.
-
WLAN Controller: A Wi-Fi Agile Multiband wireless infrastructure network contains zero or more WLAN controllers that provide centralized management and other features to the interconnected APs.
-
Client Station (STA): A Wi-Fi Agile Multiband wireless infrastructure network contains zero or more STAs. These client STAs are single WLAN capable only.
-
RADIUS Server: A Wi-Fi Agile Multiband wireless infrastructure network contains zero or more RADIUS Servers that provide Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) services.
Supported MBO Components
MBO AP CapabilityA new information element is added to the Beacon, Probe Response, Association Response and Re Association Response Frames for 802.11ax APs to inform clients about MBO support.
 Note |
The new information element indicates that Cisco APs are not cellular data aware. |
When an SSID is configured on an AP, the MBO AP capability is enabled.
802.11k/v/r SupportOne of the prerequisites for MBO is that APs need to support 802.11k/v/r standard-based technologies. Each of the technologies has their own requirements, such as:
-
802.11k – For 802.11k, send the preferred list of AP neighbors to the client upon request and send a beacon request to a client when AP requires a beacon report from the client.
-
802.11v – For 802.11v, steer the client to a less congested AP (not in a MBO client’s non-prefer/non-operable channel list that is sent during the association request and/or WNM notification request) using BSS transition.
-
802.11r – The 802.11r MBO-related capabilities are not supported.
For MBO, the 802.11ax APs must have 802.11u ANQP or GAS support.
The following are the prerequisites:
-
ANQP responds to the ANQP request for a neighbor report ANQP-element.
-
Before authentication, Layer 2 transport needs to be available in the network between a mobile device and server for an advertisement protocol frame.
Whenever an AP sends a beacon request to the client, the MBO-compliant client responds with a beacon report.
MBO Associate Disallowed IECisco APs include an Associate Disallowed IE in their Beacon/Probe response/(Re) association response when they cannot accommodate any new client.
 Feedback
Feedback