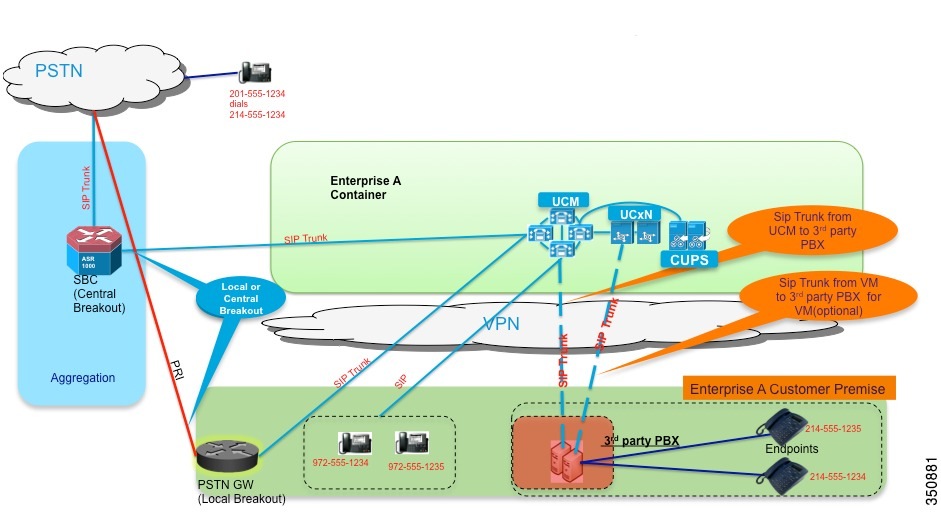
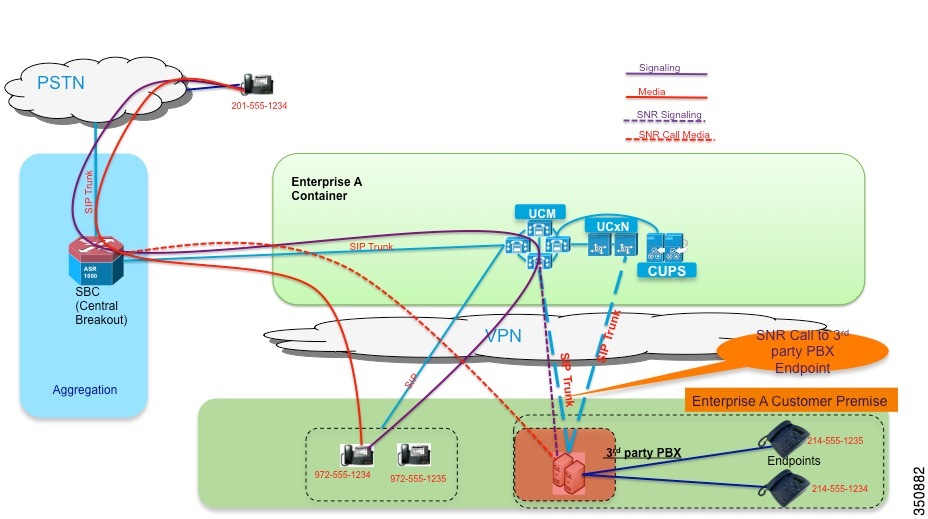
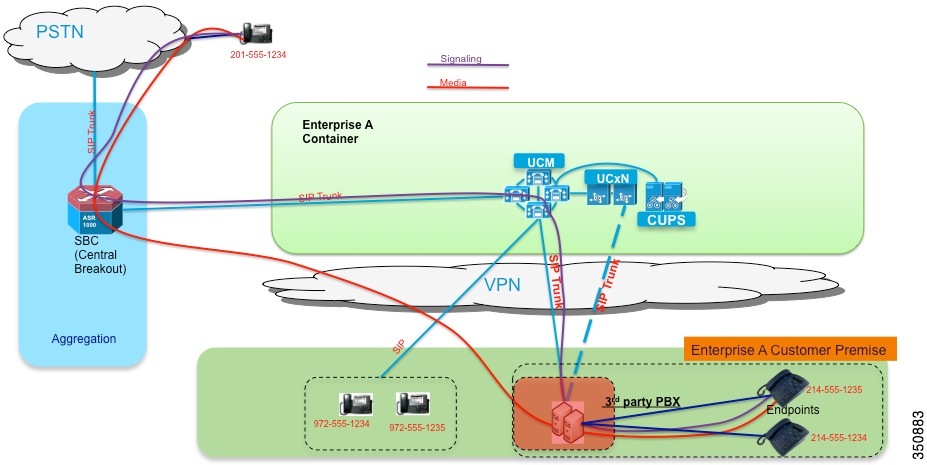
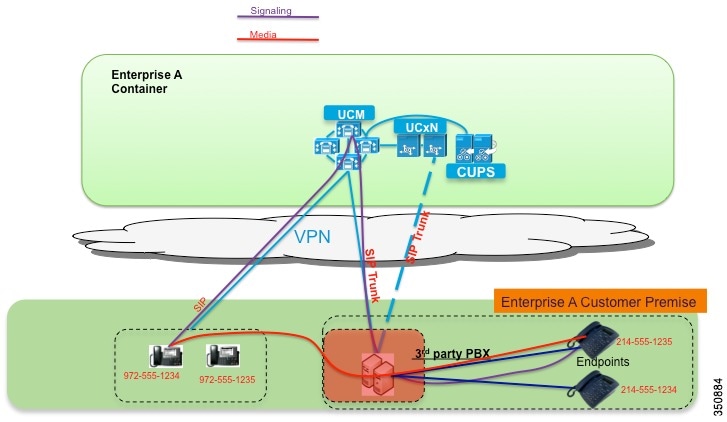
Third-Party Applications and Integrations
The Cisco Hosted Collaboration Solution (HCS) uses the same UC applications that are used to deploy on-premises deployments. Cisco and its partners certify many applications through the Interoperability Verification Testing (IVT) program for integration into Cisco UC products and these are cataloged in the Cisco Developer Network (CDN) at http://developer.cisco.com.
Because Cisco HCS uses Cisco Hosted Collaboration Mediation Fulfillment (HCM-F) with Unified Communications Domain Manager as domain manager, be aware that automated provisioning may not be available through Unified Communications Domain Manager, and manual provisioning may be necessary. HCS Service Assurance may not apply to these integrations.
 Feedback
Feedback