Supported Storage Controllers and Cables
This server supports a single, PCIe-style, SAS RAID or HBA controller that plugs into a dedicated internal socket.
 Note |
For SFF, 8-drives version only (UCSC-C240-M5S): Do not mix controller types in the server. Do not use the embedded SATA controller and a hardware-based RAID controller card to control front-loading drives at the same time. This combination is not supported and could result in data loss. |
 Note |
NVMe PCIe SSDs cannot be controlled by a SAS/SATA RAID controller. |
This server supports the RAID and HBA controller options and cable requirements shown in the following table.
|
Controller |
Server Version/Maximum Drives Controlled |
RAID Levels |
Optional Supercap Backup? |
Required Cables |
|
Embedded RAID (PCH SATA) |
|
0, 1, 10 |
No |
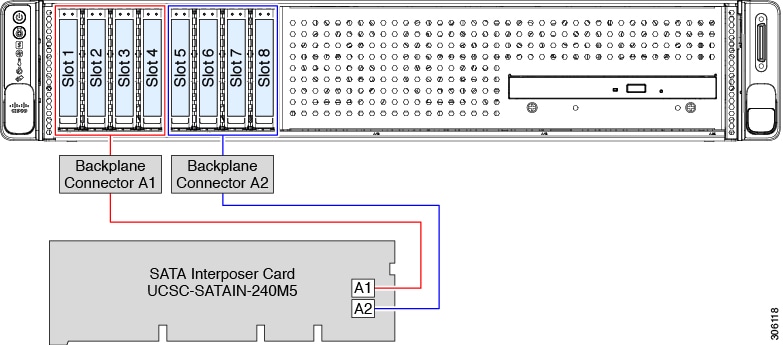
UCSC-C240-M5S only: Use the SAS/SATA cable included with the chassis to connect the interposer to the front drive backplane. No cables are required for control of internal SATA M.2 drives. |
|
Cisco 12G Modular RAID Controller UCSC-RAID-M5 Includes 2-GB cache; controls up to 16 drives. |
This controller is supported only in the following server versions:
|
0, 1, 5, 6, 10, 50, 60 JBOD mode is also supported. |
Yes |
Use SAS/SATA cable included with chassis to connect controller to drive backplanes. |
|
Cisco 12G Modular RAID Controller UCSC-RAID-M5HD Includes 4-GB cache; controls up to 26 drives |
This controller is supported only in the following server version:
|
0, 1, 5, 6, 10, 50, 60 JBOD mode is also supported. |
Yes |
Use SAS/SATA cable included with chassis to connect controller to drive backplanes. |
|
Cisco 12G Modular SAS HBA UCSC-SAS-M5 Controls up to 16 drives. |
This controller is supported only in the following server versions:
|
Non-RAID |
No |
Use SAS/SATA cable included with chassis to connect controller to drive backplanes. |
|
Cisco 12G Modular SAS HBA (For Up To 24 Drives) UCSC-SAS-M5HD Controls up to 24 drives. |
This controller is supported only in the following server version:
|
Non-RAID |
No |
Use SAS/SATA cable included with chassis to connect controller to drive backplanes. |
|
Cisco 12G 9400-8e HBA for external JBOD attach UCSC-9400-8E |
Supported in all server versions: 8 external SAS/SATA ports, controlling up to 1024 external drives. |
Non-RAID |
No |
External drive cables not sold by Cisco. NOTE: This HBA does not support optical cables for connection to external storage (copper only). |




 Feedback
Feedback