- Preface
- Installing UCS NID Controller
- Configuration Management
- Administering the Cisco ME 1200 NID
- Configuring Notifications
- Zero Touch Provisioning
- Auto Discovery of Cisco ME 1200 NIDs
- Configuring Synchronous Ethernet
- Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connections
- Configuring Switch Ports
- Configuring Spanning-Tree Protocol
- Configuring Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
- Provisioning Link Layer Discovery Protocol
- Configuring SNMP
- Configuring PTP
- Configuring ACLs
- Configuring Quality of Service (QoS)
- Configuring Ethernet OAM, Link OAM, and CFM
- Configuring Performance Monitoring
- Configuring EPS
- Configuring ERPS
- Configuring L2CP
- Configuring MAC Security
- Configuring NTP
- Configuring Storm Control
- Configuring Syslog
- Configuring SPAN
- Configuring RSPAN
- Configuring RFC 2544
- Configuring sFlow
- Configuring UDLD
- Configuring LST
- Configuring Flex Links
- Configuring Y.1564
- Configuring Bulk Provisioning
- Template Management
Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connections
Ethernet Virtual Connection (EVC) as an association between two or more user network interfaces that identifies a point-to-point or multipoint-to-multipoint path within the service provider network. An EVC is a conceptual service pipe within the service provider network. A bridge domain is a local broadcast domain that is VLAN-ID-agnostic. An ethernet flow point (EFP) service instance is a logical interface that connects a bridge domain to a physical port or to an EtherChannel group in a router.
The Cisco ME 1200 NID supports the application software control modules and interfaces related to EVC.
- How to Configure Ethernet Virtual Circuit
- Configuring Ethernet Virtual Circuit
- Creating a Policer
- EVC Control Entry (ECE) Configuration
- Ethernet Private Line or E-LAN
- Ethernet Virtual Private Line
- Other Commands For EVC Configuration
How to Configure Ethernet Virtual Circuit
Configuring Ethernet Virtual Circuit
Example
UCS# ProvisionEVC UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addEVC evcConfiguration instance 7 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addEVC evcConfiguration nni_vid 101 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addEVC evcConfiguration learning enable UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addEVC evcConfiguration nni_ports GigabitEthernet_6_NNI enable UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addEVC evcConfiguration policer_id 1 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addEVC review UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addEVC commit AddEVC Commit Success!!!
Creating a Policer
-
Maximum 510 ECEs can be configured with or without configuring QoS (0-7 COS) with one NNI port to one UNI port.
-
Maximum of 340 ECEs can be configured with or without configuring QoS (0-7 COS) with two NNI ports to one UNI or one NNI port to two UNI ports.
-
Maximum of 255 ECEs can be configured with or without configuring QoS (0-7 COS) with three NNI ports to one UNI port or one NNI port to three UNI ports.
-
Maximum of 170 ECEs can be configured with or without configuring QoS (0-7 COS) with four NNI ports to one UNI port or one NNI port to four UNI ports.
-
Maximum of 128 ECEs can be configured with or without configuring QoS (0-7 COS) with five NNI ports to one UNI port or one NNI port to five UNI ports.
EVC Control Entry (ECE) Configuration
ECE rules are used to divide the UNI traffic into two service classes.
This division of UNI traffic is achieved through:
- Simple NNI: All EVCs on the NNI
port use the same QoS mapping and statistics.

Note
This method requires fewer resources. - Advanced NNI: Each EVC on the NNI port has separate QoS mapping and statistics.
In the following example, multiple ECE rules are created:
- Configuring ECE Sample Rule 1
- Configuring the ECE Sample Rule 2
- Configuring ECE Sample Rule 3
- Configuring ECE Sample Rule 4
- Configuring ECE Sample Rule 5
Configuring ECE Sample Rule 1
For rule 1, frames received on the UNI port with PCP 4-7 values are mapped to class 4 and sent with PCP 4 in the outer tag on the NNI port.
Example
UCS# ProvisionEVC UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration ece_id 1 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration ece_id 1 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control actions evc_id specific 777 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control actions tag_pop_count 1 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control actions policer_id none UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control ingress_match uni_ports GigabitEthernet_2_UNI enable UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control ingress_match outer_tag_match match_type c_tagged UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control ingress_match outer_tag_match match_fields vlan_id_filter specific 100 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control ingress_match outer_tag_match match_fields inner_dei any UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control ingress_match outer_tag_match match_fields inner_pcp val_any UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE review Commands in queue: addECE ece_configuration ece_id 1 addECE ece_configuration ece_id 1 addECE ece_configuration control actions evc_id specific 777 addECE ece_configuration control actions tag_pop_count 1 addECE ece_configuration control actions policer_id none addECE ece_configuration control ingress_match uni_ports GigabitEthernet_2_UNI enable addECE ece_configuration control ingress_match outer_tag_match match_type c_tagged addECE ece_configuration control ingress_match outer_tag_match match_fields vlan_id_filter specific 100 addECE ece_configuration control ingress_match outer_tag_match match_fields inner_dei any addECE ece_configuration control ingress_match outer_tag_match match_fields inner_pcp val_any UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE commit Clearing Socket 4 Clearing Socket 4 AddECE Commit Success!!!
Configuring the ECE Sample Rule 2
For rule 2, other frames received on the UNI port are mapped to class 0 and sent with PCP 0 in the outer tag on the NNI port.
 Note | The configuration steps are similar to the ones mentioned in the Configuring ECE Rule 1 section. |
Example
UCS# ProvisionEVC UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control actions evc_id specific 7 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control actions tag_pop_count 1 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control actions policer_id specific 1 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control actions class specific 0 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control ingress_match uni_ports GigabitEthernet_2_UNI enable UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control ingress_match outer_tag_match match_type c_tagged UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control ingress_match outer_tag_match match_fields vlan_id_filter specific 99 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control ingress_match outer_tag_match match_fields inner_pcp val_0-3 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control egress_outer_tag pcp_mode fixed UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control egress_outer_tag pcp_value 0 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE commit
Configuring ECE Sample Rule 3
For rule 3, frames received on the NNI port 6 with S-tag 101 and C-tag 100 with any PCP values can be mapped to class 4 and sent with PCP 4 on the UNI port.
 Note | The configuration steps are similar to the ones mentioned in the Configuring ECE Rule 1 section. |
Example
UCS# ProvisionEVC UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration ece_id 3 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control actions evc_id specific 7 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control actions class specific 4 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control ingress_match uni_ports GigabitEthernet_2_UNI enable UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control egress_inner_tag pcp_mode fixed UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control egress_inner_tag pcp_value 4 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE commit
Configuring ECE Sample Rule 4
For rule 4, insert a new c-tag in frames forwarding to the NNI port.
 Note | The configuration steps are similar to the ones mentioned in the Configuring ECE Rule 1 section. |
Example
UCS# ProvisionEVC UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration ece_id 4 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control actions evc_id specific 7 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control actions tag_pop_count 1 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control actions policer_id specific 1 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control ingress_match uni_ports GigabitEthernet_2_UNI enable UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control ingress_match outer_tag_match match_type c_tagged UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control ingress_match outer_tag_match match_fields vlan_id_filter specific 99 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control egress_inner_tag type c_tagged UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control egress_inner_tag vlan_id 77 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE commit
Configuring ECE Sample Rule 5
For rule 5, insert a new tag in frames forwarding to the UNI port, the outer tag for NNI - UNI direction for the ECE.
 Note | The configuration steps are similar to the ones mentioned in the Configuring ECE Rule 1 section. |
Example
UCS# ProvisionEVC UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration ece_id 5 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control actions direction nni_to_uni ---> This field is mandatory to pass UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control actions evc_id specific 7 ---> Map this ECE rule to an EVC configured above. UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control ingress_match uni_ports GigabitEthernet_2_UNI enable UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control egress_outer_tag enabled UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control egress_outer_tag vlan_id 78 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE commit
Ethernet Private Line or E-LAN
Ethernet Private Line (EPL) or E-LAN and Ethernet Virtual Private Line (EVPL) are Carrier Ethernet data services defined by the Metro Ethernet Forum. E-LAN provides a point-to-point Ethernet virtual connection (EVC) between a pair of dedicated user–network interfaces (UNIs), with a high degree of transparency.
The following diagrams show a Provider Network offering various types of E-LAN between two UNIs.
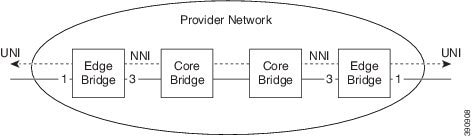
The following diagram shows an ethernet private (EP) line with 1-to-1 port protection on the network-network interface (NNI) side. This setup requires more resources compared to the unprotected EP-Line, because rules must be added for both NNI ports.
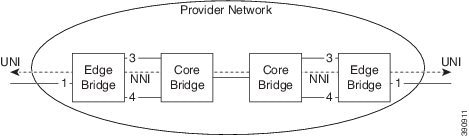
The following diagram shows an ethernet LAN with ring protection on the network-network interface (NNI) side. The resource consumption is similar to the port protection scenario, because rules are added for each NNI port.
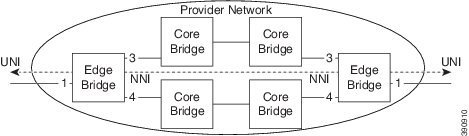
The following sections describe how to configure the Edge Bridges.
- Configuring EVC for E-LAN Between Two UNI and NNI Ports With Double Tag on the NNI Port
- Configuring EVC for E-LAN
Configuring EVC for E-LAN Between Two UNI and NNI Ports With Double Tag on the NNI Port
For more information on configuring EVC, see the Configuring Ethernet Virtual Circuit section.
Example
UCS# ProvisionEVC UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addEVC evcConfiguration instance 9 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addEVC evcConfiguration internal_vid 400 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addEVC evcConfiguration nni_vid 400 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addEVC evcConfiguration learning enable UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addEVC evcConfiguration nni_ports GigabitEthernet_6_NNI enable UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addEVC evcConfiguration policer_id 1 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addEVC review UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addEVC commit
Configuring EVC for E-LAN
For more information on configuring EVC, see the Configuring Ethernet Virtual Circuit section.
Example
UCS# ProvisionEVC UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addEVC evcConfiguration instance 9 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addEVC evcConfiguration internal_vid 400 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addEVC evcConfiguration nni_vid 400 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addEVC evcConfiguration learning enable UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addEVC evcConfiguration nni_ports GigabitEthernet_6_NNI enable UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addEVC evcConfiguration policer_id 1 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addEVC review UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addEVC commit
Ethernet Virtual Private Line
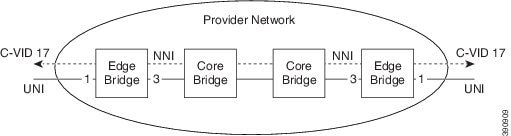
The following diagram shows an unprotected ethernet virtual private line (EVP-Line) forwarding frames with C-VID = 17 between the user-network interface (UNI) ports.
Thie following section describes the configuration of the EVPL service between the UNI and NNI ports.
Configuring ECE For EVPL Service
For more information on configuring ECE, see the Configuring EVC Control Entry section.
Example
UCS# ProvisionEVC UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration ece_id 6 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control actions evc_id specific 8 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control actions policer_id specific 1 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control ingress_match uni_ports GigabitEthernet_3_UNI enable UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control ingress_match outer_tag_match match_type c_tagged UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE ece_configuration control ingress_match outer_tag_match match_fields vlan_id_filter range 300-350 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE review UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addECE commit
 Note | The above ECE rule allows all VLANs ranging from 300 to 350. However, if you need to filter specific VLANs then you must create individual ECE rules. For more information, see Configuring ECE Rule 1. |
Configuring EVC For EVPL Service
For more information on configuring EVC, see the Configuring Ethernet Virtual Circuit section.
Example
UCS# ProvisionEVC UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addEVC evcConfiguration instance 8 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addEVC evcConfiguration internal_vid 200 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addEVC evcConfiguration nni_vid 200 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addEVC evcConfiguration learning enable UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addEVC evcConfiguration nni_ports GigabitEthernet_5_NNI enable UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addEVC evcConfiguration policer_id 1 UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addEVC review UCS(ProvisionEVC)# addEVC commit
Other Commands For EVC Configuration
Clearing EVC Statistics
{all | ece | | }
Using the Default Configuration
Switch(ProvisionEVC)# default
 Note | This command resets all configuration to default values. |
Deleting Configuration
Use this command to delete the ECE configuration.
Use this command to delete the EVC configuration.
deleteEVC deleteEVCrequest
Use this command to delete the EVC Policer request.
Editing Configuration
Use this command to edit the ECE configuration.
{ | update {class | direction | | | | | | }}
Use this command to edit the EVC configuration.
editEVCConfiguration evcupdateConfiguration {instance instance_id | update { | learning | | | }}
Enabling/Disabling/Modifying EVC Policer
Use this command to enable the EVC Policer.
Use this command to disable the EVC Policer.
Use this command to modify the EVC Policer.
 Feedback
Feedback