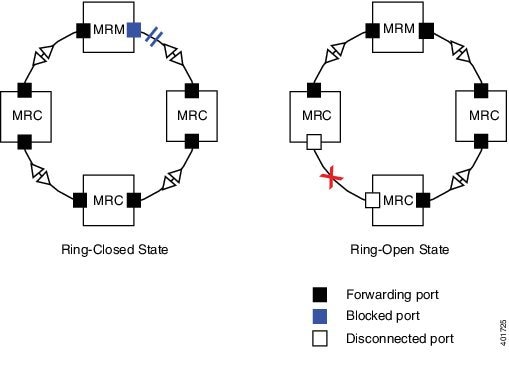
Media Redundancy Protocol
A Media Redundancy Protocol (MRP) is a network protocol for industrial automation that ensures fast convergence in ring network topologies.
-
Ensures fast convergence in ring network topologies for industrial automation
-
Operates under the IEC standard 62439-2
-
Supports recovery times of 30 ms, 200 ms, and 500 ms
Supported Switches and Feature History for MRP
List of Cisco Catalyst IE9300 Rugged Series Switches that support MRP:
-
IE-9310-26S2C-E and IE-9310-26S2C-A
-
IE-9320-26S2C-E and IE-9320-26S2C-A
-
IE-9320-22S2C4X-E and IE-9320-22S2C4X-A
-
IE-9320-24T4X-E and IE-9320-24T4X-A
-
IE-9320-24P4X-E and IE-9320-24P4X-A
-
IE-9320-16P8U4X-E and IE-9320-16P8U4X-A
-
IE-9320-24P4S-E and IE-9320-24P4S-A
-
IE-9310-16P8S4X-E and IE-9310-16P8S4X-A
|
Feature |
Release information |
Feature description |
|---|---|---|
|
Enhanced ring convergence profiles for standalone IE9300 switches |
Release 17.18.1 |
From Cisco IOS-XE 17.18.1 onwards, 12 rings of 30ms is also supported on a standalone IE9300 switch. |
|
PTP over MRP |
Release 17.18.1 |
From Cisco IOS-XE 17.18.1 onwards, PTP support over Media Redundancy Protocol (MRP) is introduced. |
|
MRP on an IE9300 Stack |
Release 17.17.1 |
From Cisco IOS-XE 17.17.1 onwards, stack support for Media Redundancy Protocol (MRP) is introduced. |
|
Media Redundancy Protocol (MRP) |
Release 17.13.1 |
From Cisco IOS-XE 17.13.1 onwards, 12 rings of 200 ms or 500 ms convergence profiles are supported on a standalone IE9300 switch. |
 Feedback
Feedback