Managing the Unicast RIB and FIB
This chapter describes how to manage routes in the unicast Routing Information Base (RIB) and the Forwarding Information Base (FIB) on the Cisco NX-OS switch.
Information About the Unicast RIB and FIB
The unicast RIB (IPv4 RIB) and FIB are part of the Cisco NX-OS forwarding architecture, as shown in Figure 13-1.
Figure 13-1 Cisco NX-OS Forwarding Architecture
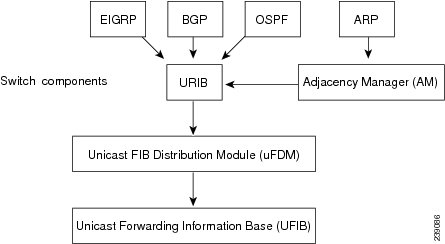
The unicast RIB maintains the routing table with directly connected routes, static routes, and routes learned from dynamic unicast routing protocols. The unicast RIB also collects adjacency information from sources such as the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP). The unicast RIB determines the best next hop for a given route and populates the unicast forwarding information base (FIBs) by using the services of the unicast FIB distribution module (FDM).
Each dynamic routing protocol must update the unicast RIB for any route that has timed out. The unicast RIB then deletes that route and recalculates the best next hop for that route (if an alternate path is available).
This section includes the following topic:
FIB Tables
The hardware provides two tables: a TCAM table and a hash table. The TCAM table is shared between longest prefix match (LPM) route /32 unicast route. The hash table is shared between the /32 unicast entries and the multicast entries. Each table has approximately 8000 routes.
If the LPM becomes 90% full, a warning messages appears. A message appears when there is sufficient space in the LPM and total usage is 70% or less. When the table is 100% full, the following message is displayed:
Licensing Requirements for the Unicast RIB and FIB
The following table shows the licensing requirements for this feature:
Managing the Unicast RIB and FIB
This section includes the following topics:
- Displaying Module FIB Information
- Configuring Load Sharing in the Unicast FIB
- Displaying Routing and Adjacency Information
- Clearing Forwarding Information in the FIB
- Estimating Memory Requirements for Routes
- Clearing Routes in the Unicast RIB

Note![]() If you are familiar with the Cisco IOS CLI, be aware that the Cisco NX-OS commands for this feature might differ from the Cisco IOS commands that you would use.
If you are familiar with the Cisco IOS CLI, be aware that the Cisco NX-OS commands for this feature might differ from the Cisco IOS commands that you would use.
Displaying Module FIB Information
DETAILED STEPS
To display the FIB information on a switchmodule, use the following commands in any mode:
This example shows how to display the FIB contents on a switch:
Configuring Load Sharing in the Unicast FIB
Dynamic routing protocols, such as Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), support load balancing with equal-cost multipath (ECMP). The routing protocol determines its best routes based on the metrics configured for the protocol and installs up to the protocol-configured maximum paths in the unicast RIB. The unicast RIB compares the administrative distances of all routing protocol paths in the RIB and selects a best path set from all of the path sets installed by the routing protocols. The unicast RIB installs this best path set into the FIB for use by the forwarding plane.
The forwarding plane uses a load-sharing algorithm to select one of the installed paths in the FIB to use for a given data packet.
You can globally configure the following load-sharing settings:
- load-share mode—Selects the best path based on the destination address and port or the source and the destination address and port.
- Universal ID—Sets the random seed for the hash algorithm. You do not need to configure the Universal ID. Cisco NX-OS chooses the Universal ID if you do not configure it.

Note![]() Load sharing uses the same path for all packets in a given flow. A flow is defined by the load-sharing method that you configure. For example, if you configure source-destination load sharing, then all packets with the same source IP address and destination IP address pair follow the same path.
Load sharing uses the same path for all packets in a given flow. A flow is defined by the load-sharing method that you configure. For example, if you configure source-destination load sharing, then all packets with the same source IP address and destination IP address pair follow the same path.
To configure the unicast FIB load-sharing algorithm, use the following command in global configuration mode:
To display the unicast FIB load-sharing algorithm, use the following command in any mode:
|
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
Displays the unicast FIB load-sharing algorithm for data traffic. |
Displaying Routing and Adjacency Information
You can display the routing and adjacency information.
To display the routing and adjacency information, use the following commands in any mode:
This example shows how to display the unicast route table:
switch# show ip route
IP Route Table for VRF "default"
'*' denotes best ucast next-hop
'**' denotes best mcast next-hop
'[x/y]' denotes [preference/metric]
192.168.0.2/24, ubest/mbest: 1/0, attached
*via 192.168.0.32, Eth1/5, [0/0], 22:34:09, direct
192.168.0.32/32, ubest/mbest: 1/0, attached
*via 192.168.0.32, Eth1/5, [0/0], 22:34:09, local
This example shows the adjacency information:
switch# show ip adjacency
IP Adjacency Table for VRF default
Total number of entries: 2
Address Age MAC Address Pref Source Interface Best
10.1.1.1 02:20:54 00e0.b06a.71eb 50 arp mgmt0 Yes
10.1.1.253 00:06:27 0014.5e0b.81d1 50 arp mgmt0 Yes
Clearing Forwarding Information in the FIB
You can clear one or more entries in the FIB. Clearing a FIB entry does not affect the unicast RIB.

To clear an entry in the FIB, including a Layer 3 inconsistency, use the following command in any mode:
Estimating Memory Requirements for Routes
You can estimate the memory that a number of routes and next-hop addresses will use.
To estimate the memory requirements for routes, use the following command in any mode:
Clearing Routes in the Unicast RIB
You can clear one or more routes from the unicast RIB.

To clear one or more entries in the unicast RIB, use the following commands in any mode:
Verifying the Unicast RIB and FIB Configuration
To display the unicast RIB and FIB configuration information, perform one of the following tasks:
|
|
|
|---|---|
Additional References
For additional information related to managing unicast RIB and FIB, see the following sections:
Related Documents
|
|
|
|---|---|
Cisco Nexus 6000 Series Command Reference, Cisco NX-OS Releases 7.x |
 Feedback
Feedback