- Overview of Cisco CSP 2100
- Installing Cisco CSP 2100
- Maintaining Cisco CSP 2100
- Cisco CSP 2100 Specifications
- Cisco CSP 2100 Power Cord Specifications
- Overview of Cisco CSP 2100 X2
- Installing Cisco CSP 2100 X2
- Maintaining Cisco CSP 2100 X2
- Cisco CSP 2100 X2 Specifications
- Cisco CSP 2100 X2 Power Cord Specifications
- Cisco CSP 2100 X2 Monitoring and Management Tools
- Status LEDs and Buttons
- Preparing for Cisco CSP 2100 X2 Component Installation
- Installing or Replacing Cisco CSP 2100 X2 Components
- Replaceable Component Locations
- Replacing SAS/SATA Hard Drives or Solid State Drives
- Replacing Fan Modules
- Replacing DIMMs
- Replacing CPUs and Heatsinks
- Replacing a Cisco Modular RAID Controller Card
- Replacing a Modular RAID Controller Transportable Memory Module (TMM)
- Replacing the Supercap Power Module (RAID Backup Battery)
- Replacing a Software RAID 5 Key Module
- Replacing the Motherboard RTC Battery
- Replacing an Internal SD Card
- Enabling or Disabling the Internal USB Port
- Replacing a PCIe Riser
- Replacing a PCIe Card
- Installing a Trusted Platform Module (TPM)
- Replacing Power Supplies
- Replacing an mLOM Card
Maintaining Cisco CSP 2100 X2
This chapter describes how to diagnose Cisco CSP 2100 X2 system problems using LEDs. It also provides information about how to install or replace hardware components, and it includes the following sections:
Cisco CSP 2100 X2 Monitoring and Management Tools
Cisco Integrated Management Interface
You can monitor the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 inventory, health, and system event logs by using the built-in Cisco Integrated Management Controller (Cisco IMC) GUI or CLI interfaces. See the user documentation for your firmware release at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps10739/products_installation_and_configuration_guides_list.html
Cisco CSP 2100 X2 Configuration Utility
The Configuration Utility for Cisco CSP 2100 X2 can aid and simplify the following tasks:
- Monitoring Cisco CSP 2100 X2 inventory and health
- Diagnosing common Cisco CSP 2100 X2 problems with diagnostic tools and logs
- Setting the BIOS booting order
- Configuring some RAID configurations
- Installing operating systems
You can also download the ISO image from Cisco.com. See the user documentation for your version of the utility at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps10493/products_user_guide_list.html
Status LEDs and Buttons
This section describes the location and meaning of LEDs and buttons and includes the following topics
Front Panel LEDs
Figure 8-1 shows the front panel LEDs. Table 8-1 defines the LED states.
The small form factor (SFF) drives, 24-drive version and the SFF drives, 16-drive version are shown.
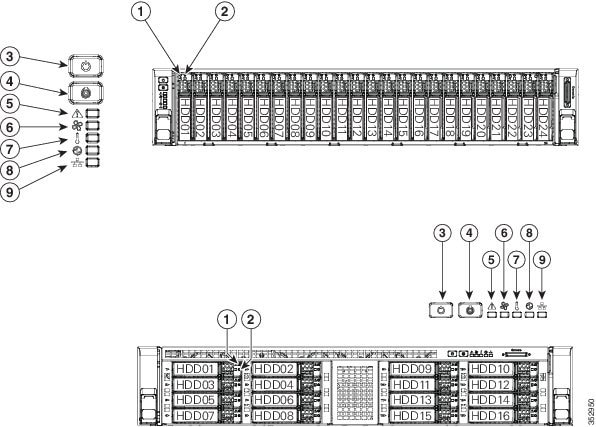
Rear Panel LEDs and Buttons
Figure 8-2 shows the rear panel LEDs and buttons. Table 8-2 defines the LED states.
Figure 8-2 Rear Panel LEDs and Buttons
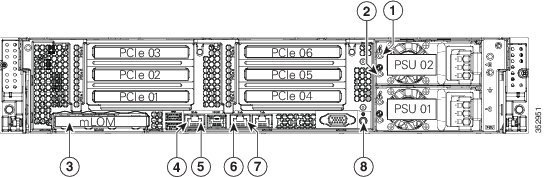
|
This is a summary; for advanced power supply LED information, see Table 8-3 . |
|
|
|
This is a summary; for advanced power supply LED information, see Table 8-3 . |
||
In Table 8-3 , read the status and fault LED states together in each row to determine the event that cause this combination.
Internal Diagnostic LEDs
Cisco CSP 2100 X2 is equipped with a supercap voltage source that can activate internal component fault LEDs up to 30 minutes after AC power is removed. Cisco CSP 2100 X2 has internal fault LEDs for CPUs, DIMMs, fan modules, SD cards, the RTC battery, and the mLOM card.
To use these LEDs to identify a failed component, press the front or rear Unit Identification button (see Figure 8-1 or Figure 8-2) with AC power removed. An LED lights amber to indicate a faulty component.
See Figure 8-3 for the locations of these internal LEDs.
Figure 8-3 Internal Diagnostic LED Locations
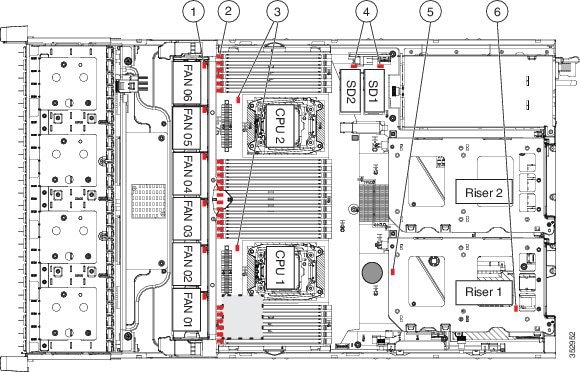
Preparing for Cisco CSP 2100 X2 Component Installation
This section describes how to prepare for component installation, and it includes the following topics:
- Required Equipment
- Shutting Down and Powering Off the Cisco CSP 2100 X2
- Removing and Replacing the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 Top Cover
- Serial Number Location
- Hot-Swap Replacement
Shutting Down and Powering Off the Cisco CSP 2100 X2
Cisco CSP 2100 X2 can run in two power modes:
- Main power mode—Power is supplied to all Cisco CSP 2100 X2 components and any operating system on your drives can run.
- Standby power mode—Power is supplied only to the service processor and the cooling fans and it is safe to power off the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 from this mode.
You can invoke a graceful shutdown or a hard shutdown by using either of the following methods:
- Use the Cisco IMC management interface.
- Use the Power button on the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 front panel. To use the Power button, follow these steps:
Step 1 Check the color of the Power Status LED (see the “Front Panel LEDs” section).
- Green—Cisco CSP 2100 X2 is in main power mode and must be shut down before it can be safely powered off. Go to Step 2.
- Amber—Cisco CSP 2100 X2 is already in standby mode and can be safely powered off. Go to Step 3.
Step 2 Invoke either a graceful shutdown or a hard shutdown:

- Graceful shutdown—Press and release the Power button. The operating system performs a graceful shutdown and the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 goes to standby mode, which is indicated by an amber Power Status LED.
- Emergency shutdown—Press and hold the Power button for 4 seconds to force the main power off and immediately enter standby mode.
Step 3 Disconnect the power cords from the power supplies in your Cisco CSP 2100 X2 to completely power off the Cisco CSP 2100 X2.
Removing and Replacing the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 Top Cover
Step 1 Remove the top cover (see Figure 8-4).
a. If the cover latch is locked, use a screwdriver to turn the lock 90-degrees counterclockwise to unlock it. See Figure 8-4.
b. Lift on the end of the latch that has the green finger grip. The cover is pushed back to the open position as you lift the latch.
c. Lift the top cover straight up from the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 and set it aside.

Note The latch must be in the fully open position when you set the cover back in place, which allows the opening in the latch to sit over a peg that is on the fan tray.
a. With the latch in the fully open position, place the cover on top of the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 about one-half inch (1.27 cm) behind the lip of the front cover panel. The opening in the latch should fit over the peg that sticks up from the fan tray.
b. Press the cover latch down to the closed position. The cover is pushed forward to the closed position as you push down the latch.
c. If desired, lock the latch by using a screwdriver to turn the lock 90-degrees clockwise.
Figure 8-4 Removing the Top Cover
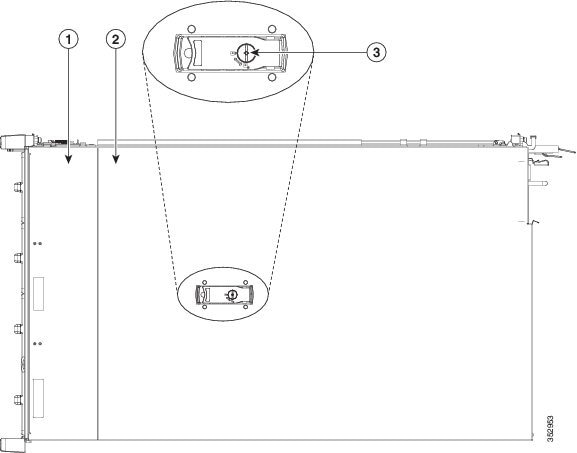
Serial Number Location
The serial number (SN) for Cisco CSP 2100 X2 is printed on a label on the top of the Cisco CSP 2100 X2, near the front.
Hot-Swap Replacement
Some components can be removed and replaced without powering off and removing AC power from the Cisco CSP 2100 X2. For hot-swap replacement, you do not have to precondition or shut down the component in the software before you remove it for the following components:
Installing or Replacing Cisco CSP 2100 X2 Components

Warning Blank faceplates and cover panels serve three important functions: they prevent exposure to hazardous voltages and currents inside the chassis; they contain electromagnetic interference (EMI) that might disrupt other equipment; and they direct the flow of cooling air through the chassis. Do not operate the system unless all cards, faceplates, front covers, and rear covers are in place.
Statement 1029


Tip You can press the Unit Identification button on the front panel or rear panel to turn on a flashing Unit Identification LED on the front and rear panels of the Cisco CSP 2100 X2. This button allows you to locate the specific Cisco CSP 2100 X2 that you are servicing when you go to the opposite side of the rack. You can also activate these LEDs remotely by using the Cisco IMC interface. See the “Status LEDs and Buttons” section for locations of these LEDs.
This section describes how to install and replace Cisco CSP 2100 X2 components, and it includes the following topics:
- Replaceable Component Locations
- Replacing SAS/SATA Hard Drives or Solid State Drives
- Replacing Fan Modules
- Replacing DIMMs
- Replacing CPUs and Heatsinks
- Replacing a Cisco Modular RAID Controller Card
- Replacing a Modular RAID Controller Transportable Memory Module (TMM)
- Replacing the Supercap Power Module (RAID Backup Battery)
- Replacing a Software RAID 5 Key Module
- Replacing the Motherboard RTC Battery
- Replacing an Internal SD Card
- Enabling or Disabling the Internal USB Port
- Replacing a PCIe Riser
- Replacing a PCIe Card
- Installing a Trusted Platform Module (TPM)
- Replacing Power Supplies
- Replacing an mLOM Card
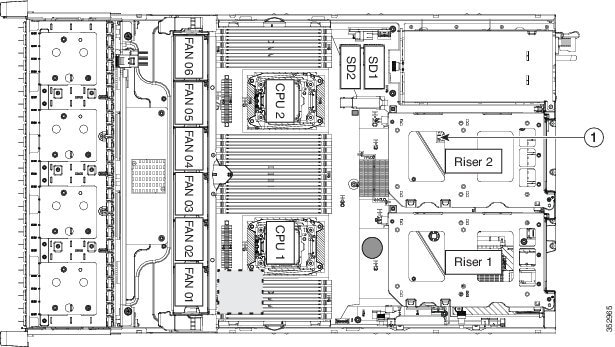
Replaceable Component Locations
Figure 8-5 shows the locations of the components that are supported as field-replaceable. The view shown is from the top down, with the top covers and air baffle removed.
Figure 8-5 Replaceable Component Locations
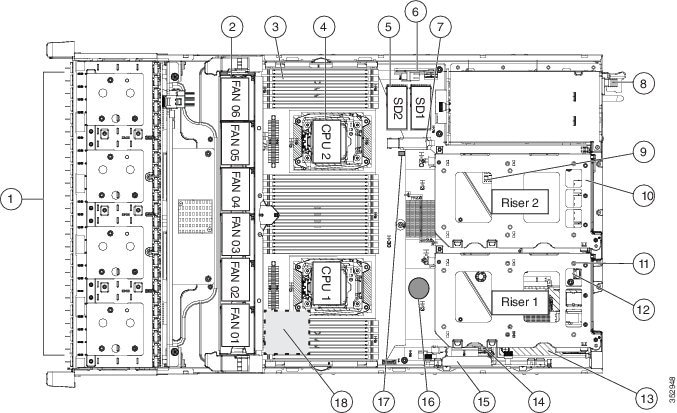
SAS/SATA Drive Population Guidelines
Cisco CSP 2100 X2 supports the small form-factor (SFF) drives with 24-drive backplane and expander.
Cisco CSP 2100 X2 holds up to 24 2.5-inch SAS/SATA hard drives or solid state drives (SSDs). SAS/SATA drives are hot-swappable.

Note You cannot change the backplane type after-factory. To change a front panel/backplane configuration, a chassis replacement is required.
The drive-bay numbering is shown in Figure 8-6.
Figure 8-6 Drive Numbering, SFF Drives, 24-Drive Version
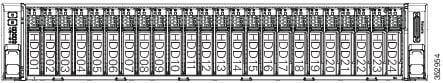
Observe these drive population guidelines for optimal performance:
- When populating drives, add drives in the lowest numbered bays first.
- Keep an empty drive blanking tray in any unused bays to ensure optimal airflow and cooling.
- You can mix hard drives and solid state drives in the same Cisco CSP 2100 X2. However, you cannot configure a logical volume (virtual drive) that contains a mix of hard drives and SSDs. That is, when you create a logical volume, it must contain all hard drives or all SSDs.
4K Sector Format Drives Considerations
- You must boot 4K sector format drives in UEFI mode, not legacy mode. See Setting Up Booting in UEFI Mode in the BIOS Setup Utility or Setting Up Booting in UEFI Mode in the Cisco IMC GUI.
- Do not configure 4K sector format and 512-byte sector format drives as part of the same RAID volume.
- Operating system support on 4K sector drives is as follows: Windows: Win2012 and Win2012R2; Linux: RHEL 6.5, 6.6, 6.7, 7.0, 7.2; SLES 11 SP3, and SLES 12. ESXi/Vmware is not supported.
Setting Up Booting in UEFI Mode in the BIOS Setup Utility
Step 1 Enter the BIOS setup utility by pressing the F2 key when prompted during bootup.
Step 2 Go to the Boot Options tab.
Step 3 Set UEFI Boot Options to Enabled .
Step 4 Under
Boot Option Priorities
, set your OS installation media (such as a virtual DVD) as your
Boot Option #1
.
Step 5 Go to the Advanced tab.
Step 6 Select LOM and PCIe Slot Configuration .
Step 7 Set the PCIe Slot ID: HBA Option ROM to UEFI Only .
Step 8 Press F10 to save changes and exit the BIOS setup utility. Allow the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 to reboot.
Step 9 After the OS installs, verify the installation:
a. Enter the BIOS setup utility by pressing the F2 key when prompted during bootup.
b. Go to the Boot Options tab.
c. Under Boot Option Priorities , verify that the OS you installed is listed as your Boot Option #1 .
Setting Up Booting in UEFI Mode in the Cisco IMC GUI
Step 1 Use a web browser and the IP address of the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 to log into the Cisco IMC GUI management interface.
Step 2 Navigate to Server > BIOS .
Step 3 Under Actions , click Configure BIOS .
Step 4 In the Configure BIOS Parameters dialog box, select the Advanced tab.
Step 5 Go to the LOM and PCIe Slot Configuration section.
Step 6 Set the PCIe Slot: HBA Option ROM to UEFI Only .
Step 7 Click Save Changes . The dialog box closes.
Step 8 Under BIOS Properties , set Configured Boot Order to UEFI .
Step 9 Under Actions , click Configure Boot Order .
Step 10 In the Configure Boot Order dialog box, click Add Local HDD .
Step 11 In the Add Local HDD dialog box, enter the information for the 4K sector format drive and make it first in the boot order.
Step 12 Save changes and reboot the Cisco CSP 2100 X2. The changes you made will be visible after the system reboots.
Replacing SAS/SATA Drives

Tip You do not have to shut down or power off the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 to replace SAS/SATA hard drives or solid state drives (SSDs) because they are hot-swappable.
Step 1 Remove the drive that you are replacing or remove a blank drive tray from an empty bay:
a. Press the release button on the face of the drive tray. See Figure 8-7.
b. Grasp and open the ejector lever and then pull the drive tray out of the slot.
c. If you are replacing an existing drive, remove the four drive-tray screws that secure the drive to the tray and then lift the drive out of the tray.
a. Place a new drive in the empty drive tray and replace the four drive-tray screws.
b. With the ejector lever on the drive tray open, insert the drive tray into the empty drive bay.
c. Push the tray into the slot until it touches the backplane, and then close the ejector lever to lock the drive in place.
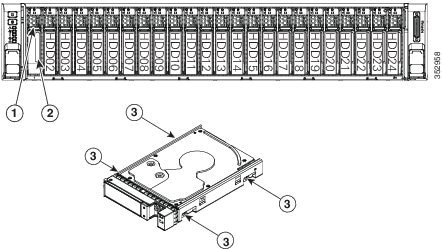
Replacing Fan Modules
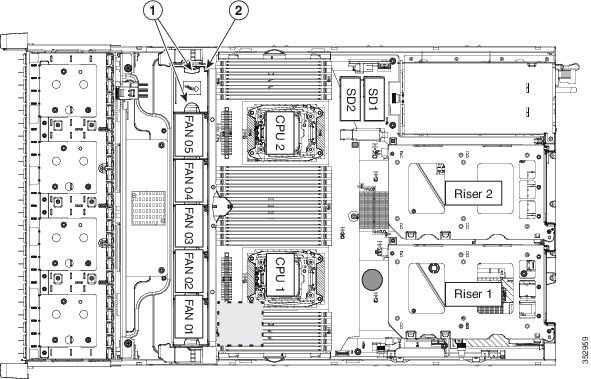
The six hot-swappable fan modules in the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 are numbered as follows when you are facing the front of the Cisco CSP 2100 X2.
Figure 8-8 Fan Module Numbering

Tip A fault LED is on the top of each fan module that lights amber if the fan module fails. To operate these LEDs from the SuperCap power source, remove AC power cords and then press the Unit Identification button. See also Internal Diagnostic LEDs.

Step 1 Slide the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 out the front of the rack far enough so that you can remove the top cover. You might have to detach cables from the rear panel to provide clearance.

Step 2 Remove the top cover as described in Removing and Replacing the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 Top Cover.
Step 3 Identify a faulty fan module by looking for a fan fault LED that is lit amber (see Figure 8-9).
Step 4 Remove a fan module that you are replacing (see Figure 8-9):
a. Grasp the top of the fan and pinch the green plastic latch toward the center.
b. Lift straight up to remove the fan module from Cisco CSP 2100 X2.
Step 5 Install a new fan module:
a. Set the new fan module in place, aligning the connector on the bottom of the fan module with the connector on the motherboard.

Note The arrow label on the top of the fan module, which indicates the direction of airflow, should point toward the rear of the Cisco CSP 2100 X2.
b. Press down gently on the fan module until the latch clicks and locks in place.
Step 7 Replace the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 in the rack.
Figure 8-9 Fan Modules Latch and Fault LED
Replacing DIMMs
This section includes the following topics:



Note To ensure the best performance, it is important that you are familiar with memory performance guidelines and population rules before you install or replace the memory.
Memory Performance Guidelines and Population Rules
This section describes the type of memory that Cisco CSP 2100 X2 requires and its effect on performance. The section includes the following topics:
DIMM Socket Numbering
Figure 8-10 shows the numbering of the DIMM sockets and CPUs.
Figure 8-10 CPUs and DIMM Socket Numbering on Motherboard
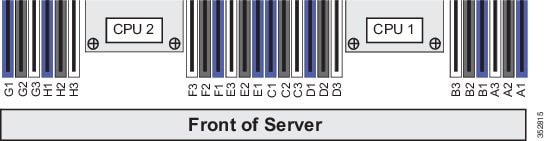
DIMM Population Rules
Observe the following guidelines when installing or replacing DIMMs:
– CPU1 supports channels A, B, C, and D.
– CPU2 supports channels E, F, G, and H.
– A channel can operate with one, two, or three DIMMs installed.
– If a channel has only one DIMM, populate slot 1 first (the blue slot).
– Fill blue #1 slots in the channels first: A1, E1, B1, F1, C1, G1, D1, H1
– Fill black #2 slots in the channels second: A2, E2, B2, F2, C2, G2, D2, H2
– Fill white #3 slots in the channels third: A3, E3, B3, F3, C3, G3, D3, H3
- Any DIMM installed in a DIMM socket for which the CPU is absent is not recognized. In a single-CPU configuration, populate the channels for CPU1 only (A, B, C, D).
- Memory mirroring reduces the amount of memory available by 50 percent because only one of the two populated channels provides data. When memory mirroring is enabled, you must install DIMMs in sets of 4, 6, 8, or 12 as described in Memory Mirroring and RAS.
- The Tesla P100 GPU can support more than 1 TB of memory in Cisco CSP 2100 X2. All other NVIDIA GPUs can support only 1 TB or less of memory in Cisco CSP 2100 X2. Therefore, do not install more than fourteen 64-GB DIMMs when using an NVIDIA GPU card (other than Tesla P100) in Cisco CSP 2100 X2.
- Observe the DIMM mixing rules shown in Table 8-5 .
Memory Mirroring and RAS
The Intel E5-2600 CPUs within the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 support memory mirroring only when an even number of channels are populated with DIMMs. If one or three channels are populated with DIMMs, memory mirroring is automatically disabled. Furthermore, if memory mirroring is used, DRAM size is reduced by 50 percent for reasons of reliability.
The memory mirroring configuration for Cisco CSP 2100 is similar to that of Cisco UCS C-Series servers. You can refer to Cisco UCS C-Series Rack Server specification sheet for details on populating recommended memory mirroring configurations:
Lockstep Channel Mode
When you enable lockstep channel mode, each memory access is a 128-bit data access that spans four channels.
Lockstep channel mode requires that all four memory channels on a CPU must be populated identically with regard to size and organization. DIMM socket populations within a channel (for example, A1, A2, A3) do not have to be identical but the same DIMM slot location across all four channels must be populated the same.
For example, DIMMs in sockets A1, B1, C1, and D1 must be identical. DIMMs in sockets A2, B2, C2, and D2 must be identical. However, the A1-B1-C1-D1 DIMMs do not have to be identical with the A2-B2-C2-D2 DIMMs.
Identifying a Faulty DIMM
Each DIMM socket has a corresponding DIMM fault LED, directly in front of the DIMM socket. See Figure 8-3 for the locations of these LEDs. The LEDs light amber to indicate a faulty DIMM. To operate these LEDs from the SuperCap power source, remove AC power cords and then press the Unit Identification button.
Replacing DIMMs
Step 1 Power off the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 as described in Shutting Down and Powering Off the Cisco CSP 2100 X2.
Step 2 Slide the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 out the front of the rack far enough so that you can remove the top cover. You might have to detach cables from the rear panel to provide clearance.

Step 3 Remove the top cover as described in Removing and Replacing the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 Top Cover.
Step 4 Remove the air baffle that sits over the DIMM sockets and set it aside.
Step 5 Identify the faulty DIMM by observing the DIMM socket fault LEDs on the motherboard (see Figure 8-3).
Step 6 Remove the DIMMs that you are replacing. Open the ejector levers at both ends of the DIMM socket, and then lift the DIMM out of the socket.

Note Before installing DIMMs, see the population guidelines. See Memory Performance Guidelines and Population Rules.
a. Align the new DIMM with the empty socket on the motherboard. Use the alignment key in the DIMM socket to correctly orient the DIMM.
b. Push down evenly on the top corners of the DIMM until it is fully seated and the ejector levers on both ends lock into place.
Step 8 Replace the air baffle.
Step 10 Replace the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 in the rack, replace cables, and then power on the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 by pressing the Power button.
Special Information For Upgrades to Intel Xeon v4 CPUs

The minimum software and firmware versions required for the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 to support Intel v4 CPUs are as follows:

Note Cisco UCS Manager Release 2.2(4) introduced a server pack feature that allows Intel v4 CPUs to run with Cisco UCS Manager Release 2.2(4) or later.
The UCS Manager Capability Catalog must be updated to 2.2(7c) or later.
The server Cisco IMC/BIOS must be running the minimum version or later as described in Table 8-6.
Do one of the following actions:
- If your Cisco CSP 2100 X2’s firmware and/or Cisco UCS Manager software are already at the required levels shown in Table 8-6 , you can replace the CPU hardware by using the procedure in this section.
- If your Cisco CSP 2100 X2’s firmware and/or Cisco UCS Manager software is earlier than the required levels, use the instructions in the Cisco UCS C-Series Servers Upgrade Guide for Intel Xeon v4 CPUs to upgrade your software. After you upgrade the software, return to the procedure in this section as directed to replace the CPU hardware.
CPU Configuration Rules
Cisco CSP 2100 X2 has two CPU sockets. Each CPU supports four DIMM channels (12 DIMM sockets). See Figure 8-10.
- Cisco CSP 2100 X2 can operate with one CPU or with two identical CPUs installed.
- The minimum configuration is that Cisco CSP 2100 X2 must have at least CPU1 installed. Install CPU1 first, and then CPU2.
- The following restrictions apply when using a single-CPU configuration:
– The maximum number of DIMMs is 12 (only CPU1 channels A, B, C, and D).
– PCIe riser 2, which contains PCIe slots 4, 5, and 6 is unavailable.
Replacing a CPU and Heatsink


Note Cisco CSP 2100 X2 uses the new independent loading mechanism (ILM) CPU sockets, so no Pick-and-Place tools are required for CPU handling or installation. Always grasp the plastic frame on the CPU when handling.
Step 1 Power off the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 as described in Shutting Down and Powering Off the Cisco CSP 2100 X2.
Step 2 Slide the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 out the front of the rack far enough so that you can remove the top cover. You might have to detach cables from the rear panel to provide clearance.

Step 3 Remove the top cover as described in Removing and Replacing the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 Top Cover.
Step 4 Remove the plastic air baffle that sits over the CPUs.
Step 5 Remove the heatsink that you are replacing:
a. Use a Number 2 Phillips-head screwdriver to loosen the four captive screws that secure the heatsink.

Note Alternate loosening each screw evenly to avoid damaging the heatsink or CPU.
b. Lift the heatsink off of the CPU.
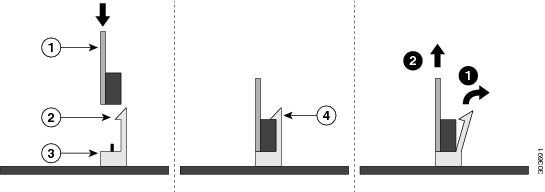
Step 6 Open the CPU retaining mechanism:
a. Unclip the first retaining latch labeled with the  icon, and then unclip the second retaining latch labeled with the
icon, and then unclip the second retaining latch labeled with the  icon. See Figure 8-11.
icon. See Figure 8-11.
b. Open the hinged CPU cover plate.
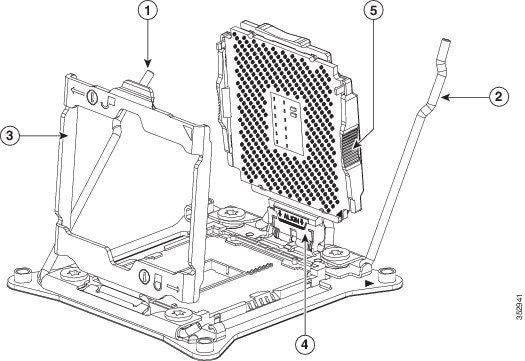
Step 7 Remove any existing CPU:
a. With the latches and hinged CPU cover plate open, swing the CPU in its hinged seat up to the open position, as shown in Figure 8-11.
b. Grasp the CPU by the finger-grips on its plastic frame and lift it up and out of the hinged CPU seat.
c. Set the CPU aside on an antistatic surface.
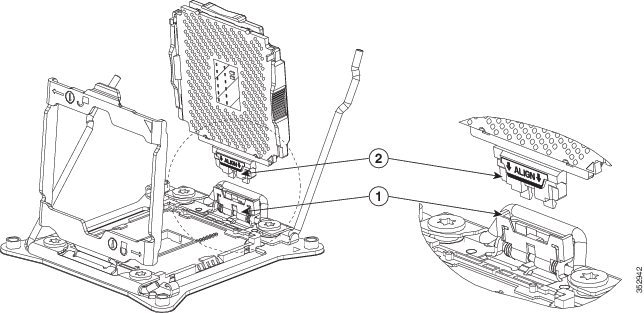
a. Grasp the new CPU by the finger-grips on its plastic frame and align the tab on the frame that is labeled “ALIGN” with the hinged seat, as shown in Figure 8-12.
b. Insert the tab on the CPU frame into the seat until it stops and is held firmly.
The line below the word “ALIGN” should be level with the edge of the seat, as shown in Figure 8-12.
c. Swing the hinged seat with the CPU down until the CPU frame clicks in place and holds flat in the socket.
d. Close the hinged CPU cover plate.
e. Clip down the CPU retaining latch with the  icon, and then clip down the CPU retaining latch with the
icon, and then clip down the CPU retaining latch with the  icon. See Figure 8-11.
icon. See Figure 8-11.
Figure 8-12 CPU and Socket Alignment Features

a. Apply the cleaning solution, which is included with the heatsink cleaning kit (UCSX-HSCK=, shipped with spare CPUs), to the old thermal grease on the heatsink and CPU and let it soak for a least 15 seconds.
b. Wipe all of the old thermal grease off the old heat sink and CPU using the soft cloth that is included with the heatsink cleaning kit. Be careful to not scratch the heat sink surface.

Note New heatsinks come with a pre-applied pad of thermal grease. If you are reusing a heatsink, you must apply thermal grease from a syringe (UCS-CPU-GREASE3=).
c. Align the four heatsink captive screws with the motherboard standoffs, and then use a Number 2 Phillips-head screwdriver to tighten the captive screws evenly.

Note Alternate tightening each screw evenly to avoid damaging the heatsink or CPU.
Step 10 Replace the air baffle.
Step 11 Replace the top cover.
Step 12 Replace the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 in the rack, replace cables, and then power on the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 by pressing the Power button.
Additional CPU-Related Parts to Order with RMA Replacement Motherboards
When a return material authorization (RMA) of the motherboard or CPU is done on a Cisco CSP 2100 X2, additional parts might not be included with the CPU or motherboard spare bill of materials (BOM). The TAC engineer might need to add the additional parts to the RMA to help ensure a successful replacement.

Note Cisco CSP 2100 X2 uses the new independent loading mechanism (ILM) CPU sockets, so no Pick-and-Place tools are required for CPU handling or installation. Always grasp the plastic frame on the CPU when handling.
– Heat sink cleaning kit (UCSX-HSCK=)
– Thermal grease kit for C240 M4 (UCS-CPU-GREASE3=)
– Heat sink cleaning kit (UCSX-HSCK=)
A CPU heatsink cleaning kit is good for up to four CPU and heatsink cleanings. The cleaning kit contains two bottles of solution, one to clean the CPU and heatsink of old thermal interface material and the other to prepare the surface of the heatsink.
New heatsink spares come with a pre-applied pad of thermal grease. It is important to clean the old thermal grease off of the CPU prior to installing the heatsinks. Therefore, when you are ordering new heatsinks, you must order the heatsink cleaning kit.
Replacing a Cisco Modular RAID Controller Card
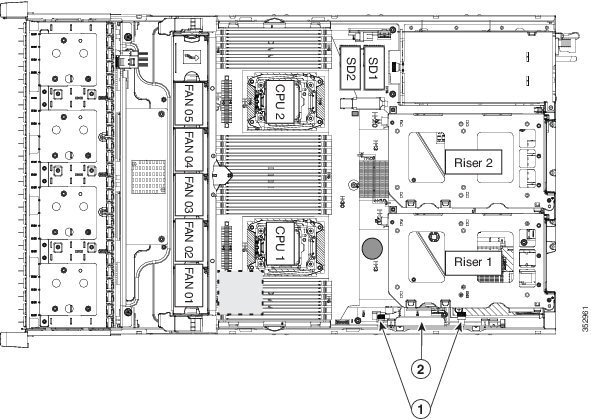
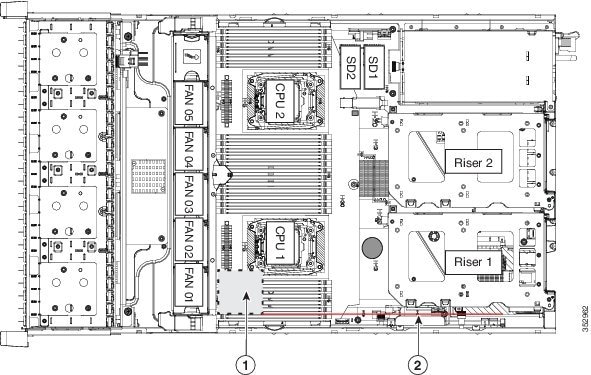
Cisco CSP 2100 X2 has an internal, dedicated PCIe slot on the motherboard for a Cisco modular RAID controller card (see Figure 8-13).
- Replacing a Modular RAID Controller Transportable Memory Module (TMM)
- Replacing the Supercap Power Module (RAID Backup Battery)

Note You cannot use a hardware RAID controller card and the embedded RAID controller at the same time.
RAID Card Firmware Compatibility
If the PCIe card that you are installing is a RAID controller card, firmware on the RAID controller must be verified for compatibility with the current Cisco IMC and BIOS versions that are installed on the Cisco CSP 2100 X2. If not compatible, upgrade or downgrade the RAID controller firmware accordingly using the Host Upgrade Utility (HUU) for your firmware release to bring it to a compatible level.
See the HUU guide for your Cisco IMC release for instructions on downloading and using the utility to bring Cisco CSP 2100 X2 components to compatible levels: HUU Guides
Replacement Procedure
Step 1 Power off the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 as described in Shutting Down and Powering Off the Cisco CSP 2100 X2.
Step 2 Slide the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 out the front of the rack far enough so that you can remove the top cover. You might have to detach cables from the rear panel to provide clearance.

Step 3 Remove the top cover as described in Removing and Replacing the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 Top Cover.
Step 4 Remove an existing RAID controller card:
a. Disconnect the data cable from the card. Depress the tab on the cable connector and pull.
b. Disconnect the supercap power module cable from the transportable memory module (TMM), if present.
c. Lift straight up on the metal bracket that holds the card. The bracket lifts off of two pegs on the chassis wall.
d. Loosen the two thumbscrews that hold the card to the metal bracket and then lift the card from the bracket.
Step 5 Install a new RAID controller card:

a. Set the new card on the metal bracket, aligned so that the thumbscrews on the card enter the threaded standoffs on the bracket. Tighten the thumbscrews to secure the card to the bracket.
b. Align the two slots on the back of the bracket with the two pegs on the chassis wall.
The two slots on the bracket must slide down over the pegs at the same time that you push the card into the motherboard socket.
c. Gently press down on both top corners of the metal bracket to seat the card into the socket on the motherboard.
d. Connect the supercap power module cable to its connector on the TMM, if present.
e. Connect the single data cable to the card.
Step 7 Replace the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 in the rack, replace cables, and then power on the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 by pressing the Power button.
Figure 8-13 Modular RAID Controller Card Location
Replacing a Modular RAID Controller Transportable Memory Module (TMM)
The transportable memory module (TMM) that attaches to the modular RAID controller card can be installed or replaced after-factory.
- Replacing a Cisco Modular RAID Controller Card
- Replacing the Supercap Power Module (RAID Backup Battery)
Step 1 Power off the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 as described in Shutting Down and Powering Off the Cisco CSP 2100 X2.
Step 2 Slide the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 out the front of the rack far enough so that you can remove the top cover. You might have to detach cables from the rear panel to provide clearance.

Step 3 Remove the top cover as described in Removing and Replacing the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 Top Cover.
Step 4 Remove the modular RAID controller card from the Cisco CSP 2100 X2:
a. Lift straight up on the metal bracket that holds the card. The bracket lifts off of two pegs on the chassis wall (see Figure 8-13).
b. Disconnect the supercap power module cable from the TMM that is attached to the card.
Step 5 Remove the TMM from the modular RAID controller card (see Figure 8-14):
a. The plastic bracket on the card has a securing plastic clip at each end of the TMM. Gently spread each clip away from the TMM.
b. Pull straight up on the TMM to lift it off the two plastic guide pegs and the socket on the card.
Step 6 Install a TMM to the modular RAID controller card (see Figure 8-14):
a. Align the TMM over the bracket on the card. Align the connector on the underside of the TMM with the socket on the card. Align the two guide holes on the TMM over the two guide pegs on the card.

b. Gently lower the TMM so that the guide holes on the TMM go over the guide pegs on the card.
c. Press down on the TMM until the plastic clips on the bracket close over each end of the TMM.
d. Press down on the TMM to fully seat its connector with the socket on the card.
Step 7 Install the modular RAID controller card back into the Cisco CSP 2100 X2:

Note If this is a first-time installation of your TMM, you must also install a supercap power module (SCPM). The SCPM cable attaches to a connector on the TMM. See Replacing the Supercap Power Module (RAID Backup Battery).
a. Connect the cable from the supercap power module (RAID battery) to the connector on the TMM (see Figure 8-14).
b. Align the two slots on the back of the RAID card bracket with the two pegs on the chassis wall.
The two slots on the bracket must slide down over the pegs at the same time that you push the card into the motherboard socket.
c. Gently press down on both top corners of the metal bracket to seat the card into the socket on the motherboard.
Figure 8-14 TMM on Modular RAID Controller Card
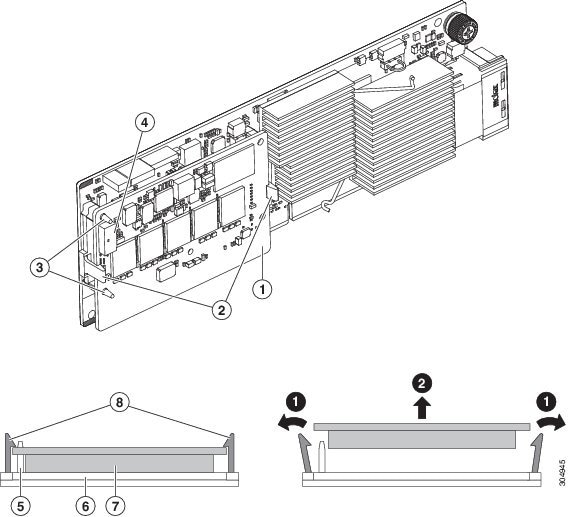
Replacing the Supercap Power Module (RAID Backup Battery)
Cisco CSP 2100 X2 supports installation of one supercap power module (SCPM). The unit mounts to a clip on the removable air baffle (see Figure 8-15). The SCPM requires that you have a transportable memory module (TMM) attached to your RAID controller card because the connector for the SCPM cable is on the TMM.
- Replacing a Cisco Modular RAID Controller Card
- Replacing a Modular RAID Controller Transportable Memory Module (TMM)
The SCPM provides approximately three years of backup for the disk write-back cache DRAM in the case of a sudden power loss by offloading the cache to the NAND flash.

Warning There is danger of explosion if the battery is replaced incorrectly. Replace the battery only with the same or equivalent type recommended by the manufacturer. Dispose of used batteries according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Statement 1015
Step 1 Power off the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 as described in Shutting Down and Powering Off the Cisco CSP 2100 X2.
Step 2 Slide the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 out the front of the rack far enough so that you can remove the top cover. You might have to detach cables from the rear panel to provide clearance.

Step 3 Remove the top cover as described in Removing and Replacing the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 Top Cover.
Step 4 Remove an existing SCPM:
a. Disconnect the existing SCPM cable from the transportable memory module (TMM) that is attached to the modular RAID controller card.
b. Pull back the plastic clip that closes over the SCPM slightly, and then slide the SCPM free of the clips on the air baffle mounting point (see Figure 8-15).
a. Slide the new backup unit into the holder on the air baffle mounting point until the clip clicks over the top edge of the SCPM.
b. Connect the cable from the SCPM to the TMM that is attached to the modular RAID controller card.

Note Put the cable through the opening on the rear of the air baffle (rather than over the air baffle) to keep the cable from interfering with the top cover of the Cisco CSP 2100 X2.
Step 7 Replace the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 in the rack, replace cables, and then power on the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 by pressing the Power button.
Figure 8-15 SCPM (RAID Backup Unit) Mounting Point and Cable Path
Replacing a Software RAID 5 Key Module
Cisco CSP 2100 X2 has a two-pin header on the motherboard for a RAID 5 key module.
Step 1 Power off the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 as described in Shutting Down and Powering Off the Cisco CSP 2100 X2.
Step 2 Slide the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 out the front of the rack far enough so that you can remove the top cover. You might have to detach cables from the rear panel to provide clearance.

Step 3 Remove the top cover as described in Removing and Replacing the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 Top Cover.
Step 4 Remove any existing software RAID key module:
a. Locate the module on the motherboard (see Figure 8-16).
b. Hold the retention clips on the header open while you grasp the RAID key board and pull straight up (see Figure 8-17).
Figure 8-16 RAID 5 Key Header Location on Motherboard
Step 5 Install a new software RAID key module:
a. Align the module with the pins in the motherboard header.
b. Gently press down on the module until it is seated and the retention clip locks over the module (see Figure 8-17).
Figure 8-17 Software RAID 5 Key Module Retention Clip
Replacing the Motherboard RTC Battery

Warning There is danger of explosion if the battery is replaced incorrectly. Replace the battery only with the same or equivalent type recommended by the manufacturer. Dispose of used batteries according to the manufacturer’s instructions. [Statement 1015]
The real-time clock (RTC) battery retains system settings when the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 is disconnected from power. The battery type is CR2032. Cisco supports the industry-standard CR2032 battery, which can be purchased from most electronic stores.
Step 1 Power off the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 as described in Shutting Down and Powering Off the Cisco CSP 2100 X2.
Step 2 Slide the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 out the front of the rack far enough so that you can remove the top cover. You might have to detach cables from the rear panel to provide clearance.

Step 3 Remove the top cover as described in Removing and Replacing the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 Top Cover.
Step 4 Remove the battery from its holder on the motherboard (see Figure 8-18):
a. Use a small screwdriver or pointed object to press inward on the battery at the prying point (see Figure 8-18).
b. Lift up on the battery and remove it from the holder.
Step 5 Install an RTC battery. Insert the battery into its holder and press down until it clicks in place.

Note The positive side of the battery marked “3V+” should face upward.
Step 7 Replace the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 in the rack, replace cables, and power on the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 by pressing the Power button.
Figure 8-18 RTC Battery Location and Prying Point
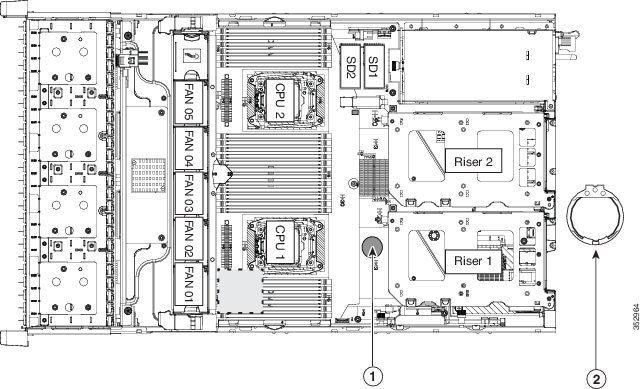
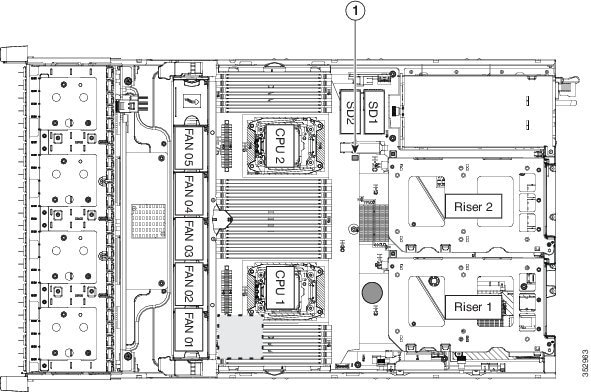
Replacing an Internal SD Card
Cisco CSP 2100 X2 has two internal SD card bays on the motherboard.
Dual SD cards are supported. RAID 1 support can be configured through the Cisco IMC interface.
Step 1 Power off the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 as described in Shutting Down and Powering Off the Cisco CSP 2100 X2.
Step 2 Slide the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 out the front of the rack far enough so that you can remove the top cover. You might have to detach cables from the rear panel to provide clearance.

Step 3 Remove the top cover as described in Removing and Replacing the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 Top Cover.
Step 4 Remove an SD card (see Figure 8-19).
a. Push on the top of the SD card, and then release it to allow it to spring out from the slot.
b. Remove the SD card from the slot.
a. Insert the SD card into the slot with the label side facing up.
b. Press on the top of the card until it clicks in the slot and stays in place.
Step 7 Replace the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 in the rack, replace cables, and then power on the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 by pressing the Power button.
Figure 8-19 SD Card Bay Location and Numbering on the Motherboard
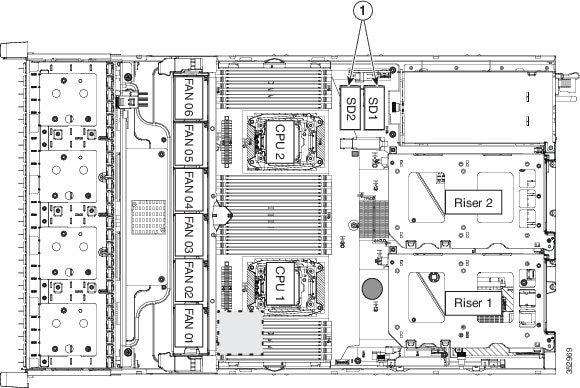
Enabling or Disabling the Internal USB Port

The factory default is for all USB ports on the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 to be enabled. However, the internal USB port can be enabled or disabled in the BIOS. See Figure 8-5 for the location of the internal USB 3.0 slot on the motherboard.
Step 1 Enter the BIOS Setup Utility by pressing the F2 key when prompted during bootup.
Step 2 Navigate to the Advanced tab.
Step 3 On the Advanced tab, select USB Configuration.
Step 4 On the USB Configuration page, choose USB Ports Configuration.
Step 5 Scroll to USB Port: Internal, press Enter, and then choose either Enabled or Disabled from the dialog box.
Step 6 Press F10 to save and exit the utility.
Replacing a PCIe Riser
Cisco CSP 2100 X2 contains two toolless PCIe risers for horizontal installation of PCIe cards. See Replacing a PCIe Card for the specifications of the PCIe slots on the risers.
Step 1 Power off the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 as described in Shutting Down and Powering Off the Cisco CSP 2100 X2.
Step 2 Slide the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 out the front of the rack far enough so that you can remove the top cover. You might have to detach cables from the rear panel to provide clearance.

Step 3 Remove the top cover as described in Removing and Replacing the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 Top Cover.
Step 4 Remove the PCIe riser that you are replacing (see Figure 8-20):
a. Grasp the top of the riser and lift straight up on both ends to disengage its circuit board from the socket on the motherboard. Set the riser on an antistatic mat.
b. If the riser has a card installed, remove the card from the riser. See Replacing a PCIe Card.
Step 5 Install a new PCIe riser:
a. If you removed a card from the old PCIe riser, install the card to the new riser (see Replacing a PCIe Card).
b. Position the PCIe riser over its socket on the motherboard and over its alignment slots in the chassis (see Figure 8-20). There are also two alignment pegs on the motherboard for each riser.

Note The PCIe risers are not interchangeable. If you plug a PCIe riser into the wrong socket, the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 will not boot. Riser 1 must plug into the motherboard socket labeled “RISER1.” Riser 2 must plug into the motherboard socket labeled “RISER2.”
c. Carefully push down on both ends of the PCIe riser to fully engage its circuit board connector with the socket on the motherboard.
Step 7 Replace the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 in the rack, replace cables, and then power on the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 by pressing the Power button.
Figure 8-20 PCIe Riser Alignment Features
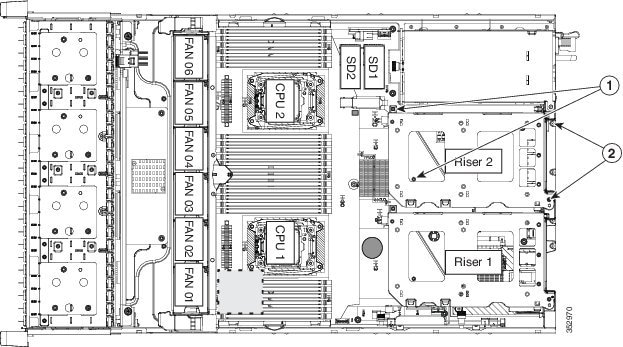
Replacing a PCIe Card

PCIe Slots
Cisco CSP 2100 X2 contains two toolless PCIe risers for horizontal installation of PCIe cards (see Figure 8-21).
Figure 8-21 Rear Panel, Showing PCIe Slots
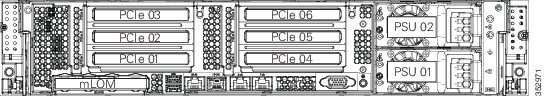
Yes2 |
|||||
Replacing a PCIe Card
To install or replace a PCIe card, follow these steps:
Step 1 Shut down and power off the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 as described in Shutting Down and Powering Off the Cisco CSP 2100 X2.
Step 2 Slide the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 out the front of the rack far enough so that you can remove the top cover. You might have to detach cables from the rear panel to provide clearance.

Step 3 Remove the top cover as described in Removing and Replacing the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 Top Cover.
Step 4 Remove a PCIe card (or a blanking panel) from the PCIe riser:
a. Lift straight up on both ends of the riser to disengage its circuit board from the socket on the motherboard. Set the riser on an antistatic mat.
b. On the bottom of the riser, loosen the single thumbscrew that holds the securing plate (see Figure 8-22).
c. Swing open the securing plate and remove it from the riser to provide access.
d. Swing open the card-tab retainer that secures the back-panel tab of the card (see Figure 8-22).
e. Pull evenly on both ends of the PCIe card to disengage it from the socket on the PCIe riser (or remove a blanking panel) and then set the card aside.
a. Align the new PCIe card with the empty socket on the PCIe riser.
b. Push down evenly on both ends of the card until it is fully seated in the socket.
Ensure that the card rear panel tab sits flat against the PCIe riser rear panel opening.
c. Close the card-tab retainer (see Figure 8-22).
d. Return the securing plate to the riser. Insert the two hinge-tabs into the two slots on the riser, and then swing the securing plate closed.
e. Tighten the single thumbscrew on the bottom of the securing plate.
f. Position the PCIe riser over its socket on the motherboard and over its alignment features in the chassis (see Figure 8-20).
g. Carefully push down on both ends of the PCIe riser to fully engage its circuit board connector with the socket on the motherboard.
Step 7 Replace the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 in the rack, replace cables, and then power on the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 by pressing the Power button.
Figure 8-22 PCIe Riser Securing Features (Three-Slot Riser Shown)
Installing Multiple PCIe Cards and Resolving Limited Resources
When a large number of PCIe add-on cards are installed in the Cisco CSP 2100 X2, the system might run out of the following resources required for PCIe devices:
The topics in this section provide guidelines for resolving the issues related to these limited resources:
Resolving Insufficient Memory Space to Execute Option ROMs
The system has very limited memory to execute PCIe legacy option ROMs, so when a large number of PCIe add-on cards are installed in the Cisco CSP 2100 X2, the system BIOS might not able to execute all of the option ROMs. The system BIOS loads and executes the option ROMs in the order that the PCIe cards are enumerated (slot 1, slot 2, slot 3, and so on).
If the system BIOS does not have sufficient memory space to load any PCIe option ROM, it skips loading that option ROM, reports a system event log (SEL) event to the Cisco IMC controller and reports the following error in the Error Manager page of the BIOS Setup utility:
To resolve this issue, disable the Option ROMs that are not needed for system booting. The BIOS Setup Utility provides the setup options to enable or disable the Option ROMs at the PCIe slot level for the PCIe expansion slots and at the port level for the onboard NICs. These options can be found in the BIOS Setup Utility Advanced > PCI Configuration page.
If the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 is configured to boot primarily from RAID storage, make sure that the option ROMs for the slots where your RAID controllers installed are enabled in the BIOS, depending on your RAID controller configuration.
If the RAID controller does not appear in the system boot order even with the option ROMs for those slots are enabled, the RAID controller option ROM might not have sufficient memory space to execute. In that case, disable other option ROMs that are not needed for the system configuration to free up some memory space for the RAID controller option ROM.
If the system is configured to primarily perform PXE boot from onboard NICs, make sure that the option ROMs for the onboard NICs to be booted from are enabled in the BIOS Setup Utility. Disable other option ROMs that are not needed to create sufficient memory space for the onboard NICs.
Resolving Insufficient 16-Bit I/O Space
The system has only 64 KB of legacy 16-bit I/O resources available. This 64 KB of I/O space is divided between the CPUs in the system because the PCIe controller is integrated into the CPUs. Cisco CSP 2100 X2 BIOS has the capability to dynamically detect the 16-bit I/O resource requirement for each CPU and then balance the 16-bit I/O resource allocation between the CPUs during the PCI bus enumeration phase of the BIOS POST.
When a large number of PCIe cards are installed in the system, the system BIOS might not have sufficient I/O space for some PCIe devices. If the system BIOS is not able to allocate the required I/O resources for any PCIe devices, the following symptoms have been observed:
- The system might get stuck in an infinite reset loop.
- The BIOS might appear to hang while initializing PCIe devices.
- The PCIe option ROMs might take excessive time to complete, which appears to lock up the system.
- PCIe boot devices might not be accessible from the BIOS.
- PCIe option ROMs might report initialization errors. These errors are seen before the BIOS passes control to the operating system.
- The keyboard might not work.
To work around this problem, rebalance the 16-bit I/O load using the following methods:
1. Physically remove any unused PCIe cards.
2. If the system has one or more Cisco virtual interface cards (VICs) installed, disable the PXE boot on the VICs that are not required for the system boot configuration by using the Network Adapters page in Cisco IMC Web UI to free up some 16-bit I/O resources. Each VIC uses a minimum 16 KB of 16-bit I/O resource, so disabling PXE boot on Cisco VICs would free up some 16-bit I/O resources that can be used for other PCIe cards that are installed in the system.
Installing a Trusted Platform Module (TPM)
The trusted platform module (TPM) is a small circuit board that connects to a motherboard socket and is secured by a one-way screw.
TPM 2.0 Considerations
Trusted platform module (TPM) version 2.0 is supported on Intel v3- or Intel v4-based platforms.
If there is an existing TPM 1.2 installed in the Cisco CSP 2100 X2, you cannot upgrade to TPM 2.0.
If there is no existing TPM in the Cisco CSP 2100 X2, you can install TPM 2.0. You must first upgrade to Intel v4 code, regardless of whether the installed CPU is Intel v3 or v4. TPM 2.0 requires Intel v4 code or later.


Note If the TPM 2.0 becomes unresponsive, reboot the Cisco CSP 2100 X2.
Installing the TPM Hardware
This section contains the following procedures, which must be followed in this order when installing and enabling a TPM:
1. Installing the TPM Hardware
2. Enabling TPM Support in the BIOS
3. Enabling the Intel TXT Feature in the BIOS

Note For security purposes, the TPM is installed with a one-way screw. It cannot be removed with a standard screwdriver.
Step 1 Prepare the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 for component installation:
Step 2 Power off the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 as described in Shutting Down and Powering Off the Cisco CSP 2100 X2.
Step 3 Slide the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 out the front of the rack far enough so that you can remove the top cover. You might have to detach cables from the rear panel to provide clearance.

Step 4 Remove the top cover as described in Removing and Replacing the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 Top Cover.
Step 5 Remove PCIe riser 2 to provide clearance. See Replacing a PCIe Riser for instructions.
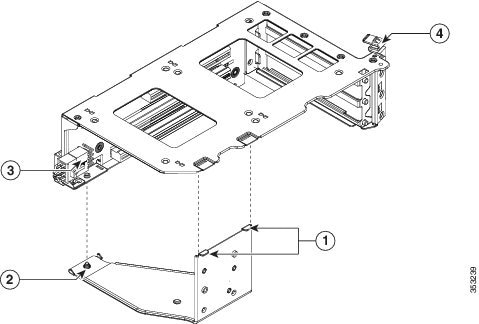
a. Locate the TPM socket on the motherboard, as shown in Figure 8-23.
b. Align the connector that is on the bottom of the TPM circuit board with the motherboard TPM socket. Align the screw hole and standoff on the TPM board with the screw hole that is adjacent to the TPM socket.
c. Push down evenly on the TPM to seat it in the motherboard socket.
d. Install the single one-way screw that secures the TPM to the motherboard.
Step 7 Replace PCIe riser 2 to the Cisco CSP 2100 X2. See Replacing a PCIe Riser for instructions.
Step 9 Replace the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 in the rack, replace cables, and then power on the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 by pressing the Power button.
Step 10 Continue with Enabling TPM Support in the BIOS.
Figure 8-23 TPM Socket Location on Motherboard
Enabling TPM Support in the BIOS

Note After hardware installation, you must enable TPM support in the BIOS:
a. Watch during bootup for the F2 prompt, and then press F2 to enter BIOS setup.
b. Log in to the BIOS Setup Utility with your BIOS Administrator password.
c. On the BIOS Setup Utility window, choose the Advanced tab.
d. Choose Trusted Computing to open the TPM Security Device Configuration window.
e. Change TPM SUPPORT to Enabled .
f. Press F10 to save your settings and reboot the Cisco CSP 2100 X2.
Step 2 Verify that TPM support is now enabled:
a. Watch during bootup for the F2 prompt, and then press F2 to enter BIOS setup.
b. Log into the BIOS Setup utility with your BIOS Administrator password.
d. Choose Trusted Computing to open the TPM Security Device Configuration window.
e. Verify that TPM SUPPORT and TPM State are Enabled.
Step 3 Continue with Enabling the Intel TXT Feature in the BIOS.
Enabling the Intel TXT Feature in the BIOS
Intel Trusted Execution Technology (TXT) provides greater protection for information that is used and stored on the business server. A key aspect of that protection is the provision of an isolated execution environment and associated sections of memory where operations can be conducted on sensitive data, invisibly to the rest of the system. Intel TXT provides for a sealed portion of storage where sensitive data such as encryption keys can be kept, helping to shield them from being compromised during an attack by malicious code.
Step 1 Reboot the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 and watch for the prompt to press F2.
Step 2 When prompted, press F2 to enter the BIOS Setup utility.
Step 3 Verify that the prerequisite BIOS values are enabled:
b. Choose Intel TXT(LT-SX) Configuration to open the Intel TXT(LT-SX) Hardware Support window.
c. Verify that the following items are listed as Enabled:
– VT-d Support (default is Enabled)
– VT Support (default is Enabled)
- If VT-d Support and VT Support are already enabled, skip to Step 4.
- If VT-d Support and VT Support are not enabled, continue with the next steps to enable them.
d. Press Escape to return to the BIOS Setup utility Advanced tab.
e. On the Advanced tab, choose Processor Configuration to open the Processor Configuration window.
f. Set Intel (R) VT and Intel (R) VT-d to Enabled.
Step 4 Enable the Intel Trusted Execution Technology (TXT) feature:
a. Return to the Intel TXT(LT-SX) Hardware Support window if you are not already there.
b. Set TXT Support to Enabled .
Step 5 Press F10 to save your changes and exit the BIOS Setup utility.
Replacing Power Supplies
Cisco CSP 2100 X2 can have one or two power supplies. When two power supplies are installed they are redundant as 1+1 and hot-swappable.
- Replacing an AC Power Supply
- Replacing a DC Power Supply
- Installation Grounding
- See Power Specifications for more information about the supported power supplies.
- See Rear Panel LEDs and Buttons for information about the power supply LEDs.
- See Replacing a DC Power Supply for information about wiring a DC power supply.
Replacing an AC Power Supply

Note If you have ordered a Cisco CSP 2100 X2 with power supply redundancy (two power supplies), you do not have to power off the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 to replace power supplies because they are redundant as 1+1 and hot-swappable.

Note Do not mix power supply types in the Cisco CSP 2100 X2. Both power supplies must be the same wattage and Cisco product ID (PID).
Step 1 Remove the power supply that you are replacing or a blank panel from an empty bay:
a. Perform one of the following actions:
– If your Cisco CSP 2100 X2 has only one power supply, shut down and power off the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 as described in Shutting Down and Powering Off the Cisco CSP 2100 X2.
– If your Cisco CSP 2100 X2 has two power supplies, you do not have to shut down the Cisco CSP 2100 X2.
b. Remove the power cord from the power supply that you are replacing.
For a DC power supply, release the electrical connector block from the power supply by pushing the orange plastic button on the top of the connector inward toward the power supply. Pull the connector block from the power supply.
c. Grasp the power supply handle while pinching the green release lever towards the handle.
d. Pull the power supply out of the bay.
Step 2 Install a new power supply:
a. Grasp the power supply handle and insert the new power supply into the empty bay.
b. Push the power supply into the bay until the release lever locks.
c. Connect the power cord to the new power supply.
For a DC power supply, push the electrical connector block into the power supply.
d. If you shut down the Cisco CSP 2100 X2, press the Power button to return the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 to main power mode.
Replacing a DC Power Supply

Warning A readily accessible two-poled disconnect device must be incorporated in the fixed wiring. Statement 1022

Warning This product requires short-circuit (overcurrent) protection, to be provided as part of the building installation. Install only in accordance with national and local wiring regulations. Statement 1045

Warning When installing or replacing the unit, the ground connection must always be made first and disconnected last. Statement 1046

Warning Installation of the equipment must comply with local and national electrical codes. Statement 1074

Warning Hazardous voltage or energy may be present on DC power terminals. Always replace cover when terminals are not in service. Be sure uninsulated conductors are not accessible when cover is in place. Statement 1075
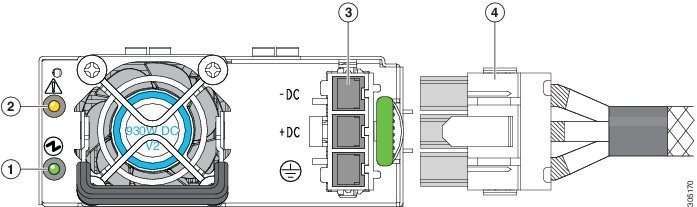
Installing a Version 2 930W DC Power Supply, UCSC-PSU2V2-930DC
If you are using the Version 2 930W DC power supply, you connect power using a 3-wire cable with a keyed connector that plugs into a fixed power input socket on the power supply. .

Step 1 Turn off the DC power source from your facility’s circuit breaker to avoid electric shock hazard.
Step 2 Wire the supplied 3-wire connector cable to your facility’s DC power source.

Note The supplied connector cable contains 8 AWG gauge wires. The recommended facility wire gauge is 8 AWG. The minimum facility wire gauge is 10 AWG.
Step 3 Plug the supplied connector cable into the power input socket on the power supply. The connector is keyed to the socket so that the polarity is aligned correctly.
Step 4 Return power from your facility’s DC power source at the circuit breaker.
Step 5 See Installation Grounding for additional information about chassis grounding.
Figure 8-25 Version 2 930 W, –48 VDC Power Supply Connector Block
Installation Grounding
The AC power supplies have internal grounding and so no additional grounding is required when the supported AC power cords are used.
When using a DC power supply, additional grounding of Cisco CSP 2100 X2 chassis to the earth ground of the rack is available. Screw holes for use with your grounding lugs and grounding wires are supplied on the chassis rear panel.

Note The grounding points on the chassis are sized for M5 screws. The grounding points are spaced at 0.625 inches (15.86 mm). You must provide your own screws, grounding lug, and grounding wire. The grounding lug required is a Panduit LCD10-14AF-L or equivalent. The grounding cable that you provide must be 14 AWG (2 mm), minimum 60° C wire, or as permitted by the local code.
See Figure 8-24 for the location of the grounding lug screw-holes on the chassis rear panel.
Replacing an mLOM Card
Cisco CSP 2100 X2 can use an mLOM card to provide additional connectivity. The mLOM card socket remains powered when the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 is in 12 V standby power mode and it supports the network communications services (NCSI) protocol.
Step 1 Power off the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 as described in Shutting Down and Powering Off the Cisco CSP 2100 X2.
Step 2 Slide the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 out the front of the rack far enough so that you can remove the top cover. You might have to detach cables from the rear panel to provide clearance.

Step 3 Remove the top cover as described in Removing and Replacing the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 Top Cover.
Step 4 Remove PCIe riser 1 to provide clearance. See Replacing a PCIe Riser for instructions.
Step 5 Remove any existing mLOM card or a blanking panel (see Figure 8-26):
a. Loosen the single thumbscrew that secures the mLOM card to the chassis floor.
b. Slide the mLOM card horizontally to disengage its connector from the motherboard socket.
Step 6 Install a new mLOM card:
a. Set the mLOM card on the chassis floor so that its connector is aligned with the motherboard socket and its thumbscrew is aligned with the standoff on the chassis floor.
b. Push the card’s connector into the motherboard socket horizontally.
c. Tighten the thumbscrew to secure the card to the chassis floor.
Step 7 Return PCIe riser 1 to the Cisco CSP 2100 X2. See Replacing a PCIe Riser for instructions.
Step 9 Replace the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 in the rack, replace cables, and then power on the Cisco CSP 2100 X2 by pressing the Power button.
Figure 8-26 mLOM Card Location

 Feedback
Feedback