Alert Types and Publishers
Alerts in Secure Workload consist of the following components:
-
Alert Visibility:
-
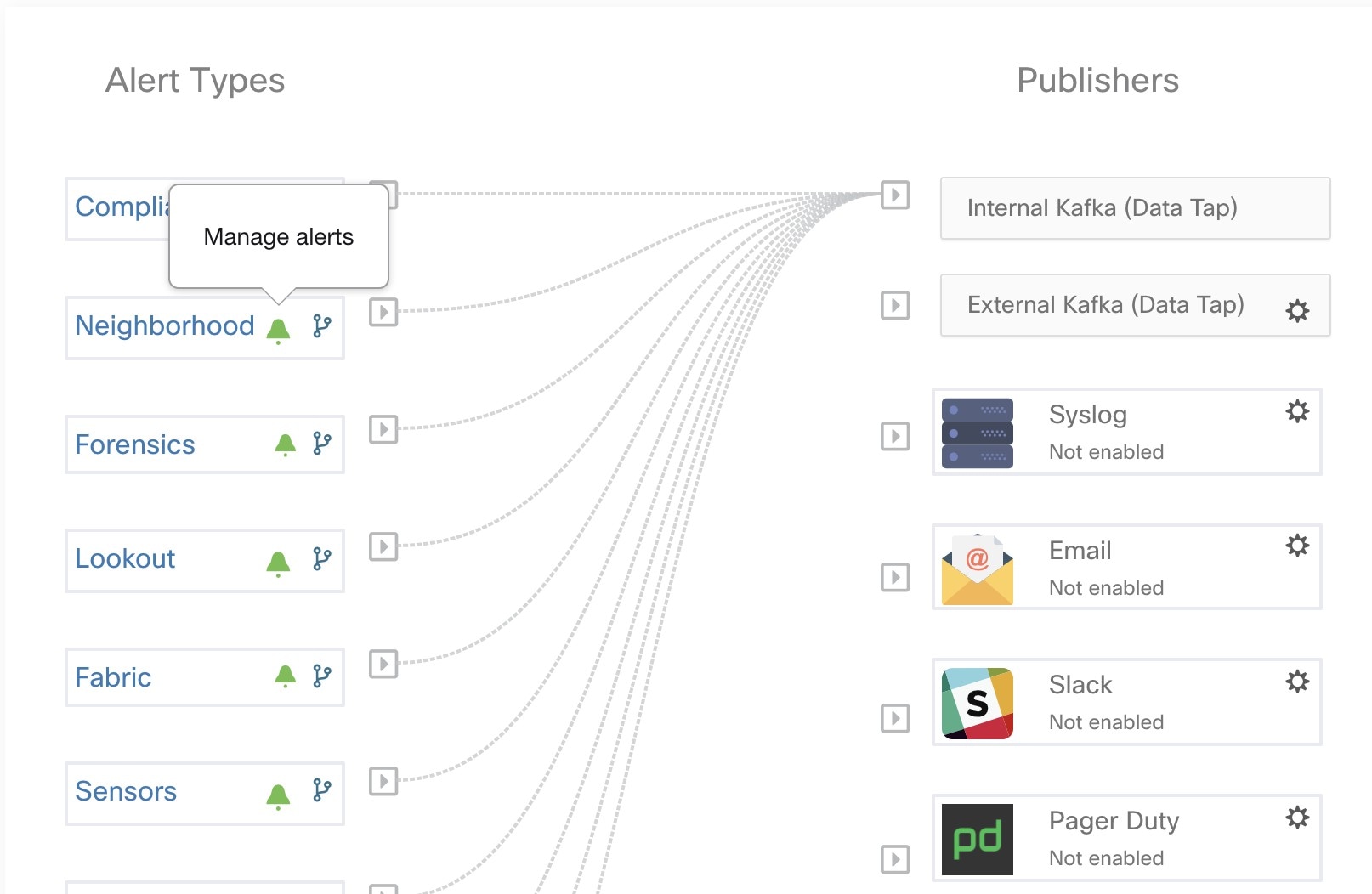
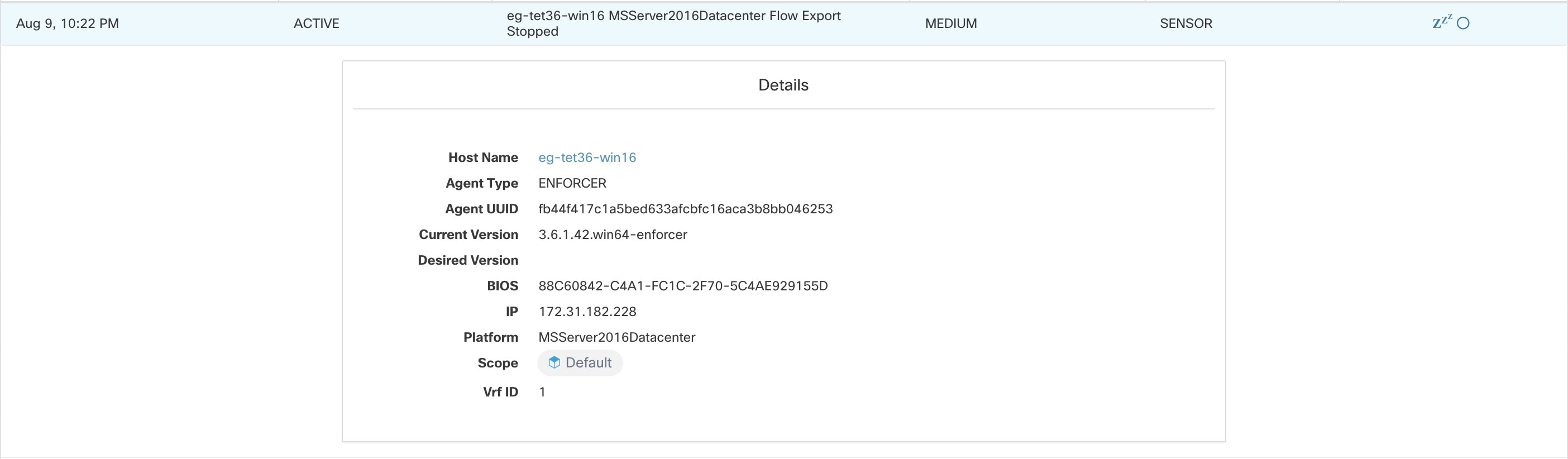
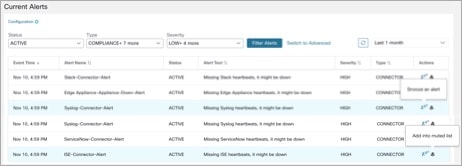
Current Alerts: Navigate to . Preview of alerts sent to a Data Tap is available.
-
-
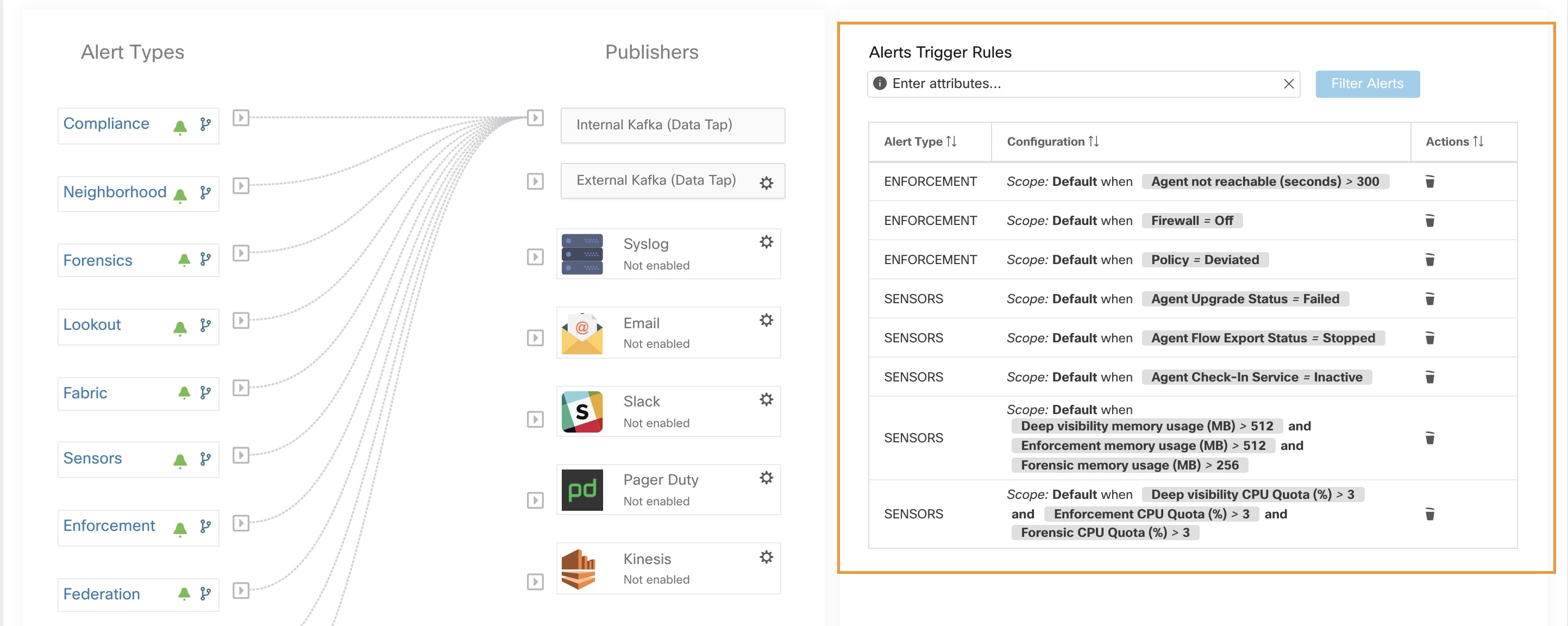
Alert Sources and Configuration:
-
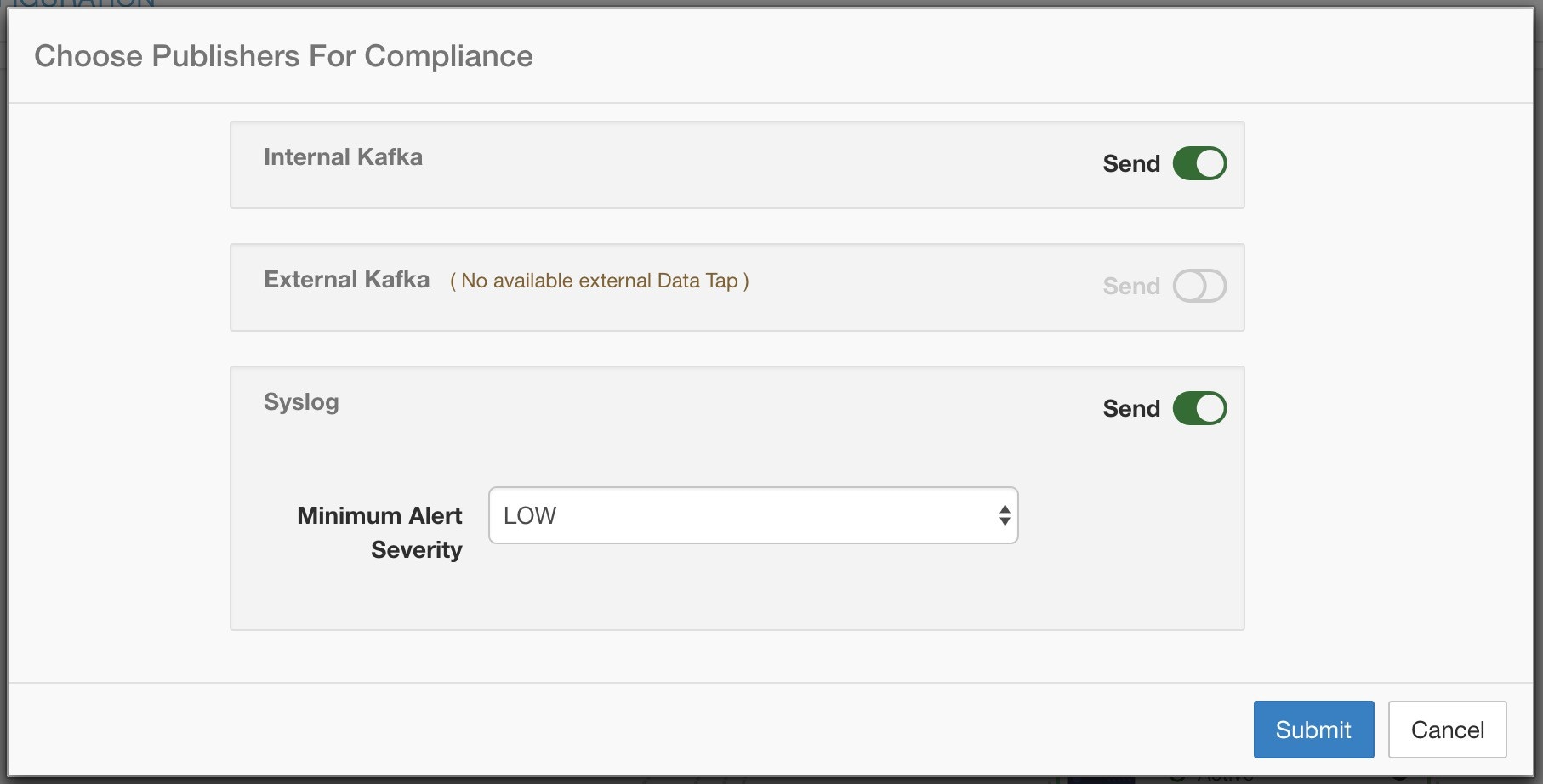
Alerts - Configuration: Navigate to . Both alert configurations that are configured using the common modal and alert publisher, and notifier settings are displayed.
-
-
Send Alerts:
-
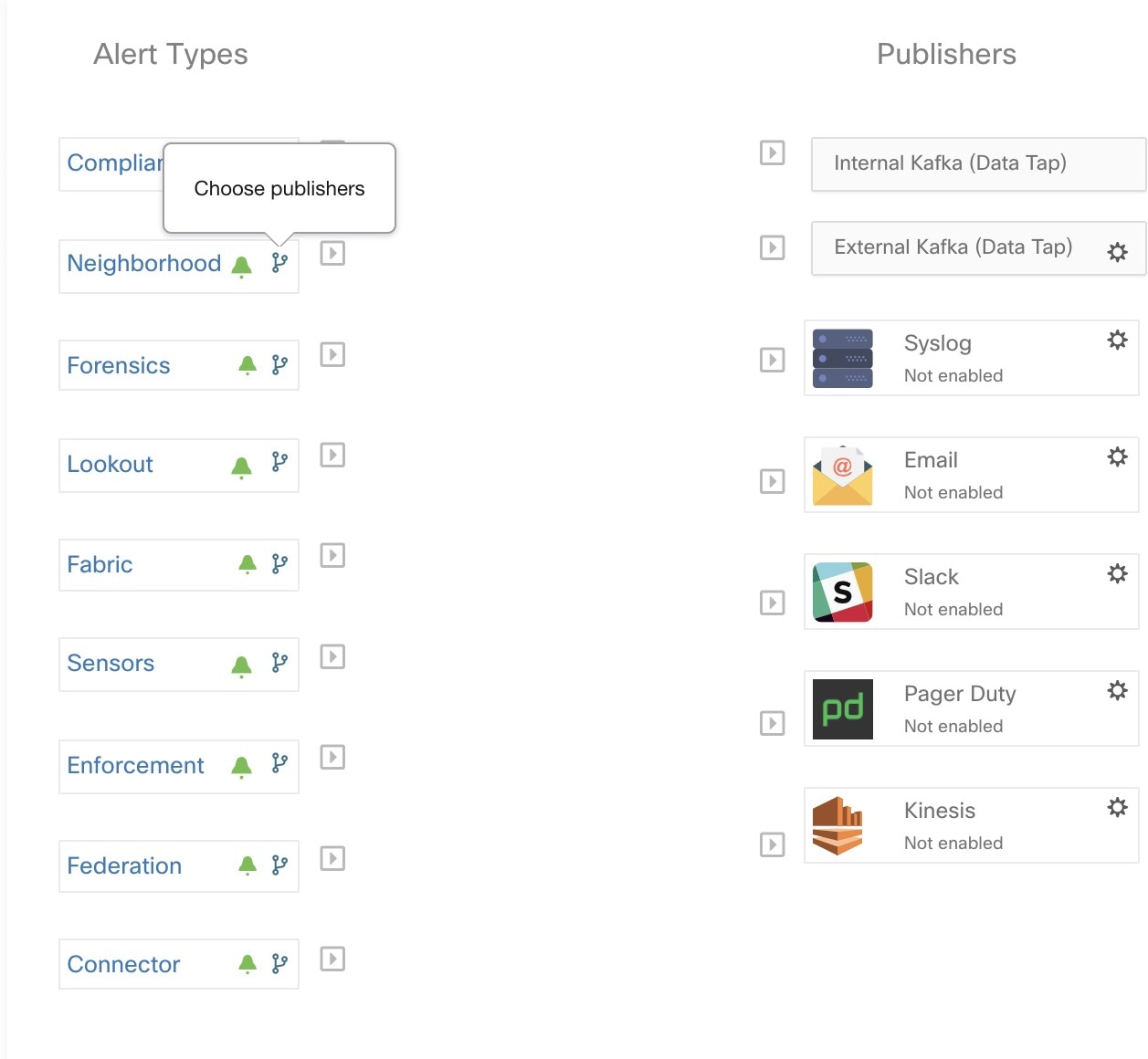
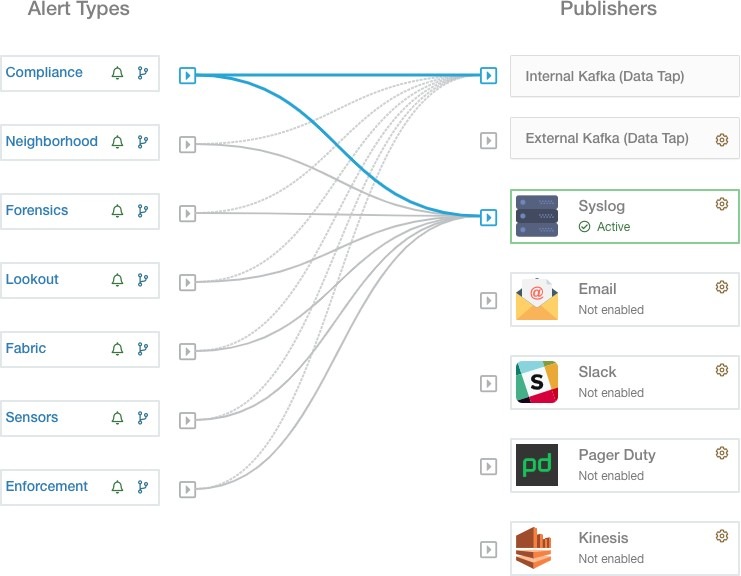
Alerts App: An implicit Secure Workload app that sends generated alerts to a configured Data Tap. The Alerts App handles features such as Snooze and Mute.
-
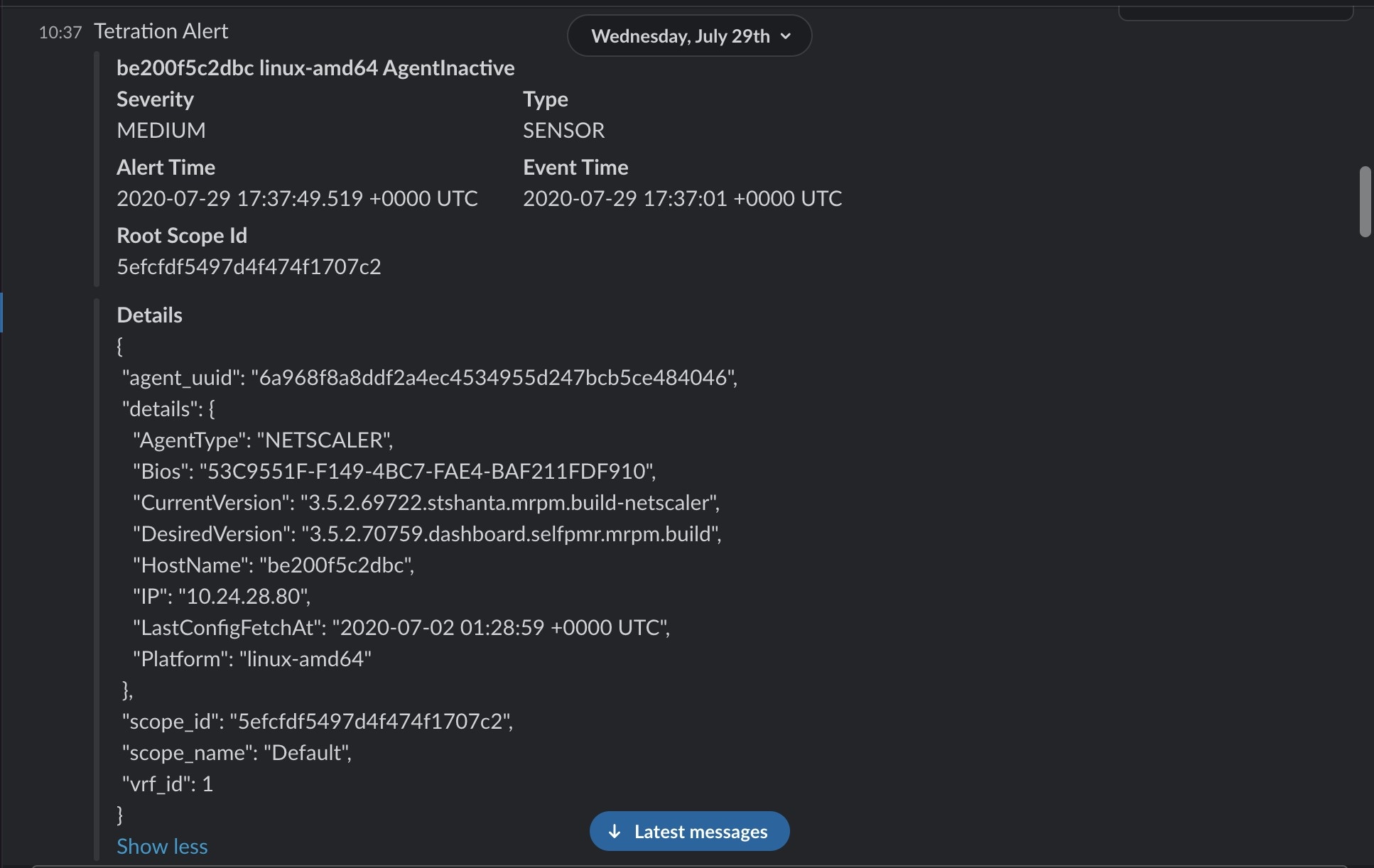
Alerts Publisher: Limits the number of alerts that are displayed and pushes alerts to Kafka (MDT or DataTap) for external consumption.
-
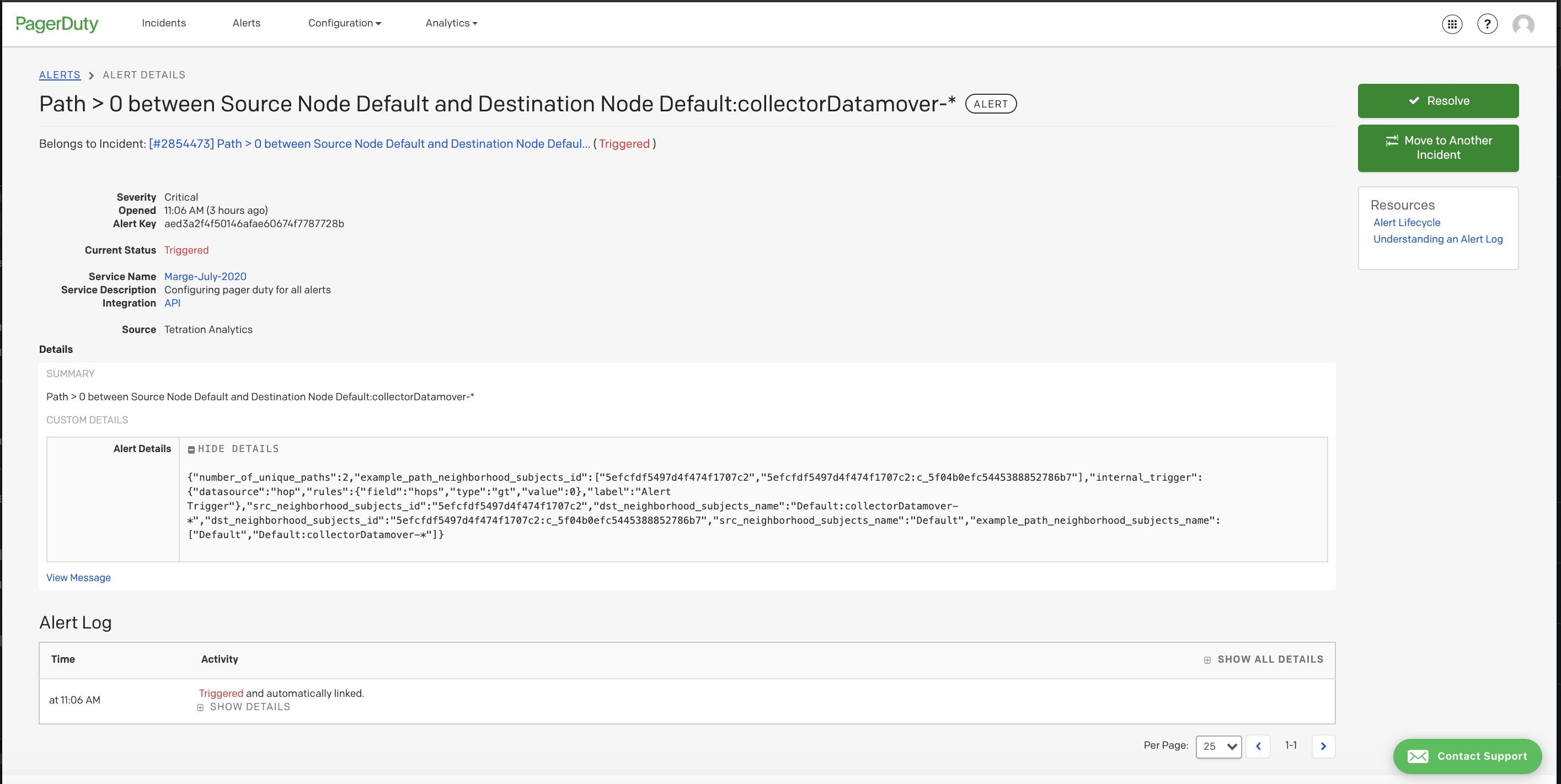
Edge Appliance: Pushes alerts to other systems such as Slack, PagerDuty, Email, and so on.
-

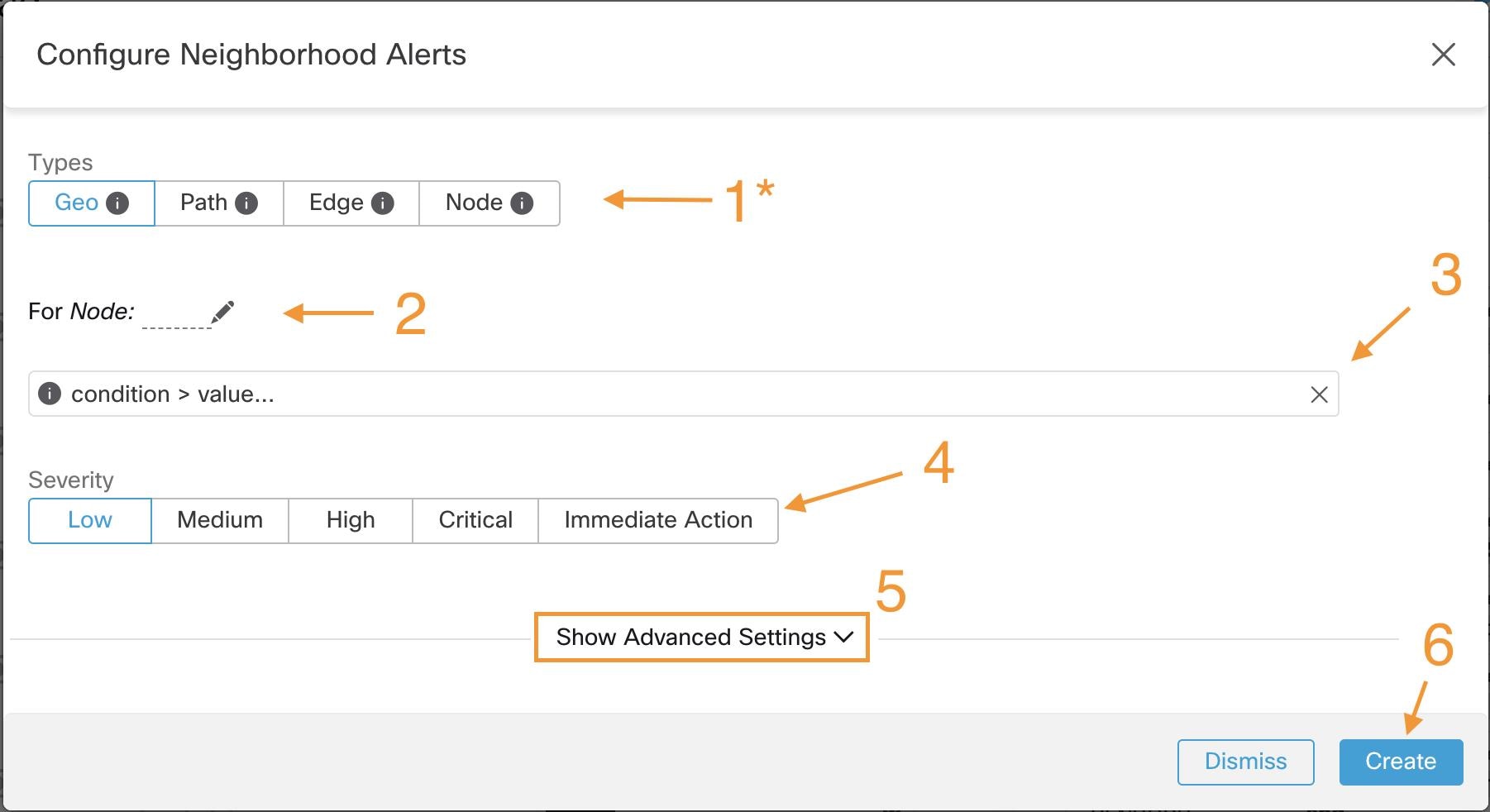
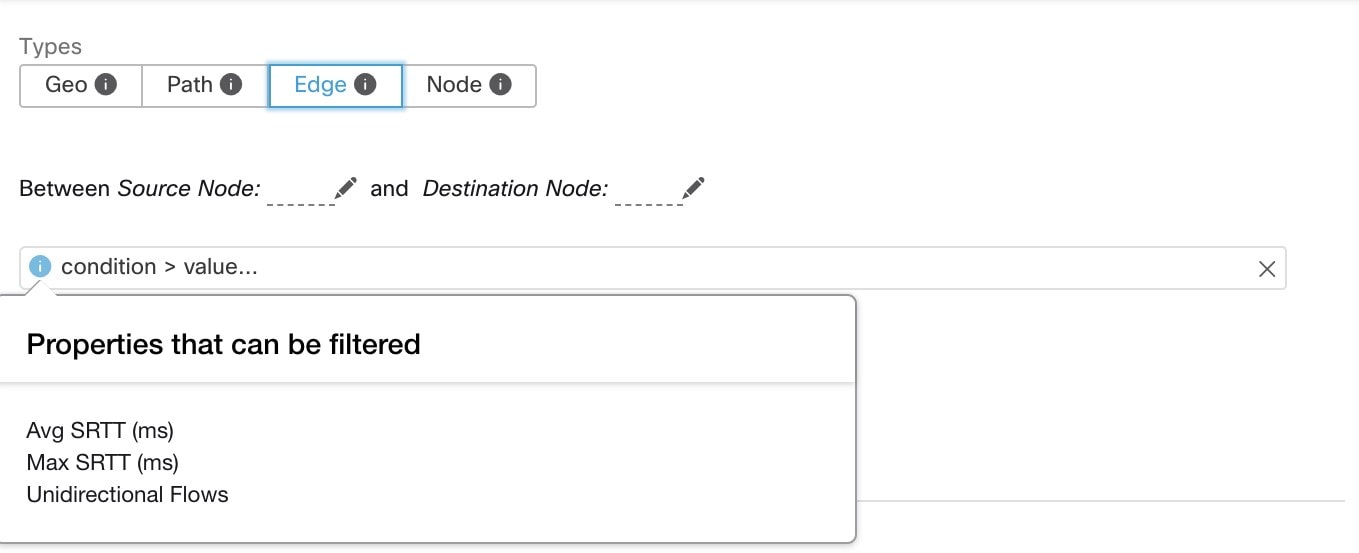
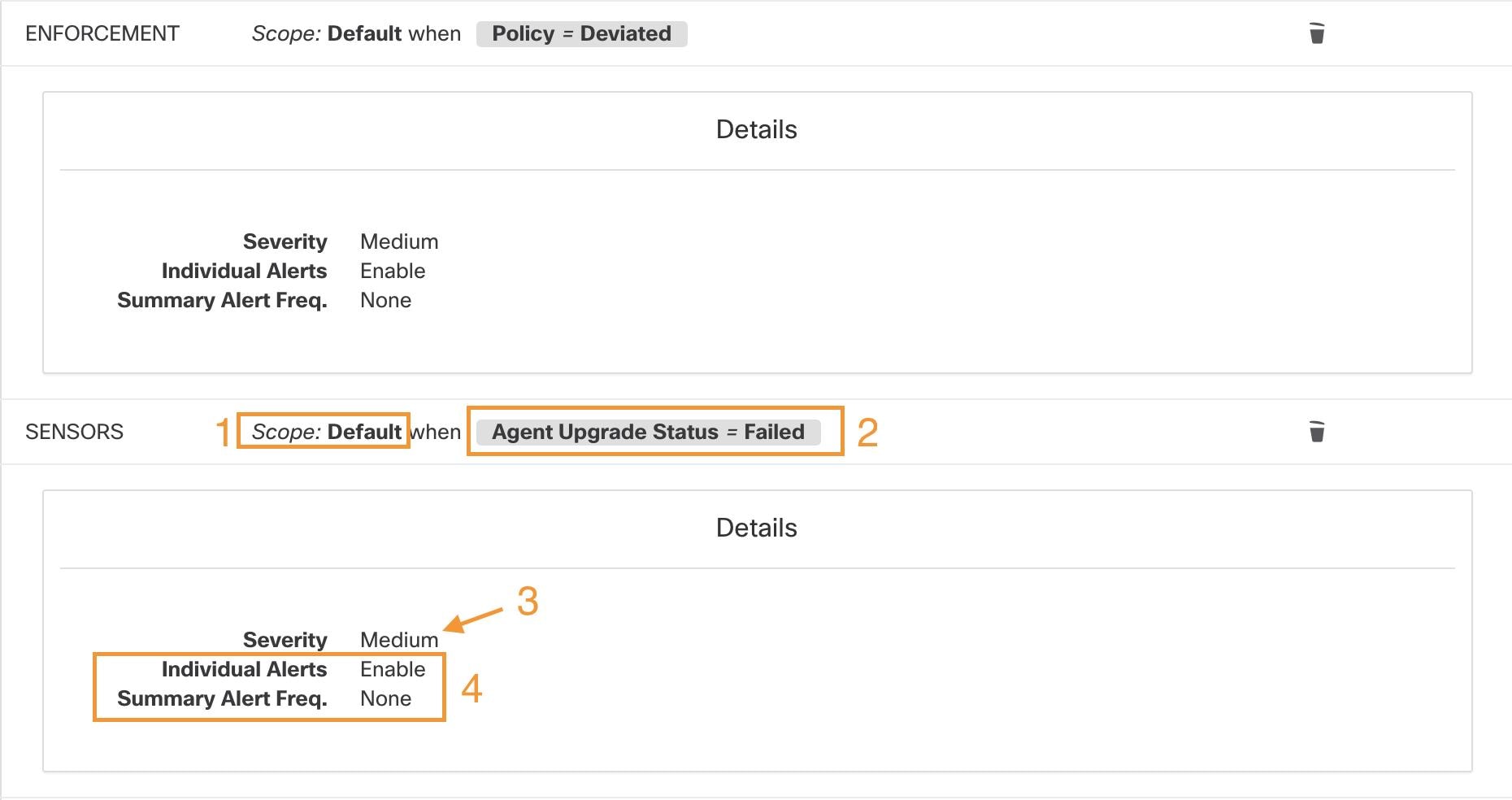
 Note: this list will show those conditions available specifically for the type of alert alert currently being configured.
Note: this list will show those conditions available specifically for the type of alert alert currently being configured.


 Feedback
Feedback