|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
exploits
|
Array of structured types
|
exploits
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
fixes
|
Array of structured types
|
fixes
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
threat_actors
|
Array of structured types
|
threat_actors
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
created_at
|
time
|
created_at
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
daily_trend
|
string
|
daily_trend
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
predicted_exploitable
|
boolean
|
predicted_exploitable
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
predicted_exploitable_confidence
|
float
|
predicted_exploitable_confidence
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
successful_exploitations
|
number
|
successful_exploitations
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
velocity_day
|
number
|
velocity_day
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
velocity_month
|
number
|
velocity_month
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
velocity_week
|
number
|
velocity_week
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
cve_id
|
string
|
cve_id
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
cvss_score
|
float
|
cvss_score
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
cvss_exploit_subscore
|
float
|
cvss_exploit_subscore
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
cvss_impact_subscore
|
float
|
cvss_impact_subscore
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
cvss_vector
|
float
|
cvss_vector
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
cvss_temporal_score
|
float
|
cvss_temporal_score
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
cvss_v3_score
|
float
|
cvss_v3_score
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
cvss_v3_exploit_subscore
|
float
|
cvss_v3_exploit_subscore
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
last_modified_on
|
_time
|
last_modified_on
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
published_on
|
_time
|
published_on
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
vulnerable_products
|
string
|
vulnerable_products
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
vuln_state
|
string
|
state
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
id
|
number
|
id
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
cve_description
|
string
|
cve_description
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
cvss_access_complexity
|
string
|
cvss_access_complexity
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
cvss_access_vector
|
string
|
cvss_access_vector
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
cvss_authentication
|
string
|
cvss_authentication
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
description
|
string
|
description
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
cisco_security_risk_score
|
float
|
risk_meter_score
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
cvss_availability_impact
|
string
|
cvss_availability_impact
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
cvss_confidentiality_impact
|
string
|
cvss_confidentiality_impact
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
cvss_integrity_impact
|
string
|
cvss_integrity_impact
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
easily_exploitable
|
boolean
|
easily_exploitable
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
malware_exploitable
|
boolean
|
malware_exploitable
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
active_internet_breach
|
boolean
|
active_internet_breach
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
malware_count
|
number
|
malware_count
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
chatter_count
|
boolean
|
chatter_count
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
popular_target
|
boolean
|
popular_target
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
remote_code_execution
|
boolean
|
remote_code_execution
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
pre_nvd_chatter
|
boolean
|
pre_nvd_chatter
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
stride_threat
|
Array of strings
|
stride_threat
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
vulnerability_type
|
Array of strings
|
vulnerability_type
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
exploitation_methodology
|
Array of strings
|
exploitation_methodology
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
affected_source_file_module
|
Array of strings
|
affected_source_file_module
|
|
Cisco Security.CVM VI Dataset
|
mitre_techniques
|
Array of strings
|
mitre_techniques
|
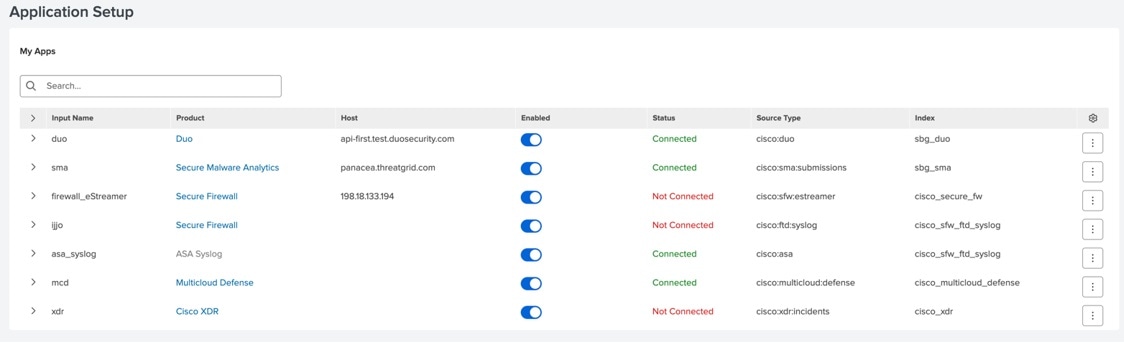

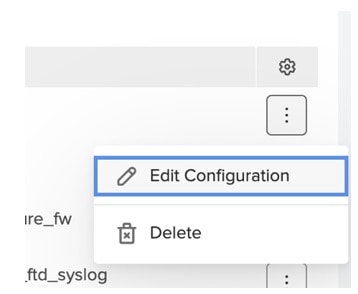
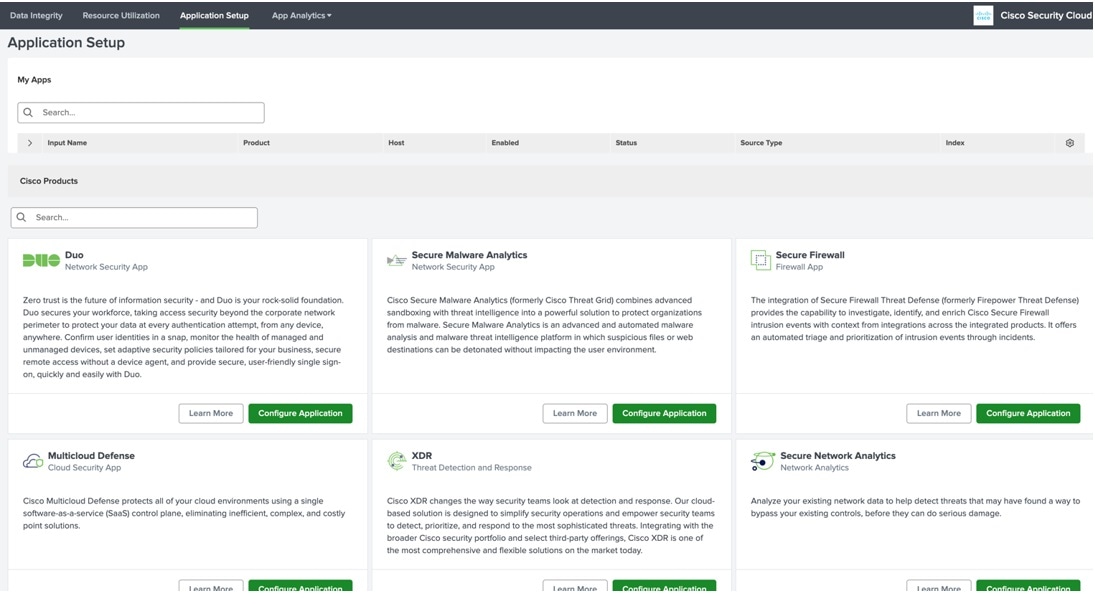



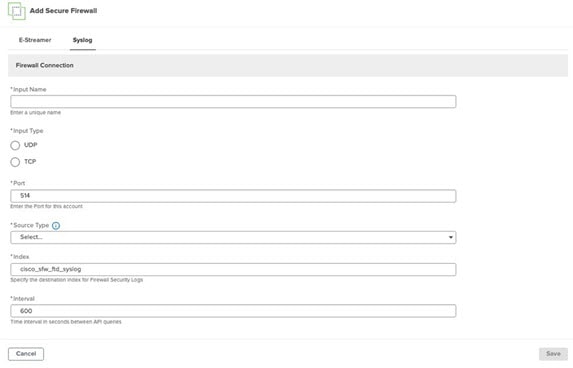
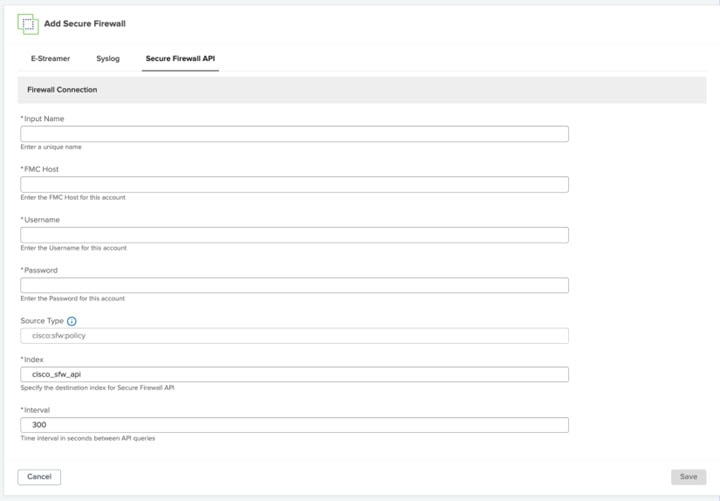
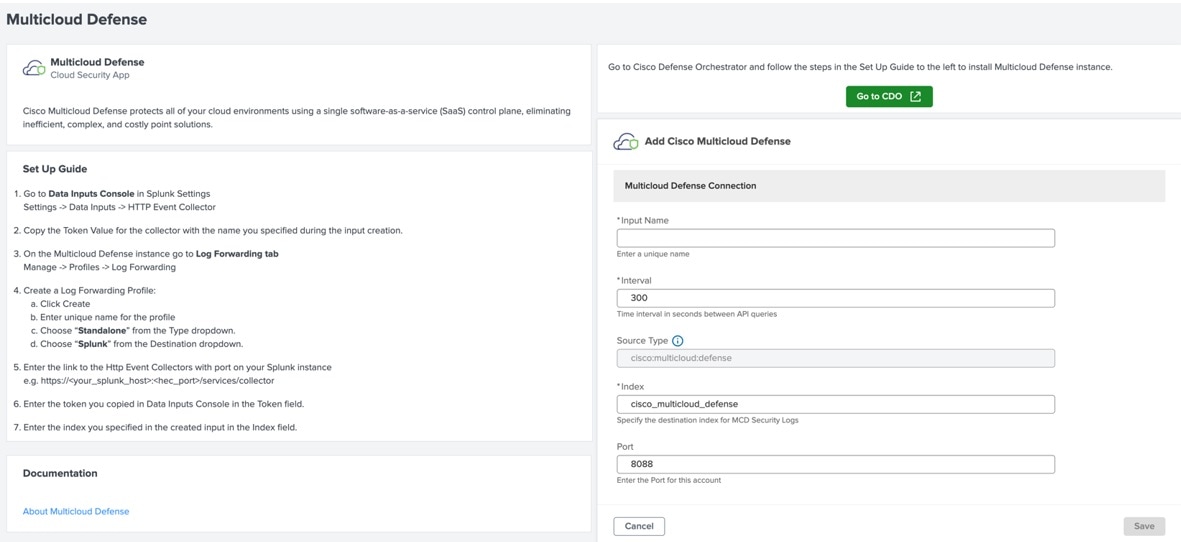

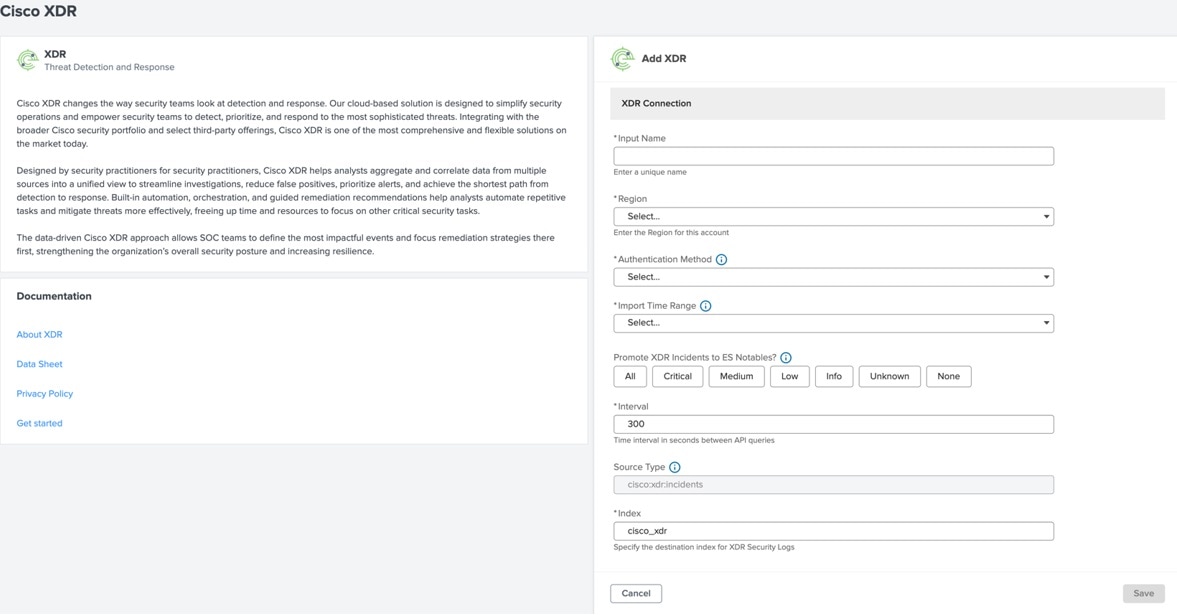

 Feedback
Feedback