- About This Guide
-
- Information about AAA
- Configuring the Local Database for AAA
- Configuring RADIUS Servers for AAA
- Configuring TACACS+ Servers for AAA
- Configuring LDAP Servers for AAA
- Configuring Windows NT Servers for AAA
- Configuring the Identity Firewall
- Configuring the ASA to Integrate with Cisco TrustSec
- Configuring Digital Certificates
- Index
- Information About the ASDM User Interface
- Navigating in the ASDM User Interface
- Menus
- Toolbar
- ASDM Assistant
- Status Bar
- Device List
- Common Buttons
- Keyboard Shortcuts
- Find Function
- Enabling Extended Screen Reader Support
- Organizational Folder
- About the Help Window
- Home Pane (Single Mode and Context)
- Home Pane (System)
- Defining ASDM Preferences
- Using the ASDM Assistant
- Enabling History Metrics
- Unsupported Commands
Using ASDM
This chapter describes how to use the ASDM user interface, and includes the following sections:
- Information About the ASDM User Interface
- Navigating in the ASDM User Interface
- Menus
- Toolbar
- ASDM Assistant
- Status Bar
- Device List
- Common Buttons
- Keyboard Shortcuts
- Find Function
- Enabling Extended Screen Reader Support
- Organizational Folder
- About the Help Window
- Home Pane (Single Mode and Context)
- Home Pane (System)
- Defining ASDM Preferences
- Using the ASDM Assistant
- Enabling History Metrics
- Unsupported Commands
Information About the ASDM User Interface
The ASDM user interface is designed to provide easy access to the many features that the ASA supports. The ASDM user interface includes the following elements:
- A menu bar that provides quick access to files, tools, wizards, and help. Many menu items also have keyboard shortcuts.
- A toolbar that enables you to navigate ASDM. From the toolbar you can access the home, configuration, and monitoring panes. You can also get help and navigate between panes.
- A dockable left Navigation pane to move through the Configuration and Monitoring panes. You can click one of the three buttons in the header to maximize or restore this pane, make it a floating pane that you can move, hide it, or close it. To access the Configuration and Monitoring panes, you can do one of the following:
–![]() Click links on the left side of the application window in the left Navigation pane. The Content pane then displays the path (for example, Configuration > Device Setup > S tartup Wizard) in the title bar of the selected pane.
Click links on the left side of the application window in the left Navigation pane. The Content pane then displays the path (for example, Configuration > Device Setup > S tartup Wizard) in the title bar of the selected pane.
–![]() If you know the exact path, you can type it directly into the title bar of the Content pane on the right side of the application window, without clicking any links in the left Navigation pane.
If you know the exact path, you can type it directly into the title bar of the Content pane on the right side of the application window, without clicking any links in the left Navigation pane.
- A maximize and restore button in the right corner of the Content pane that lets you hide and show the left Navigation pane.
- A dockable device list pane with a list of devices that you can access through ASDM. You can click one of the three buttons in the header to maximize or restore this pane, make it a floating pane that you can move, hide it, or close it. For more information, see the “Device List” section.
- A status bar that shows the time, connection status, user, memory status, running configuration status, privilege level, and SSL status at the bottom of the application window.
- A left Navigation pane that shows various objects that you can use in the rules tables when you create access rules, NAT rules, AAA rules, filter rules, and service rules. The tab titles within the pane change according to the feature that you are viewing. In addition, the ASDM Assistant appears in this pane.
Figure 4-1 shows the elements of the ASDM user interface.
Figure 4-1 ASDM User Interface
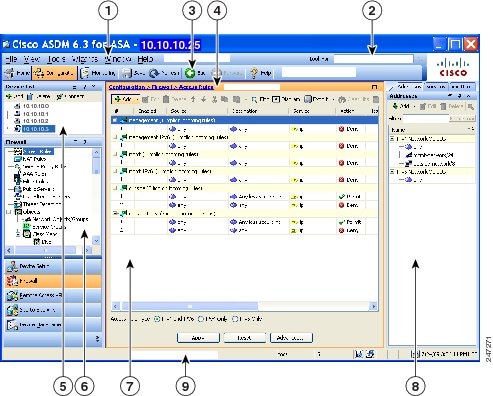
|
|
|
|---|---|

Note![]() Tool tips have been added for various parts of the GUI, including Wizards, the Configuration and Monitoring panes, and the Status Bar. To view tool tips, hover your mouse over a specific user interface element, such as an icon in the status bar.
Tool tips have been added for various parts of the GUI, including Wizards, the Configuration and Monitoring panes, and the Status Bar. To view tool tips, hover your mouse over a specific user interface element, such as an icon in the status bar.
Navigating in the ASDM User Interface
To move efficiently throughout the ASDM user interface, you may use a combination of menus, the toolbar, dockable panes, and the left and right Navigation panes, which are described in the previous section. The available functions appear in a list of buttons below the Device List pane. An example list could include the following function buttons:
- Device Setup
- Firewall
- Trend Micro Content Security
- Botnet Traffic Filter
- Remote Access VPN
- Site to Site VPN
- Device Management
The list of function buttons that appears is based on the licensed features that you have purchased. Click each button to access the first pane in the selected function for either the Configuration view or the Monitoring view. The function buttons are not available in the Home view.
To change the display of function buttons, perform the following steps:
Step 1![]() Choose the drop-down list below the last function button to display a context menu.
Choose the drop-down list below the last function button to display a context menu.
Step 2![]() Choose one of the following options:
Choose one of the following options:
- To show more buttons, click Show More Buttons .
- To show fewer buttons, click Show Fewer Buttons .
- To add or remove buttons, click Add or Remove Buttons , then click the button to add or remove from the list that appears.
- To change the sequence of the buttons, choose Option to display the Option dialog box, which displays a list of the buttons in their current order. Then choose one of the following:
–![]() To move up a button in the list, click Move Up .
To move up a button in the list, click Move Up .
–![]() To move down a button in the list, click Move Down .
To move down a button in the list, click Move Down .
–![]() To return the order of the items in the list to the default setting, click Reset .
To return the order of the items in the list to the default setting, click Reset .
Step 3![]() To save your settings and close this dialog box, click OK .
To save your settings and close this dialog box, click OK .
Menus
You can access ASDM menus using the mouse or keyboard. For information about accessing the menu bar from the keyboard, see the “Keyboard Shortcuts” section.
File Menu
The File menu lets you manage ASA configurations. The following table lists the tasks that you can perform using the File menu.
|
|
|
|---|---|
Ensures that ASDM has a current copy of the running configuration. |
|
Restores the configuration to the factory default. See the “Restoring the Factory Default Configuration” section for more information. |
|
Stores a copy of the current running configuration file on a TFTP server. See the “Saving the Running Configuration to a TFTP Server” section for more information. |
|
Sends a copy of the running configuration file on the primary unit to the running configuration of a failover standby unit. |
|
Prints the current page. We recommend landscape page orientation when you print rules. When you use Internet Explorer, permission to print was already granted when you originally accepted the signed applet. |
|
Removes local ASDM images. ASDM downloads images locally when you connect to ASDM. |
|
Removes the password cache if you have defined a new password and still have a existing password that is different than the new password. |
|
View Menu
The View menu lets you display various parts of the ASDM user interface. Certain items are dependent on the current view. You cannot select items that cannot be displayed in the current view. The following table lists the tasks that you can perform using the View menu.
|
|
|
|---|---|
Display a list of devices in a dockable pane. See the “Device List” section for more information. |
|
Shows and hides the display of the Navigation pane in the Configuration and Monitoring views. |
|
Searches and finds useful ASDM procedural help about certain tasks. See the “ASDM Assistant” section for more information. |
|
Shows and hides the display of the Latest ASDM Syslog Messages pane in the Home view. This pane is only available in the Home view. If you do not have sufficient memory to upgrade to the most current release, syslog message %ASA-1-211004 is generated, indicating what the installed memory is and what the required memory is. This message reappears every 24 hours until the memory is upgraded. |
|
Shows and hides the display of the Addresses pane. The Addresses pane is only available for the Access Rules, NAT Rules, Service Policy Rules, AAA Rules, and Filter Rules panes in the Configuration view. |
|
Shows and hides the display of the Services pane. The Services pane is only available for the Access Rules, NAT Rules, Service Policy Rules, AAA Rules, and Filter Rules panes in the Configuration view. |
|
Shows and hides the display of the Time Ranges pane. The Time Ranges pane is only available for the Access Rules, Service Policy Rules, AAA Rules, and Filter Rules panes in the Configuration view. |
|
Shows and hides the display of the Global Pools pane. The Global Pools pane is only available for the NAT Rules pane in the Configuration view. |
|
Locates an item for which you are searching, such as a feature or the ASDM Assistant. |
|
Returns to the previous pane. See the “Common Buttons” section for more information. |
|
Goes to the next pane previously visited. See the “Common Buttons” section for more information. |
|
Changes the screen fonts and colors to the Microsoft Office settings. |
Tools Menu
The Tools menu provides you with the following series of tools to use in ASDM.
|
|
|
|---|---|
Sends commands to the ASA and view the results. See the “Using the Command Line Interface Tool in ASDM” section for more information. |
|
Displays unsupported commands that have been ignored by ASDM. See the “Showing Commands Ignored by ASDM on the Device” section for more information. |
|
Traces a packet from a specified source address and interface to a destination. You can specify the protocol and port of any type of data and view the lifespan of a packet, with detailed information about actions taken on it. See the Tracing Packets with Packet Tracer section in the firewall configuration guide for more information. |
|
Verifies the configuration and operation of the ASA and surrounding communications links, as well as performs basic testing of other network devices. See the Disabling the Test Configuration section in the firewall configuration guide for more information. |
|
Determines the route that packets will take to their destination. See the Determining Packet Routing with Traceroute section in the firewall configuration guide for more information. |
|
Views, moves, copies, and deletes files stored in flash memory. You can also create a directory in flash memory. See the “Managing Files” section for more information. You can also transfer files between various file systems, including TFTP, flash memory, and your local PC. See the “Transferring Files” section for more information. |
|
Uploads an ASA image, ASDM image, or another image on your PC to flash memory. See the “Managing Files” section dialog box for more information. |
|
Upgrades ASA software and ASDM software through a wizard. See the “The Upgrade Software from Cisco.com Wizard lets you automatically upgrade the ASDM and ASA to more current versions.” section for more information. |
|
Backs up the ASA configuration, a Cisco Secure Desktop image, and SSL VPN Client images and profiles. See the “Backing Up Configurations” section for more information. |
|
Restores the ASA configuration, a Cisco Secure Desktop image, and SSL VPN Client images and profiles. See the “Restoring Configurations” section for more information. |
|
Restarts the ASDM and reload the saved configuration into memory. See the “Scheduling a System Restart” section for more information. |
|
Enables an administrator to send an alert message to clientless SSL VPN users. See the Capturing Data section in the VPN configuration guide for more information. |
|
If you migrate to 8.3 or later, the ASA creates named network objects to replace inline IP addresses in some features. In addition to named objects, ASDM automatically creates non-named objects for any IP addresses used in the configuration. These auto-created objects are identified by the IP address only, do not have a name, and are not present as named objects in the platform configuration. When the ASA creates named objects as part of the migration, the matching non-named ASDM-only objects are replaced with the named objects. The only exception are non-named objects in a network object group. When the ASA creates named objects for IP addresses that are inside a network object group, ASDM retains the non-named objects as well, creating duplicate objects in ASDM. To merge these objects, choose Tools > Migrate Network Object Group Members . See Cisco ASA 5500 Migration to Version 8.3 and Later for more information. |
|
Changes the behavior of specified ASDM functions between sessions. See the “Defining ASDM Preferences” section for more information. |
|
Shows the Java console. See the “Viewing and Copying Logged Entries with the ASDM Java Console” section for more information. |
Wizards Menu
The Wizards menu lets you run a wizard to configure multiple features. The following table lists the available Wizards and their features.
|
|
|
|---|---|
Guides you, step-by-step, through the initial configuration of the ASA. For more information, see Chapter7, “Using the Startup Wizard”. |
|
Enables you to configure an IPsec VPN policy on the ASA. For more information, see Chapter 73, “VPN Wizards,” in the VPN configuration guide. |
|
Enables you to configure an SSL VPN policy on the ASA. For more information, see Chapter 73, “VPN Wizards,” in the VPN configuration guide. |
|
Allows you to configure failover: VPN cluster load balancing, or ASA clustering on the ASA. For more information, see:
|
|
Enables you to configure unified communication features, such as an IP phone, on the ASA. For more information, see Chapter 15, “Information about the Cisco Unified Communication Wizard,” in the firewall configuration guide. |
|
Allows you to configure packet capture on the ASA. The wizard runs one packet capture on each ingress and egress interface. After you run the capture, you can save it on your computer, and then examine and analyze the capture with a packet analyzer. For more information, see the “Configuring and Running Captures with the Packet Capture Wizard” section. |
Window Menu
The Window menu enables you to move between ASDM windows. The active window appears as the selected window.
Help Menu
The Help menu provides links to online Help, as well as information about ASDM and the ASA. The following table lists the tasks that you can perform using the Help menu.
Toolbar
The Toolbar below the menus provides access to the Home view, Configuration view, and Monitoring view. It also lets you choose between the system and security contexts in multiple context mode, and provides navigation and other commonly used features. The following table lists the tasks that you can perform using the Toolbar.
|
|
|
|---|---|
Shows which context you are in. To open the context list in the left-hand pane, click the down arrow, then click the up arrow to restore the context drop-down list. After you have expanded this list, click the left arrow to collapse the pane, then the right arrow to restore the pane. To manage the system, choose System from the drop-down list. To manage the context, choose one from the drop-down list. |
|
Displays the Home pane, which lets you view important information about your ASA such as the status of your interfaces, the version you are running, licensing information, and performance. See the “Home Pane (Single Mode and Context)” section for more information. In multiple mode, the system does not have a Home pane. |
|
Configures the ASA. Click a function button in the left Navigation pane to configure that function. |
|
Monitors the ASA. Click a function button in the left Navigation pane to configure that function. |
|
Searches for a feature in ASDM. The Search function looks through the titles of each pane and presents you with a list of matches, and gives you a hyperlink directly to that pane. If you need to switch quickly between two different panes that you found, click Back or Forward . See the “ASDM Assistant” section for more information. |
|
Refreshes ASDM with the current running configuration, except for graphs in any of the Monitoring panes. |
|
Saves the running configuration to the startup configuration for write-accessible contexts only. |
|
Shows context-sensitive help for the screen that is currently open. |
ASDM Assistant
The ASDM Assistant lets you search and view useful ASDM procedural help about certain tasks. This feature is available in routed and transparent modes, and in the single and system contexts.
To access information, choose View > ASDM Assistant > How Do I? or enter a search request from the Look For field in the menu bar. From the Find drop-down list, choose How Do I? to begin the search.
To use the ASDM Assistant, perform the following steps:
Step 1![]() In the main ASDM application window, choose View > ASDM Assistant .
In the main ASDM application window, choose View > ASDM Assistant .
The ASDM Assistant pane appears.
Step 2![]() In the Search field, enter the information that you want to find, and click Go .
In the Search field, enter the information that you want to find, and click Go .
The requested information appears in the Search Results pane.
Step 3![]() Click any links that appear in the Search Results and Features areas to obtain more details.
Click any links that appear in the Search Results and Features areas to obtain more details.
Status Bar
The status bar appears at the bottom of the ASDM window. The following table lists the areas shown from left to right.
|
|
|
|---|---|
The status of the configuration (for example, “Device configuration loaded successfully.”) |
|
The username of the ASDM user. If you logged in without a username, the username is “admin.” |
|
Click the icon to show a list of commands from your configuration that ASDM did not process. These commands will not be removed from the configuration. |
|
The ASDM connection status to the ASA. See the “Connection to Device” section for more information. |
|
The syslog connection is up, and the ASA is being monitored. |
|
Connection to Device
ASDM maintains a constant connection to the ASA to maintain up-to-date Monitoring and Home pane data. This dialog box shows the status of the connection. When you make a configuration change, ASDM opens a second connection for the duration of the configuration, and then closes it; however, this dialog box does not represent the second connection.
Device List
The device list is a dockable pane. You can click one of the three buttons in the header to maximize or restore this pane, make it a floating pane that you can move, hide it, or close it. This pane is available in the Home, Configuration, Monitoring, and System views. You can use this pane to switch to another device; however, that device must run the same version of ASDM that you are currently running. To display the pane fully, you must have at least two devices listed. This feature is available in routed and transparent modes, and in the single, multiple, and system contexts.
To use this pane to connect to another device, perform the following steps:
Step 1![]() Click Add to add another device to the list.
Click Add to add another device to the list.
The Add Device dialog box appears.
Step 2![]() In the Device/IP Address/Name field, type the device name or IP address of the device, and then click OK .
In the Device/IP Address/Name field, type the device name or IP address of the device, and then click OK .
Step 3![]() Click Delete to remove a selected device from the list.
Click Delete to remove a selected device from the list.
Step 4![]() Click Connect to connect to another device.
Click Connect to connect to another device.
The Enter Network Password dialog box appears.
Step 5![]() Type your username and password in the applicable fields, and then click Login.
Type your username and password in the applicable fields, and then click Login.
Common Buttons
Many ASDM panes include buttons that are listed in the following table. Click the applicable button to complete the desired task:
Keyboard Shortcuts
You can use the keyboard to navigate the ASDM user interface.
Table 4-1 lists the keyboard shortcuts you can use to move across the three main areas of the ASDM user interface.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Table 4-2 lists the keyboard shortcut you can use to navigate within a pane.
|
|
|
|---|---|
Table 4-3 lists the keyboard shortcuts you can use with the Log Viewers.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Table 4-4 lists the keyboard shortcuts you can use to access menu items.
|
|
|
|---|---|
Find Function
This section includes the following topics:
Using the Find Function in Most ASDM Panes
Some ASDM panes contain tables with many elements. To make it easier for you to search, highlight, and then edit a particular entry, several ASDM panes have a find function that allows you to search on objects within those panes.
To perform a search, you can type a phrase into the Find field to search on all columns within any given pane. The phrase can contain the wild card characters “*” and “?”. The * matches one or more characters, and ? matches one character. The up and down arrows to the right of the Find field locate the next (up) or previous (down) occurrence of the phrase. Check the Match Case check box to find entries with the exact uppercase and lowercase characters that you enter.
For example, entering B*ton-L* might return the following matches:
Entering Bo?ton might return the following matches:
The following list shows the ASDM panes in which you can use the find function:
- AAA Server Groups panes
- ACL Manager panes—The find function in the ACL Manager pane differs from that of the other panes. See the “Using the Find Function in the ACL Manager Pane” section for more information.
- Certificate-to-Conn Profile Maps-Rules pane
- DAP panes
- Identity Certificates pane
- IKE Policies pane
- IPSec Proposals (Transform Sets) pane
- Local User panes
- Portal-Bookmark pane
- Portal-Customization panes
- Portal-Port Forwarding pane
- CA Certificates pane
- Portal-Smart Tunnels pane
- Portal-Web Contents pane
- VPN Connection Profiles panes
- VPN Group Policies panes
Using the Find Function in the ACL Manager Pane
Because ACLs and ACEs contain many elements of different types, the find function in the ACL Manager pane allows for a more targeted search than the find function in other panes.
To find elements within the ACL Manager pane, perform the following steps:
Step 2![]() In the Filter field, choose one of the following options from the drop-down list:
In the Filter field, choose one of the following options from the drop-down list:
- Source—The search includes a source IP address of a the network object group, interface IP, or any address from which traffic is permitted or denied. You specify this address in Step 4.
- Destination—The search includes a destination IP address (host or network) that is permitted or denied to send traffic to the IP addresses listed in the Source section. You specify this address in Step 4.
- Source or Destination—The search includes either a source or a destination address that you specify in Step 4.
- Service—The search includes a service group or predefined service policy that you specify in Step 4.
- Query—When you choose Query from the drop-down list, click Query to specify a detailed search by all four of the preceding options: Source, Destination, Source or Destination, and Service.
Step 3![]() In the second field, choose one of the following options from the drop-down list:
In the second field, choose one of the following options from the drop-down list:
Step 4![]() In the third field, enter specific criteria about ACLs or ACEs that you would like to find, or click the browse button to search for key elements in your ACL/ACE configuration.
In the third field, enter specific criteria about ACLs or ACEs that you would like to find, or click the browse button to search for key elements in your ACL/ACE configuration.
Step 5![]() Click Filter to perform the search.
Click Filter to perform the search.
The ASDM find function returns a list of ACLs and ACEs that contain your specified criteria.
Step 6![]() Click Clear to clear the list of found ACLs and ACEs.
Click Clear to clear the list of found ACLs and ACEs.
Step 7![]() Click the red x to close the find function box.
Click the red x to close the find function box.
Enabling Extended Screen Reader Support
By default, labels and descriptions are not included in tab order when you press the Tab key to navigate a pane. Some screen readers, such as JAWS, only read screen objects that have the focus. You can include the labels and descriptions in the tab order by enabling extended screen reader support.
To enable extended screen reader support, perform the following steps:
Step 1![]() In the main ASDM application window, choose Tools > Preferences .
In the main ASDM application window, choose Tools > Preferences .
The Preferences dialog box appears.
Step 2![]() On the General tab, check the Enable screen reader support check box.
On the General tab, check the Enable screen reader support check box.
Step 4![]() Restart ASDM to activate screen reader support.
Restart ASDM to activate screen reader support.
Organizational Folder
Some folders in the navigation pane for the configuration and monitoring views do not have associated configuration or monitoring panes. These folders are used to organize related configuration and monitoring tasks. Clicking these folders displays a list of sub-items in the right Navigation pane. You can click the name of a sub-item to go to that item.
About the Help Window
To obtain the information that you need, click the applicable button listed in the following table.
|
|
|
|---|---|
Displays information about ASDM, including the hostname, version number, device type, ASA software version number, privilege level, username, and operating system being used. |
|
Home Pane (Single Mode and Context)
The ASDM Home pane lets you view important information about your ASA. Status information in the home pane is updated every ten seconds. This pane usually has two tabs: Device Dashboard and Firewall Dashboard.
If you have a CSC SSM installed in your ASA, the Content Security tab also appears in the Home pane. The additional tab displays status information about the CSC SSM software.
If you have IPS software installed in your ASA, the Intrusion Prevention tab also appears in the Home pane. The additional tab displays status information about the IPS software.
This section includes the following topics:
- Device Dashboard Tab
- Firewall Dashboard Tab
- Cluster Dashboard Tab
- Cluster Firewall Dashboard Tab
- Content Security Tab
- Intrusion Prevention Tab
- ASA CX Status Tab
Device Dashboard Tab
The Device Dashboard tab lets you view, at a glance, important information about your ASA, such as the status of your interfaces, the version you are running, licensing information, and performance.
Figure 4-2 shows the elements of the Device Dashboard tab.
Figure 4-2 Device Dashboard Tab
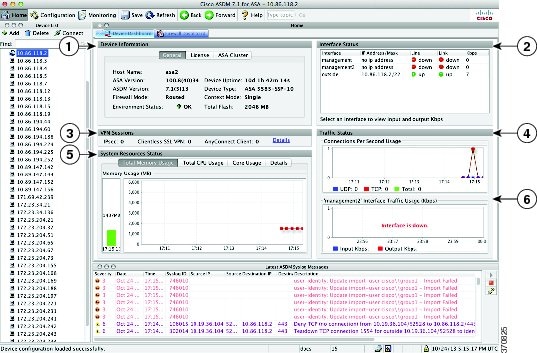
|
|
|
|---|---|
Device Information Pane
The Device Information pane includes two tabs that show device information: General tab and License tab. Under the General tab you have access to the Environment Status button, which provides an at-a-glance view of the system health:
General Tab
This tab shows basic information about the ASA:
- Host name—Shows the hostname of the device.
- ASA version—Lists the version of ASA software that is running on the device.
- ASDM version—Lists the version of ASDM software that is running on the device.
- Firewall mode—Shows the firewall mode in which the device is running.
- Total flash—Displays the total RAM that is currently being used.
- ASA Cluster Role—When you enable clustering, shows the role of this unit, either Master or Slave.
- Device uptime—Shows the time in which the device has been operational since the latest software upload.
- Context mode—Shows the context mode in which the device is running.
- Total Memory—Shows the DRAM installed on the ASA.
- Environment status—Shows the system health. The ASA 5580 and 5585 chassis models provide a set of hardware statistics that is available by clicking the plus sign (+) to the right of the Environment Status label in the General tab. You can see how many power supplies are installed, track the operational status of the fan and power supply modules, and track the temperatures of the CPUs and the ambient temperature of the system.
In general, the Environment Status button provides an at-a-glance view of the system health. If all monitored hardware components within the system are operating within normal ranges, the plus sign (+) button shows OK in green. Conversely, if any one component within the hardware system is operating outside of normal ranges, the plus sign (+) button turns into a red circle to show Critical status and to indicate that a hardware component requires immediate attention.
For more information about specific hardware statistics, see the hardware guide for your particular device.

Note![]() If you do not have enough memory to upgrade to the most current release of the ASA, the Memory Insufficient Warning dialog box appears. Follow the directions that appear in this dialog box to continue using the ASA and ASDM in a supported manner. Click OK to close this dialog box.
If you do not have enough memory to upgrade to the most current release of the ASA, the Memory Insufficient Warning dialog box appears. Follow the directions that appear in this dialog box to continue using the ASA and ASDM in a supported manner. Click OK to close this dialog box.
License Tab
This tab shows a subset of licensed features. To view detailed license information, or to enter a new activation key, click More Licenses ; the Configuration > Device Management > Licensing > Activation Key pane appears. See Chapter5, “Managing Feature Licenses”
Cluster Tab
This tab shows the cluster interface mode, as well as the cluster status
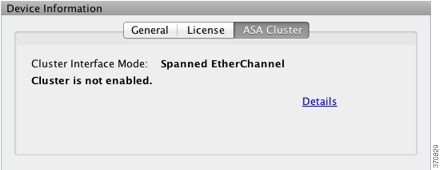
Interface Status Pane
This pane shows the status of each interface. If you select an interface row, the input and output throughput in Kbps displays below the table.
VPN Sessions Pane
This pane shows the VPN tunnel status. Click Details to go to the Monitoring > VPN > VPN Statistics > Sessions pane.
Failover Status Pane
This pane shows the failover status.
Click Configure to start the High Availability and Scalability Wizard. After you have completed the wizard, the failover configuration status (either Active/Active or Active/Standby) appears.
If failover is configured, click Details to open the Monitoring > Properties > Failover > Status pane.
System Resources Status Pane
Traffic Status Pane
This pane shows graphs for connections per second for all interfaces and for the traffic throughput of the lowest security interface.
When your configuration contains multiple lowest security level interfaces, and any one of them is named “outside,” then that interface is used for the traffic throughput graphs. Otherwise, ASDM picks the first interface from the alphabetical list of lowest security level interfaces.
Latest ASDM Syslog Messages Pane
This pane shows the most recent system messages generated by the ASA, up to a maximum of 100 messages. If logging is disabled, click Enable Logging to enable logging.
Figure 4-3 shows the elements of the Latest ASDM Syslog Messages pane.
Figure 4-3 Latest ASDM Syslog Messages Pane
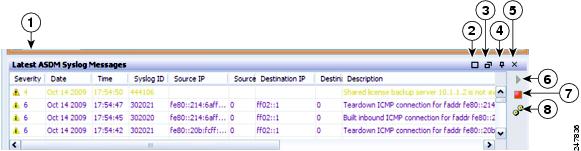
- To clear the current messages, right-click an event and click Clear Content .
- To save the current messages to a file on your PC, right-click an event and click Save Content .
- To copy the current content, right-click an event and click Copy .
- To change the background and foreground colors of syslog messages according to their severity, right-click an event and click Color Settings .
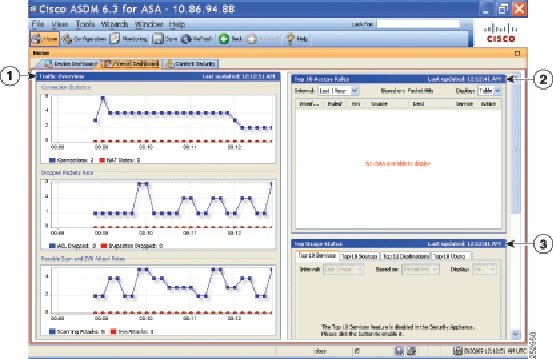
Firewall Dashboard Tab
The Firewall Dashboard tab lets you view important information about the traffic passing through your ASA. This dashboard differs depending on whether you are in single context mode or multiple context mode. In multiple context mode, the Firewall Dashboard is viewable within each context.
Figure 4-4 shows some of the elements of the Firewall Dashboard tab.
Figure 4-4 Firewall Dashboard Tab
|
|
|
|---|---|
Traffic Overview Pane
Enabled by default. If you disable basic threat detection (see the Configuring Basic Threat Detection Statistics section in the firewall configuration guide), then this area includes an Enable button that lets you enable basic threat detection. The runtime statistics include the following information, which is display-only :
- The number of connections and NAT translations.
- The rate of dropped packets per second caused by access list denials and application inspections.
- The rate of dropped packets per second that are identified as part of a scanning attack, or that are incomplete sessions detected, such as TCP SYN attack detected or no data UDP session attack detected.
Top 10 Access Rules Pane
Enabled by default. If you disable threat detection statistics for access rules (see the Configuring Advanced Threat Detection Statistics section in the firewall configuration guide), then this area includes an Enable button that lets you enable statistics for access rules.
In the Table view, you can select a rule in the list and right-click the rule to display a popup menu item, Show Rule . Choose this item to go to the Access Rules table and select that rule in this table.
Top Usage Status Pane
Disabled by default. This pane contains the following four tabs:
- Top 10 Services—Threat Detection feature
- Top 10 Sources—Threat Detection feature
- Top 10 Destinations—Threat Detection feature
- Top 10 Users—Identity Firewall feature
The first three tabs—Top 10 Services, Top 10 Sources, and Top 10 Destinations—provide statistics for threat detection features. Each tab includes an Enable button that let you enable each threat detection feature. You can enable them according to the Configuring Basic Threat Detection Statistics section in the firewall configuration guide.
The Top 10 Services Enable button enables statistics for both ports and protocols (both must be enabled for the display). The Top 10 Sources and Top 10 Destinations Enable buttons enable statistics for hosts. The top usage status statistics for hosts (sources and destinations), and ports and protocols are displayed.
The fourth tab for Top 10 Users provides statistics for the Identity Firewall feature. The Identity Firewall feature provides access control based on users’ identities. You can configure access rules and security policies based on user names and user groups name rather than through source IP addresses. The ASA provides this feature by accessing an IP-user mapping database.
The Top 10 Users tab displays data only when you have configured the Identity Firewall feature in the ASA, which includes configuring these additional components—Microsoft Active Directory and Cisco Active Directory (AD) Agent. See the Configuring the Identity Firewall for information.
Depending on which option you choose, the Top 10 Users tab shows statistics for received EPS packets, sent EPS packets, and sent attacks for the top 10 users. For each user (displayed as domain \ user_name ), the tab displays the average EPS packet, the current EPS packet, the trigger, and total events for that user.

Top Ten Protected Servers Under SYN Attack Pane
Disabled by default. This area includes an Enable button that lets you enable the feature, or you can enable it according to the Configuring Basic Threat Detection Statistics section in the firewall configuration guide. Statistics for the top ten protected servers under attack are displayed.
For the average rate of attack, the ASA samples the data every 30 seconds over the rate interval (by default 30 minutes).
If there is more than one attacker, then “<various>” displays, followed by the last attacker IP address.
Click Detail to view statistics for all servers (up to 1000) instead of just 10 servers. You can also view history sampling data. The ASA samples the number of attacks 60 times during the rate interval, so for the default 30-minute period, statistics are collected every 60 seconds.
Top 200 Hosts Pane
Disabled by default. Shows the top 200 hosts connected through the ASA. Each entry of a host contains the IP address of the host and the number of connections initiated by the host, and is updated every 120 seconds. To enable this display, enter the hpm topnenable command.
Top Botnet Traffic Filter Hits Pane
Disabled by default. This area includes links to configure the Botnet Traffic Filter. Reports of the top ten botnet sites, ports, and infected hosts provide a snapshot of the data, and may not match the top ten items since statistics started to be collected. If you right-click an IP address, you can invoke the whois tool to learn more about the botnet site.
For more information, see Chapter 26, “Configuring the Botnet Traffic Filter,” in the firewall configuration guide.
Cluster Dashboard Tab
The Cluster Dashboard tab shows a summary of cluster membership and resource utilization.
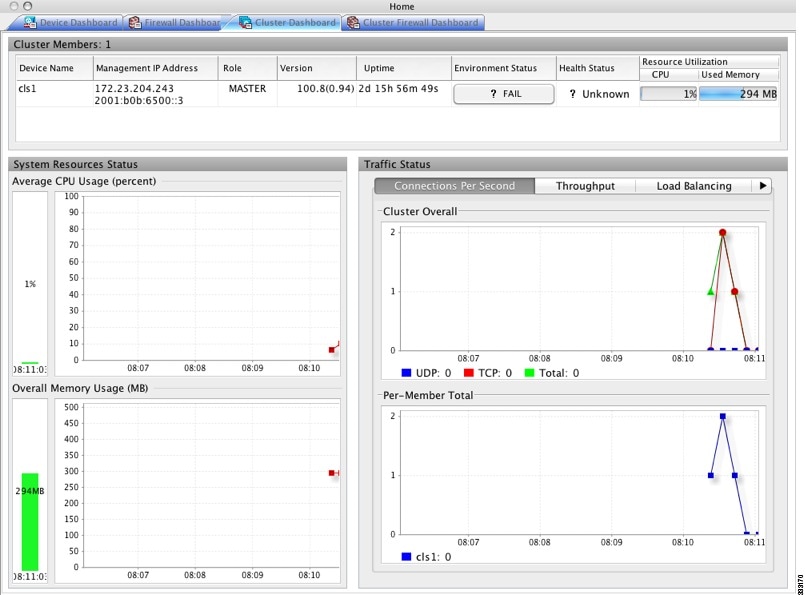
- Cluster Members—Shows the names and basic information about the members comprising the cluster (their management IP address, version, role in the cluster, etc.) and their health status (environment status, Health Status, and resource utilization meters).

Note In multiple context mode, if you connect ASDM to the admin context, and then change to a different context, the Management IP Address listed does not change to show the current context management IP addresses; it continues to show the admin context management IP addresses, including the main cluster IP address to which ASDM is currently connected.
- System Resource Status—Shows resource utilization (CPU and memory) across the cluster and traffic graphs, both cluster-wide and per-device.
- Traffic Status—Each tab has the following graphs.
Cluster Overall—Shows the connections per second throughout the cluster.
Per-Member Total—Shows the average connections per second for each member.
Cluster Overall—Shows the aggregated egress throughput throughout the cluster.
Per-Member Throughput—Shows the member throughput, one line per member.
Per-Member Percentage of Total Traffic—For each member, shows the percentage of total cluster traffic that the member receives.
Per-Member Locally Processed Traffic—For each member, shows the percentage of traffic that was processed locally.
Per-Member Receival Capacity Utilization—For each member, shows the usage of the transmittal capacity.
Per-Member Transmittal Capacity Utilization—For each member, shows the usage of the receival capacity.
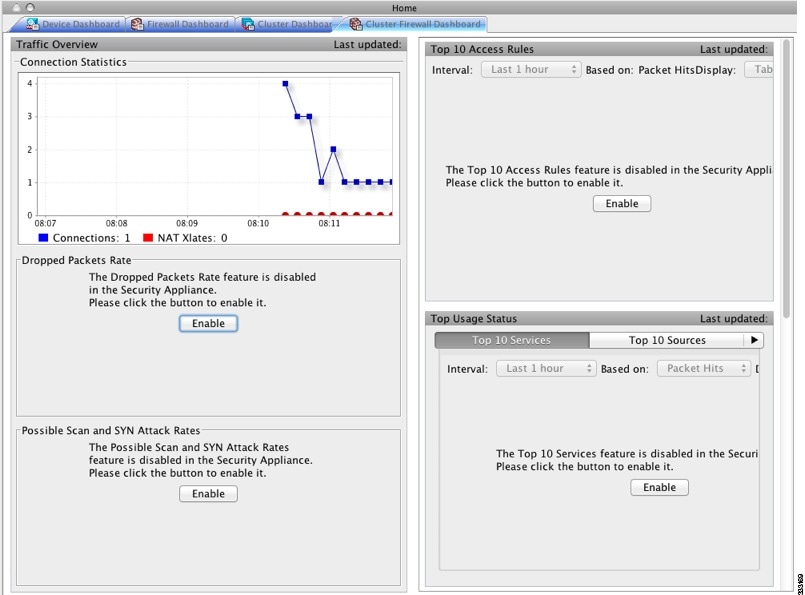
Cluster Firewall Dashboard Tab
The Cluster Firewall Dashboard tab shows Traffic Overview and the “top N” statistics, similar to those shown in the Firewall Dashboard, but aggregated across the whole cluster.
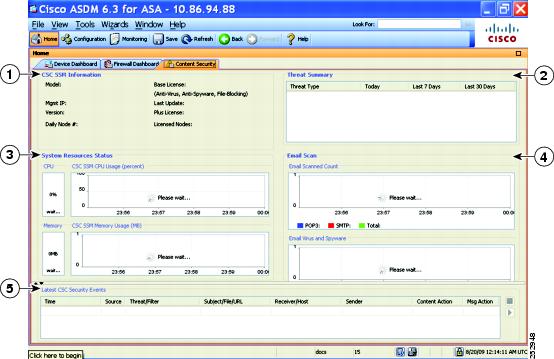
Content Security Tab
The Content Security tab lets you view important information about the Content Security and Control (CSC) SSM. This pane appears only if CSC software running on the CSC SSM is installed in the ASA.
For an introduction to the CSC SSM, see the Information About the CSC SSM section in the firewall configuration guide.

Note![]() If you have not completed the CSC Setup Wizard by choosing Configuration > Trend Micro Content Security > CSC Setup, you cannot access the panes under Home > Content Security. Instead, a dialog box appears and lets you access the CSC Setup Wizard directly from this location.
If you have not completed the CSC Setup Wizard by choosing Configuration > Trend Micro Content Security > CSC Setup, you cannot access the panes under Home > Content Security. Instead, a dialog box appears and lets you access the CSC Setup Wizard directly from this location.
Figure 4-5 shows the elements of the Content Security tab.
Figure 4-5 Content Security Tab
Intrusion Prevention Tab
The Intrusion Prevention tab lets you view important information about IPS. This tab appears only when you have an IPS module installed on the ASA.
To connect to the IPS module, perform the following steps:
Step 1![]() In the main ASDM application window, click the Intrusion Prevention tab.
In the main ASDM application window, click the Intrusion Prevention tab.
The Connecting to IPS dialog box appears.
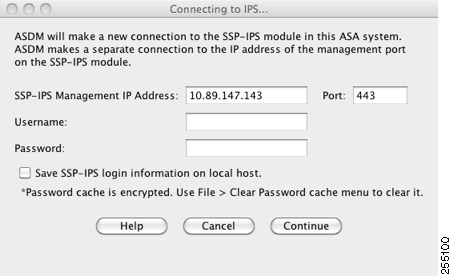
Step 2![]() Enter the IP address, port, username and password.The default IP address and port is 192.168.1.2:443. The default username and password is cisco and cisco
Enter the IP address, port, username and password.The default IP address and port is 192.168.1.2:443. The default username and password is cisco and cisco
Step 3![]() To save the login information on your local PC, check the Save IPS login information on local host check box.
To save the login information on your local PC, check the Save IPS login information on local host check box.
For more information about intrusion prevention, see Chapter 31, “Configuring the ASA IPS Module,” in the firewall configuration guide.
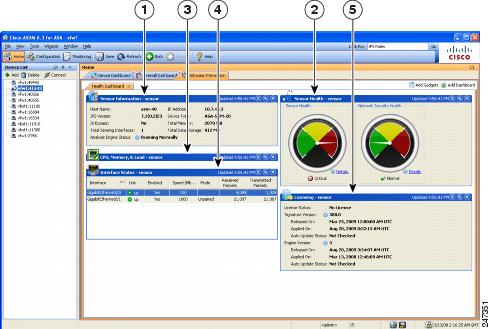
Figure 4-6 shows the elements of the Health Dashboard tab, located on the Intrusion Prevention tab.
Figure 4-6 Intrusion Prevention Tab (Health Dashboard)
|
|
|
|---|---|
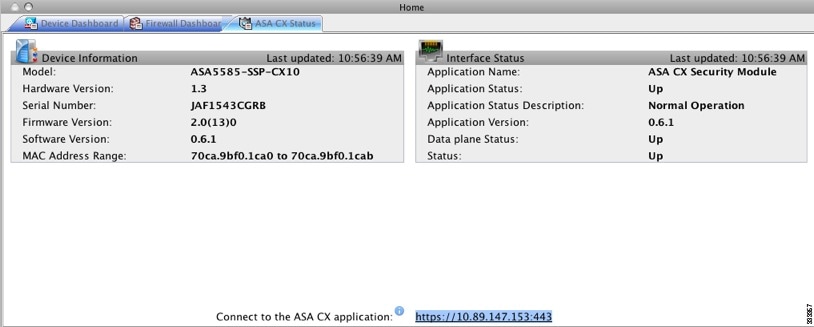
ASA CX Status Tab
The ASA CX Status tab lets you view important information about the ASA CX module. This tab appears only when you have an ASA CX module installed on the ASA.
Home Pane (System)
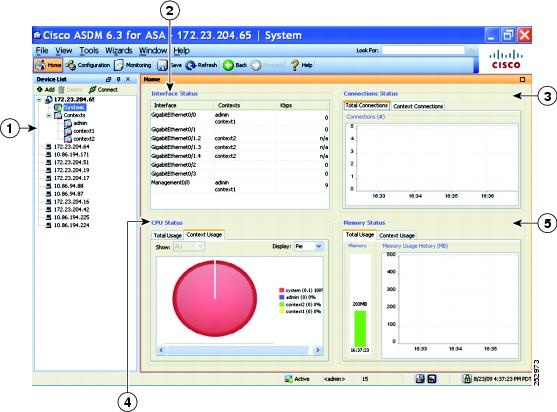
The ASDM System Home pane lets you view important status information about your ASA. Many of the details available in the ASDM System Home pane are available elsewhere in ASDM, but this pane shows at-a-glance how your ASA is running. Status information in the System Home pane is updated every ten seconds.
Figure 4-7 shows the elements of the System Home pane.
|
|
|
|---|---|
Interface Status pane. Choose an interface to view the total amount of traffic through the interface. |
|
Defining ASDM Preferences
This feature lets you define the behavior of certain ASDM settings.
To change various settings in ASDM, perform the following steps:
Step 1![]() In the main ASDM application window, choose Tools > Preferences .
In the main ASDM application window, choose Tools > Preferences .
The Preferences dialog box appears, with three tabs: General, Rules Table, and Syslog.
Step 2![]() To define your settings, click one of these tabs: the General tab to specify general preferences; the Rules Table tab to specify preferences for the Rules table; and the Syslog tab to specify the appearance of syslog messages displayed in the Home pane and to enable the display of a warning message for NetFlow-related syslog messages.
To define your settings, click one of these tabs: the General tab to specify general preferences; the Rules Table tab to specify preferences for the Rules table; and the Syslog tab to specify the appearance of syslog messages displayed in the Home pane and to enable the display of a warning message for NetFlow-related syslog messages.
Step 3![]() On the General tab, specify the following:
On the General tab, specify the following:
a.![]() Check the Warn that configuration in ASDM is out of sync with the configuration in ASA check box to be notified when the startup configuration and the running configuration are no longer in sync with each other.
Check the Warn that configuration in ASDM is out of sync with the configuration in ASA check box to be notified when the startup configuration and the running configuration are no longer in sync with each other.
b.![]() Check the Show configuration restriction message to read-only user check box to display the following message to a read-only user at startup. This option is checked by default.
Check the Show configuration restriction message to read-only user check box to display the following message to a read-only user at startup. This option is checked by default.
c.![]() Check the Confirm before exiting ASDM check box to display a prompt when you try to close ASDM to confirm that you want to exit. This option is checked by default.
Check the Confirm before exiting ASDM check box to display a prompt when you try to close ASDM to confirm that you want to exit. This option is checked by default.
d.![]() Check the Enable screen reader support (requires ASDM restart) check box to enable screen readers to work. You must restart ASDM to enable this option.
Check the Enable screen reader support (requires ASDM restart) check box to enable screen readers to work. You must restart ASDM to enable this option.
e.![]() Check the Warn of insufficient ASA memory when ASDM loads check box to receive notification when the minimum amount of ASA memory is insufficient to run complete functionality in the ASDM application. ASDM displays the memory warning in a text banner message at bootup, displays a message in the title bar text in ASDM, and sends a syslog alert once every 24 hours.
Check the Warn of insufficient ASA memory when ASDM loads check box to receive notification when the minimum amount of ASA memory is insufficient to run complete functionality in the ASDM application. ASDM displays the memory warning in a text banner message at bootup, displays a message in the title bar text in ASDM, and sends a syslog alert once every 24 hours.
f.![]() Check the Preview commands before sending them to the device check box to view CLI commands generated by ASDM.
Check the Preview commands before sending them to the device check box to view CLI commands generated by ASDM.
g.![]() Check the Enable cumulative (batch) CLI delivery check box to send multiple commands in a single group to the ASA.
Check the Enable cumulative (batch) CLI delivery check box to send multiple commands in a single group to the ASA.
h.![]() Enter the minimum amount of time in seconds for a configuration to send a timeout message. The default is 60 seconds.
Enter the minimum amount of time in seconds for a configuration to send a timeout message. The default is 60 seconds.
i.![]() To allow the Packet Capture Wizard to display captured packets, enter the name of the network sniffer application or click Browse to find it in the file system.
To allow the Packet Capture Wizard to display captured packets, enter the name of the network sniffer application or click Browse to find it in the file system.
Step 4![]() On the Rules Table tab, specify the following:
On the Rules Table tab, specify the following:
a.![]() Display settings let you change the way rules appear in the Rules table.
Display settings let you change the way rules appear in the Rules table.
–![]() Check the Auto-expand network and service object groups with specified prefix check box to display the network and service object groups automatically expanded based on the Auto-Expand Prefix setting.
Check the Auto-expand network and service object groups with specified prefix check box to display the network and service object groups automatically expanded based on the Auto-Expand Prefix setting.
–![]() In the Auto-Expand Prefix field, enter the prefix of the network and service object groups to expand automatically when displayed.
In the Auto-Expand Prefix field, enter the prefix of the network and service object groups to expand automatically when displayed.
–![]() Check the Show members of network and service object groups check box to display members of network and service object groups and the group name in the Rules table. If the check box is not checked, only the group name is displayed.
Check the Show members of network and service object groups check box to display members of network and service object groups and the group name in the Rules table. If the check box is not checked, only the group name is displayed.
–![]() In the Limit Members To field, enter the number of network and service object groups to display. When the object group members are displayed, then only the first n members are displayed.
In the Limit Members To field, enter the number of network and service object groups to display. When the object group members are displayed, then only the first n members are displayed.
–![]() Check the Show all actions for service policy rules check box to display all actions in the Rules table. When unchecked, a summary appears.
Check the Show all actions for service policy rules check box to display all actions in the Rules table. When unchecked, a summary appears.
b.![]() Deployment settings let you configure the behavior of the ASA when deploying changes to the Rules table.
Deployment settings let you configure the behavior of the ASA when deploying changes to the Rules table.
–![]() Check the Issue “clear xlate” command when deploying access lists check box to clear the NAT table when deploying new access lists. This setting ensures the access lists that are configured on the ASA are applied to all translated addresses.
Check the Issue “clear xlate” command when deploying access lists check box to clear the NAT table when deploying new access lists. This setting ensures the access lists that are configured on the ASA are applied to all translated addresses.
c.![]() Access Rule Hit Count Settings let you configure the frequency for which the hit counts are updated in the Access Rules table. Hit counts are applicable for explicit rules only. No hit count will be displayed for implicit rules in the Access Rules table .
Access Rule Hit Count Settings let you configure the frequency for which the hit counts are updated in the Access Rules table. Hit counts are applicable for explicit rules only. No hit count will be displayed for implicit rules in the Access Rules table .
–![]() Check the Update access rule hit counts automatically check box to have the hit counts automatically updated in the Access Rules table.
Check the Update access rule hit counts automatically check box to have the hit counts automatically updated in the Access Rules table.
–![]() In the Update Frequency field, specify the frequency in seconds in which the hit count column is updated in the Access Rules table. Valid values are 10 - 86400 seconds.
In the Update Frequency field, specify the frequency in seconds in which the hit count column is updated in the Access Rules table. Valid values are 10 - 86400 seconds.
Step 5![]() On the Syslog tab, specify the following:
On the Syslog tab, specify the following:
- In the Syslog Colors area, you can customize the message display by configuring background or foreground colors for messages at each severity level. The Severity column lists each severity level by name and number. To change the background color or foreground color for messages at a specified severity level, click the corresponding column. The Pick a Color dialog box appears. Click one of the following tabs:
–![]() On the Swatches tab, choose a color from the palette, and click OK .
On the Swatches tab, choose a color from the palette, and click OK .
–![]() On the HSB tab, specify the H, S, and B settings, and click OK .
On the HSB tab, specify the H, S, and B settings, and click OK .
–![]() On the RGB tab, specify the Red, Green, and Blue settings, and click OK .
On the RGB tab, specify the Red, Green, and Blue settings, and click OK .
- In the NetFlow area, to enable the display of a warning message to disable redundant syslog messages, check the Warn to disable redundant syslog messages when NetFlow action is first applied to the global service policy rule check box.
Step 6![]() After you have specified settings on these three tabs, click OK to save your settings and close the Preferences dialog box.
After you have specified settings on these three tabs, click OK to save your settings and close the Preferences dialog box.

Note![]() Each time that you check or uncheck a preferences setting, the change is saved to the .conf file and becomes available to all the other ASDM sessions running on the workstation at the time. You must restart ASDM for all changes to take effect.
Each time that you check or uncheck a preferences setting, the change is saved to the .conf file and becomes available to all the other ASDM sessions running on the workstation at the time. You must restart ASDM for all changes to take effect.
Using the ASDM Assistant
The ASDM Assistant tool lets you search and view useful ASDM procedural help about certain tasks.
To access information, choose View > ASDM Assistant > How Do I? or enter a search request from the Look For field in the menu bar. From the Find drop-down list, choose How Do I? to begin the search.

Note![]() This feature is not available on the PIX security appliance.
This feature is not available on the PIX security appliance.
To view the ASDM Assistant, perform the following steps:
Step 1![]() In the main ASDM application window, choose View > ASDM Assistant .
In the main ASDM application window, choose View > ASDM Assistant .
The ASDM Assistant pane appears.
Step 2![]() In the Search field, enter the information that you want to find, and click Go .
In the Search field, enter the information that you want to find, and click Go .
The requested information appears in the Search Results pane.
Step 3![]() Click any links that appear in the Search Results and Features sections to obtain more details.
Click any links that appear in the Search Results and Features sections to obtain more details.
Enabling History Metrics
The Configuration > Device Management > Advanced > History Metrics pane lets you configure the adaptive ASA to keep a history of various statistics, which ASDM can display on any Graph/Table. If you do not enable history metrics, you can only monitor statistics in real time. Enabling history metrics lets you view statistics graphs from the last 10 minutes, 60 minutes, 12 hours, and 5 days.
To configure history metrics, perform the following steps:
Step 1![]() Choose Configuration > Device Management > Advanced > History Metrics .
Choose Configuration > Device Management > Advanced > History Metrics .
The History Metrics pane appears.
Step 2![]() Check the ASDM History Metrics check box to enable history metrics, and then click Apply .
Check the ASDM History Metrics check box to enable history metrics, and then click Apply .
Unsupported Commands
ASDM supports almost all commands available for the adaptive ASA, but ASDM ignores some commands in an existing configuration. Most of these commands can remain in your configuration; see Tools > Show Commands Ignored by ASDM on Device for more information.
This section includes the following topics:
- Ignored and View-Only Commands
- Effects of Unsupported Commands
- Discontinuous Subnet Masks Not Supported
- Interactive User Commands Not Supported by the ASDM CLI Tool
Ignored and View-Only Commands
Table 4-5 lists commands that ASDM supports in the configuration when added through the CLI, but that cannot be added or edited in ASDM. If ASDM ignores the command, it does not appear in the ASDM GUI at all. If the command is view-only, then it appears in the GUI, but you cannot edit it.
Effects of Unsupported Commands
If ASDM loads an existing running configuration and finds other unsupported commands, ASDM operation is unaffected. To view the unsupported commands, choose Tools > Show Commands Ignored by ASDM on Device .
Discontinuous Subnet Masks Not Supported
ASDM does not support discontinuous subnet masks such as 255.255.0.255. For example, you cannot use the following:
Interactive User Commands Not Supported by the ASDM CLI Tool
The ASDM CLI tool does not support interactive user commands. If you enter a CLI command that requires interactive confirmation, ASDM prompts you to enter “[yes/no]” but does not recognize your input. ASDM then times out waiting for your response.
1.![]() Choose Tools > Command Line Interface .
Choose Tools > Command Line Interface .
2.![]() Enter the crypto key generate rsa command.
Enter the crypto key generate rsa command.
ASDM generates the default 1024-bit RSA key.
3.![]() Enter the crypto key generate rsa command again.
Enter the crypto key generate rsa command again.
Instead of regenerating the RSA keys by overwriting the previous one, ASDM displays the following error:
- You can configure most commands that require user interaction by means of the ASDM panes.
- For CLI commands that have a noconfirm option, use this option when entering the CLI command. For example:
 Feedback
Feedback