- Safety Warnings
- Preparing to Connect the Router
- Connecting a PC, Server, or Workstation
- Connecting a Phone
- Connecting an External Ethernet Switch
- Connecting the V.92 modem Port
- Connecting a Terminal or PC to the Console Port
- Connecting a Modem to the Auxiliary Port
- Connecting the 3G Card
- Installing the 3G Adapter for Extended Cable/Antenna
- Connecting a Data BRI Port
- Connecting an FE Line to an FE WAN Port
- Connecting a GE Line to an GE WAN Port
- Connecting an xDSL Line
- Connecting Power over Ethernet
- Connecting the AC Adapter
- Connecting an FXS Line
- Connecting an FXO Line
- Connecting a Voice ISDN BRI Line
- Verifying Connections
Connecting the Router
This chapter describes how to install the Cisco 860, 880, 890 ISRs and the Cisco 819 ISR.
Cisco 810 Series
Cisco 819 Series
This section describes how to connect Cisco 819 ISRs to Ethernet devices and a network. The section contains the following topics:
- Preparing to Connect the Router
- Connecting a PC, Server, or Workstation
- Connecting an External Ethernet Switch
- Connecting a Terminal or PC to the Console Port
- Connecting a Modem to the Console Port
- Connecting the AC Adapter
- Connecting the DC Adapter
- Verifying Connections

Note![]() For compliance and safety information, see the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information Roadmap that ships with the router and Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for Cisco 800 Series Routers.
For compliance and safety information, see the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information Roadmap that ships with the router and Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for Cisco 800 Series Routers.
Preparing to Connect the Router
Before you connect the router to the devices, install the router according to the instructions in the “Installing the Router” section.
Preventing Damage to the Router
To prevent damage to your router, follow these guidelines when connecting devices to your router:

- If you must supply your own cable, see the “Cisco 860, 880, 890 Series” section for cabling specifications. If this appendix does not provide specifications for a particular cable, we strongly recommend ordering the cable from Cisco.
Connecting a PC, Server, or Workstation
To connect a PC (or other Ethernet devices) to an Ethernet switch port, follow these steps:
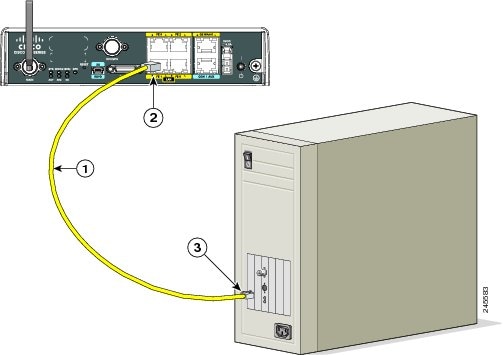
Step 1![]() Connect one end of the yellow Ethernet cable to an Ethernet switch port on the router. See Figure 3-1.
Connect one end of the yellow Ethernet cable to an Ethernet switch port on the router. See Figure 3-1.
Figure 3-1 Connecting a Server, PC, or Workstation
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Step 2![]() Connect the other end of the cable to the RJ-45 port on the network interface card (NIC) that is installed in the PC, server, or workstation.
Connect the other end of the cable to the RJ-45 port on the network interface card (NIC) that is installed in the PC, server, or workstation.
Step 3![]() (Optional) Connect additional servers, PCs, or workstations to the other Ethernet switch ports.
(Optional) Connect additional servers, PCs, or workstations to the other Ethernet switch ports.

Note![]() Use the Cisco Configuration Express to configure the Internet connection settings. See Cisco Configuration Professional Quick Start Guide for more information.
Use the Cisco Configuration Express to configure the Internet connection settings. See Cisco Configuration Professional Quick Start Guide for more information.
Connecting an External Ethernet Switch
If more than four PCs in an office must be connected to each other, you can add Ethernet connections to the router by connecting an external Ethernet switch to the Ethernet switch on the router.
To connect an external Ethernet switch to an Ethernet switch port on the router, perform these steps:
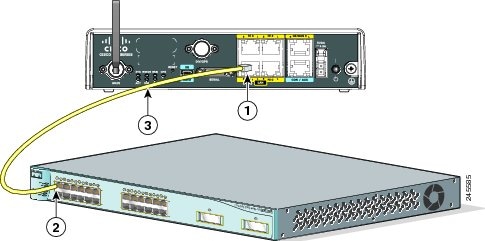
Step 1![]() Connect one end of the yellow Ethernet cable to an Ethernet switch port on the router. (See Figure 3-2.)
Connect one end of the yellow Ethernet cable to an Ethernet switch port on the router. (See Figure 3-2.)
Figure 3-2 Connecting to an Ethernet Switch
|
|
|
Yellow CAT5 Ethernet cable, RJ-45–to–RJ-45, connecting to an external Ethernet switch port |
|
|
|
|
Step 2![]() Connect the other end of the cable to the available port on the Ethernet switch to add additional Ethernet connections.
Connect the other end of the cable to the available port on the Ethernet switch to add additional Ethernet connections.
Step 3![]() Turn on the Ethernet switch.
Turn on the Ethernet switch.
Connecting a Terminal or PC to the Console Port
Connect a terminal or PC to the Console port either to configure the software by using the CLI or to troubleshoot problems with the router.
To connect a terminal or PC to the console port on the router and access the CLI, follow these steps:
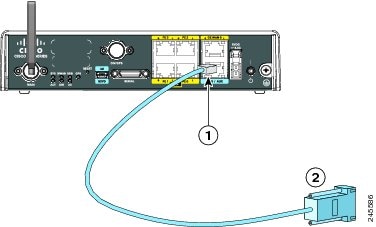
Step 1![]() Connect the RJ-45 end of a DB-9-to-RJ-45 serial cable to the RJ-45 Console port on the router. Figure 3-3 shows the RJ-45 end of the serial cable connected to the Console port on the router.
Connect the RJ-45 end of a DB-9-to-RJ-45 serial cable to the RJ-45 Console port on the router. Figure 3-3 shows the RJ-45 end of the serial cable connected to the Console port on the router.
Figure 3-3 Connecting a Terminal or PC to the Console Port
|
|
|
Step 2![]() Connect the DB-9 end of the DB-9-to-RJ-45 serial cable to the COM port on your laptop or PC.
Connect the DB-9 end of the DB-9-to-RJ-45 serial cable to the COM port on your laptop or PC.

Note![]() Some laptops and PCs do not come with DB-9 serial port connectors and may require a USB-to-serial port adapter.
Some laptops and PCs do not come with DB-9 serial port connectors and may require a USB-to-serial port adapter.
Step 3![]() To communicate with the router, start a terminal emulator application.
To communicate with the router, start a terminal emulator application.
For more information, see the Terminal Emulator Settings, and Applying Correct Terminal Emulator Settings for Console Connections.
Connecting a Modem to the Console Port
To connect a modem to the router, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() Connect the RJ-45 end of the adapter cable to the Console port on the router as shown in Figure 3-4.
Connect the RJ-45 end of the adapter cable to the Console port on the router as shown in Figure 3-4.
Figure 3-4 Connecting a Modem to the Console Port
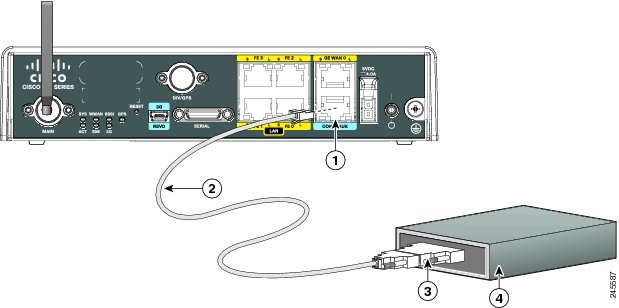
Step 2![]() Connect the DB-9 end of the console cable to the DB-9 end of the modem adapter.
Connect the DB-9 end of the console cable to the DB-9 end of the modem adapter.
Step 3![]() Connect the DB-25 end of the modem adapter to the modem.
Connect the DB-25 end of the modem adapter to the modem.
Step 4![]() Make sure that your modem and the router console port are configured for the same transmission speed (up to 115200 b/s is supported) and support mode control with data carrier detect (DCD) and data terminal ready (DTR).
Make sure that your modem and the router console port are configured for the same transmission speed (up to 115200 b/s is supported) and support mode control with data carrier detect (DCD) and data terminal ready (DTR).
Connecting the AC Adapter

Warning![]() The device is designed to work with TN power systems. Statement 19
The device is designed to work with TN power systems. Statement 19

Warning![]() This product relies on the building’s installation for short-circuit (overcurrent) protection. Ensure that the protective device is rated not greater than: 120VAC, 20A U.S (240VAC, 16 to 20A international). Statement 1005
This product relies on the building’s installation for short-circuit (overcurrent) protection. Ensure that the protective device is rated not greater than: 120VAC, 20A U.S (240VAC, 16 to 20A international). Statement 1005

Warning![]() This product requires short-circuit (overcurrent) protection, to be provided as part of the building installation. Install only in accordance with national and local wiring regulations. Statement 1045
This product requires short-circuit (overcurrent) protection, to be provided as part of the building installation. Install only in accordance with national and local wiring regulations. Statement 1045
To connect your Cisco 819 ISR to an AC power outlet, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() Connect the AC adapter to an AC power outlet.
Connect the AC adapter to an AC power outlet.
Step 2![]() Plug the adapter cord into the router.
Plug the adapter cord into the router.
Connecting the DC Adapter

Warning![]() This product relies on the building’s installation for short-circuit (overcurrent) protection. Ensure that the protective device is rated not greater than 36 VDC, 5A Statement 1005
This product relies on the building’s installation for short-circuit (overcurrent) protection. Ensure that the protective device is rated not greater than 36 VDC, 5A Statement 1005

Warning![]() This product requires short-circuit (overcurrent) protection, to be provided as part of the building installation. Install only in accordance with national and local wiring regulations. Statement 1045
This product requires short-circuit (overcurrent) protection, to be provided as part of the building installation. Install only in accordance with national and local wiring regulations. Statement 1045

Warning![]() The device is designed to work with TN power systems. Statement 19
The device is designed to work with TN power systems. Statement 19
To connect the DC power on your Cisco 819 ISR, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() Connect the black and white lead wires to a 12 VDC source.
Connect the black and white lead wires to a 12 VDC source.
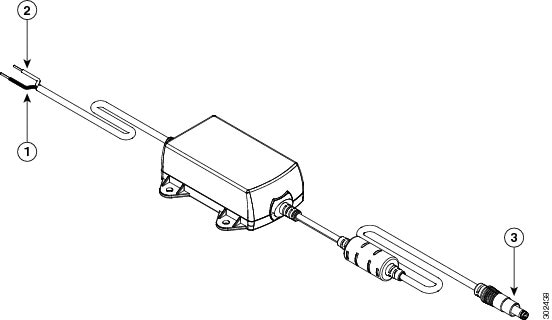
The black lead is negative or ground and the white lead is positive. The output cable is 1.3 meters while the input cable is 1 meter in length. (See Figure 3-5 and Figure 3-6.). For the complete list of supported power adapters, see the “Supported Power Adapters” section.
Figure 3-5 DC Power Supply PWR1-20W-12VDC and PWR1-20W-24VDC
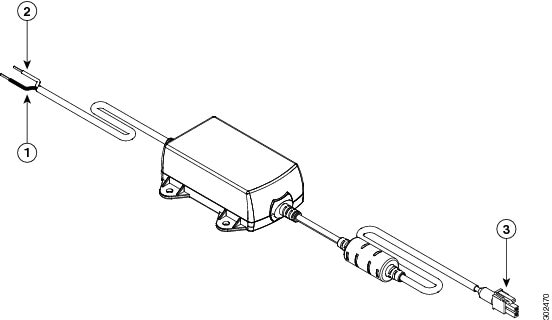
Figure 3-6 DC Power Supply PWR2-20W-12VDC and PWR2-20W-24VDC
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Step 2![]() Plug the adapter cord into the router.
Plug the adapter cord into the router.

Note![]() The power adapters have 18 AWG wires for the input connection. Tinned bare wires are used for the input connection as there is no standard established for connector type. Screw terminal blocks are most often used.
The power adapters have 18 AWG wires for the input connection. Tinned bare wires are used for the input connection as there is no standard established for connector type. Screw terminal blocks are most often used.
Verifying Connections
To verify that all devices are properly connected to the router, first turn on all the connected devices, then check the LEDs. To verify router operation, refer to Table 3-1 .
For full LED description, see Table 1-45 .
Cisco 860, 880, 890 Series
This section describes how to connect Cisco 860 series, Cisco 880 series, and Cisco 890 series ISRs to Ethernet devices, Power over Ethernet (PoE), and a network.

Note![]() Depending on the features available for your router, some content in this section may not apply to your router.
Depending on the features available for your router, some content in this section may not apply to your router.
The section contains the following topics:
- Safety Warnings
- Preparing to Connect the Router
- Connecting a PC, Server, or Workstation
- Connecting a Phone
- Connecting an External Ethernet Switch
- Connecting the V.92 modem Port
- Connecting a Terminal or PC to the Console Port
- Connecting a Modem to the Console Port
- Connecting the 3G Card
- Installing the 3G Adapter for Extended Cable/Antenna
- Connecting a Data BRI Port
- Connecting an FE Line to an FE WAN Port
- Connecting a GE Line to an GE WAN Port
- Connecting an xDSL Line
- Connecting Power over Ethernet
- Connecting the AC Adapter
- Connecting an FXS Line
- Connecting an FXO Line
- Connecting a Voice ISDN BRI Line
- Verifying Connections

Note![]() For compliance and safety information, see Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information Roadmap that ships with the router and Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for Cisco 800 Series Routers.
For compliance and safety information, see Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information Roadmap that ships with the router and Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for Cisco 800 Series Routers.

Note![]() The illustrations in this chapter show a wireless router with antennas attached. Non-wireless routers do not have antennas or antenna connectors on the back panel. However, the procedures for connecting devices to the router are the same for both wireless and non-wireless routers.
The illustrations in this chapter show a wireless router with antennas attached. Non-wireless routers do not have antennas or antenna connectors on the back panel. However, the procedures for connecting devices to the router are the same for both wireless and non-wireless routers.
Safety Warnings

Warning![]() When installing the product, please use the provided or designated connection cables/power cables/AC adaptors/batteries. Using any other cables/adaptors could cause a malfunction or a fire. Electrical Appliance and Material Safety Law prohibits the use of UL-certified cables (that have the “UL” or “CSA” shown on the cord), not regulated with the subject law by showing “PSE” on the cord, for any other electrical devices than products designated by CISCO. Statement 371
When installing the product, please use the provided or designated connection cables/power cables/AC adaptors/batteries. Using any other cables/adaptors could cause a malfunction or a fire. Electrical Appliance and Material Safety Law prohibits the use of UL-certified cables (that have the “UL” or “CSA” shown on the cord), not regulated with the subject law by showing “PSE” on the cord, for any other electrical devices than products designated by CISCO. Statement 371

Warning![]() Do not work on the system or connect or disconnect cables during periods of lightning activity. Statement 1001
Do not work on the system or connect or disconnect cables during periods of lightning activity. Statement 1001

Warning![]() This equipment has been designed for connection to TN and IT power systems. Statement 1007
This equipment has been designed for connection to TN and IT power systems. Statement 1007

Warning![]() There is the danger of explosion if the battery is replaced incorrectly. Replace the battery only with the same or equivalent type recommended by the manufacturer. Dispose of used batteries according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Statement 1015
There is the danger of explosion if the battery is replaced incorrectly. Replace the battery only with the same or equivalent type recommended by the manufacturer. Dispose of used batteries according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Statement 1015

Warning![]() Take care when connecting units to the supply circuit so that wiring is not overloaded. Statement 1018
Take care when connecting units to the supply circuit so that wiring is not overloaded. Statement 1018

Warning![]() To avoid electric shock, do not connect safety extra-low voltage (SELV) circuits to telephone-network voltage (TNV) circuits. LAN ports contain SELV circuits, and WAN ports contain TNV circuits. Some LAN and WAN ports both use RJ-45 connectors. Use caution when connecting cables. Statement 1021
To avoid electric shock, do not connect safety extra-low voltage (SELV) circuits to telephone-network voltage (TNV) circuits. LAN ports contain SELV circuits, and WAN ports contain TNV circuits. Some LAN and WAN ports both use RJ-45 connectors. Use caution when connecting cables. Statement 1021

Warning![]() Hazardous network voltages are present in WAN ports regardless of whether power to the unit is OFF or ON. To avoid electric shock, use caution when working near WAN ports. When detaching cables, detach the end away from the unit first. Statement 1026
Hazardous network voltages are present in WAN ports regardless of whether power to the unit is OFF or ON. To avoid electric shock, use caution when working near WAN ports. When detaching cables, detach the end away from the unit first. Statement 1026

Warning![]() Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install, replace, or service this equipment. Statement 1030
Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install, replace, or service this equipment. Statement 1030

Warning![]() Do not use this product near water; for example, near a bath tub, wash bowl, kitchen sink or laundry tub, in a wet basement, or near a swimming pool. Statement 1035
Do not use this product near water; for example, near a bath tub, wash bowl, kitchen sink or laundry tub, in a wet basement, or near a swimming pool. Statement 1035

Warning![]() Never install telephone jacks in wet locations unless the jack is specifically designed for wet locations. Statement 1036
Never install telephone jacks in wet locations unless the jack is specifically designed for wet locations. Statement 1036

Warning![]() Never touch uninsulated telephone wires or terminals unless the telephone line has been disconnected at the network interface. Statement 1037
Never touch uninsulated telephone wires or terminals unless the telephone line has been disconnected at the network interface. Statement 1037

Warning![]() Avoid using a telephone (other than a cordless type) during an electrical storm. There may be a remote risk of electric shock from lightning. Statement 1038
Avoid using a telephone (other than a cordless type) during an electrical storm. There may be a remote risk of electric shock from lightning. Statement 1038

Warning![]() To report a gas leak, do not use a telephone in the vicinity of the leak. Statement 1039
To report a gas leak, do not use a telephone in the vicinity of the leak. Statement 1039

Warning![]() Before opening the unit, disconnect the telephone-network cables to avoid contact with telephone-network voltages. Statement 1041
Before opening the unit, disconnect the telephone-network cables to avoid contact with telephone-network voltages. Statement 1041

Warning![]() This equipment contains a ring signal generator (ringer), which is a source of hazardous voltage. Do not touch the RJ-11 (phone) port wires (conductors), the conductors of a cable connected to the RJ-11 port, or the associated circuit-board when the ringer is active. The ringer is activated by an incoming call. Statement 1042
This equipment contains a ring signal generator (ringer), which is a source of hazardous voltage. Do not touch the RJ-11 (phone) port wires (conductors), the conductors of a cable connected to the RJ-11 port, or the associated circuit-board when the ringer is active. The ringer is activated by an incoming call. Statement 1042

Warning![]() Do not locate the antenna near overhead power lines or other electric light or power circuits, or where it can come into contact with such circuits. When installing the antenna, take extreme care not to come into contact with such circuits, because they may cause serious injury or death. For proper installation and grounding of the antenna, please refer to national and local codes (for example, U.S.:NFPA 70, National Electrical Code, Article 810, Canada: Canadian Electrical Code, Section 54). Statement 1052
Do not locate the antenna near overhead power lines or other electric light or power circuits, or where it can come into contact with such circuits. When installing the antenna, take extreme care not to come into contact with such circuits, because they may cause serious injury or death. For proper installation and grounding of the antenna, please refer to national and local codes (for example, U.S.:NFPA 70, National Electrical Code, Article 810, Canada: Canadian Electrical Code, Section 54). Statement 1052

Warning![]() No user-serviceable parts inside. Do not open. Statement 1073
No user-serviceable parts inside. Do not open. Statement 1073

Warning![]() Installation of the equipment must comply with local and national electrical codes. Statement 1074
Installation of the equipment must comply with local and national electrical codes. Statement 1074
Preparing to Connect the Router
Before you connect the router to the devices, install the router according to the instructions in “Installing the Cisco 860, 880, 890 ISR” section.
Preventing Damage to the Router
To prevent damage to your router, follow these guidelines when connecting devices to your router:

- Connect the color-coded cables supplied by Cisco to the color-coded ports on the back panel.
- If you must supply your own cable, see “Cable Specifications” section for cabling specifications. If this appendix does not provide specifications for a particular cable, we strongly recommend ordering the cable from Cisco.
Connecting a PC, Server, or Workstation
To connect a PC (or other Ethernet devices) to an Ethernet switch port, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() Connect one end of the yellow Ethernet cable to an Ethernet switch port on the router.
Connect one end of the yellow Ethernet cable to an Ethernet switch port on the router.
Figure 3-1 shows a Cisco 888W router connected to a PC.
Figure 3-7 Connecting a Server, PC, or Workstation
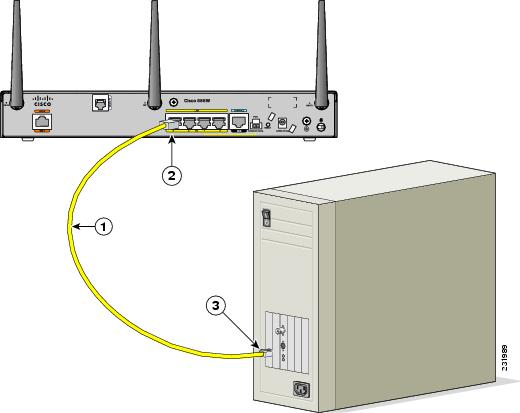
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Step 2![]() Connect the other end of the cable to the RJ-45 port on the network interface card (NIC) that is installed in the PC, server, or workstation.
Connect the other end of the cable to the RJ-45 port on the network interface card (NIC) that is installed in the PC, server, or workstation.
Step 3![]() (Optional) Connect additional servers, PCs, or workstations to the other Ethernet switch ports.
(Optional) Connect additional servers, PCs, or workstations to the other Ethernet switch ports.

Note![]() Use the Cisco Configuration Express to configure the Internet connection settings. See Cisco Configuration Professional Quick Start Guide for more information.
Use the Cisco Configuration Express to configure the Internet connection settings. See Cisco Configuration Professional Quick Start Guide for more information.
Connecting a Phone
To connect an 802.3af-compliant phone to an Ethernet switch port, follow these steps:

Note![]() A power source must be provided for the phone to function. This can be done in two ways: the phone can be powered via the PoE function using the PoE enabled Ethernet ports, or by using an external AC power source connected to the phone.
A power source must be provided for the phone to function. This can be done in two ways: the phone can be powered via the PoE function using the PoE enabled Ethernet ports, or by using an external AC power source connected to the phone.
Step 1![]() Connect one end of the yellow Ethernet cable to Ethernet switch port 0 or port 1 on the router. Figure 3-8 shows a Cisco 888W router connected to a phone.
Connect one end of the yellow Ethernet cable to Ethernet switch port 0 or port 1 on the router. Figure 3-8 shows a Cisco 888W router connected to a phone.
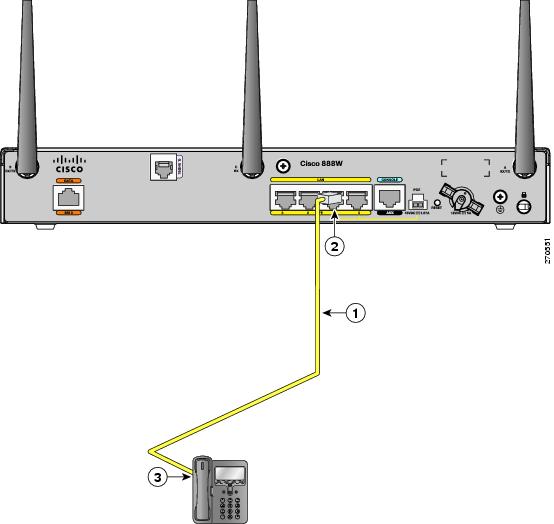
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Step 2![]() Connect the other end of the cable to the RJ-45 port on the phone.
Connect the other end of the cable to the RJ-45 port on the phone.
Connecting an External Ethernet Switch
If more than four PCs in an office must be connected to each other, you can add Ethernet connections to the router by connecting an external Ethernet switch to the Ethernet switch on the router.
To connect an external Ethernet switch to an Ethernet switch port on the router, perform these steps:
Step 1![]() Connect one end of the yellow Ethernet cable to an Ethernet switch port on the router. Figure 3-2 shows a Cisco 888W router connected to an Ethernet switch.
Connect one end of the yellow Ethernet cable to an Ethernet switch port on the router. Figure 3-2 shows a Cisco 888W router connected to an Ethernet switch.
Figure 3-9 Connecting to an Ethernet Switch
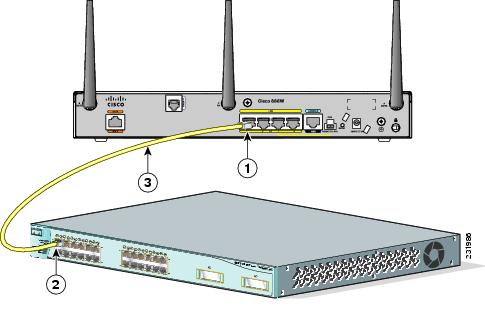
|
|
|
Yellow CAT5 Ethernet cable, RJ-45–to–RJ-45, connecting to an external Ethernet switch port |
|
|
|
|
Step 2![]() Connect the other end of the cable to the available port on the Ethernet switch to add additional Ethernet connections.
Connect the other end of the cable to the available port on the Ethernet switch to add additional Ethernet connections.
Step 3![]() Turn on the Ethernet switch.
Turn on the Ethernet switch.
Connecting the V.92 modem Port

Warning![]() Hazardous network voltages are present in WAN ports regardless of whether power to the unit is OFF or ON. To avoid electric shock, use caution when working near WAN ports. When detaching cables, detach the end away from the unit first. Statement 1026
Hazardous network voltages are present in WAN ports regardless of whether power to the unit is OFF or ON. To avoid electric shock, use caution when working near WAN ports. When detaching cables, detach the end away from the unit first. Statement 1026
To connect the router to your service provide network through the V.92 port, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() Connect one end of the straight-through R-J11 cable to the V.92 port.
Connect one end of the straight-through R-J11 cable to the V.92 port.
Figure 3-10 shows how to connect the router to the service provide through the V.92 port.
Figure 3-10 Connecting to Your Service Provider Through the V.92 port
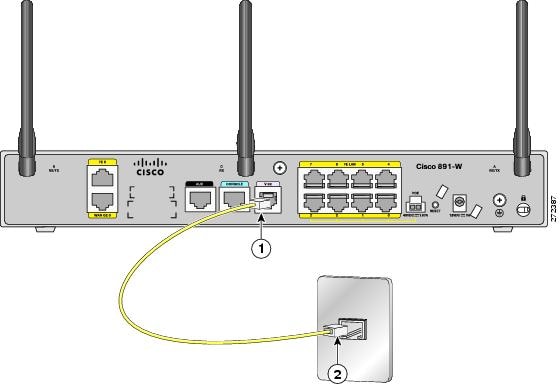
|
|
|
Step 2![]() Connect the other end of the straight through R-J11 cable to an RJ-11 telephone wall outlet.
Connect the other end of the straight through R-J11 cable to an RJ-11 telephone wall outlet.
Connecting a Terminal or PC to the Console Port
Connect a terminal or PC to the Console Auxiliary (Aux) port either to configure the software by using the CLI or to troubleshoot problems with the router.
To connect a terminal or PC to the console port on the router and access the CLI, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() Connect the RJ-45 end of a DB-9–to–RJ-45 serial cable to the RJ-45 Console Aux port on the router. Figure 3-3 shows the RJ-45 end of the serial cable connected to the Console Aux port on the router.
Connect the RJ-45 end of a DB-9–to–RJ-45 serial cable to the RJ-45 Console Aux port on the router. Figure 3-3 shows the RJ-45 end of the serial cable connected to the Console Aux port on the router.
Figure 3-11 Connecting a Terminal or PC to the Console Port
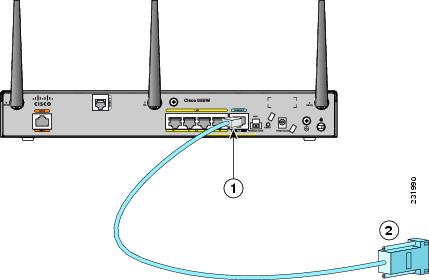
|
|
|
Step 2![]() Connect the DB-9 end of the DB-9–to–RJ-45 serial cable to the to the COM port on your laptop or PC.
Connect the DB-9 end of the DB-9–to–RJ-45 serial cable to the to the COM port on your laptop or PC.

Note![]() Some laptops and PCs do not come with DB-9 serial port connectors and may require a USB-to-serial port adapter.
Some laptops and PCs do not come with DB-9 serial port connectors and may require a USB-to-serial port adapter.
Step 3![]() To communicate with the router, start a terminal emulator application.
To communicate with the router, start a terminal emulator application.
Terminal Emulator Settings
Use the following settings for the terminal emulator connection:
When the terminal emulator establishes communications, the router prompt is displayed.
For more information on terminal emulation settings, see Applying Correct Terminal Emulator Settings for Console Connections.
Connecting a Modem to the Auxiliary Port
To connect a modem to the router, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() Connect the RJ-45 end of the adapter cable to the Aux port on the router as shown in Figure 3-4.
Connect the RJ-45 end of the adapter cable to the Aux port on the router as shown in Figure 3-4.
Figure 3-12 Connecting a Modem to the Aux Port
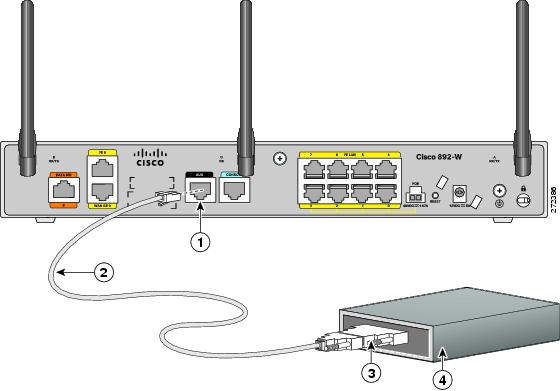
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Step 2![]() Connect the DB-9 end of the console cable to the DB-9 end of the modem adapter.
Connect the DB-9 end of the console cable to the DB-9 end of the modem adapter.
Step 3![]() Connect the DB-25 end of the modem adapter to the modem.
Connect the DB-25 end of the modem adapter to the modem.
Step 4![]() Make sure that your modem and the router auxiliary port are configured for the same transmission speed (up to 115200 bits per second [b/s] is supported) and support mode control with data carrier detect (DCD) and data terminal ready (DTR).
Make sure that your modem and the router auxiliary port are configured for the same transmission speed (up to 115200 bits per second [b/s] is supported) and support mode control with data carrier detect (DCD) and data terminal ready (DTR).
Connecting the 3G Card

Note![]() For information on embedded multiband, multiservice WAN modems, see Configuring Cisco EHWIC and 880G for 3G (EV-DO Rev A) and Configuring Cisco EHWIC and 880G for 3.7G (HSPA+)/3.5G (HSPA).
For information on embedded multiband, multiservice WAN modems, see Configuring Cisco EHWIC and 880G for 3G (EV-DO Rev A) and Configuring Cisco EHWIC and 880G for 3.7G (HSPA+)/3.5G (HSPA).

Note![]() The Cisco 880G router does not support online insertion and removal (OIR) of the 3G card. You must enter the shutdown command on the cellular interface before you remove the 3G card from the router.
The Cisco 880G router does not support online insertion and removal (OIR) of the 3G card. You must enter the shutdown command on the cellular interface before you remove the 3G card from the router.
To connect and secure the 3G card, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() Align the 3G card to the 3G express card slot, as shown in Figure 3-13. Keep the card parallel to the surface and firmly push the card into the slot.
Align the 3G card to the 3G express card slot, as shown in Figure 3-13. Keep the card parallel to the surface and firmly push the card into the slot.

Tip Holding the 3G card on the flat metal surface makes it easier to align and insert the 3G card.

Note![]() When inserting the card into the 3G express card slot, you may hear a metal-on-metal sound as the 3G card rubs against the internal metal cage. The 3G card is designed to fit tightly into the 3G express card slot. Firm pressure may be required to insert the card.
When inserting the card into the 3G express card slot, you may hear a metal-on-metal sound as the 3G card rubs against the internal metal cage. The 3G card is designed to fit tightly into the 3G express card slot. Firm pressure may be required to insert the card.

Note![]() Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) customers need to insert a SIM card, provided by their network carrier, into the 3G card.
Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) customers need to insert a SIM card, provided by their network carrier, into the 3G card.
Figure 3-13 Inserting the 3G Card
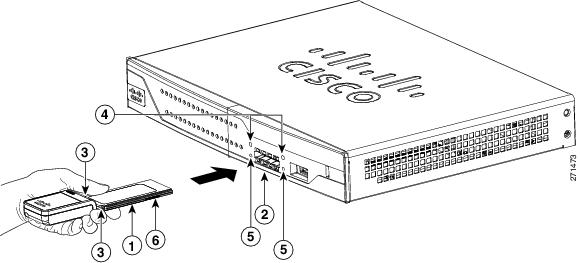
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
SIM slot (in HSPA1 cards only) |
|
|
Step 2![]() Open the top of the anti-theft locking bracket, as shown in Figure 3-14.
Open the top of the anti-theft locking bracket, as shown in Figure 3-14.
Figure 3-14 Opening the Anti-theft Locking Bracket
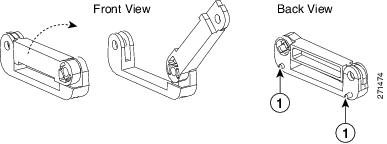
|
|
|
Step 3![]() Slide the opened locking bracket under the 3G card. The locking bracket should align with the notches on either side of the 3G card, as shown in Figure 3-15, and the pins on the locking bracket should be inserted into the corresponding holes in the router.
Slide the opened locking bracket under the 3G card. The locking bracket should align with the notches on either side of the 3G card, as shown in Figure 3-15, and the pins on the locking bracket should be inserted into the corresponding holes in the router.
Figure 3-15 Installing the Locking Bracket
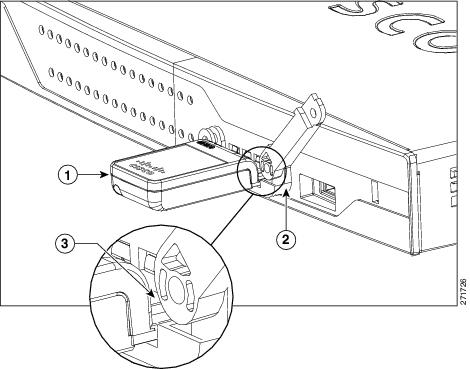
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Step 4![]() Close the locking bracket, as shown in Figure 3-16.
Close the locking bracket, as shown in Figure 3-16.
Figure 3-16 Closing the Locking Bracket
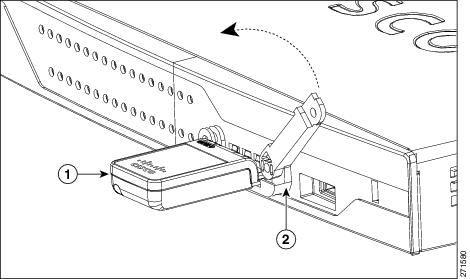
|
|
|
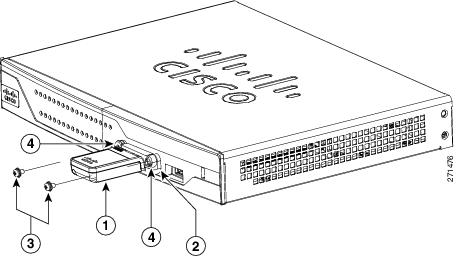
Step 5![]() Insert the screws, as shown in Figure 3-17, and tighten with a number 2 Phillips screwdriver.
Insert the screws, as shown in Figure 3-17, and tighten with a number 2 Phillips screwdriver.
Figure 3-17 Inserting the Screws
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Step 6![]() To connect the antenna to the 3G card, insert the antenna connector into the antenna connector receptacle on the 3G card.
To connect the antenna to the 3G card, insert the antenna connector into the antenna connector receptacle on the 3G card.

Note![]() The antenna connector receptacle may be located on the left, right, or front of the 3G card, depending on your card.
The antenna connector receptacle may be located on the left, right, or front of the 3G card, depending on your card.
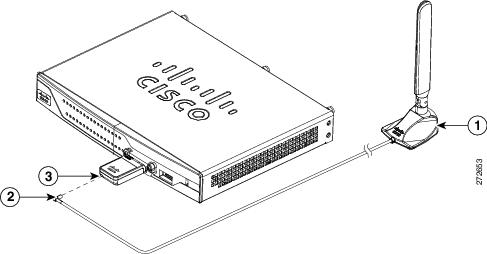
Figure 3-18 and Figure 3-19 show the antenna connected to the 3G card with an SSMB type plug, and the antenna with the SMK-TS-9 connector.
Figure 3-18 Antenna connected to the 3G Card with SSMB connector
|
|
|
Antenna connector receptacle2 |
|
|
|
|
|
2.The antenna connector receptacle is located on either the left, right or front of the card for different SKUs. Please locate the receptacle of your card before plugging in the cable. |
Figure 3-19 Antenna with the SMK-TS- 9 Connector
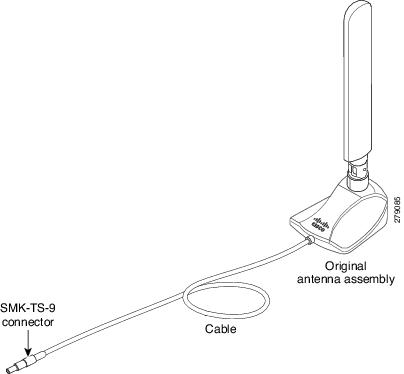
If you are using an extension cable, you must attach the 3G adapter for extended cable antenna to the body of the router. Depending on the SKU ordered, the adapters come with different connectors. Table 3-2 lists the different adapters and SKUs supported by each adapter. For instructions on how to install the adapter, see the “Installing the 3G Adapter for Extended Cable/Antenna” section. Otherwise, follow Step 7.
Step 7![]() Clean the flat surface to which you will affix the antenna.
Clean the flat surface to which you will affix the antenna.
Step 8![]() Remove the protective tape from the adhesive on the bottom of the antenna cradle, then firmly press the cradle to the flat surface.
Remove the protective tape from the adhesive on the bottom of the antenna cradle, then firmly press the cradle to the flat surface.
Installing the 3G Adapter for Extended Cable/Antenna
For better signal and reception, if you are using the Cisco 3G Adapter for Extended Cable/Antenna, 3G-ACC-SMKTS9-TNC, follow these steps to install it:
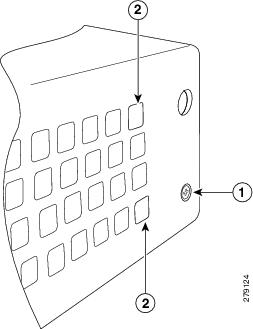
Step 1![]() Locate and remove the Phillips screw on the left side of the router as shown in Figure 3-20. Keep the screw aside for Step 4.
Locate and remove the Phillips screw on the left side of the router as shown in Figure 3-20. Keep the screw aside for Step 4.
Figure 3-20 Locating the Phillips Screw
|
|
|
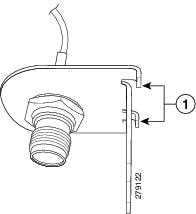
Step 2![]() Locate the hooks on the adapter as shown in Figure 3-21.
Locate the hooks on the adapter as shown in Figure 3-21.
Figure 3-21 Locating the Hooks on the Adapter
|
|
|||
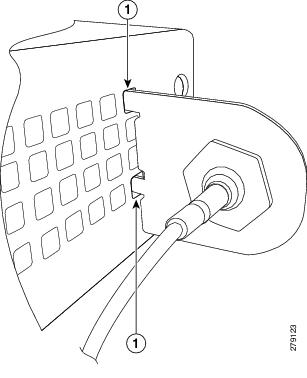
Step 3![]() Align and insert the hooks of the adapter into the air vent holes on the left side router body as shown in Figure 3-22.
Align and insert the hooks of the adapter into the air vent holes on the left side router body as shown in Figure 3-22.
Figure 3-22 Inserting the Hooks
|
|
|||
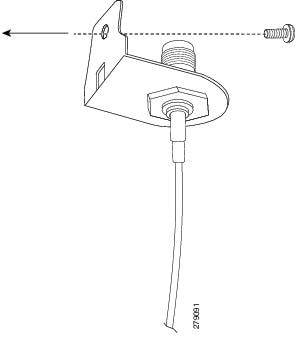
Step 4![]() Align the circular adapter hole with the hole on the router chassis from where you removed the screw in Step 1 and use the screw to attach the adapter to the router as shown in Figure 3-23.
Align the circular adapter hole with the hole on the router chassis from where you removed the screw in Step 1 and use the screw to attach the adapter to the router as shown in Figure 3-23.
Figure 3-23 Attaching the Adapter
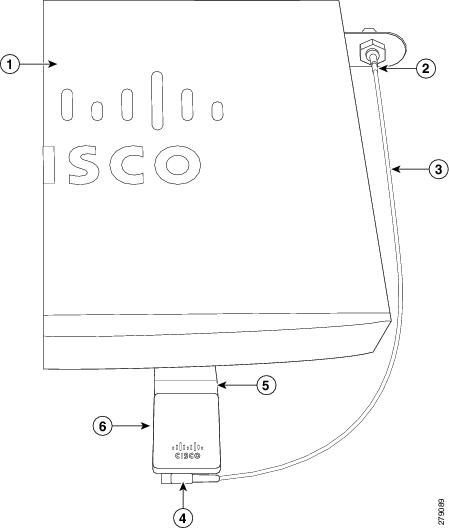
Step 5![]() Connect the extension cable to the 3G card, as described in the “Connecting the 3G Card” section. The complete assembly is shown in Figure 3-24.
Connect the extension cable to the 3G card, as described in the “Connecting the 3G Card” section. The complete assembly is shown in Figure 3-24.
Figure 3-24 Adapter Connected to 3G Card and Router Chassis
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Now the adapter is ready for use with the extension cable.
Table 3-3 lists the loss information for the ultra-low-loss (ULL) LMR 400 cables available with the adapter for the 3G fixed platforms.
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|

Note![]() Antenna orientation can increase or decrease signal reception due to polarization. Typically, an SP’s transmitting antenna on the BTS is a vertically polarized omnidirectional antenna, which means the electromagnetic waves are transmitted from it in a vertical plane. Hence, the receiving antenna needs to be vertically oriented too in order to receive the best signal. As the angle of the antenna orientation is changed from vertical to horizontal, only an angular component of the signal is picked up by the antenna. Therefore, if the antenna orientation is horizontal, the antenna picks up the least signal. The signal is received by the antenna as a result of it bouncing off of reflective surfaces. Hence, depending on where the antenna is placed, it may receive different signal strengths. However, the recommended position is vertical.
Antenna orientation can increase or decrease signal reception due to polarization. Typically, an SP’s transmitting antenna on the BTS is a vertically polarized omnidirectional antenna, which means the electromagnetic waves are transmitted from it in a vertical plane. Hence, the receiving antenna needs to be vertically oriented too in order to receive the best signal. As the angle of the antenna orientation is changed from vertical to horizontal, only an angular component of the signal is picked up by the antenna. Therefore, if the antenna orientation is horizontal, the antenna picks up the least signal. The signal is received by the antenna as a result of it bouncing off of reflective surfaces. Hence, depending on where the antenna is placed, it may receive different signal strengths. However, the recommended position is vertical.
For additional information on all the available cables and antennas available for 3G, go to: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/routers/access/1800/1861/software/feature/guide/mrwlsgsm.html#wp1262730
Connecting a Data BRI Port
You can connect the Data BRI port to the ISDN service provider as a backup link to the WAN port in case the primary xDSL (general term referring to various forms of DSL, including global industry standard symmetrical high-speed DSL [G.SHDSL]) WAN service fails. The Data BRI connection is not available on the third-generation (3G) models.
The cabling requirements for the ISDN S/T connection are as follows:
- You must provide two unshielded Category 5 cables. The first cable connects the NT1 box to the splitter, and the second cable connects the splitter to the wall jack.
- There are RJ-45 connectors at both ends of the default orange ISDN S/T cable. However, an RJ-45–to–RJ-11 ISDN S/T cable is available upon request if the wall jack at the site requires an RJ-11 connector. Contact your router reseller for the appropriate cable.

To connect the Data BRI port to the ISDN service provider, follow these steps:

Note![]() Although the following procedure shows a Cisco 888W data router, this procedure applies to all Cisco 880 series router with a Data BRI port.
Although the following procedure shows a Cisco 888W data router, this procedure applies to all Cisco 880 series router with a Data BRI port.
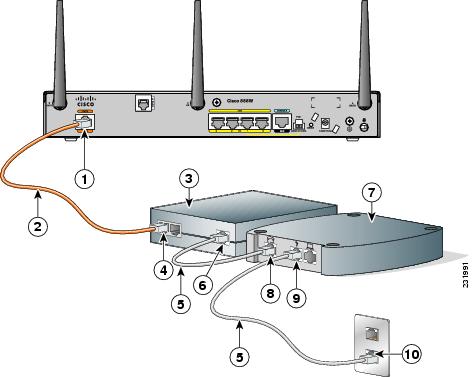
Step 1![]() Connect one end of the orange ISDN S/T cable to the Data BRI port on the router. Figure 3-25 shows a Data BRI connection.
Connect one end of the orange ISDN S/T cable to the Data BRI port on the router. Figure 3-25 shows a Data BRI connection.
Figure 3-25 Connecting the Data BRI Port to the ISDN Line
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Step 2![]() Connect the other end of the orange ISDN S/T cable to the S/T port on the NT1 box.
Connect the other end of the orange ISDN S/T cable to the S/T port on the NT1 box.
Step 3![]() Connect the first unshielded CAT 5 cable from the U-port on the NT1 box to the telephone line port on the splitter.
Connect the first unshielded CAT 5 cable from the U-port on the NT1 box to the telephone line port on the splitter.
Step 4![]() Connect the second unshielded Category 5 cable from the telecommunication service port on the splitter to the wall jack to allow a link to the network service provider.
Connect the second unshielded Category 5 cable from the telecommunication service port on the splitter to the wall jack to allow a link to the network service provider.
Connecting an FE Line to an FE WAN Port
To connect the Fast Ethernet (FE) WAN port on the router, follow these steps:
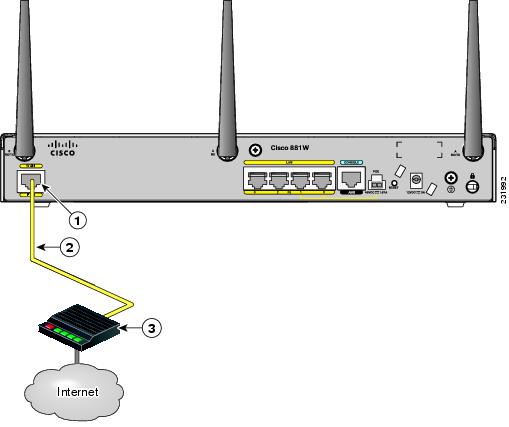
Step 1![]() Connect one end of the yellow cable to the FE WAN port as shown in Figure 3-26.
Connect one end of the yellow cable to the FE WAN port as shown in Figure 3-26.
Figure 3-26 Connecting the FE WAN Port
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Step 2![]() Connect the other end of cable to an available port on the modem.
Connect the other end of cable to an available port on the modem.
Connecting a GE Line to an GE WAN Port
To connect the Gigabit Ethernet (GE) WAN port on the router, follow these steps:
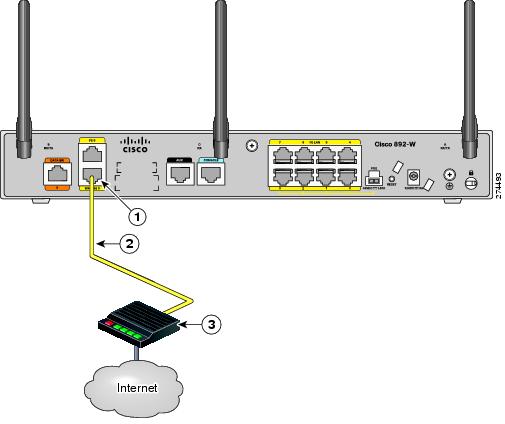
Step 1![]() Connect one end of the yellow cable to the GE WAN port as shown in Figure 3-27.
Connect one end of the yellow cable to the GE WAN port as shown in Figure 3-27.
Figure 3-27 Connecting the GE WAN Port
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Step 2![]() Connect the other end of cable to an available port on the modem.
Connect the other end of cable to an available port on the modem.
Connecting an xDSL Line

Warning![]() Hazardous network voltages are present in WAN ports regardless of whether power to the unit is OFF or ON. To avoid electric shock, use caution when working near WAN ports. When detaching cables, detach the end away from the unit first. Statement 1026
Hazardous network voltages are present in WAN ports regardless of whether power to the unit is OFF or ON. To avoid electric shock, use caution when working near WAN ports. When detaching cables, detach the end away from the unit first. Statement 1026



Warning![]() Do not use this product near water; for example, near a bath tub, wash bowl, kitchen sink or laundry tub, in a wet basement, or near a swimming pool. Statement 1035
Do not use this product near water; for example, near a bath tub, wash bowl, kitchen sink or laundry tub, in a wet basement, or near a swimming pool. Statement 1035

Warning![]() Avoid using a telephone (other than a cordless type) during an electrical storm. There may be a remote risk of electric shock from lightning. Statement 1038
Avoid using a telephone (other than a cordless type) during an electrical storm. There may be a remote risk of electric shock from lightning. Statement 1038

Warning![]() To report a gas leak, do not use a telephone in the vicinity of the leak. Statement 1039
To report a gas leak, do not use a telephone in the vicinity of the leak. Statement 1039

Warning![]() There is the danger of explosion if the battery is replaced incorrectly. Replace the battery only with the same or equivalent type recommended by the manufacturer. Dispose of used batteries according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Statement 1015
There is the danger of explosion if the battery is replaced incorrectly. Replace the battery only with the same or equivalent type recommended by the manufacturer. Dispose of used batteries according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Statement 1015
Figure 3-28 Primary Protection Device Location
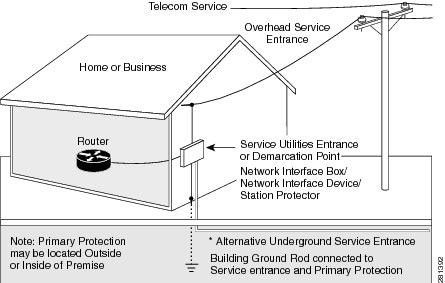
To connect the router to a global industry standard symmetrical high-speed DSL (G.SHDSL) line, very-high-speed digital subscriber line 2 (VDSL2) port, or an ADSL2+ line, follow these steps:
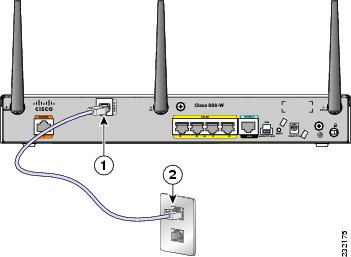
Step 1![]() Connect one end of an RJ-11 (RJ-45 on 880 E models) cable to the port on the router. See Figure 3-29.
Connect one end of an RJ-11 (RJ-45 on 880 E models) cable to the port on the router. See Figure 3-29.
Figure 3-29 Connecting the xDSL Line
|
|
|
Step 2![]() Connect the other end of the cable to the DSL wall jack.
Connect the other end of the cable to the DSL wall jack.


Note![]() The DSL line must be provisioned by your service provider and correctly configured so that the LED shows the carrier detect (CD) status. On Cisco 860VAE routers, check the DSL Link LED.
The DSL line must be provisioned by your service provider and correctly configured so that the LED shows the carrier detect (CD) status. On Cisco 860VAE routers, check the DSL Link LED.
Connecting Power over Ethernet

Warning![]() This unit might have more than one power supply connection. All connections must be removed to de-energize the unit. Statement 1028
This unit might have more than one power supply connection. All connections must be removed to de-energize the unit. Statement 1028

Warning![]() This product must be connected to a power-over-ethernet (PoE) IEEE 802.3af compliant power source or an IEC60950 compliant limited power source. Statement 353
This product must be connected to a power-over-ethernet (PoE) IEEE 802.3af compliant power source or an IEC60950 compliant limited power source. Statement 353
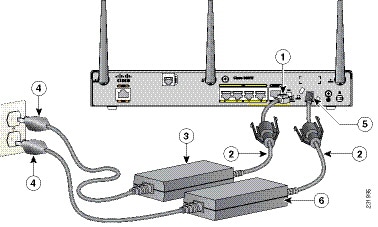
Figure 3-30 shows how to connect the 48-VDC Power over Ethernet (PoE) power adapter to your router. The PoE adapter provides power to ports 0 and 1 of the 4-port 10/100 FE switch on the Cisco 880 series routers and ports 0,1, 2, and 3 of the 8-port 10/100 FE switch on the Cisco 890 series routers.

Note![]() The router must also be connected to an AC power outlet through a 12-VDC adapter. To connect the router to an AC outlet, see the“Connecting the AC Adapter” section.
The router must also be connected to an AC power outlet through a 12-VDC adapter. To connect the router to an AC outlet, see the“Connecting the AC Adapter” section.

Note![]() Be sure that the internal PoE is enabled for this connection procedure to work.
Be sure that the internal PoE is enabled for this connection procedure to work.
Figure 3-30 Connecting PoE for the Cisco 880 and the Cisco 890 Series Routers
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
The Cisco 880 series ISRs with embedded WLAN antennas require a single external power supply: a 30-W power supply for non-POE-enabled routers or a 60-W power supply for POE-enabled routers. For the back panels of some of these routers, see Figure 1-33 and Figure 1-35.
Connecting the AC Adapter

Warning![]() The device is designed to work with TN power systems. Statement 19
The device is designed to work with TN power systems. Statement 19

Warning![]() This product relies on the building’s installation for short-circuit (overcurrent) protection. Ensure that the protective device is rated not greater than:
This product relies on the building’s installation for short-circuit (overcurrent) protection. Ensure that the protective device is rated not greater than:
120 VAC, 20 A U.S. (240 VAC, 16 to 20 A international). Statement 1005

Warning![]() This unit might have more than one power supply connection. All connections must be removed to de-energize the unit. Statement 1028
This unit might have more than one power supply connection. All connections must be removed to de-energize the unit. Statement 1028

Note![]() The Cisco 892FSP utilizes a single 4-pin power connector type. Figure 3-33 shows the pin number assignment of the Cisco 892FSP Power Adapter Connector.
The Cisco 892FSP utilizes a single 4-pin power connector type. Figure 3-33 shows the pin number assignment of the Cisco 892FSP Power Adapter Connector.
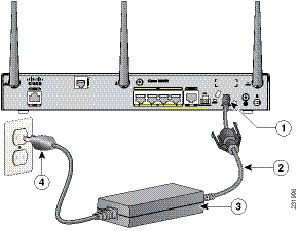
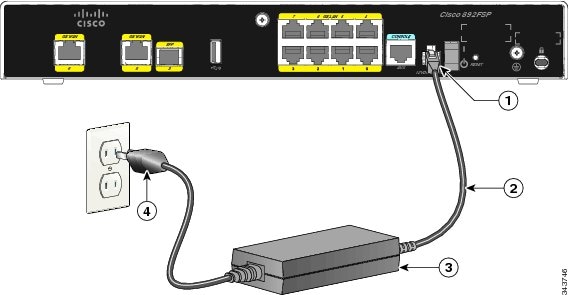
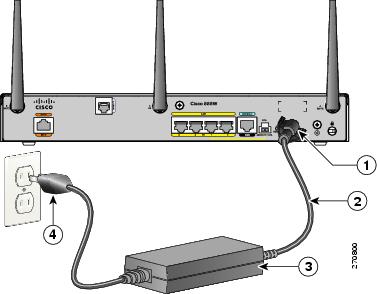
To connect your Cisco 860 series, Cisco 880 series, or the Cisco 890FSP ISR to an AC power outlet, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() Connect the router to an AC power outlet as shown in Figure 3-31.
Connect the router to an AC power outlet as shown in Figure 3-31.
To connect the AC power outlet for the Cisco 892FSP router, see Figure 3-32.
Figure 3-31 Connecting the AC Adapter
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Figure 3-32 Connecting the AC Adapter for the Cisco 892FSP
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Figure 3-33 Cisco 892FSP, 896VA, 897VA, and 898EA Power Adapter Connector Pin Assignment
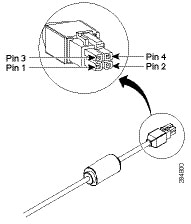
|
|
|
||
|
|
NC3 |
|
|
|
Step 2![]() To secure the power cord to the router, attach the power lock clip to the power cord, slide the clip to the end of the DC plug, and secure the retaining clip into the router chassis. See Figure 3-34.
To secure the power cord to the router, attach the power lock clip to the power cord, slide the clip to the end of the DC plug, and secure the retaining clip into the router chassis. See Figure 3-34.
Figure 3-34 Securing the Power Cord

|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Step 3![]() Snap the latches into the holes on either side of the power connector. See Figure 3-35.
Snap the latches into the holes on either side of the power connector. See Figure 3-35.
Figure 3-35 Power Lock Clip Latched Into the Holes on Either Side of the Power Connector
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Connecting an FXS Line
Use a standard straight-through RJ-11 modular telephone cable to connect a Foreign Exchange Service (FXS) port to a telephone or fax machine.

Warning![]() This equipment contains a ring signal generator (ringer), which is a source of hazardous voltage. Do not touch the RJ-11 (phone) port wires (conductors), the conductors of a cable connected to the RJ-11 port, or the associated circuit-board when the ringer is active. The ringer is activated by an incoming call. Statement 1042
This equipment contains a ring signal generator (ringer), which is a source of hazardous voltage. Do not touch the RJ-11 (phone) port wires (conductors), the conductors of a cable connected to the RJ-11 port, or the associated circuit-board when the ringer is active. The ringer is activated by an incoming call. Statement 1042

Warning![]() Hazardous network voltages are present in WAN ports regardless of whether power to the unit is OFF or ON. To avoid electric shock, use caution when working near WAN ports. When detaching cables, detach the end away from the unit first. Statement 1026
Hazardous network voltages are present in WAN ports regardless of whether power to the unit is OFF or ON. To avoid electric shock, use caution when working near WAN ports. When detaching cables, detach the end away from the unit first. Statement 1026

Warning![]() For connections outside the building where the equipment is installed, the following ports must be connected through an approved network termination unit with integral circuit protection: FXS. Statement 1044
For connections outside the building where the equipment is installed, the following ports must be connected through an approved network termination unit with integral circuit protection: FXS. Statement 1044
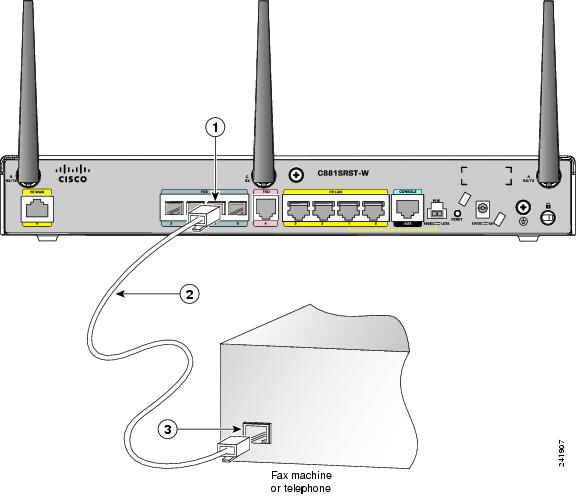
To connect the FXS line, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() Connect one end of the straight-through RJ-11 cable to the FXS port.
Connect one end of the straight-through RJ-11 cable to the FXS port.
Figure 3-36 shows an FXS line connection.
Figure 3-36 Connecting an FXS Line
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Step 2![]() Connect the other end of the cable to the RJ-11 port on the fax machine or telephone.
Connect the other end of the cable to the RJ-11 port on the fax machine or telephone.
Connecting an FXO Line
Use a straight-through RJ-11 cable to connect the FXO voice port to the PSTN or PBX through a telephone wall outlet.

Warning![]() Hazardous network voltages are present in WAN ports regardless of whether power to the unit is OFF or ON. To avoid electric shock, use caution when working near WAN ports. When detaching cables, detach the end away from the unit first. Statement 1026
Hazardous network voltages are present in WAN ports regardless of whether power to the unit is OFF or ON. To avoid electric shock, use caution when working near WAN ports. When detaching cables, detach the end away from the unit first. Statement 1026
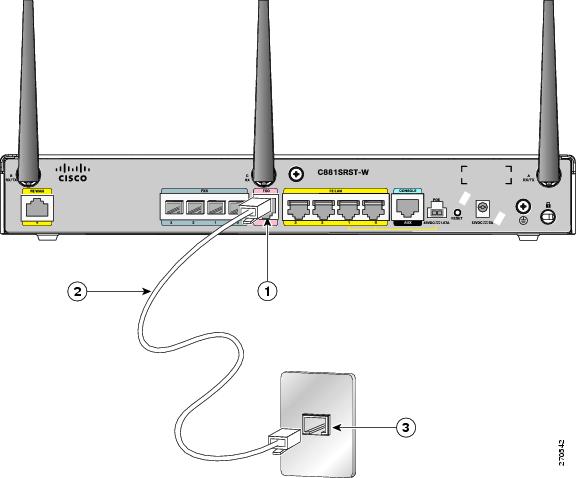
To connect the FXO line, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() Connect one end of the straight-through RJ-11 cable to the FXO port. See Figure 3-37.
Connect one end of the straight-through RJ-11 cable to the FXO port. See Figure 3-37.
Figure 3-37 Connecting an FXO Line
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Step 2![]() Connect the other end of the RJ-11 cable to a telephone wall outlet.
Connect the other end of the RJ-11 cable to a telephone wall outlet.

Note![]() If you have specified the use of a private line automatic ringdown (PLAR) off-premises extension (OPX) connection mode for an FXO voice port (with loop resistance less than 8000 Ohm), you must ensure that the soft-offhook option is enabled on the port.
If you have specified the use of a private line automatic ringdown (PLAR) off-premises extension (OPX) connection mode for an FXO voice port (with loop resistance less than 8000 Ohm), you must ensure that the soft-offhook option is enabled on the port.
This option allows a stepped offhook resistance during seizure, which avoids overloading the circuit during offhook in the event that ringing voltage is present on the circuit at the same time as the trunk seizure. The stepped offhook resistance is initially set to 800 Ohms, then adjusts to 50 Ohms when ringing voltage is not present.
To enable the soft-offhook command on the port, and to access the connection command with plar opx syntax, see the Cisco Command Lookup Tool.
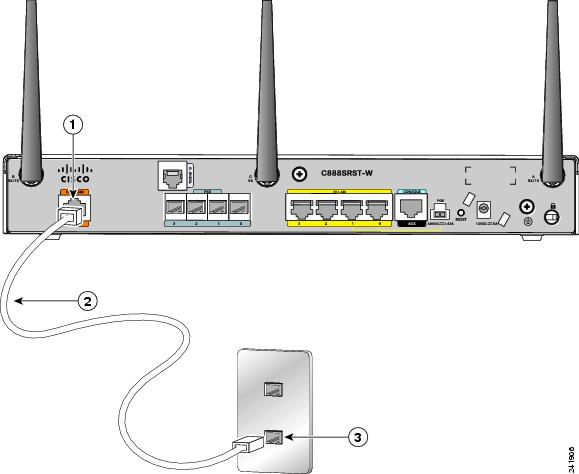
Connecting a Voice ISDN BRI Line
Use a straight-through RJ-45 cable to connect the voice BRI port to the ISDN network through a telephone outlet or other device.

To connect the voice BRI line, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() Connect one end of a straight-through RJ-45–to–RJ-45 cable to the Voice BRI port.
Connect one end of a straight-through RJ-45–to–RJ-45 cable to the Voice BRI port.

Note![]() When the interface is configured as NT and is connecting to a TE device, use a crossover cable. See Table A-27.
When the interface is configured as NT and is connecting to a TE device, use a crossover cable. See Table A-27.
Figure 3-38 shows a voice BRI line connection.
Figure 3-38 Connecting a Voice BRI Line
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Step 2![]() Connect the other end of the cable to the RJ-45 telephone outlet or other device.
Connect the other end of the cable to the RJ-45 telephone outlet or other device.

Warning![]() Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from disconnected fibers or connectors. Do not stare into beams or view directly with optical instruments. Statement 1051
Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from disconnected fibers or connectors. Do not stare into beams or view directly with optical instruments. Statement 1051

Warning![]() Do not stare into the laser beam. Statement 1010
Do not stare into the laser beam. Statement 1010

Warning![]() Invisible laser radiation present. Statement 1016
Invisible laser radiation present. Statement 1016

Warning![]() Ultimate disposal of this product should be handled according to all national laws and regulations. Statement 1040
Ultimate disposal of this product should be handled according to all national laws and regulations. Statement 1040

Warning![]() Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the end of the unterminated fiber cable or connector. Do not view directly with optical instruments. Viewing the laser output with certain optical instruments (for example, eye loupes, magnifiers, and microscopes) within a distance of 100 mm may pose an eye hazard. Statement 1056
Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the end of the unterminated fiber cable or connector. Do not view directly with optical instruments. Viewing the laser output with certain optical instruments (for example, eye loupes, magnifiers, and microscopes) within a distance of 100 mm may pose an eye hazard. Statement 1056

Warning![]() Use of controls, adjustments, or performing procedures other than those specified may result in hazardous radiation exposure. Statement 1057
Use of controls, adjustments, or performing procedures other than those specified may result in hazardous radiation exposure. Statement 1057

Warning![]() Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from disconnected fibers or connectors. Do not stare into beams or view directly with optical instruments. Statement 1051
Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from disconnected fibers or connectors. Do not stare into beams or view directly with optical instruments. Statement 1051
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Verifying Connections
To verify that all devices are properly connected to the router, first turn on all the connected devices, then check the LEDs. To verify router operation, refer to Table 3-1 .
For the full LED descriptions, see the “LEDs” section.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
To servers, PCs, workstations, or an external Ethernet switch connected to the LAN ports (FE04, FE1, FE2, or FE3) |
On when the FE LAN port is physically connected to a server, PC, workstation, or external Ethernet switch. |
|
| To xDSL5 line |
Green when the line is connected to the xDSL DSLAM6. |
|
Green when receiving or sending data. |
||
| 3G7 |
WWAN8 |
|
RSSI9 |
Amber when service is not established. Green when signal strength is high. |
|
CDMA10 |
||
GSM11 |
||
To PPP12 clients |
||
To VPN15 tunnel |
||
|
||
| PoE17 |
||
Blinking when there is LAN activity (traffic in either direction). |
||
On when DSL WAN mode is selected and DSL training complete. Blinking when DSL WAN mode is selected but incomplete DSL LinkUp state such as in-training (slow initially, fast when almost connected), or controller "OFF", or no cable attached to DSL connector. Off when the device is powered off; or GE WAN mode is selected. |
||
On when the DSL interface is up. Blinking when there is DSL WAN activity (traffic in either direction). Faster blinking when there is heavier traffic. Off when the device is powered off or the DSL WAN interface is down. |
||
On when GE WAN mode is selected. Off when the device is powered off or when DSL WAN mode is selected. |
||
On when the GE WAN interface is up. Blinking when there is GE WAN activity (traffic in either direction). Off when the device is powered off or when the GE WAN interface is down. |
|
5.xDSL = General term referring to various forms of DSL, including ADSL (asymmetric digital subscriber line), VDSL (very-high-data-rate digital subscriber line), and G.SHDSL. |
 Feedback
Feedback