Overview of Cisco 4000 Series ISRs
Cisco 4000 Series Integrated Services Routers (ISRs) are modular routers with LAN and WAN connectivity. They support several interface modules, including Cisco Enhanced Service Modules (SM-X) and Cisco Network Interface Modules (NIMs).
Cisco 4000 Series ISRs target these applications:
- Enterprise applications—Intended for mid-size aggregation and gateway router that is located in a regional or large branch office:
–![]() WAN aggregation at Cisco Enterprise core
WAN aggregation at Cisco Enterprise core
–![]() Branch or regional office aggregation
Branch or regional office aggregation
–![]() High-end customer premises equipment (CPE) for business-quality Internet access
High-end customer premises equipment (CPE) for business-quality Internet access
–![]() Service provider leased line aggregation
Service provider leased line aggregation
–![]() Provider edge (PE) and high-end customer edge (CE) for Layer 2 VPN or Layer 3 VPN services
Provider edge (PE) and high-end customer edge (CE) for Layer 2 VPN or Layer 3 VPN services
–![]() Low-end Ethernet aggregation
Low-end Ethernet aggregation
Cisco 4000 Series ISRs are available in these models:
- Cisco 4461 ISR
- Cisco 4451-X ISR
- Cisco 4431 ISR
- Cisco 4351 ISR
- Cisco 4331 ISR
- Cisco 4321 ISR
- Cisco 4221 ISR
For more information on the features and specifications of Cisco 4000 Series Integrated Services Routers (ISRs), refer to the Cisco 4000 Series Integrated Services Routers datasheet .

Note![]() Sections in this documentation apply to all models of Cisco 4000 Series ISRs unless a reference to a specific model is made explicitly.
Sections in this documentation apply to all models of Cisco 4000 Series ISRs unless a reference to a specific model is made explicitly.
Chassis Views
This section contains views of the front and back panels of the Cisco 4000 Series ISRs, showing the locations of power and signal interfaces, module slots, status indicators, and chassis identification labels:
- Cisco 4461 ISR Chassis
- Cisco 4451-X ISR Chassis
- Cisco 4431 ISR Chassis
- Cisco 4351 ISR Chassis
- Cisco 4331 ISR Chassis
- Cisco 4321 ISR Chassis
- Cisco 4221 ISR Chassis
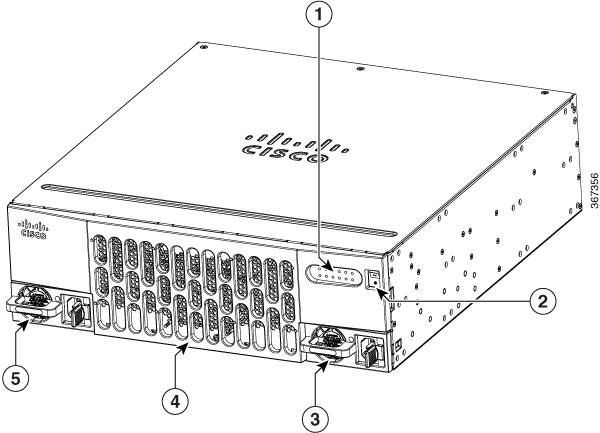
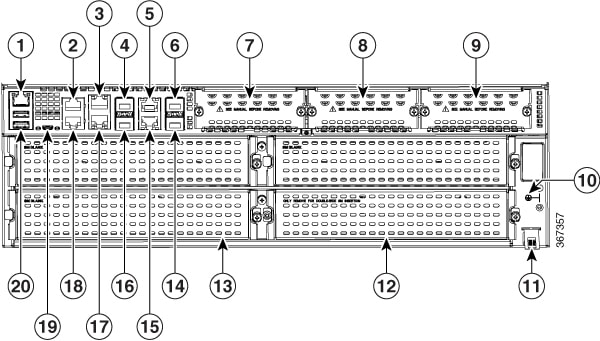
Cisco 4461 ISR Chassis
Cisco 4461 ISR routers support these slot types:
- Network Interface Modules (NIMs)
- Service modules (SM-X, like SM-X-1T3/E3)
- E-Series Server Modules
Figure 1-1 Bezel Side of Cisco 4461 ISR with Two PSUs
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Figure 1-2 Back Panel (I/O Side) Slots and Connectors on Cisco 4461 ISR
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Step 1![]() Read the “Safety Warnings” section and disconnect the power supply before you replace any module.
Read the “Safety Warnings” section and disconnect the power supply before you replace any module.
Step 2![]() Access the SM-X slot. See Figure 1-3 for the various NIM and SM-X slot locations.
Access the SM-X slot. See Figure 1-3 for the various NIM and SM-X slot locations.
Step 3![]() Loosen the captive screws to open the slot cover.
Loosen the captive screws to open the slot cover.
Step 4![]() Pull the SM-X out of the connector on the motherboard. Keep the SM-X parallel with the motherboard to prevent damage to the slot and standoff.
Pull the SM-X out of the connector on the motherboard. Keep the SM-X parallel with the motherboard to prevent damage to the slot and standoff.

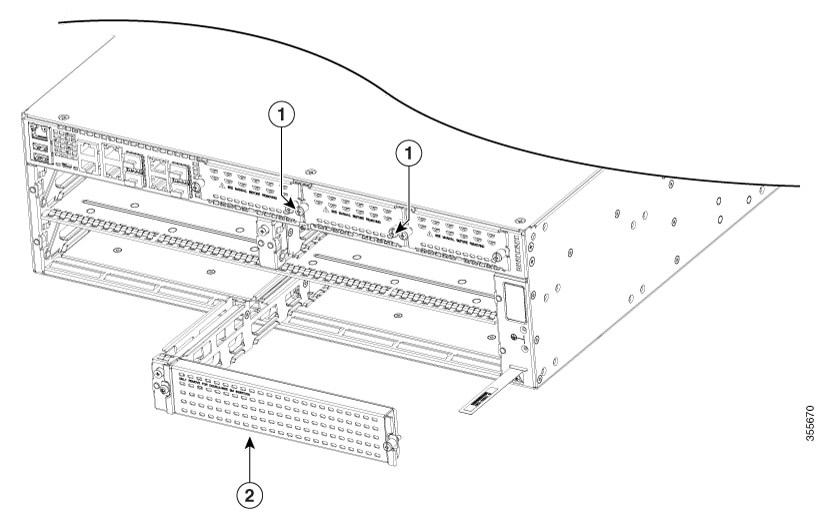
Note![]() When you remove the SM-X slot 2, it removes the blank slot which is attached to the special divider. See Figure 1-4.
When you remove the SM-X slot 2, it removes the blank slot which is attached to the special divider. See Figure 1-4.
Step 5![]() Place the SM-X in an anti-static bag to protect it from ESD damage.
Place the SM-X in an anti-static bag to protect it from ESD damage.

Note![]() For more details on installation of SM-Xs, NIMs, and Cisco E-Series Server Modules, see the hardware installation guide for the particular module you have purchased.
For more details on installation of SM-Xs, NIMs, and Cisco E-Series Server Modules, see the hardware installation guide for the particular module you have purchased.
Figure 1-4 NIM and SM-X Slot with Divider
|
|
|
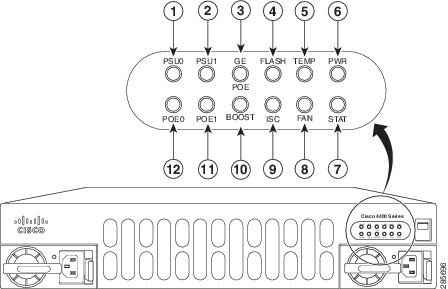
Figure 1-5 Bezel Side LEDS of the Cisco 4461 ISR Model
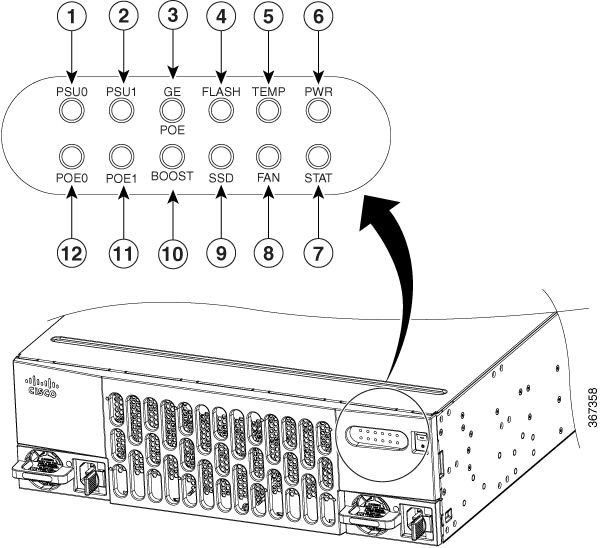
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
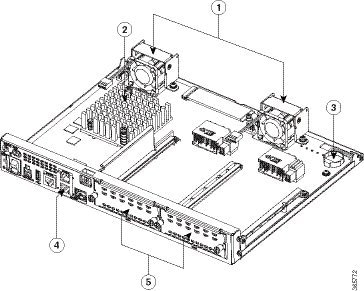
Platform Summary
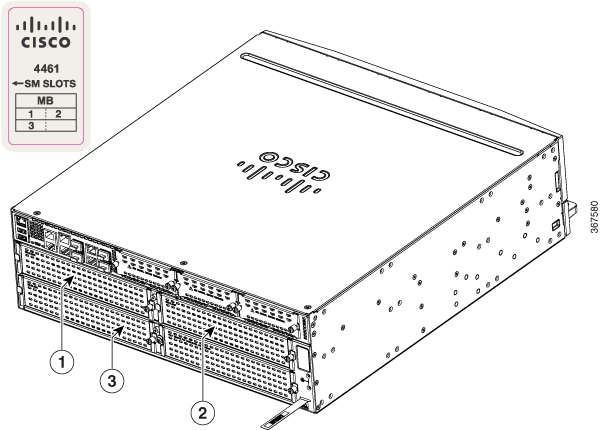
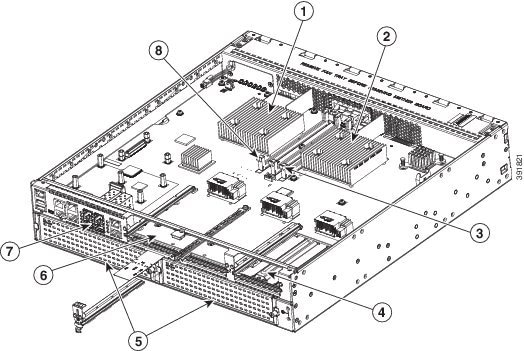
Figure 1-6 shows the internal view of Cisco 4461 with parts and module locations.
Figure 1-6 Platform Summary of Cisco 4461 ISR
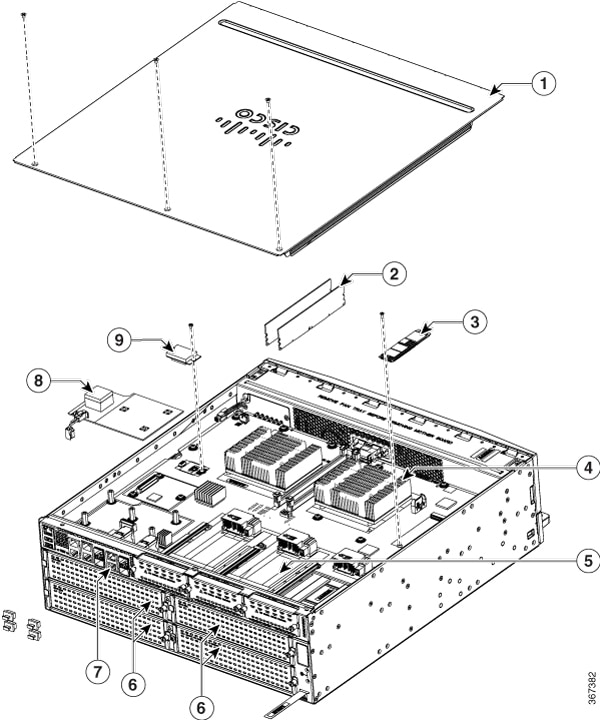
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Cisco 4451-X ISR Chassis
Bezel view of the Cisco 4451-X ISR with two PSUs. Cisco 4451-X ISR routers support these slot types:
- Network Interface Modules (NIMs)
- Service modules (SM-X, like SM-X-1T3/E3)
- E-Series Server Modules.
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Back panel slots and ports of the Cisco 4451-X ISR.
Figure 1-8 Back Panel (I/O Side) Slots and Connectors on Cisco 4451-X ISR
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
LEDs for the GE 0/0/0 interface (See Table 1-1 for detailed LED information) |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Figure 1-9 Bezel Side LEDS of the Cisco 4451-X ISR Model
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Figure 1-6 shows the internal view of Cisco 4451-X ISR with parts and module locations.
Figure 1-10 E-USB on the Cisco 4451-X ISR
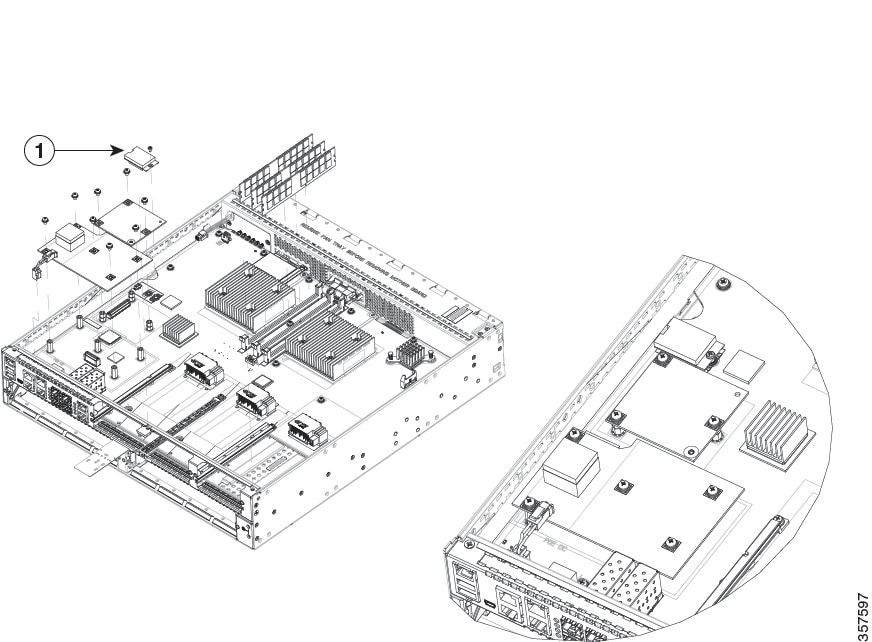
|
|
|
Figure 1-6 shows the internal view of Cisco 4451-X ISR with parts and module locations.
Figure 1-11 Compact Flash on the Cisco 4451-X ISR
|
|
|
Platform Summary
Figure 1-6 shows the internal view of Cisco 4451-X ISR with parts and module locations.
Figure 1-12 Platform Summary of Cisco 4451-X ISR
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Cisco 4431 ISR Chassis
Cisco 4431 ISR supports the Network Interface Modules (NIMs) and Integrated Services Card (ISC slots for PVDM4s).
Figure 1-13 Bezel View of Cisco 4431 ISR with Two Power Supply Units

|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Figure 1-14 View of Cisco 4431 ISR Chassis
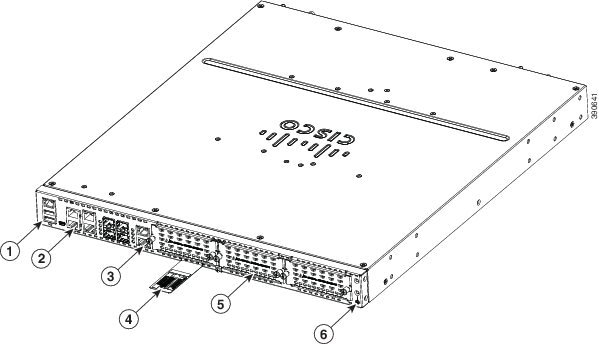
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Figure 1-15 LEDs on the Cisco 4431 ISR
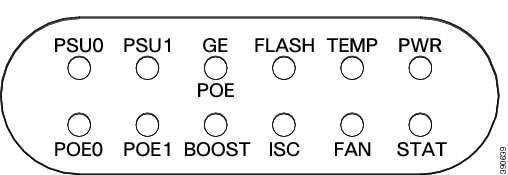
For detailed information on LEDs, see the “LED Indicators” section.
Platform Summary
Figure 1-16 shows the internal view of Cisco 4431 ISR with parts and module locations.
Figure 1-16 Platform Summary of the Cisco 4431 ISR
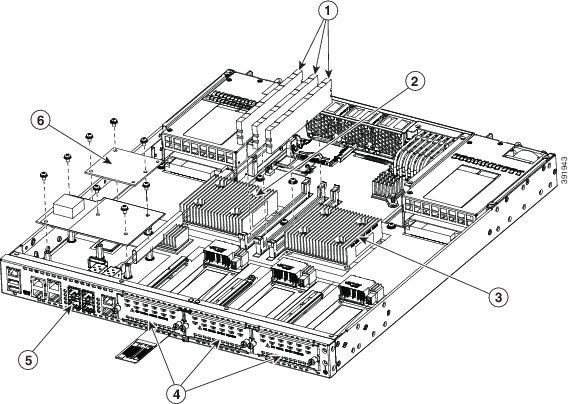
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Cisco 4351 ISR Chassis
This section contains the following views of Cisco 4351ISR chassis:
- Power Supply and Bezel Side View of Cisco 4351 ISR (Figure 1-17)
- Back Panel Ports, Slots, and Serial Number on Cisco 4351 ISR (Figure 1-18)
- Ports on Cisco 4351 ISR (Figure 1-19)
- LEDs on Cisco 4351 ISR (Figure 1-20)
Figure 1-17 Power Supply and Bezel Side View of Cisco 4351 ISR

|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Figure 1-18 Back Panel Ports, Slots, and Serial Number on Cisco 4351 ISR
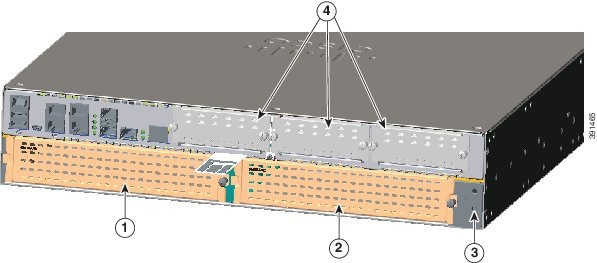
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Figure 1-19 Ports on Cisco 4351 ISR
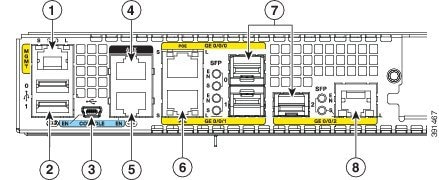
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Figure 1-20 LEDs on Cisco 4351 ISR

For detailed information on LEDs, see the “LED Indicators” section.
Platform Summary
Figure 1-21 shows the internal view of Cisco 4351 ISR chassis with parts and module locations.
Figure 1-21 Platform Summary of Cisco 4351 ISR Chassis
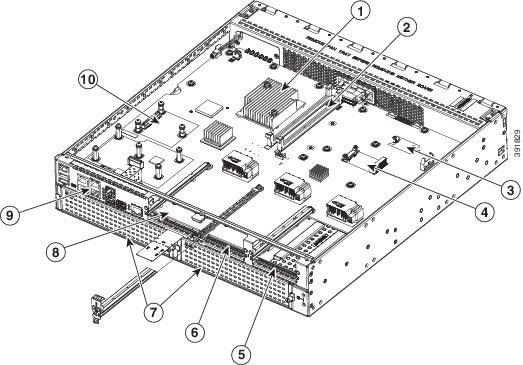
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Cisco 4331 ISR Chassis
This section contains the following views of Cisco 4331 ISR router:
- Bezel Side Ports and LEDs on Cisco 4331 ISR (Figure 1-22)
- Back Panel Ports and Slots on Cisco 4331 ISR (Figure 1-23)
- Ground Connection on Cisco 4331 ISR (Figure 1-24)
Figure 1-22 Bezel Side Ports and LEDs on Cisco 4331 ISR
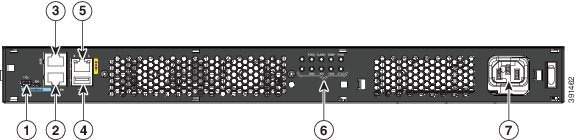
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Figure 1-23 Back Panel Ports and Slots on Cisco 4331 ISR
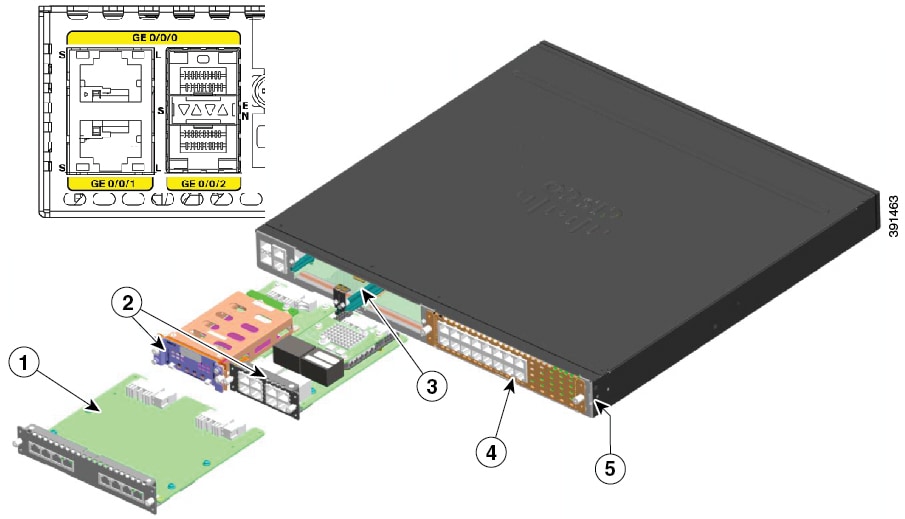
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
For detailed information on LEDs, see the “LED Indicators” section.
Figure 1-24 Ground Connection on Cisco 4331 ISR
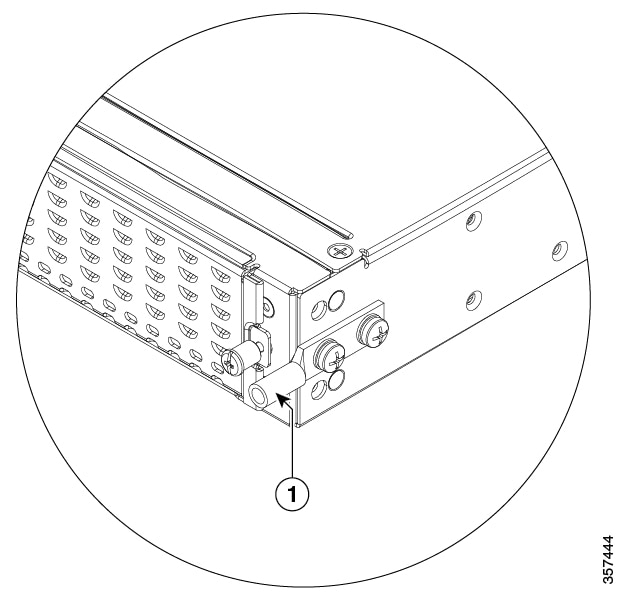
|
|
|
Platform Summary
Figure 1-25 shows the internal view of the Cisco 4431 ISR with parts and module locations.
Figure 1-25 Platform Summary of Cisco 4331 ISR Chassis
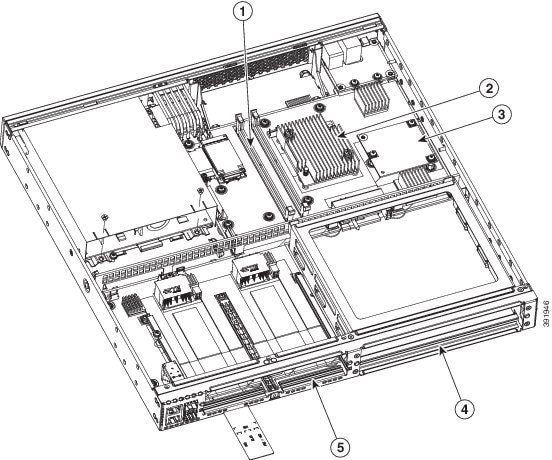
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Cisco 4321 ISR Chassis
This section contains the following views of Cisco 4321 ISR router:
- Back Panel Ports on Cisco 4321 ISR (Figure 1-26)
- Back Panel (I/O Side) View of Cisco 4321 ISR (Figure 1-27)
- LEDs on Cisco 4321 ISR (Figure 1-28)
Figure 1-26 Back Panel Ports on Cisco 4321 ISR
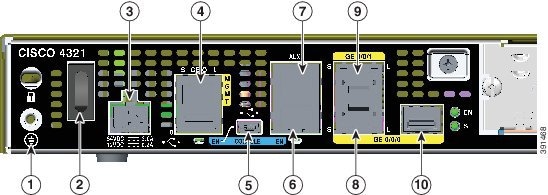
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Figure 1-27 Back Panel (I/O Side) View of Cisco 4321 ISR
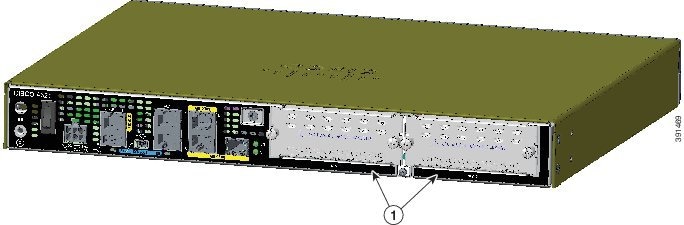
|
|
Figure 1-28 LEDs on Cisco 4321 ISR
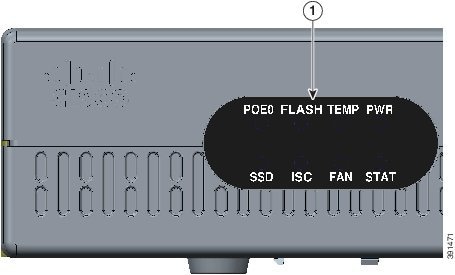
|
|
For detailed information on LEDs, see the “LED Indicators” section.
Platform Summary
Figure 1-29 shows the internal view of Cisco 4321 ISR with parts and module locations.
Figure 1-29 Platform Summary of Cisco 4321 ISR Chassis
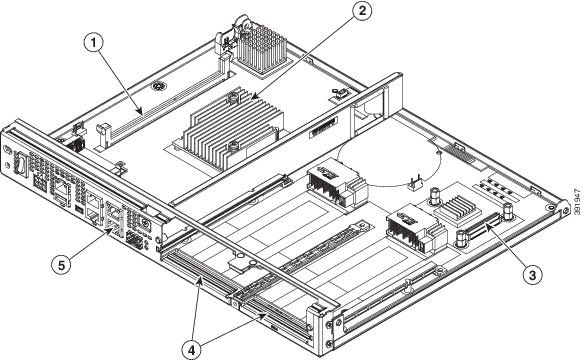
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Cisco 4221 ISR Chassis
This section contains the following views of Cisco 4221 ISR router:
- Back Panel Ports on Cisco 4221 ISR (Figure 1-30)
- Back Panel (I/O Side) View of Cisco 4221 ISR (Figure 1-31)
- LEDs on Cisco 4221 ISR (Figure 1-32)
Figure 1-30 Back Panel Ports on Cisco 4221 ISR
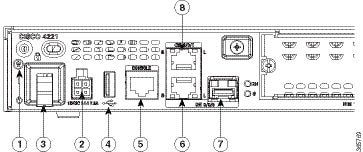
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Figure 1-31 Back Panel (I/O Side) View of Cisco 4221 ISR

|
|
Figure 1-32 LEDs on Cisco 4221 ISR
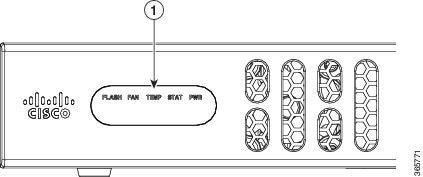
|
|
For detailed information on LEDs, see the “LED Indicators” section.
Platform Summary
Figure 1-33 shows the internal view of Cisco 4221 ISR with parts and module locations.
Figure 1-33 Platform Summary of Cisco 4221 ISR Chassis
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Locate Product Identification Details
The serial number (SN), product ID (PID), version ID (VID), and Common Language Equipment Identifier (CLEI) are printed on a label on the back of the router or on a label tray located on the router chassis or motherboard.
To obtain a software license, you need a product authorization key (PAK) and the unique device identifier (UDI) of the device where the license is to be installed.
The UDI has two main components:
The UDI can be viewed using the show license udi command in privileged Exec mode in Cisco Internet Operating System (IOS) software.
For additional information on the UDI or how to obtain a PAK, see the Cisco Software Activation on Integrated Services Routers and Cisco Integrated Service Routers Generation 2 document at cisco.com.
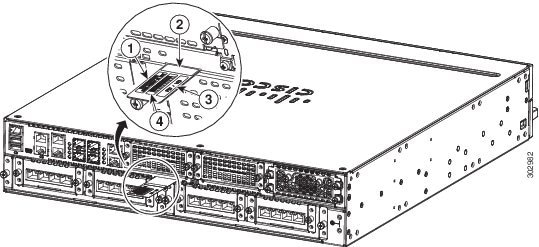
Labels on Cisco 4000 Series ISRs
Figure 1-34 shows the location of the labels on Cisco 4451-X ISR. Label are located at the same location on all routers in the Cisco 4000 series. Though your router may be different from the one shown in Figure 1-34.
Figure 1-34 Label Location on Cisco 4451-X ISR
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Additional Help for Locating Cisco 4000 Series ISRs Labels
Use the Cisco Product Identification (CPI) tool to find labels on the router. The tool provides detailed illustrations and descriptions of where labels are located on Cisco products. It includes the following features:
- A search option that allows browsing for models by using a tree-structured product hierarchy
- A search field on the final results page that makes it easier to look up multiple products
- End-of-sale products clearly identified in results lists
The tool streamlines the process of locating serial number labels and identifying products. Serial number information expedites the entitlement process and is required for access to support services.
Hardware Features of Cisco 4000 Series ISRs
This section describes the hardware features of Cisco 4000 Series ISRs.
Built-In Interface Ports
Cisco 4000 Series ISRs have multiple 10/100/1000 front panel ports, SFPs, and 10/100/1000 management ports.
Dual Mode GE or SFP Ports
There are dual mode ports available on the router which can function as GE or SFP ports.
The GE RJ-45 copper interface ports support 10BASE-T, 100BASE-TX, and 1000BASE-T.
The small-form-factor pluggable (SFP) ports support, 1000BASE-LX/LH, 1000BASE-SX, 1000BASE-ZX, and Coarse Wavelength-Division Multiplexing (CWDM-8) modules, as well as 100Mbs SFP modules.
The SFP port shares the same physical port as an RJ-45 GE port with the same number. At a time, it can be used for only one function. As described in the IEEE 802.3ah specification, the SFP port supports auto-media-detection, auto-failover, and remote fault indication (RFI).
Use the media-type command to enable the auto-media-detection and auto-failover features.
You can configure the SFP port by using the media-type configuration command to select either the RJ-45 or the SFP connector. When the media-type is not configured, by default, the auto-select feature is enabled. The auto-select feature automatically detects the media that is connected and links it up. If both media are connected, the media that comes up first is linked, and it is treated as the primary media. This primary media is explicitly indicated as an SFP or RJ-45 link. When the router receives an indication that the primary media is down, the secondary failover media is enabled. After the switchover, when the primary media is later restored, the media does not switch back to the primary media. By default, the RJ-45 port is configured as the primary media-type and if it fails, the media failovers to the SFP port. Conversely, when the SFP port is configured as the primary media-type and if it fails, the media switches to the RJ-45 port.
USB Serial Console Port
The Mini-USB type B serial port can be used as an alternative to the RJ-45 console port. For Windows operating systems earlier than Windows 7, you must install a Windows USB device driver before using the USB console port.

Note![]() Cisco 4461 supports Mini-USB type B serial port and Micro-USB type B serial port.
Cisco 4461 supports Mini-USB type B serial port and Micro-USB type B serial port.
Front Panel PoE+ Ports
On Cisco 4451-X ISR and Cisco 4351 ISR, two front panel Ethernet ports are PoE+ (802.3at) compliant ports. These are ports GE 0/0/0 and GE 0/0/1. Cisco 4431 ISR, Cisco 4321 ISR and Cisco 4221 do not support front panel PoE+.
System PoE power supplies do not provide power to the front panel ports.
Internal PoE Daughter Card
The internal PoE daughter card provides a total of 30.8 watts of power across the two ports.
LED Indicators
Table 1-1 summarizes the LED indicators that are located in the router bezel or chassis, but not on the interface cards and modules.

Note![]() For module LEDs, please refer to the respective module installation guides for each module.
For module LEDs, please refer to the respective module installation guides for each module.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
BIOS/Rommon has completed booting, and system is at Rommon prompt or booting platform software. |
|||||
| All temperature sensors in the system are within acceptable range. |
|||||
One or more temperature sensors in the system are outside the acceptable range. |
|||||
Two or more fans have stopped working, or the fan tray has been removed. |
|||||
Ethernet cable is present and link is established with other side or PoE power is enabled for this port. |
|||||
No link or a non-Ethernet 802.3af/t capable device is plugged in and powered over the PoE. |
|||||
| Ethernet ports 2 and 3 1 and Management Ethernet Link |
Ethernet cable is present and link is established with other side. |
||||
| Ethernet ports 2, and 3 1 and Management Ethernet Speed |
|||||
| All models2 |
|||||
Blinking frequency indicates port speed. See the definition for the S LED. |
All models 1 |
||||
| All models3 |
|||||
| Compact flash/eUSB flash is present and is currently being accessed. Note Do not remove the flash device while the system is powered on. |
|||||
| All models4 |
|||||
| All models1 3 |
|||||
Two PoE power supplies are installed and operating in boost mode. |
|||||
System power is up, but low level initialization has failed. |
|||||
System power is up, but the system has failed to come out of reset. |
|||||
|
|
Table 1-2 LED Descriptions (Applies to the Cisco 4331 ISR and the Cisco 4321 ISR Routers)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
BIOS/Rommon has completed booting, and system is at Rommon prompt or booting platform software. |
|||||
| All temperature sensors in the system are within acceptable range. |
|||||
One or more temperature sensors in the system are outside the acceptable range. |
|||||
Two or more fans have stopped working, or the fan tray is removed. |
|||||
| Ethernet ports 0 and 15 |
Ethernet cable is present and link is established with other side. |
||||
No link or a non-Ethernet 802.3af/t capable device is plugged in and powered over the PoE. |
|||||
| Port 0, and 1 (for Cisco 4331 ISR), and Port 0 for Cisco 4321 ISR) Enable |
|||||
| Status of port 0, and 1 (for Cisco 4331 ISR), and Port 0 for Cisco 4321 ISR) |
|||||
| I/O side 2 |
|||||
I/O side6 |
|||||
| Compact flash/eUSB flash is present and currently being accessed. Note Do not remove the flash device while the system is powered on. |
|||||
System power is up, but low level initialization has failed. |
|||||
System power is up, but the system has failed to come out of reset. |
|||||
|
|
Table 1-3 LED Descriptions (Applies to the Cisco 4221 ISR Router)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
BIOS/Rommon has completed booting, and system is at Rommon prompt or booting platform software. |
|||||
| All temperature sensors in the system are within acceptable range. |
|||||
One or more temperature sensors in the system are outside the acceptable range. |
|||||
Two or more fans have stopped working, or the fan tray is removed. |
|||||
| Ethernet ports 0 and 17 |
Ethernet cable is present and link is established with other side. |
||||
No link or a non-Ethernet 802.3af/t capable device is plugged in and powered over the PoE. |
|||||
| I/O side 2 |
|||||
I/O side8 |
|||||
| Compact flash/eUSB flash is present and currently being accessed. Note Do not remove the flash device while the system is powered on. |
|||||
System power is up, but low level initialization bas failed. |
|||||
System power is up, but the system has failed to come out of reset. |
|||||
|
|
Removable and Interchangeable Modules and Cards
Service Modules (SM-Xs), Network Interface Modules (NIMs), and E-Series Server Modules, fit into external slots and can be removed or replaced without opening the chassis.
See the Overview of Cisco Network Modules and Service Modules for Cisco Access Routers document for general information and single- and double-wide slot numbering.
See the “Install and Remove NIMs and SM-Xs on Cisco 4000 Series ISRs” section for instructions that describe how to install SM-Xs and NIMs in the router.
See the Overview of Cisco Interface Cards for Cisco Access Routers for general interface card information.
See the Installing Cisco Interface Cards in Cisco Access Routers document, for instructions that describe how to install legacy interface cards in the router.

Note![]() See the router product page at cisco.com for a list of supported network modules and interface cards.
See the router product page at cisco.com for a list of supported network modules and interface cards.
Network Interface Modules and Service Modules
To install NIMs and SM-Xs on the router chassis, see the “Install and Remove NIMs and SM-Xs on Cisco 4000 Series ISRs” section.
Cisco UCS E-Series Server Modules
Cisco UCS E-Series Servers (E-Series Servers) are the next generation of Cisco UCS Express servers. E-Series Servers are a family of size-, weight-, and power-efficient blade servers that are housed within the Generation 2 Cisco Integrated Services Routers (ISR G2) and Cisco 4000 Series Integrated Services Router. For more information on the E-Series Server Modules, see the Cisco UCS E-Series Servers Configuration Guides.
System Flash
Depending on the model that you have purchased, the routers use a CompactFlash or an eUSB flash for the internal bootflash memory. The CompactFlash and eUSB flash stores the operating system software image.
The CompactFlash is applicable to only Cisco 4451-X ISR. Each model supports 1 internal CompactFlash 8-GB, 16-GB, or 32-GB memory card. The CompactFlash is located behind the fan tray on the router chassis.
Cisco 4431 ISRs have a eMMC flash device. The device supports 8GB, 16GB, or 32 GB.
Cisco 4300 Series ISRs have an onboard flash device or an eMMC flash device. It supports 8GB or 16GB.

Note![]() For Cisco 4451-X ISR, you must use Cisco-qualified CompactFlash cards. The use of any other cards during normal network operation can affect system performance or reliability.
For Cisco 4451-X ISR, you must use Cisco-qualified CompactFlash cards. The use of any other cards during normal network operation can affect system performance or reliability.

Note![]() Do not run the router without a CompactFlash card installed. Cisco IOS XE software does not boot without a flash card in the router.
Do not run the router without a CompactFlash card installed. Cisco IOS XE software does not boot without a flash card in the router.

Note![]() Depending on the model that you have purchased, the routers use a CompactFlash, or an eUSB flash for the internal bootflash memory. Cisco 4431 ISRs have a eMMC flash device. The device supports 8GB, 16GB, or 32 GB. The latest model of Cisco 4451x ISRs support both eUSB and CompactFlash. If a CompactFlash is installed, it will disable the eUSB. However, you can use the old CompactFlash that is available with the routers.
Depending on the model that you have purchased, the routers use a CompactFlash, or an eUSB flash for the internal bootflash memory. Cisco 4431 ISRs have a eMMC flash device. The device supports 8GB, 16GB, or 32 GB. The latest model of Cisco 4451x ISRs support both eUSB and CompactFlash. If a CompactFlash is installed, it will disable the eUSB. However, you can use the old CompactFlash that is available with the routers.
Solid State Drives
The NIM slots in the router support a field-replaceable solid state drive module with a dual-SSD SATA slot. The NIM can be installed in any bay slot 0. The SSDs are hot-swappable as part of normal operation. See the “Locate Internal and External Slots for Modules on Cisco 4331 ISR” section on page 6-9 section for more information.
Cisco 4300 ISR platforms support an optional internal SSD mSATA. This device is not hot-swappable and requires opening the chassis to service or upgrade.
Cisco 4461 ISR platform supports an optional internal M2.SSD with the capacity of 800 G. See the “Locate Internal and External Slots for Modules on Cisco 44611 ISR” section on page 6-9 section for more information.
Packet Voice Digital Signal Processor Modules
The Packet Voice Digital Signal Processor Modules (PVDM4s) add additional voice capabilities to the
routers. The PVDM4 is installed inside the chassis of the router. See the “Install PVDM4 on the
Motherboard of Cisco 4400 Series ISRs” section on page 6-33 for installation instructions.
Memory
The routers contain the following types of memory:
- DIMMs—Stores the running configuration and routing tables and is used for packet buffering by the network interfaces. Cisco IOS XE software executes from memory. Supported module types are Dual In-Line Memory Modules (DIMMs).

Note![]() The DIMMs are interchangeable although the same sizes are not supported in all locations. The Cisco 4300 ISRs use a different type of DIMM compared to the 4400 ISRs. For proper operation, the DIMMs for the Cisoc 4400 ISR should not be installed in an Cisco 4300 ISR, and vice a versa. The single forwarding plane DIMM must have a 2-GB DIMM that is exactly like one of the two DIMMs used for the control plane with 4 GB of default memory. The control plane uses two DIMMs and they must be exactly the same type and density. This applies to only Cisco 4400 Series ISRs. Cisco 4300 Series ISRs do not have a distinct forwarding plane DIMM.
The DIMMs are interchangeable although the same sizes are not supported in all locations. The Cisco 4300 ISRs use a different type of DIMM compared to the 4400 ISRs. For proper operation, the DIMMs for the Cisoc 4400 ISR should not be installed in an Cisco 4300 ISR, and vice a versa. The single forwarding plane DIMM must have a 2-GB DIMM that is exactly like one of the two DIMMs used for the control plane with 4 GB of default memory. The control plane uses two DIMMs and they must be exactly the same type and density. This applies to only Cisco 4400 Series ISRs. Cisco 4300 Series ISRs do not have a distinct forwarding plane DIMM.
- Boot/NVRAM—Stores the bootstrap program (ROM monitor) and the configuration register. The boot/NVRAM is not serviceable.
- Flash memory—Internal bootflash memory. For details, see the“System Flash” section.
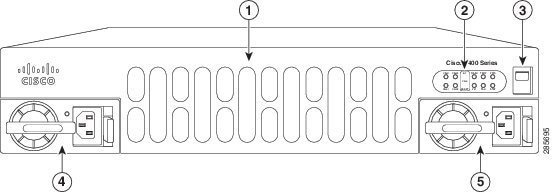
Power Supply
The routers support a variety of power supply configurations. The power supplies module are field-replaceable and externally accessible. Cisco 4331 ISR power supply module is inside the chassis.
Table 1-4 summarizes the power options.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
Fans, Ventilation, and Airflow
Chassis Ventilation
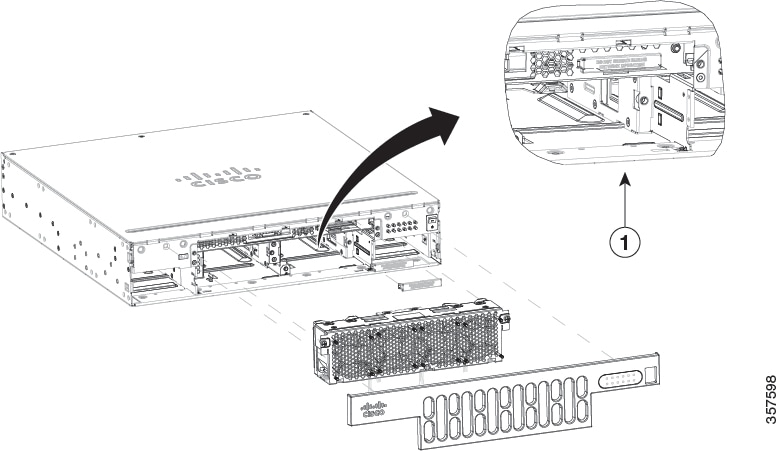
Router and chassis temperature is regulated with internal fans. An onboard temperature sensor controls the fan speed. The fans are always on when the router is powered on. Under most conditions, the fans operate at the slowest speed to conserve power and reduce noise. When necessary, the fans operate at higher speeds under conditions of higher ambient temperature. To replace Cisco 4451-X ISR, Cisco 4431 ISR, and Cisco ISR4351 fan trays, see the “Replace a Fan Tray” section.
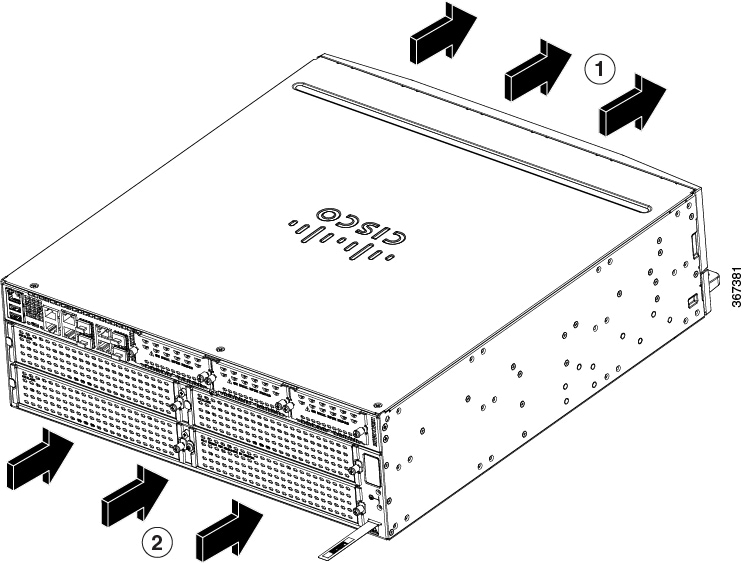
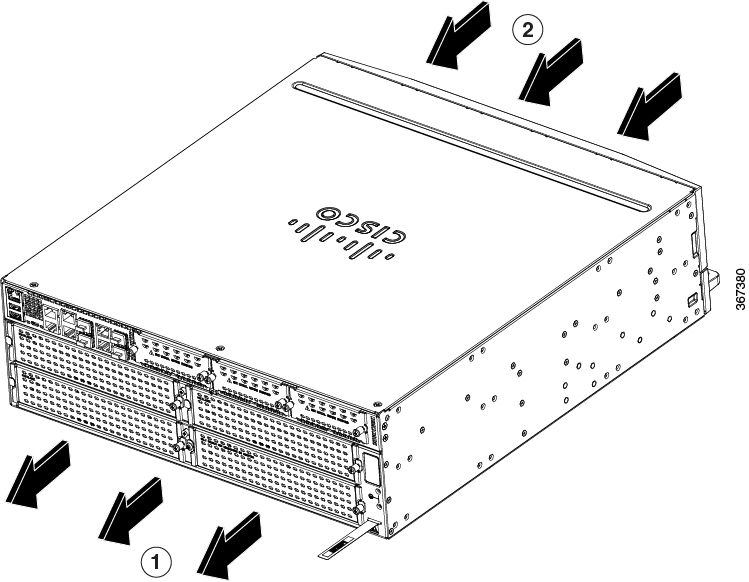
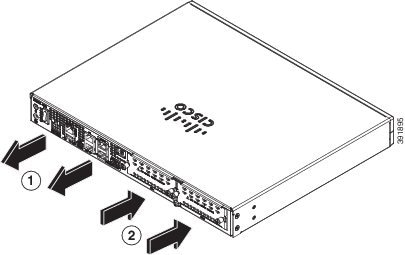
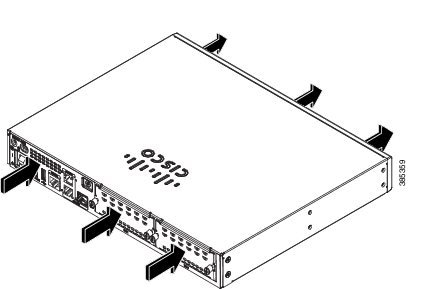
Figure 1-35 and Figure 1-36 show Cisco 4461airflow, Figure 1-37 shows Cisco 4451-X ISR airflow, Figure 1-38 showsCisco 4431 ISR airflow, Figure 1-39 shows Cisco 4321 ISR airflow, and Figure 1-40 shows Cisco 4221 ISR airflow.
Figure 1-35 Cisco 4461 ISR Airflow
|
|
|
Figure 1-36 Cisco 4461 ISR Airflow (NEBS View)
|
|
|
Figure 1-37 Cisco 4451-X ISR Airflow
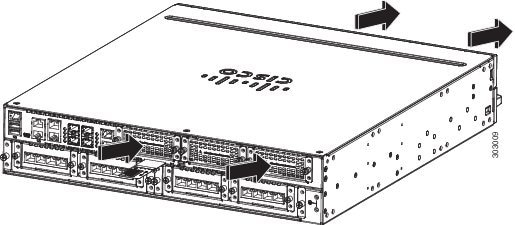
Figure 1-38 Cisco 4431 ISR Airflow
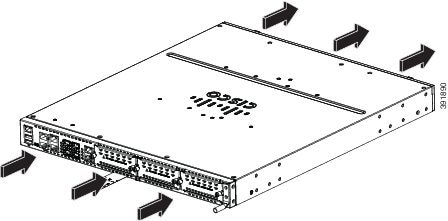
Figure 1-39 Cisco 4321 ISR Airflow
|
|
|
Figure 1-40 Cisco 4221 ISR Airflow
Slots, Subslots (Bay), Ports, and Interfaces in Cisco 4000 Series ISRs
The routers supports two types of interface modules: Enhanced Service Modules (SM-X) and Network Modules (NIMs).
In most cases, the router designates its interfaces using a 3-tuple notation that lists the slot, bay, and port. The 3-tuple value is zero based. An example of a 3-tuple is 0/1/2. This refers to slot 0, the second bay in slot 0 (the first bay is 0 so the second bay is 1), and the third port in bay 1. See Table 1-5 for more examples.
Table 1-5 Slot, Subslot (Bay) and Port Numbering
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
- Slots and bays are numbered from the left to the right, and from the top to the bottom.
- The auxiliary (AUX) serial port and console (CON) serial port do not have slot, bay, or port numbers.
- The GE management port is named GE 0 and has a port number. It does not have a slot or bay number.
- The two USB ports are named USB0 and USB1. They do not have slot or bay numbers. Cisco 4331 ISR and Cisco 4321 ISR have only one USB port.

Note![]() USB0 and USB1 can be used to insert flash drives.
USB0 and USB1 can be used to insert flash drives.
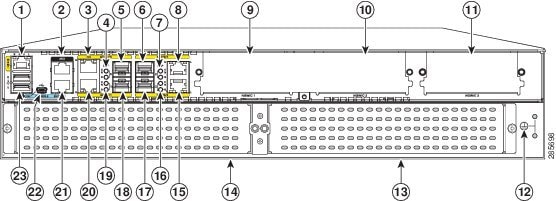
Figure 1-41 shows the ports and slots on Cisco 4451-X ISRs.
Figure 1-41 Ports and Slots on the Cisco 4451-X ISRs
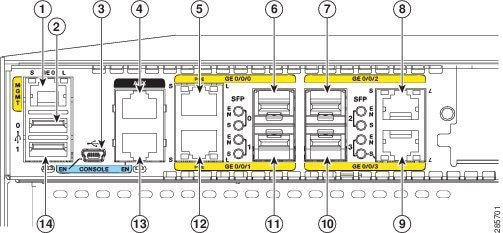
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Small-form-factor pluggable (SFP) 0/Gigabit Ethernet port (GE 0/0/0) |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Slot Numbering
About Slot 0
The following are the main features of Slot 0:
- Slot 0 is the motherboard and not removable. It is reserved for integrated ports and NIMs.
- NIMs are designated by the number of the first slot that they occupy. A double-wide NIM occupies two slots, but its designation is only the left-most slot number.
- The front panel GE ports (or native interface ports) always reside in slot 0 and bay 0. The ports are called Gigabitethernet 0/0/0, Gigabitethernet 0/0/1, Gigabitethernet 0/0/2, and Gigabitethernet 0/0/3 (up to as many ports supported on the particular router).
- PVDM4s do not have an external slot number. Therefore, the nomenclature for PVDM4s always has 0 in the first tuple. For example, the 3-tuple for an PVDM4 can be 0/4/x.
Subslot/Bay Numbering
- Integrated devices, also known as integrated ports or FPGEs, and integrated NIMs reside in a fixed section of bay 0.
- Main board NIMs bays start at bay 1, because the integrated devices and integrated NIMs take up bay 0.
- The bay numbers for PVDM4s start with the next bay number after the last NIM bay number.
Gigabit Ethernet Management
Cisco 4000 Series ISRs provides a Gigabit Ethernet Management port, called GE0. This port is the only 1-tuple port on the system. See the Gigabit Ethernet Management Port section in the Software Configuration Guide for the Cisco ISR 4400 Series and Cisco ISR 4300 Series Routers for additional information about the Gigabit Ethernet Management port.
Specifications
For information on specifications of the Cisco 4000 Series ISRs, see, https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/routers/4000-series-integrated-services-routers-isr/datasheet-c78-732542.html.
This table describes the regulatory compliance information of the Cisco 4000 Series ISRs,
IEC 60950-1, Safety of information technology equipment [world-wide] EN 60950-1:2006, Safety of information technology equipment [EU] UL 60950-1, Second Edition, Standard of safety for information technology equipment [US] CAN/CSA C22.2 No. 60950-1-07, Safety of information technology equipment including electrical business equipment [Canada] AS/NZS 60950.1: 2011 [Australia] IEC 60950-1: 2005 plus Am1: 2009, [World-wide] EC 62368-1, Second Edition, Audio/video, information and communication technology equipment-Part 1: Safety requirements [World-Wide] EN 62368-1, Second Edition, Audio/video, information and communication technology equipment-Part 1: Safety requirements [EU] CAN/CSA C22.2 No. 62368-1, Audio/video, information and communication technology equipment-Part 1: Safety requirements [Canada] UL 62368-1, Audio/video, information and communication technology equipment-Part 1: Safety requirements [US] For detailed compliance information, see the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Cisco 4000 Series Router s document. |
|
CISPR24 ITE-Immunity characteristics, Limits and methods of measurement EN 55024 ITE-Immunity characteristics, Limits and methods of measurement EN 50082-1 Electromagnetic compatibility - Generic immunity standard - Part 1 EN 300-386 V1.6.1 Electromagnetic compatibility for TNE For detailed compliance information, see the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Cisco ISR 4400 and Cisco ISR 4300 Series Router s document. |
|
| CFR47, Part 15, Subpart B, class A Harmonic Current Emission For detailed compliance information, see the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Cisco ISR 4400 and Cisco ISR 4300 Series Router s document. |
Periodic Inspection and Cleaning
To minimize the negative impact of environmental dust or debris, we recommend periodic inspection and cleaning of the external surface of the router. The frequency of inspection and cleaning is dependent upon the severity of the environmental conditions, but we recommend a minimum frequency of every six months. Cleaning involves vacuuming of router air intake and exhaust vents. See the “Fans, Ventilation, and Airflow” section.

 Feedback
Feedback