- Overview of Prime Network GUI clients
- Setting Up the Prime Network Clients
- Setting Up Change and Configuration Management
- Setting Up Vision Client Maps
- Setting Up Native Reports
- Setting Up Fault Management and the Events Client Default Settings
- Viewing Devices, Links, and Services in Maps
- Drilling Down into an NE’s Physical and Logical Inventories and Changing Basic NE Properties
- Manage Device Configurations and Software Images
- How Prime Network Handles Incoming Events
- Managing Tickets with the Vision Client
- Viewing All Event Types in Prime Network
- Cisco Path Tracer
- Managing IP Address Pools
- Monitoring AAA Configurations
- Managing DWDM Networks
- Managing MPLS Networks
- Managing Carrier Ethernet Configurations
- Managing Ethernet Networks Using Operations, Administration, and Maintenance Tools
- Monitoring Carrier Grade NAT Configurations
- Monitoring Quality of Service
- Managing IP Service Level Agreement (IP SLA) Configurations
- Monitoring IP and MPLS Multicast Configurations
- Managing Session Border Controllers
- Monitoring BNG Configurations
- Managing Mobile Transport Over Pseudowire (MToP) Networks
- Managing Mobile Networks
- Managing Data Center Networks
- Monitoring Cable Technologies
- Monitoring ADSL2+ and VDSL2 Technologies
- Monitoring Quantum Virtualized Packet Core
- VSS Redundancy System
- Icon Reference
- Permissions Required to Perform Tasks Using the Prime Network Clients
- Correlation Examples
- Managing certificates
Monitoring Carrier Grade NAT Configurations
Carrier Grade NAT is a large-scale Network Address Translation (NAT) that provides translation of millions of private IPv4 addresses to public IPv4 addresses. These translations support subscribers and content providers with a bandwidth throughput of at least 10 Gbps full-duplex.
Carrier Grade NAT addresses the IPv4 address completion problem. It employs Network Address and Port Translation (NAPT) to aggregate many private IPv4 addresses into fewer public IPv4 addresses. For example, a single public IPv4 address with a pool of 32,000 port numbers supports 320 individual private IP subscribers, assuming that each subscriber requires 100 ports. Carrier Grade NAT also offers a way to implement a graceful transition to IPv6 addresses.
To route internal public addresses to external public addresses, a VPN Routing and Forwarding (VRF) instance is created. Interfaces are created for the VRF at the subscriber-side (private) and the Internet-side (public). The VRF enables static or dynamic routing of protocols on the interfaces.
Prime Network supports the following instances for Carrier Grade NAT:
- Stateful Address Translation- NAT44 Stateful
- Stateless Address Translation- NAT 64 Stateless (X-LAT)
- IPv6 rapid deployment (6rd)
Each Carrier Grade NAT instance has several attributes listed under them, such as preferred location, address pools, associated interfaces, and statistics. The attributes are grouped under related categories. The categories and attributes are listed below:

Note![]() IPv4 Network Address Translation (NAT44) is not supported for devices running Cisco IOS XR software version 4.1.
IPv4 Network Address Translation (NAT44) is not supported for devices running Cisco IOS XR software version 4.1.
For information on the devices that support Carrier Grade NAT, refer to Cisco Prime Network 5.0 Supported VNEs.
The following topics describe how to use the Vision client to view Carrier Grade NAT properties. If you cannot perform an operation that is described in these topics, you may not have sufficient permissions; see Permissions for Managing Carrier Grade NAT.
Viewing Carrier Grade NAT Properties in Logical Inventory
To view Carrier Grade NAT properties in logical inventory:
Step 1![]() In the Vision client, double-click the Cisco CRS device configured for Carrier Grade NAT.
In the Vision client, double-click the Cisco CRS device configured for Carrier Grade NAT.
Step 2![]() In the Inventory window, click Logical Inventory > Carrier Grade NAT.
In the Inventory window, click Logical Inventory > Carrier Grade NAT.
The Carrier Grade NAT properties are displayed in logical inventory as shown in Figure 20-1.
Figure 20-1 Carrier Grade NAT in Logical Inventory
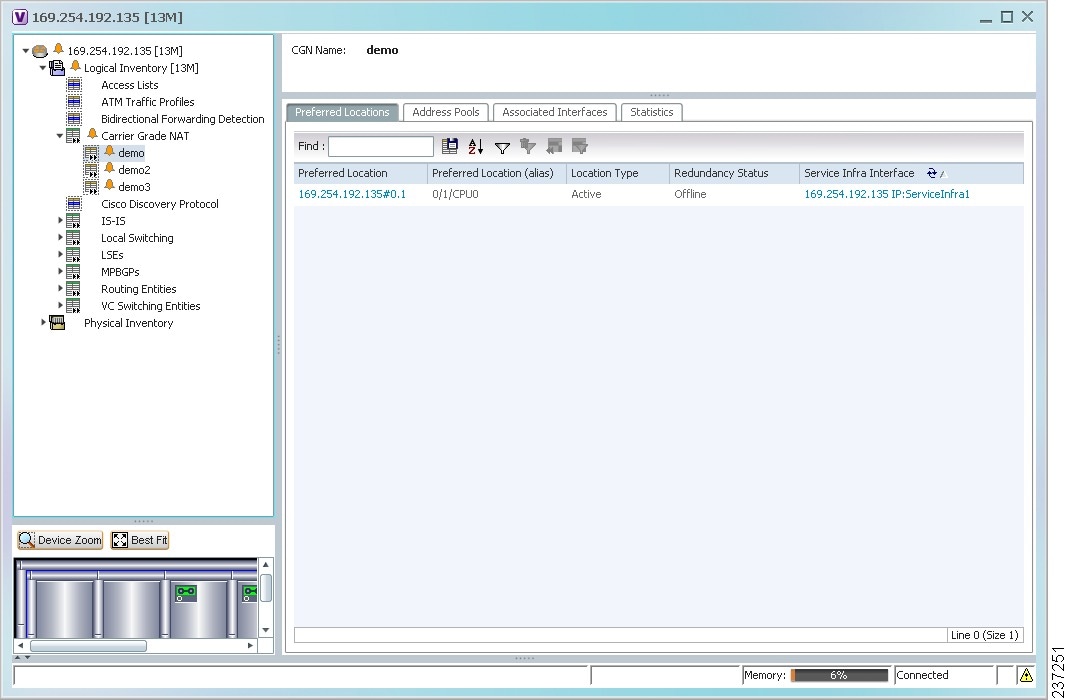
Table 20-1 describes the Carrier Grade NAT properties that are displayed.
|
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
Redundancy state: Online or Offline. If the field is empty, it means the data was not collected from the device. |
|
Hyperlinked entry to the routing entity in logical inventory. For more information about routing entities in logical inventory, see Viewing Routing Entities. |
|
|
|
|
Hyperlinked entry to the inside VRF in logical inventory. For more information about VRF properties in logical inventory, see Viewing VRF Properties. |
|
Hyperlinked entry to the outside VRF in logical inventory. For more information about VRF properties in logical inventory, see Viewing VRF Properties. |
|
Range of IP addresses that can be used for the service instance. If an end address is not specified, the entire range of 255 addresses is used for the address pool. |
|
|
|
|
Hyperlinked entry to the associated entry in logical inventory: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| For statistic names and descriptions, see Table 20-2 . |
|
You can also display pool utilization by right-clicking a VNE and choosing Commands > Show > Pool Utilization.
Viewing Carrier Grade NAT Properties in Physical Inventory
To view Carrier Grade NAT properties in physical inventory (in this example, a Cisco CRS device):
Step 1![]() In the Vision client, double-click the Cisco CRS device.
In the Vision client, double-click the Cisco CRS device.
Step 2![]() To view Carrier Grade NAT properties configured on a specific interface, click Physical Inventory > chassis > shelf > slot > card > interface. See Drilling Down Into a Port’s Configuration Details (Including Services and Subinterfaces) for a description of the information displayed in the Subinterfaces table.
To view Carrier Grade NAT properties configured on a specific interface, click Physical Inventory > chassis > shelf > slot > card > interface. See Drilling Down Into a Port’s Configuration Details (Including Services and Subinterfaces) for a description of the information displayed in the Subinterfaces table.
Step 3![]() To view Carrier Grade NAT properties configured on a Cisco CRS-CGSE-PLIM card, click Physical Inventory > chassis > shelf > slot > PLIM-card. Figure 20-2 shows an example of Carrier Grade NAT properties in physical inventory.
To view Carrier Grade NAT properties configured on a Cisco CRS-CGSE-PLIM card, click Physical Inventory > chassis > shelf > slot > PLIM-card. Figure 20-2 shows an example of Carrier Grade NAT properties in physical inventory.
Figure 20-2 Carrier Grade NAT Properties in Physical Inventory
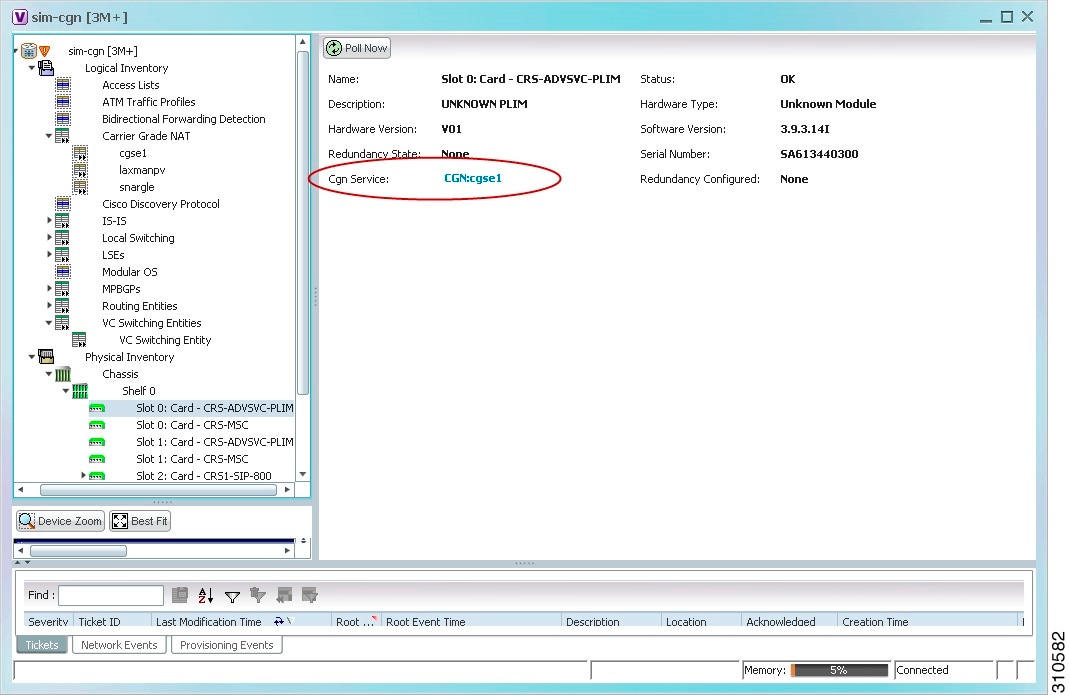
The field CGN Service is displayed, and the entry is hyperlinked to the associated Carrier Grade NAT service in logical inventory.
Configuring a CG NAT Service
The following CG NAT commands can be launched from the inventory by right-clicking the appropriate node and choosing Commands > Configuration. Your permissions determine whether you can run these commands (see Permissions for Managing Carrier Grade NAT). To find out if a device supports these commands, see the Cisco Prime Network 5.1 Supported Cisco VNEs.
|
|
|
|---|---|
Configures CG NAT service instance for static port forwarding. |
|
Displays the CGN instance name, inside VRF name, start and end address |
 Feedback
Feedback