What is a Network Wired/Wireless Client
A client is a device that is connected to an access point or a switch. supports both wired and wireless clients. After you add controllers and switches to , the client discovery process starts. Wireless clients are discovered from managed controllers or autonomous access points. The controllers are polled during regular client status poll. The wireless client count includes autonomous clients as well. In the case of switches, polls for clients immediately after the device is added and updates the device information in the database. For wired clients, the client status polling to discover client associations occurs every two hours (by default). A complete polling happens twice every day to poll complete information of all wired clients connected to all switches.
uses background tasks to perform the data polling operations. There are three tasks associated with clients:
- Autonomous AP Client Status
- Lightweight Client Status
- Wired Client Status
You can refresh the data collection tasks (such as polling interval) from the page. See Managing Data Collection and Retention
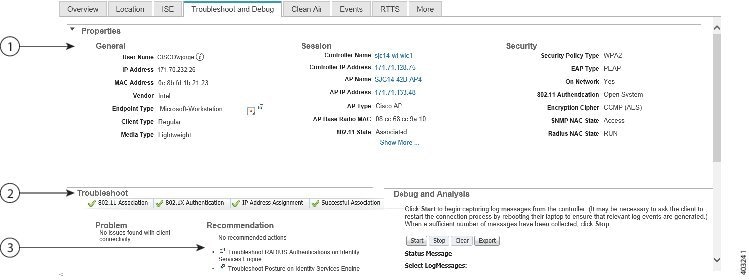
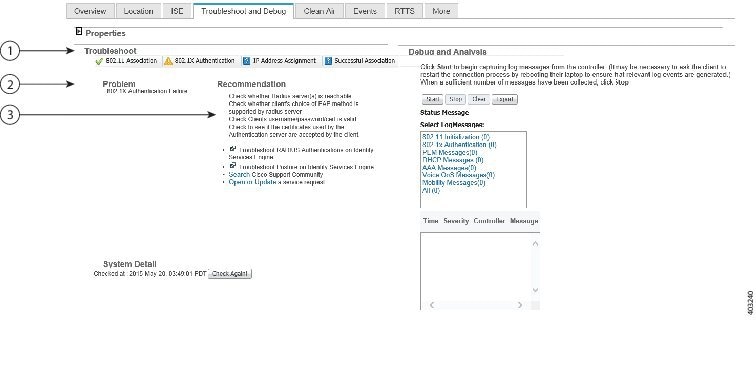
Client status (applicable only for wired clients) is noted as connected, disconnected, or unknown:
- Connected clients—Clients that are active and connected to a wired switch.
- Disconnected clients—Clients that are disconnected from the wired switch.
- Unknown clients—Clients that are marked as unknown when the SNMP connection to the wired switch is lost.
For the clients of autonomous access point managed by and for the clients authenticated using Local Extensible Authentication Protocol (LEAP), the username is not registered and is displayed as unknown.
supports both identity and non-identity wired clients. The support for wired clients is based on the identity service. The identity service provides secure network access to users and devices and it also enables the network administrators to provision services and resources to the users based on their job functions.
do not poll end hosts connected through VLAN 1000-1024.
does not support VRF. Therefore, if a client is connected to a VRF-configured device, you cannot view client information.
 Note |
If Prime Infrastructure is unable to retrieve information about wired devices with SNMPv3, apply SNMPv2. |
 Feedback
Feedback