Secure Key Integration Protocol
A Secure Key Integration Protocol is a protocol that
-
enables routers to communicate with external quantum devices
-
facilitates the exchange of MACsec encryption keys using Quantum Key Distribution (QKD), and
-
addresses the key distribution problem in a post-quantum world.
A Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) is a cryptographic technique that
-
uses the laws of quantum mechanics to ensure secure transmission of a secret key between two parties
-
encodes the key in the quantum states of single photons and transmits it over optical fiber or free space (vacuum), and
-
provides security by making any interception detectable, since measuring a quantum state changes it, thus alerting the communicating parties to eavesdropping attempts.
QKD is resistant to quantum attacks and is expected to remain secure even as cryptanalysis and quantum computing advance. Unlike traditional cryptographic algorithms, QKD does not require continual updates in response to new vulnerabilities.
|
Feature Name |
Release Information |
Feature Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Secure Key Integration Protocol for Routers |
Release 25.1.1 |
Introduced in this release on: Fixed Systems (8700 [ASIC: K100])(select variants only*) *This feature is supported on the Cisco 8712-MOD-M routers. |
|
Secure Key Integration Protocol for Routers |
Release 24.4.1 |
Introduced in this release on: Fixed Systems (8200 [ASIC: P100], 8700 [ASIC: P100])(select variants only*); Modular Systems (8800 [LC ASIC: P100])(select variants only*) *This feature is supported on:
|
|
Secure Key Integration Protocol for Routers |
Release 7.9.1 |
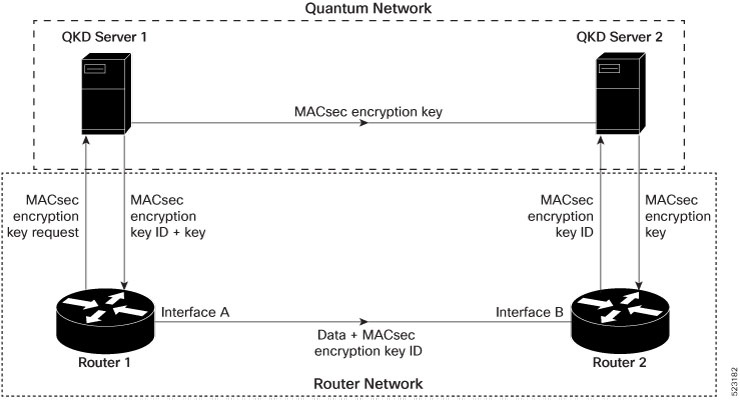
Your routers are now capable of handling the Secure Key Integration Protocol (SKIP) protocol. The SKIP protocol enables your routers to communicate with external quantum devices. With this ability, you can use the Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) devices for exchanging MACsec encryption keys between routers. Using QKD eliminates the key distribution problem in a post quantum world where the current cryptographic systems are no longer secure due to the advent of quantum computers. This feature introduces the following:
For more information on Quantum Key Distribution, see Post Quantum Security Brief. |
Supported configuration strategies for QKD devices
Secure Key Integration Protocol allows various configurations for utilizing QKD devices:
-
Single QKD device configuration: Use the same QKD device at the end ports of the peer routers to exchange encryption keys efficiently.
-
Multiple QKD device configuration: Configure different QKD devices on the end ports of peer routers for improved flexibility and security.
-
Multi-link QKD device detup: Establish multiple communication links between the same peer routers using different QKD devices for enhanced security.
Options for router communication with QKD devices
To ensure efficient and secure integration between routers and Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) devices, certain router configurations are recommended.
These options optimize routing communication with QKD devices:
-
Source interface configuration: Specify an explicit source interface for QKD device communication using the source interface command within the SKS (Secure Key Service) profile settings. Defining the source interface controls which interface initiates outbound communication and is critical for both security and routing policies.
Router# config Router(config)# sks profile ProfileR1toR2 type remote Router(config-sks-profile)# kme server ipv4 192.0.2.34 port 10001 Router(config-sks-profile)# source interface hundredGigE 0/1/0/17 Router(config-sks-profile)# commit -
HTTP proxy configuration: In environments requiring proxy intermediaries, configure routers to use an HTTP proxy when communicating with QKD devices. The http proxy server command allows specifying the IPv4 or IPv6 proxy address or hostname and the required TCP port.
Router# config Router(config)# sks profile ProfileR1toR2 type remote Router(config-sks-profile)# kme server ipv4 192.0.2.34 port 10001 Router(config-sks-profile)# http proxy ipv4 192.0.2.68 port 804 Router(config-sks-profile)# commit
 Feedback
Feedback