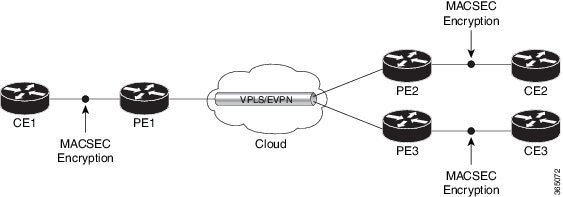
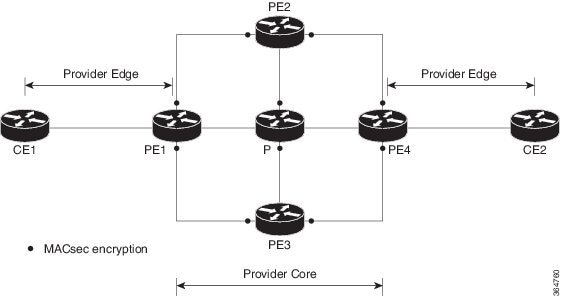
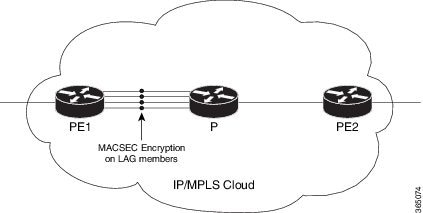
WAN MACsec encryption
WAN MACsec encryption is a solution that
-
provides end-to-end encryption across Layer 2 Ethernet WAN services,
-
supports both point-to-point (P2P) and point-to-multipoint (P2MP) topologies, and
-
is based on the IEEE 802.1AE standard for MACsec, which offers hop-by-hop encryption at the data link layer.
Use WAN MACsec to protect Ethernet frames with confidentiality, integrity, and origin authentication. You can extend traditional MACsec LAN encryption to WAN environments to achieve robust, standards-based, high-speed encryption across Ethernet WAN services. WAN MACsec helps you secure your data in transit across various WAN topologies while maintaining flexibility, performance, and interoperability.
 Feedback
Feedback