MACsec encryption
MACsec encryption is a Layer 2 security technology that
-
protects data on physical media from common attacks such as MAC address spoofing, ARP spoofing, Denial of Service (DoS) attacks targeting DHCP servers, and VLAN hopping
-
provides data confidentiality and integrity by encrypting traffic at the physical layer,
-
precedence over higher-layer encryption methods such as IPsec and SSL, and
-
deploys on Customer Edge (CE) router interfaces that connect to Provider Edge (PE) routers and on all provider router interfaces.
Benefits of MACsec encryption
-
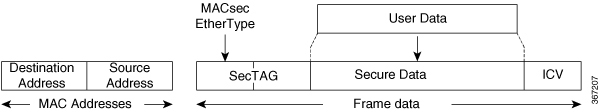
Data integrity check: Uses an Integrity Check Value (ICV) sent with the protected data unit. The receiver recalculates and compares the ICV to detect any data modification.
-
Data encryption: Enables a port to encrypt outbound frames and decrypt inbound frames encrypted with MACsec.
-
Replay protection: Provides a configurable window that accepts a specified number of out-of-sequence frames to handle frames transmitted out of order.
-
Support for clear traffic: Allows unencrypted data to transit through the port if configured accordingly.
Hardware support for MACsec encryption
The table lists the compatibility between specific Cisco IOS XR Software Releases and the corresponding hardware Product IDs (PIDs) that support MACsec encryption.
| Cisco IOS XR Software Release | Product ID (PID) |
|---|---|
| Release 25.4.1 |
|
| Release 25.3.1 |
8011-4G24Y4H-I |
| Release 25.1.1 | 8712-MOD-M |
| Release 24.4.1 | 8711-32FH-M |
| Release 24.3.1 |
|
| Release 7.10.1 |
Cisco 8608:
|
| Release 7.5.2 | 8202-32FH-M |
| Release 7.3.3 | 88-LC0-34H14FH |
| Release 7.3.15 | 88-LC0-36FH-M |
| Release 7.0.12 | 8800-LC-48H |
MACsec encryption by interface type
-
Physical interfaces (Standard MACsec): Applies security directly to a physical Ethernet port. This provides standard link-layer security within a LAN or between directly connected devices.
-
L3 subinterfaces (WAN MACsec): Designed for service provider networks. It preserves the provider’s outer VLAN tag in clear text while encrypting the customer’s data payload. This allows the provider’s network to switch traffic correctly and ensures end-to-end security.
Both physical interfaces and L3 subinterfaces support point-to-point (P2P) and point-to-multipoint (P2MP) MACsec encryption deployment models.
MACsec encryption deployment models
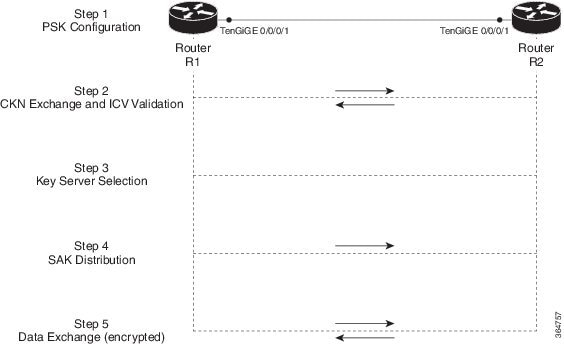
MACsec encryption supports two primary deployment models:
-
Point-to-Point (P2P): Secures a direct link between two endpoints.
-
Point-to-Multipoint (P2MP): Enables a single device to establish secure communications with multiple remote devices.
-
LAN: Establishes secure Ethernet connectivity between two devices on the same local network.
-
Over L2VPN (Pseudowire): Extends MACsec protection across a service provider network by encapsulating encrypted traffic over Layer 2 VPNs or pseudowires.
-
LAN: Establishes separate secure sessions from a central device to multiple peers on the same local network segment.
-
Over VPLS (Virtual Private LAN Service):
Establishes encrypted multipoint connectivity by creating a secure hub-and-spoke topology over a provider’s VPLS network, connecting a central site with multiple branch locations.
P2P is suitable for securing direct links on LANs and across service provider networks. P2MP is ideal when a single device must securely communicate with multiple endpoints, especially in hub-and-spoke topologies over VPLS. Both deployment models, P2P and P2MP MACsec encryption, are supported on physical interfaces and L3 subinterfaces.
 Feedback
Feedback