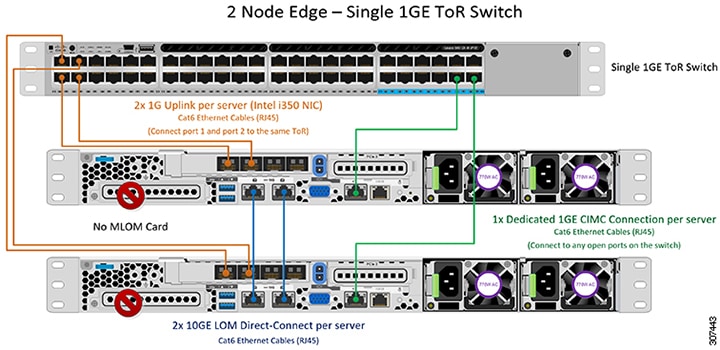
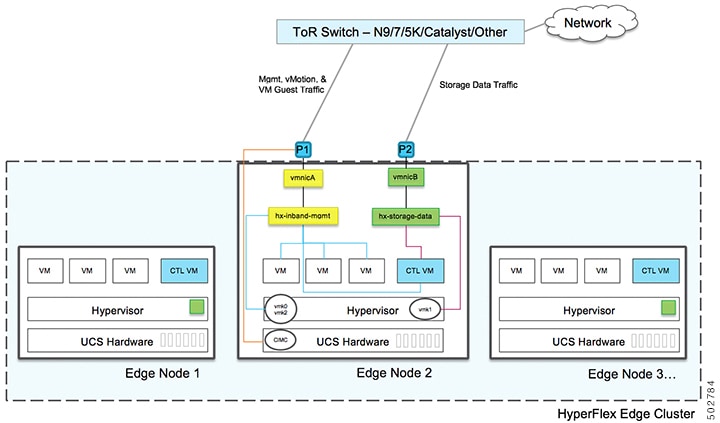
1GE Single Switch
Nexus 5548 using trunk ports
vlan 101
name HX-MGMT
vlan 102
name HX-STORAGE
vlan 103
name HX-vMOTION
vlan 104
name HX-GUESTVM
…
interface Ethernet2/11
description HX-01-Port1
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 101-104
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
speed 1000
interface Ethernet2/12
description HX-01-Port2
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 101-104
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
speed 1000
interface Ethernet2/13
description HX-02-Port1
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 101-104
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
speed 1000
interface Ethernet2/14
description HX-02-Port2
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 101-104
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
speed 1000
interface Ethernet2/15
description HX-03-Port1
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 101-104
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
speed 1000
interface Ethernet2/16
description HX-03-Port2
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 101-104
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
speed 1000
Catalyst 3850-48T using trunk ports
vlan 101
name HX-MGMT
vlan 102
name HX-STORAGE
vlan 103
name HX-vMOTION
vlan 104
name HX-GUESTVM
…
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
description HX-01-Port1
switchport trunk allowed vlan 101-104
switchport mode trunk
speed 1000
spanning-tree portfast trunk
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
description HX-01-Port2
switchport trunk allowed vlan 101-104
switchport mode trunk
speed 1000
spanning-tree portfast trunk
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
description HX-02-Port1
switchport trunk allowed vlan 101-104
switchport mode trunk
speed 1000
spanning-tree portfast trunk
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/4
description HX-02-Port2
switchport trunk allowed vlan 101-104
switchport mode trunk
speed 1000
spanning-tree portfast trunk
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/5
description HX-03-Port1
switchport trunk allowed vlan 101-104
switchport mode trunk
speed 1000
spanning-tree portfast trunk
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/6
description HX-03-Port2
switchport trunk allowed vlan 101-104
switchport mode trunk
speed 1000
spanning-tree portfast trunk
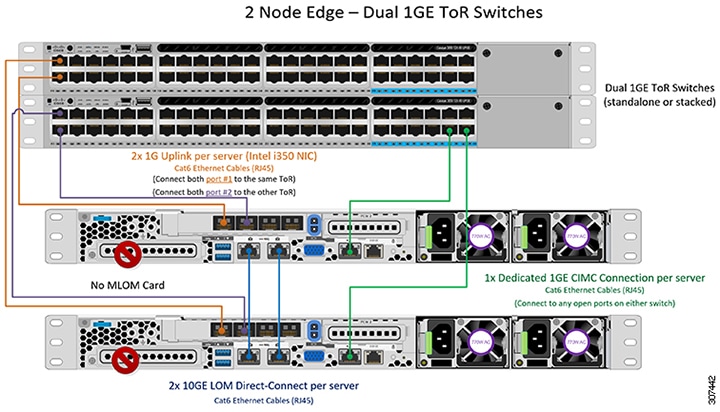
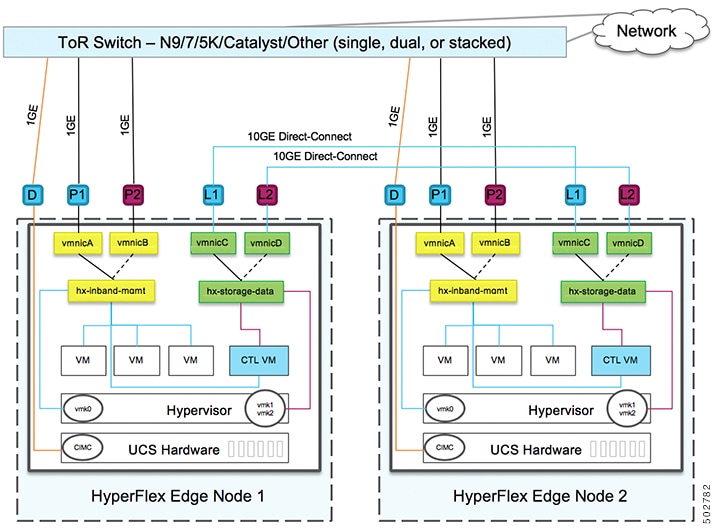
1GE Dual Switch
Nexus 5548 using trunk ports
This configuration uses DHCP with in-band management using native vlan 105. This switch connects to both 1GE LOMs and uses dhcp relay.
ip dhcp relay
…
interface Vlan105
ip address 10.1.2.1/24
ip dhcp relay address 10.1.1.2
no shutdown
vlan 101
name HX-MGMT
vlan 102
name HX-STORAGE
vlan 103
name HX-vMOTION
vlan 104
name HX-GUESTVM
vlan 105
name HX-DHCP-CIMC
…
interface Ethernet2/11
description HX-01-Port1
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk native vlan 105
switchport trunk allowed vlan 101-105
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
speed 1000
interface Ethernet2/12
description HX-01-Port2
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk native vlan 105
switchport trunk allowed vlan 101-105
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
speed 1000
interface Ethernet2/13
description HX-02-Port1
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk native vlan 105
switchport trunk allowed vlan 101-105
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
speed 1000
interface Ethernet2/14
description HX-02-Port2
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk native vlan 105
switchport trunk allowed vlan 101-105
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
speed 1000
interface Ethernet2/15
description HX-03-Port1
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk native vlan 105
switchport trunk allowed vlan 101-105
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
speed 1000
interface Ethernet2/16
description HX-03-Port2
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk native vlan 105
switchport trunk allowed vlan 101-105
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
speed 1000
Repeat the same configuration on switch #2. Eliminate the dhcp relay and interface Vlan 105 commands.
Catalyst 3850-48T using trunk ports
This configuration uses statically-assigned CIMC IPs on vlan 105. All vlans are allowed on all trunk interfaces. For security purposes, we recommend restricting the VLANs to those required for a HyperFlex
deployment by adding the switchport trunk allowed vlan statement into all your port configurations.
vlan 101
name HX-MGMT
vlan 102
name HX-STORAGE
vlan 103
name HX-vMOTION
vlan 104
name HX-GUESTVM
vlan 105
name HX-CIMC
…
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
description HX-01-Port1
switchport mode trunk
speed 1000
spanning-tree portfast trunk
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
description HX-01-Port2
switchport mode trunk
speed 1000
spanning-tree portfast trunk
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
description HX-02-Port1
switchport mode trunk
speed 1000
spanning-tree portfast trunk
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/4
description HX-02-Port2
switchport mode trunk
speed 1000
spanning-tree portfast trunk
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/5
description HX-03-Port1
switchport mode trunk
speed 1000
spanning-tree portfast trunk
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/6
description HX-03-Port2
switchport mode trunk
speed 1000
spanning-tree portfast trunk
Repeat the same configuration on switch #2.
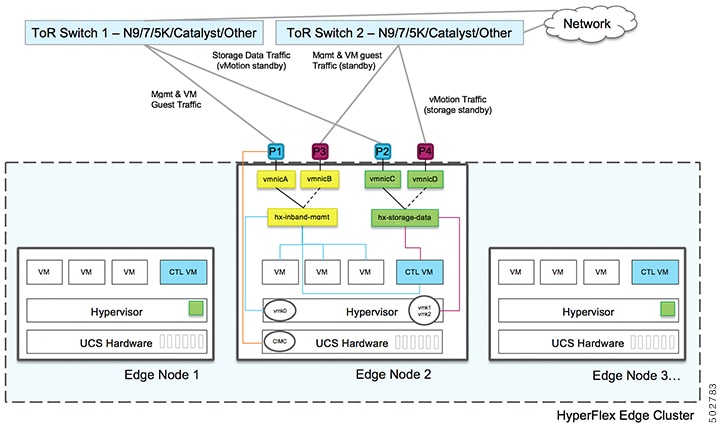
10GE Dual Switch
Nexus 9000 using trunk ports
vlan 101
name HX-MGMT
vlan 102
name HX-STORAGE
vlan 103
name HX-vMOTION
vlan 104
name HX-GUESTVM
vlan 105
name HX-DHCP-CIMC
...
interface Ethernet1/35
description M5-Edge-Node1-VIC1
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk native vlan 105
switchport trunk allowed vlan 101-105
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
interface Ethernet1/36
description M5-Edge-Node1-VIC2
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk native vlan 105
switchport trunk allowed vlan 101-105
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
interface Ethernet1/37
description M5-Edge-Node2-VIC1
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk native vlan 105
switchport trunk allowed vlan 101-105
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
interface Ethernet1/38
description M5-Edge-Node2-VIC2
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk native vlan 105
switchport trunk allowed vlan 101-105
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
interface Ethernet1/39
description M5-Edge-Node3-VIC1
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk native vlan 105
switchport trunk allowed vlan 101-105
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
interface Ethernet1/40
description M5-Edge-Node3-VIC2
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk native vlan 105
switchport trunk allowed vlan 101-105
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
Catalyst 9300 using trunk ports
vlan 101
name HX-MGMT
vlan 102
name HX-STORAGE
vlan 103
name HX-vMOTION
vlan 104
name HX-GUESTVM
vlan 105
name HX-CIMC
…
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
description M5-Edge-16W9-LOM1
switchport trunk allowed vlan 101-105
switchport mode trunk
spanning-tree portfast trunk
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
description M5-Edge-16W9-LOM2
switchport trunk allowed vlan 101-105
switchport mode trunk
spanning-tree portfast trunk
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
description M5-Edge-16UQ-LOM1
switchport trunk allowed vlan 101-105
switchport mode trunk
spanning-tree portfast trunk
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/4
description M5-Edge-16UQ-LOM2
switchport trunk allowed vlan 101-105
switchport mode trunk
spanning-tree portfast trunk
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/5
description M5-Edge-05G9-LOM1
switchport trunk allowed vlan 101-105
switchport mode trunk
spanning-tree portfast trunk
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/6
description M5-Edge-05G9-LOM2
switchport trunk allowed vlan 101-105
switchport mode trunk
spanning-tree portfast trunk
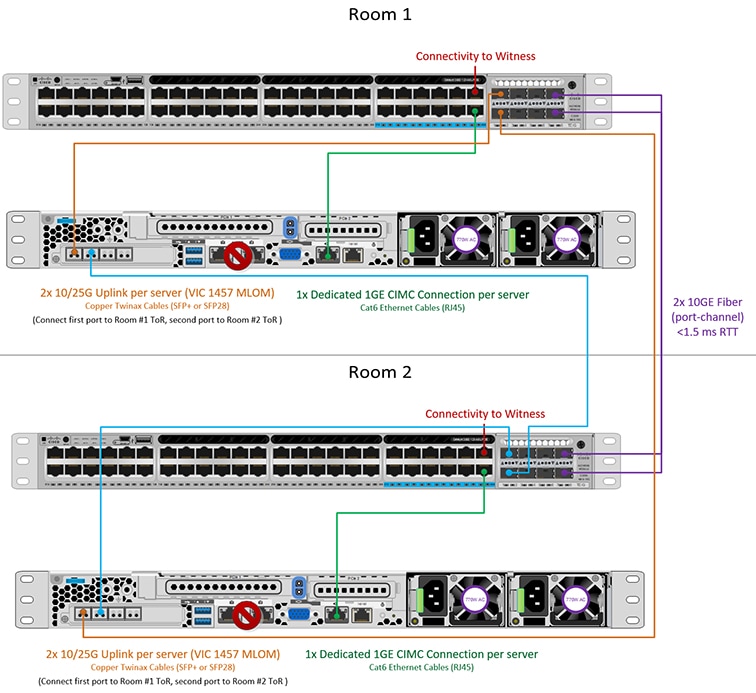
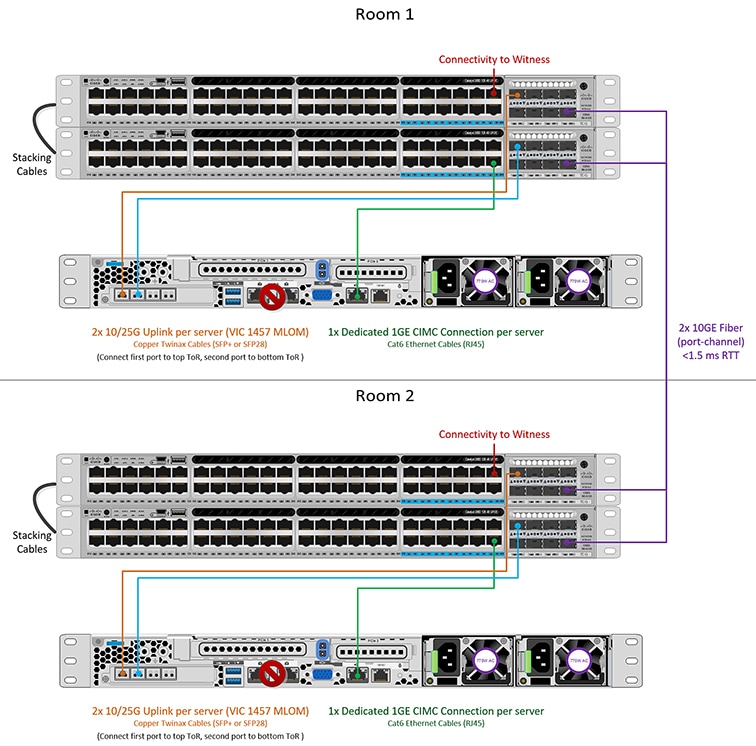
10/25GE 2-Node 2-Room
Catalyst 9300 with QoS
This configuration uses quality of service to mark and prioritize HyperFlex storage traffic using the 10 or 25 Gigabit Ethernet
Stacked Switches Per Room Topology
class-map match-all PQ_Storage
match dscp ef
class-map match-all Storage
match access-group name Storage
...
policy-map Storage_Mark
class Storage
set dscp ef
class class-default
policy-map Storage_Queue
class PQ_Storage
priority level 1
queue-buffers ratio 80
class class-default
bandwidth remaining percent 100
queue-buffers ratio 20
...
interface Port-channel98
switchport trunk allowed vlan 101,102,103,104,105
switchport mode trunk
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
description SERVER1-Dedicated-CIMC
switchport access vlan 145
switchport mode access
spanning-tree portfast
!
interface TenGigabitEthernet1/1/1
description SERVER1-VIC-1
switchport trunk allowed vlan 101,102,103,104,105
switchport mode trunk
spanning-tree portfast trunk
service-policy input Storage_Mark
!
interface TenGigabitEthernet2/1/1
description SERVER1-VIC-2
switchport trunk allowed vlan 101,102,103,104,105
switchport mode trunk
spanning-tree portfast trunk
service-policy input Storage_Mark
!
interface TenGigabitEthernet1/1/8
description cross-connect-01
switchport trunk allowed vlan 101,102,103,104,105
switchport mode trunk
channel-group 98 mode on
service-policy output Storage_Queue
!
interface TenGigabitEthernet2/1/8
description cross-connect-02
switchport trunk allowed vlan 101,102,103,104,105
switchport mode trunk
shutdown
channel-group 98 mode on
service-policy output Storage_Queue
!
...
ip access-list extended Storage
10 permit ip 169.254.1.0 0.0.0.255 169.254.1.0 0.0.0.255
Repeat the same configuration on switch stack #2.




 Feedback
Feedback