|
Step 2
|
If you are an admin user logging in for the first time, enter your email address in the Email ID field and click Submit.
You can subscribe to Amazon SNS to receive alerts about deployed resources, changes, and resource over-utilization. Alarms can be set up to notify you if
Amazon CloudWatch detects any unusual behavior in Cisco Global Launchpad. In addition, AWS Config evaluates your configured resources and sends audit logs of the results. For more information, see "Subscribe to the Amazon SNS Email Subscription" and "View Amazon CloudWatch Alarms" in the Cisco Global Launchpad Administrator Guide.
After you enter your email, several processes happen:
-
The CiscoDNACenter user group is created in your AWS account with all the required policies attached. The admin user can add subusers to this group to allow subusers to log in
to Cisco Global Launchpad.
-
An Amazon S3 bucket is automatically created to store the state of the deployment. We recommend that you do not delete this bucket or
any other bucket from the AWS account, either globally or for each region. Deleting this or another bucket could impact the Cisco Global Launchpad deployment workflow.
-
If you are logging in to a region for the first time, Cisco Global Launchpad creates several resources in AWS. This process can take some time, depending on if the region is already enabled. Until the process completes, you cannot
create a new VA pod. During this time, this message is displayed:
"Setting up the initial region configuration. This might take a couple of minutes."
After you log in successfully, the Dashboard pane is displayed.
|
|
Step 4
|
Configure the AWS infrastructure (including the region, VPC, private subnet, routing table, security group, virtual gateway, and CGW) by completing
these steps:
-
Configure these VA pod environment details fields:
-
Region name: From this drop-down list, choose a region.
-
VA pod name: Assign a name to the new VA pod.
|
Note
|
The VA pod name must meet these requirements:
-
The name must be unique within the region. (This means that you can use the same name across multiple regions.)
-
The name must be between four to 12 characters.
-
The name can include letters (A through Z), numbers (0 to 9), and dashes (-).
|
-
Availability zone: From this drop-down list, choose an availability zone.
An availability zone is an isolated location within your selected region.
-
AWS VPC CIDR: Enter a unique VPC subnet to use to launch the AWS resources.
|
Note
|
Keep these guidelines in mind:
-
The recommended CIDR range is /25.
-
In IPv4 CIDR notation, the last octet (the fourth octet) of the IP address can be either 0 or 128.
-
This subnet should not overlap with your corporate subnet.
|
-
Under Transit gateway (TGW), choose a gateway option.
|
If you have...
|
And you want to...
|
Then choose...
|
|
a single VA pod,
|
use a VPN gateway,
|
VPN GW.
A VPN GW is the VPN endpoint on the Amazon side of your Site-to-Site VPN connection. It can be attached to only one VPC.
|
|
multiple VA pods or VPCs,
|
use the TGW as a transit hub to interconnect multiple VPCs and on-premises networks,
|
New VPN GW + New TGW.
|
|
an existing TGW,
|
use the existing TGW,
|
Existing TGW.
|
If you chose Existing TGW, under VPN/Direct Connect Attachment, choose a gateway option.
|
If you want to...
|
Then choose...
|
|
create a new VPN gateway for your existing TGW,
|
New VPN GW.
|
|
use an existing VPN or direct-connect attachment,
|
Existing attachment.
From the Select attachment ID drop-down list, choose an attachment ID.
|
Note
|
To view the direct connect gateway name in the drop-down list, you must log in to Cisco Global Launchpad with an administrator account to grant the required permissions.
|
If you choose this option, you must also configure routing on your existing gateway or direct connect attachment. For instructions,
see Manually configure routing on your existing gateway or direct-connect attachment.
|
-
Complete this step depending on your gateway selection.
|
If you chose...
|
Then...
|
|
Existing TGW and Existing attachments as your preferred connectivity options,
|
continue to Step 4.d.
|
|
VPN GW, New VPN GW + New TGW, or Existing TGW + New VPN GW,
|
provide these VPN details:
-
Customer gateway (Enterprise firewall/router): Enter the IP address of your enterprise firewall or router to form an IPsec tunnel with the AWS VPN gateway.
-
VPN vendor: From this drop-down list, choose a VPN vendor.
Barracuda, Sophos, Vyatta, and Zyxel are not supported VPN vendors. For more information, see VA pod configuration errors and possible solutions.
-
Platform: From this drop-down list, choose a platform.
-
Software: From this drop-down list, choose a software.
|
-
For the Customer profile size, leave the default Medium setting.
The customer profile size applies to both the Catalyst Center VA instance and the backup instance. For information about the Catalyst Center instance size and Catalyst Center backup instance size, see Prerequisites for automated deployment.
-
For the Backup target (NFS), choose a destination for your backups.
|
If you want...
|
Then choose...
|
|
the backup to be stored in the on-premises servers,
|
Enterprise backup.
For information about the backup storage requirements, see “Backup storage requirements” in the Cisco Catalyst Center Administrator Guide.
|
|
the backup to be stored in AWS,
|
Cloud backup.
|
If you chose Cloud backup, record this information because you will use it later to log in to the cloud backup server:
-
SSH IP address: <BACKUP VM IP>
-
SSH port: 22
-
Server path: /var/catalyst-backup/
-
Username: maglev
-
Password: <xxxx##########>
Your backup server password is dynamically created. The password is composed of the first four characters of the VA pod name
and the backup server IP address without the periods.
For example, if the VA pod name is DNAC-SJC and the backup server IP address is 10.0.0.1, the backup server password is DNAC10001.
|
Note
|
-
You can find the VA pod name on the Dashboard pane after you choose the region that it's deployed in.
-
You can find the backup server IP address on the View Catalyst Center pane. For more information, see "View Catalyst Center VA Details" in the Cisco Global Launchpad Administrator Guide.
|
-
Passphrase: <Passphrase>
Your passphrase is used to encrypt the security-sensitive components of the backup. These security-sensitive components include
certificates and credentials.
This passphrase is required. When you restore the backup files, you are prompted to enter this passphrase. You cannot restore
backup files without this passphrase.
-
Open ports: 22, 2049, 873, and 111
-
Click Next.
-
On the Summary pane, review the environment and VPN details that you entered. When you're satisfied, click Start configuring AWS infrastructure.
|
Important
|
This setup takes about 20 minutes to complete.
You can navigate from this screen to another page in Cisco Global Launchpad, and the process continues in the background. If you close the tab or window, or refresh the page, any active background
process pauses.
|
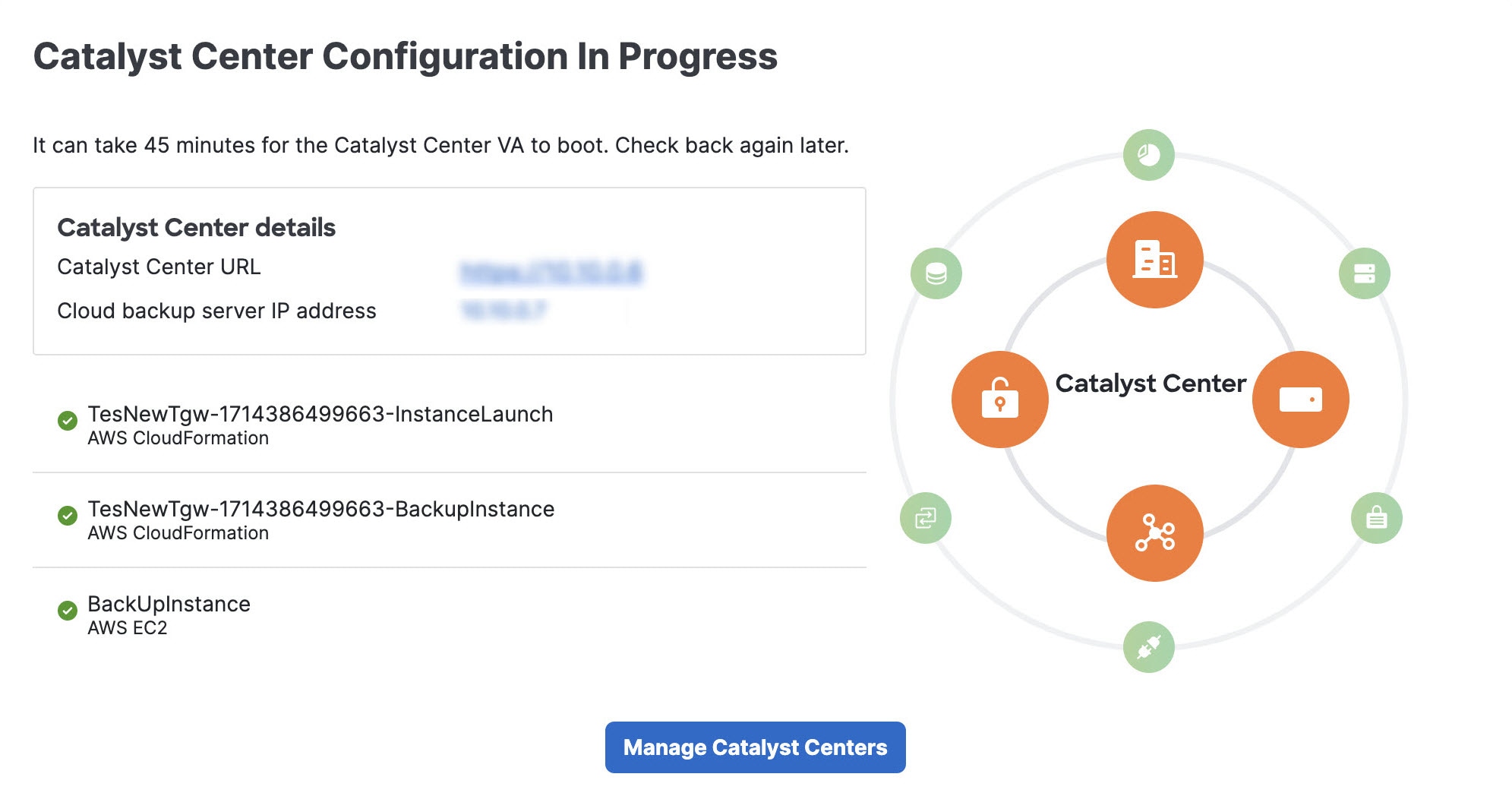
After the AWS infrastructure is successfully configured, the AWS Infrastructure Configured pane is displayed.
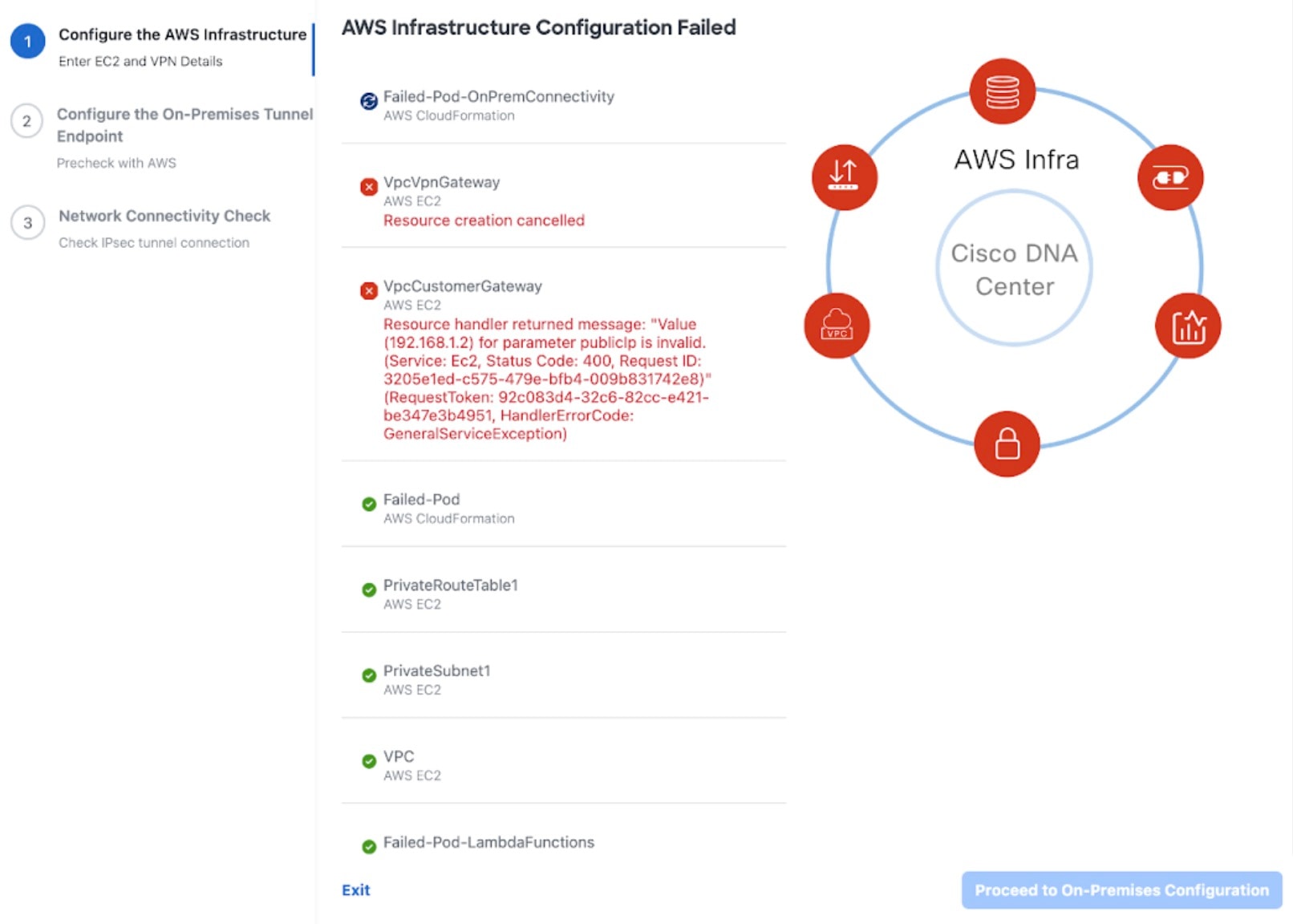
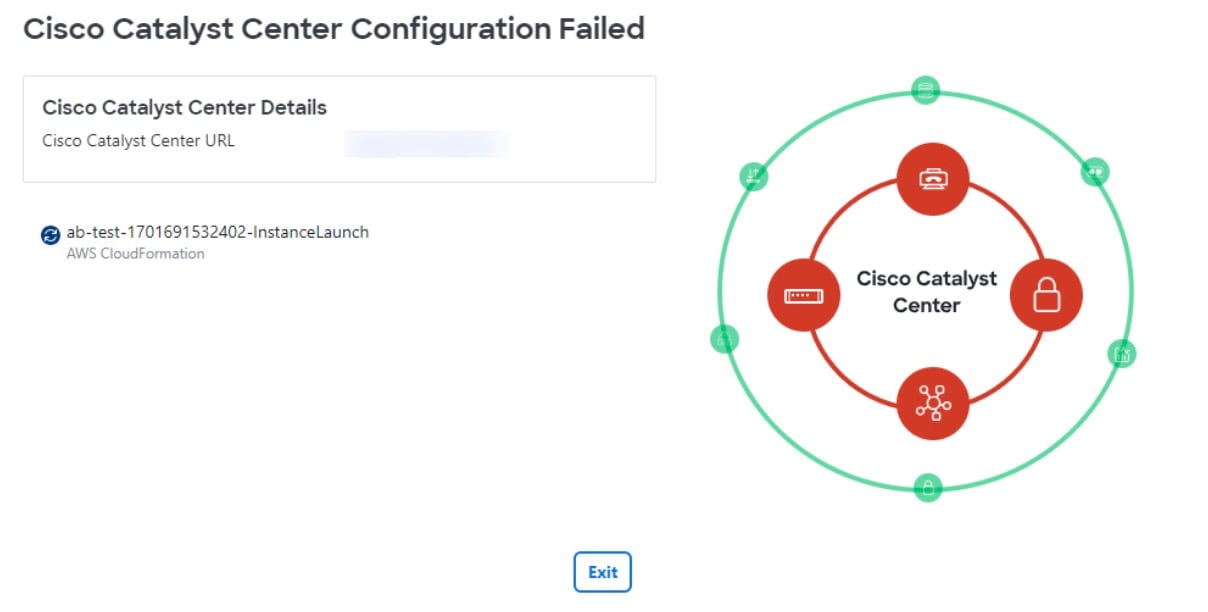
 If the AWS infrastructure configuration fails, exit Cisco Global Launchpad and see VA pod configuration errors and possible solutions.
|
|
Step 5
|
Download the on-premises configuration file by completing these steps:
-
After the AWS infrastructure is successfully configured, click Proceed to on-premises configuration.
-
In the Configure the On-Premises Tunnel Endpoint pane, click Download configuration file. Forward this file to your network administrator to configure the on-premises-side IPsec tunnel.
This file is generated based on the on-premises vendor, platform, and version that were selected during the AWS infrastructure configuration. The file contains the unique VPN connection IDs that were created for the VPC. Only a few things
need to be modified according to the on-premises firewall or router. For example, if you have an ASA firewall or router, you
need to modify the static route configuration to the selected VPC subnet.
route Tunnel-int-vpn-0bbef6e1331a37048-0 10.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 169.254.184.85 100
Make sure your network administrator configures only one IPsec tunnel.
|
Note
|
-
The network administrator can make the necessary changes to this configuration file and apply it to your enterprise firewall
or router to bring up the IPsec tunnels.
The provided configuration file enables you to bring up two tunnels between AWS and the enterprise router or firewall.
-
Most virtual private gateway solutions have one tunnel up and the other down. You can have both tunnels up and use the Equal
Cost Multiple Path (ECMP) networking feature. ECMP processing enables the firewall or router to use equal-cost routes to transmit
traffic to the same destination. To do this, your router or firewall must support ECMP. Without ECMP, we recommend that you
either keep one tunnel down and manually failover or use a solution, such as an IP SLA, to automatically bring up the tunnel
in a failover scenario.
|
-
Click Proceed to network connectivity check.
|
|
Step 6
|
Check the status of your network configuration based on the on-premises connectivity preferences that you selected during
the AWS infrastructure configuration.
-
If you chose VPN GW as your preferred on-premises connectivity option, the IPsec tunnel configuration status is displayed.
-
If the network administrator hasn't configured the IPsec tunnel yet, a padlock is displayed on the IPsec tunnel. 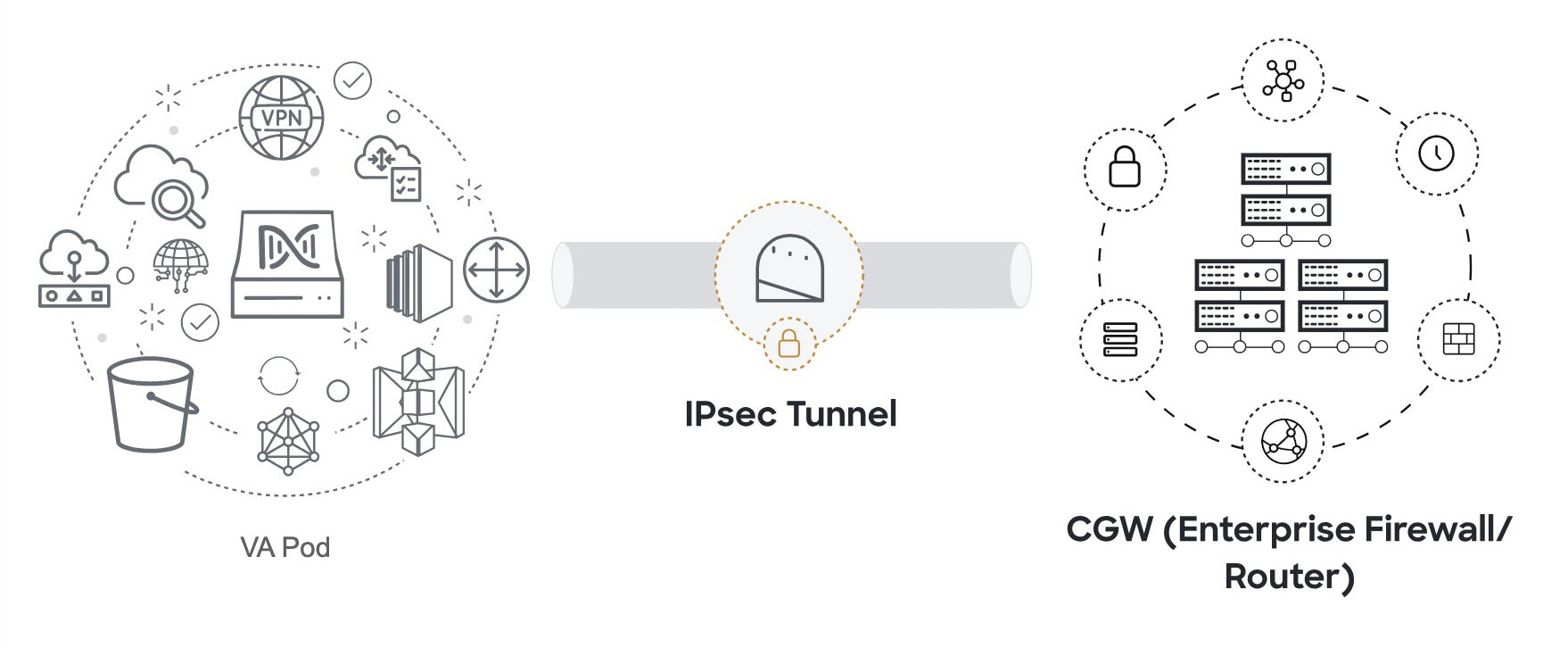
-
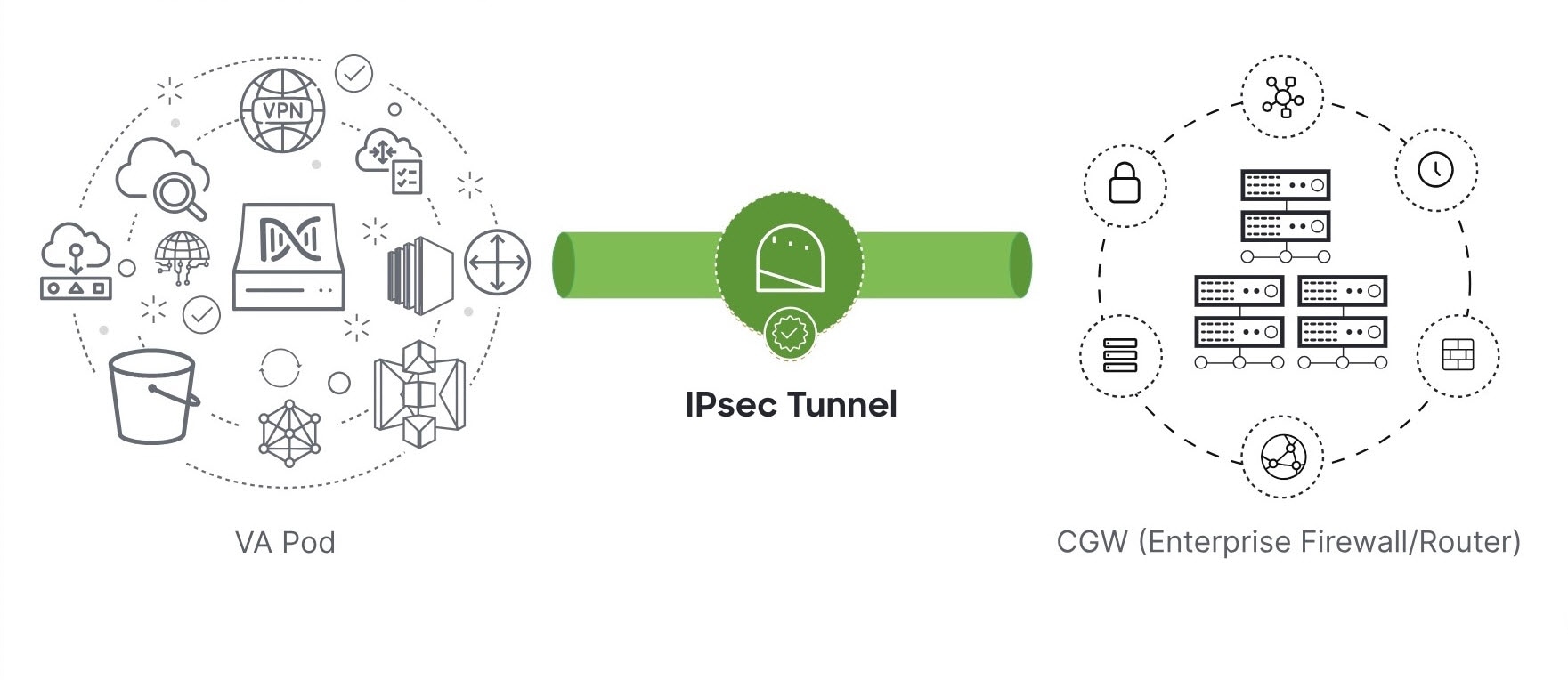
Ask your network administrator to verify that the IPsec tunnel on the enterprise firewall or router is up. After the IPsec
tunnel comes up, the IPsec tunnel turns green.
|
Note
|
If the IPsec tunnel is up and you cannot access Catalyst Center VA from the CGW, check that the correct values were passed during the IPsec tunnel configuration. Cisco Global Launchpad reports the tunnel status from AWS and doesn't perform additional checks.
|
-
If you chose New VPN GW + New TGW or Existing TGW and new VPN GW as your preferred on-premises connectivity option, Cisco Global Launchpad checks whether your VPC is connected to the TGW, which in turn is connected to your on-premises firewall or router.
|
Note
|
For the TGW-to-enterprise firewall or router connection to succeed, your network administrator must add the configuration
to your on-premises firewall or router.
|
-
If the connection from the TGW to your on-premises firewall or router isn't connected yet, it's grayed out. 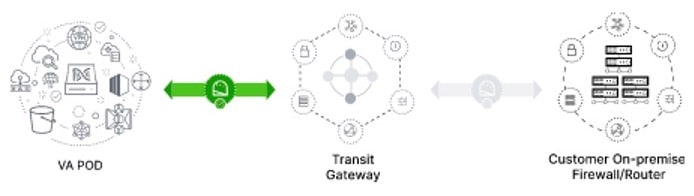
-
After TGW connectivity is successfully established, the TGW connection is green. 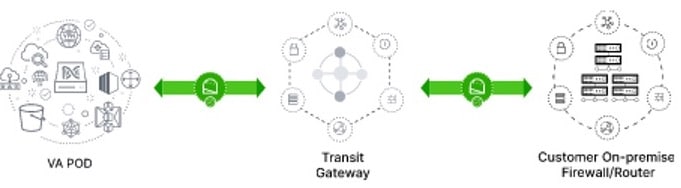
-
If you chose Existing TGW and Existing Attachment as your preferred on-premises connectivity option, make sure that routing is configured between the existing TGW and the
newly attached VPC, where Catalyst Center VA is launched. For information, see Manually configure routing on your existing gateway or direct-connect attachment.
-
If your VPC is not attached to the TGW, the TGW connection is grayed out. 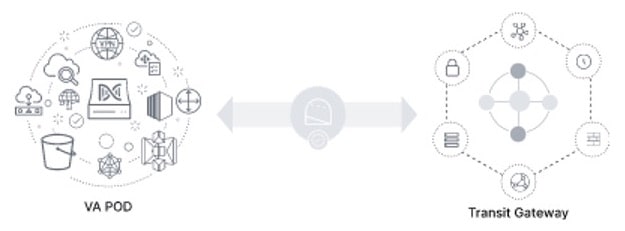
-
After TGW connectivity is successfully established, the TGW connection is green. 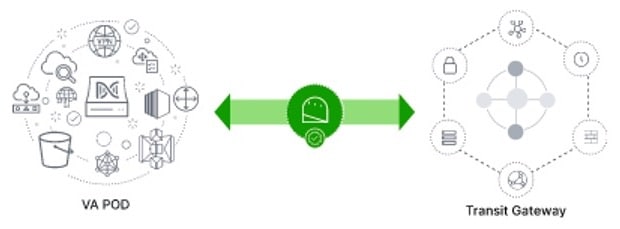
|











 Feedback
Feedback