Core capabilities of Cisco Crosswork Planning
Cisco Crosswork Planning provides tools to create a model of the existing network by continuously monitoring the network and its traffic demands. At any given time, this network model contains all relevant information about a network, including topology, configuration, and traffic information. You can use this information as a basis for analyzing the impact on the network due to changes in traffic demands, paths, node and link failures, network optimizations, or other changes.
Key features
Some important features of Cisco Crosswork Planning include:
-
Traffic engineering and network optimization: Compute TE LSP configuration to meet service level requirements, perform capacity management, and perform local or global optimization in order to maximize efficiency of deployed network resources.
-
Demand engineering: Examine the impact on network traffic flow of adding, removing, or modifying traffic demands on the network.
-
Topology and predictive analysis: Observe the impact to network performance of changes in the network topology, which is driven either by design or by network failures.
-
TE tunnel programming: Examine the impact of modifying tunnel parameters, such as the tunnel path and reserved bandwidth.
-
Class of service (CoS)-aware bandwidth on demand: Examine existing network traffic and demands, and admit a set of service-class-specific demands between routers.
Components
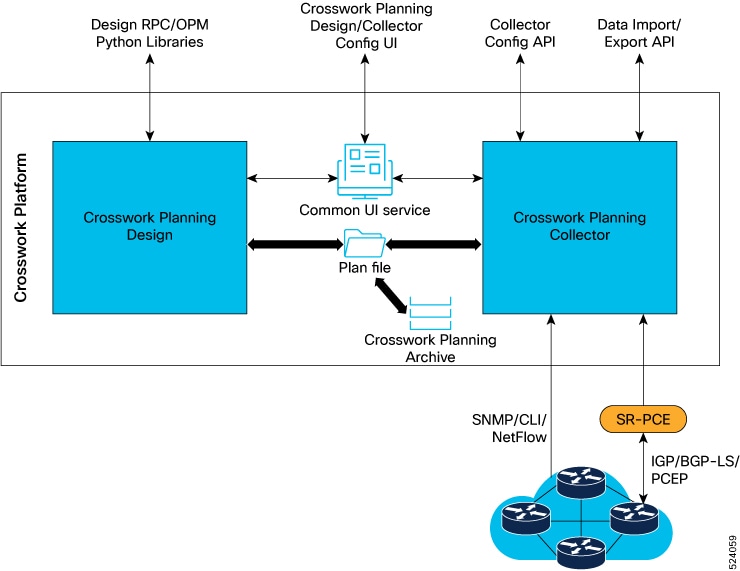
Cisco Crosswork Planning comprises two primary components:
-
Cisco Crosswork Planning Collector: This component consists of a set of services that create, maintain, and archive a model of the current network. It achieves this through continual monitoring and analysis of the network and the traffic demands placed on it.
-
Cisco Crosswork Planning Design: This component helps network engineers and operators predict growth in their network, simulate failures, and optimize the network design to meet performance objectives while minimizing cost.
 Feedback
Feedback