View Monitored Services
You can view the monitored services in any of the following ways:
From the Crosswork Home Page
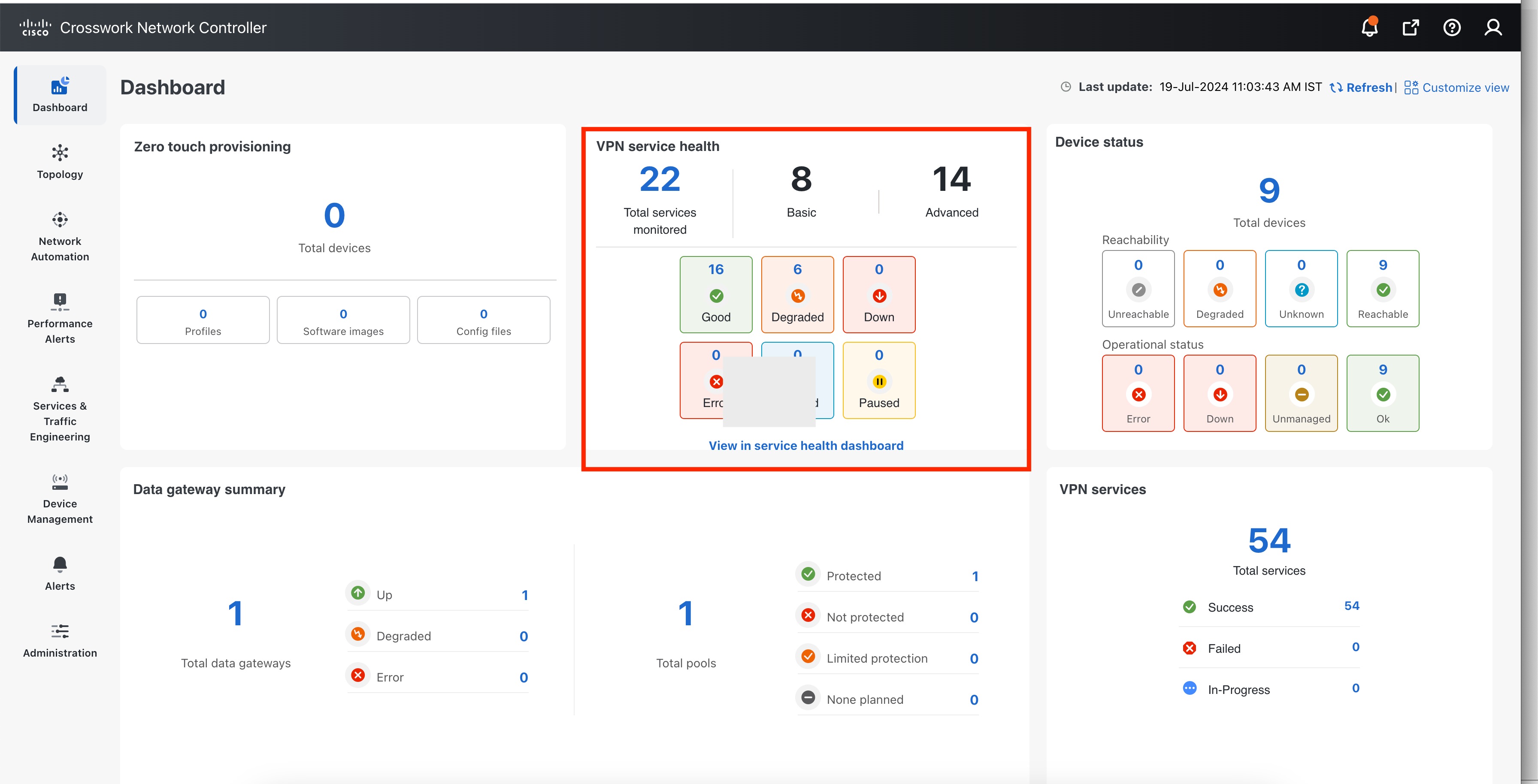
You will see the VPN Service Health dashlet on the Crosswork Home Page. This dashlet provides an overview of all the VPN services that are being monitored. From the dashlet you can click any of the status indicators to be taken to the VPN Services page with a filter set for the status you selected. To view the degraded services, click the Degraded box within the dashlet. This will take you to the VPN Services page, where only the degraded VPN services are displayed.
From the VPN Services Page
From the main menu, choose Services & Traffic Engineering > VPN Services. All the VPN services are listed on this page. The degraded services show an orange icon in the Health column.
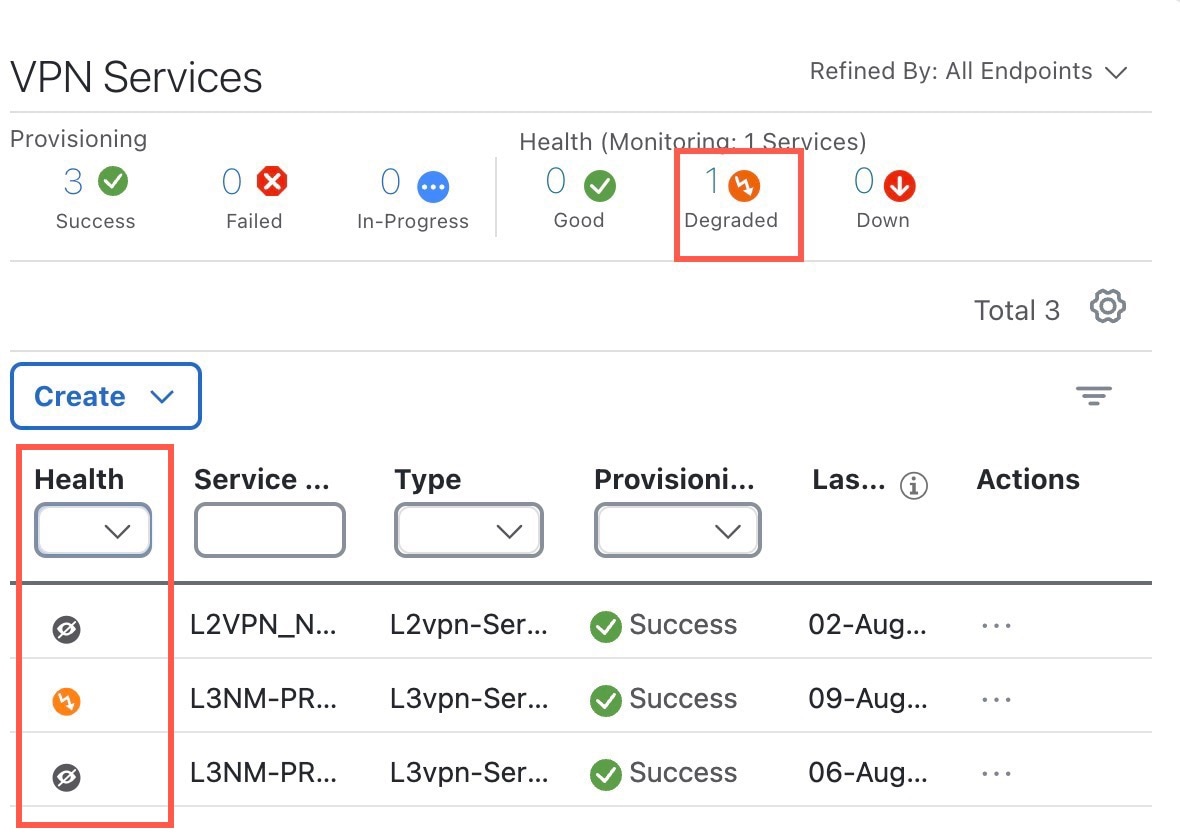
You can filter the services by their health (Down, Degraded, Good, Paused, Initiated, Error, Unmonitored). You can also click the Degraded tab in the Health tab in this page to filter and view only the Degraded services.
To clear the filter, click X next to the designated filter appearing in the space at the top of the column. To remove all the filters and to show all the VPN services, click the X icon in the Filters field above the table.
 Note |
If a service is not yet being monitored, a gray icon is displayed in the Health column. To enable monitoring for such a service,
click |
Use the Service Health Monitoring Dashboard
To access the dashboard, click View in service health dashboard in the VPN Service Health dashlet on the Crosswork Home Page. The Service Health Dashboard displays consolidated view of L2VPN and L3VPN services including the total number of provisioned Services and number of monitored services. The dashboard also displays active monitoring sessions for L2VPN and L3VPN services, and indicates any SLA breaches for measured metrics such as latency, jitter, and packet loss in both directions.
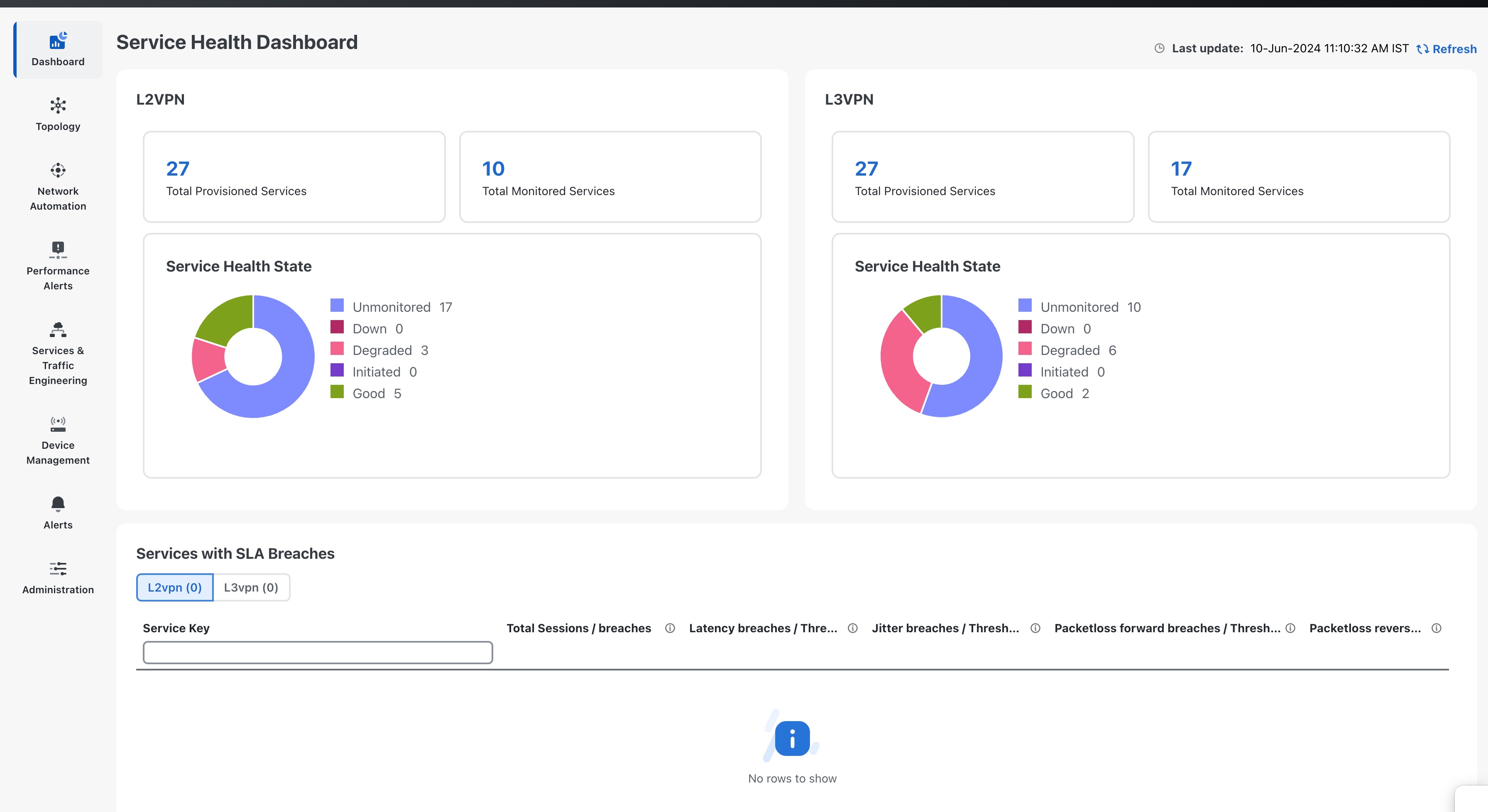
Clicking on any of the status indicators redirects you to the VPN Services page with a filter set for the status you selected.
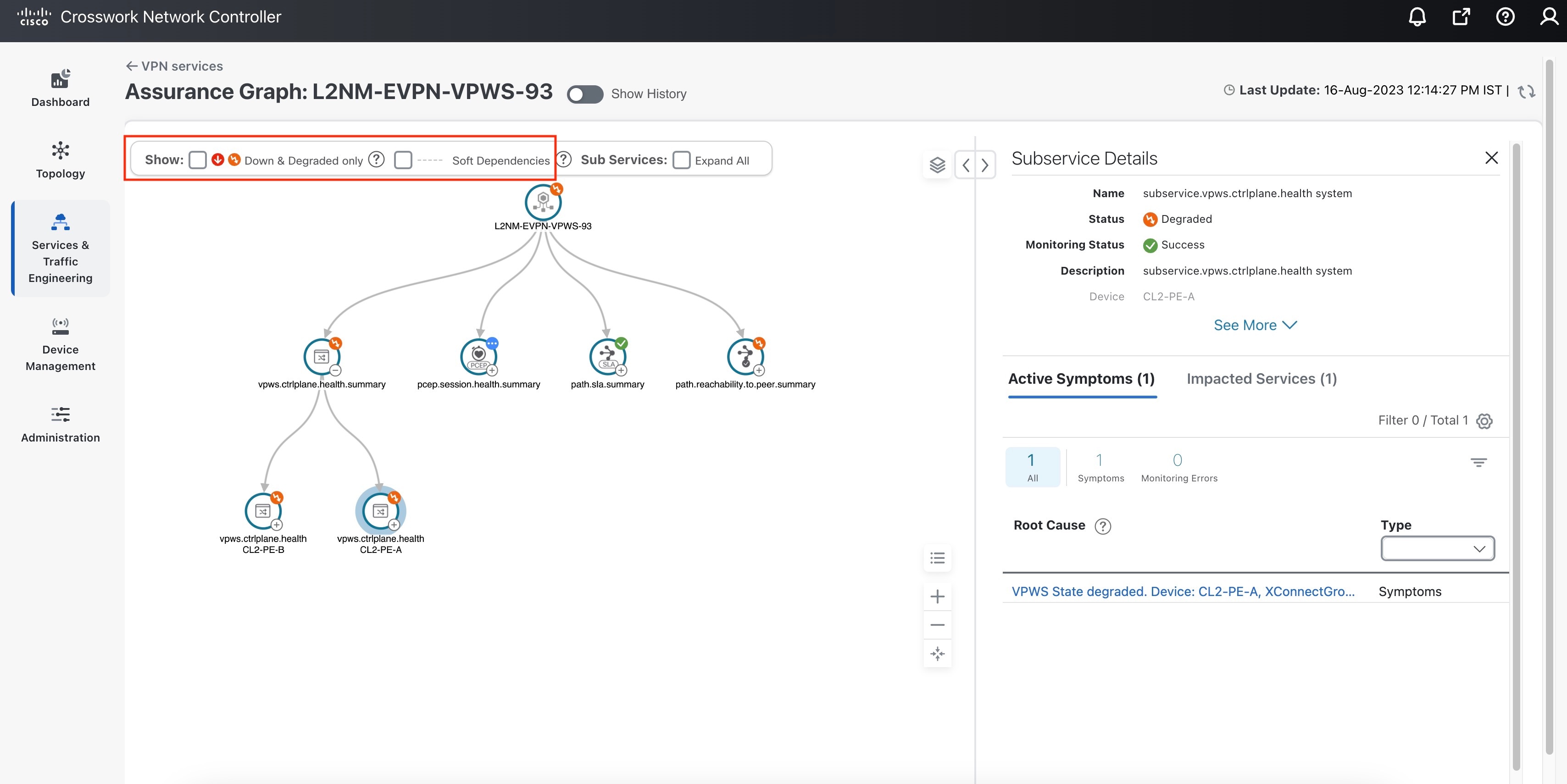
View Monitoring Status of a Service
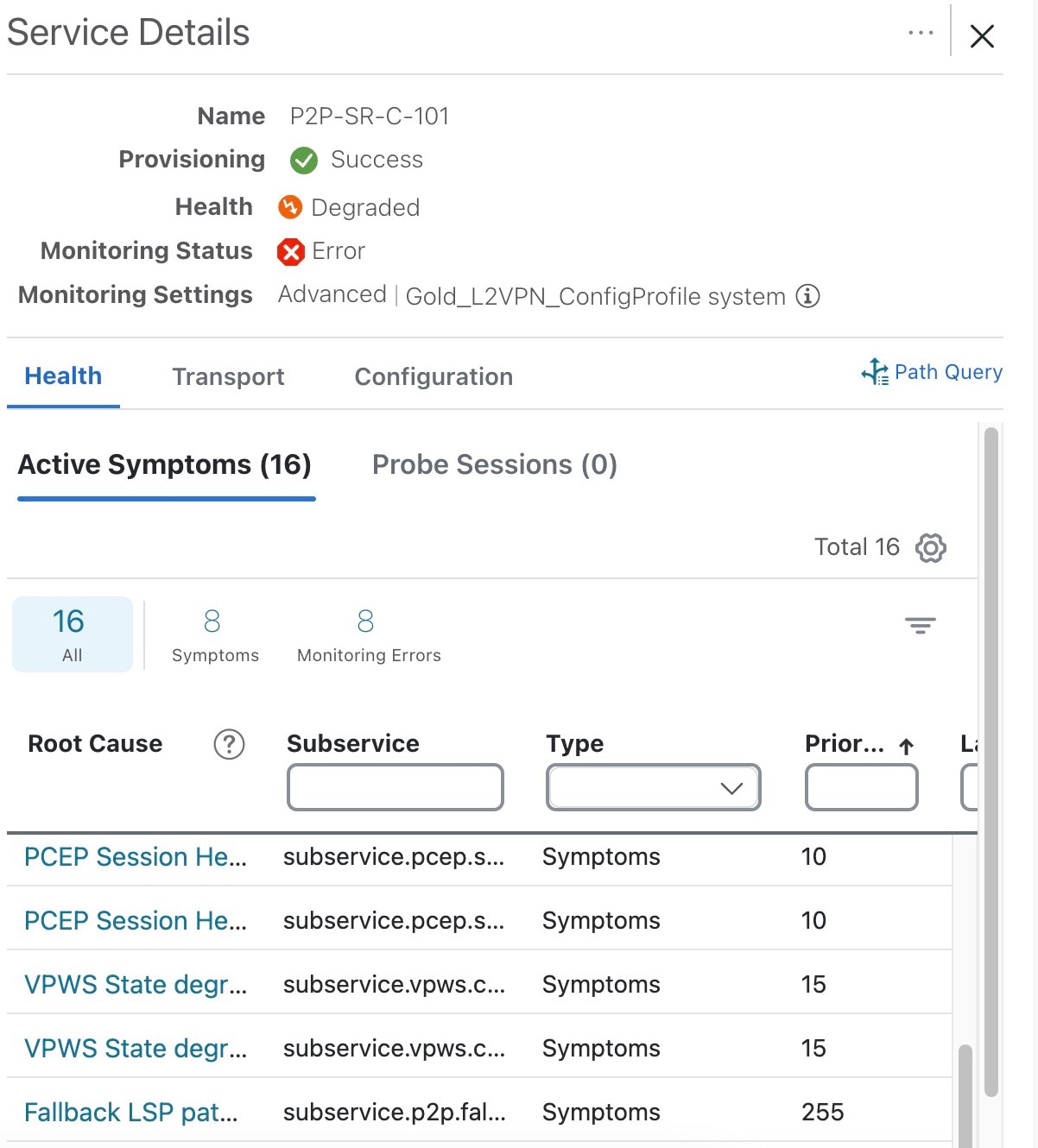
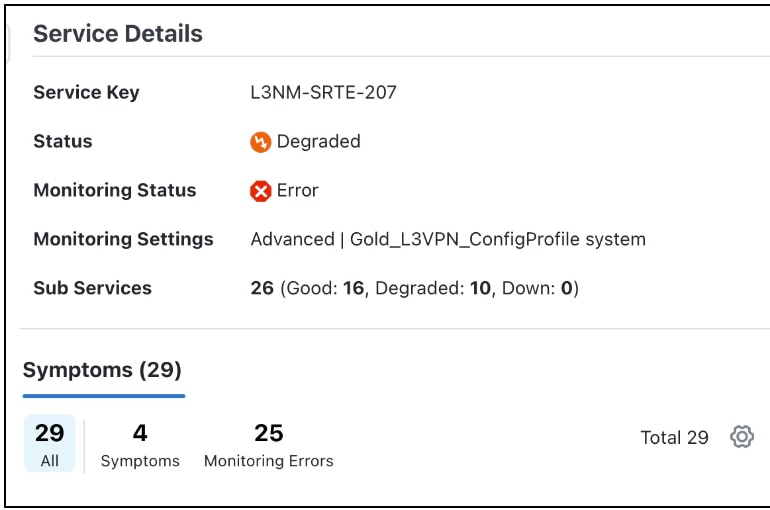
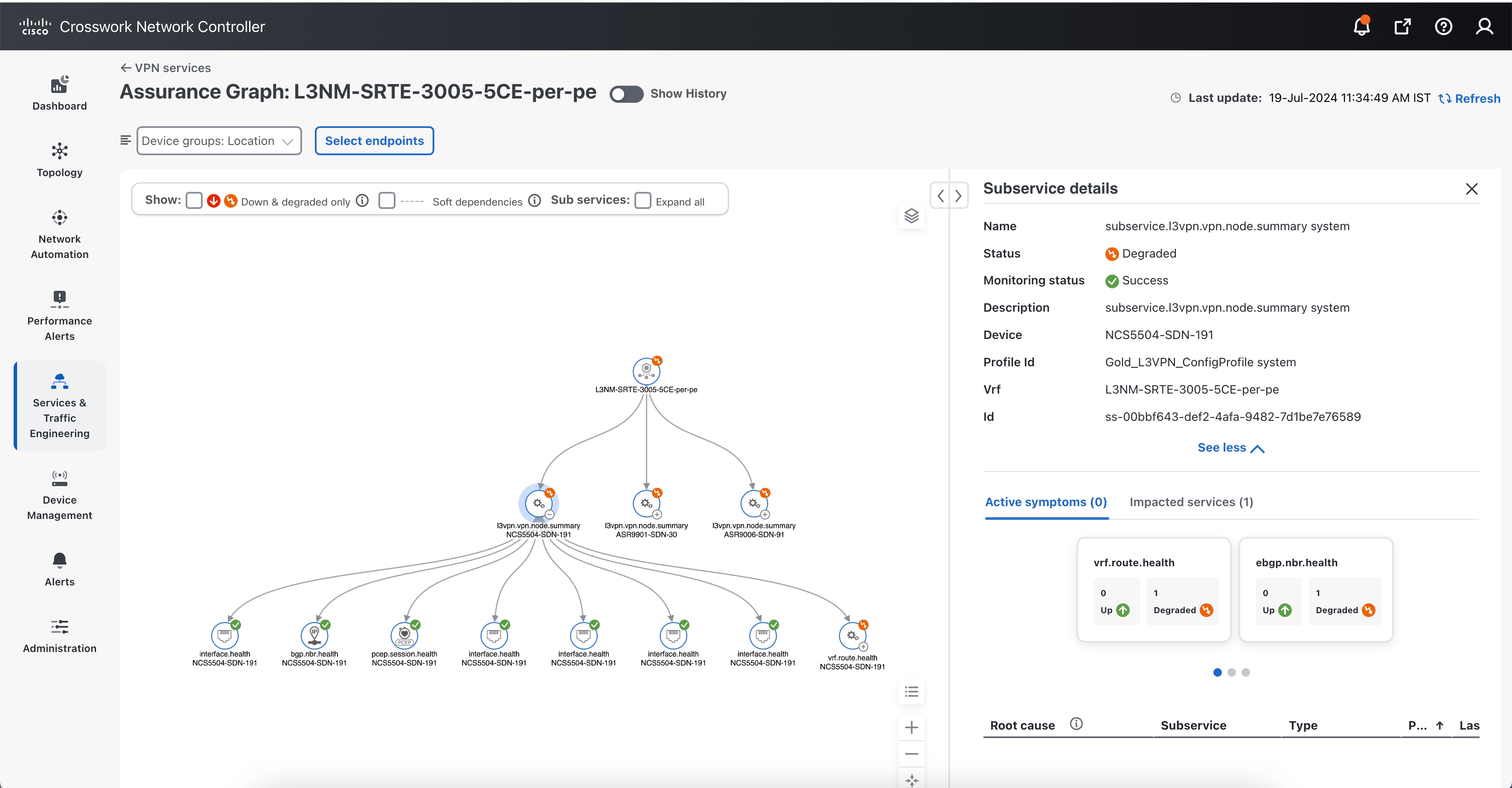
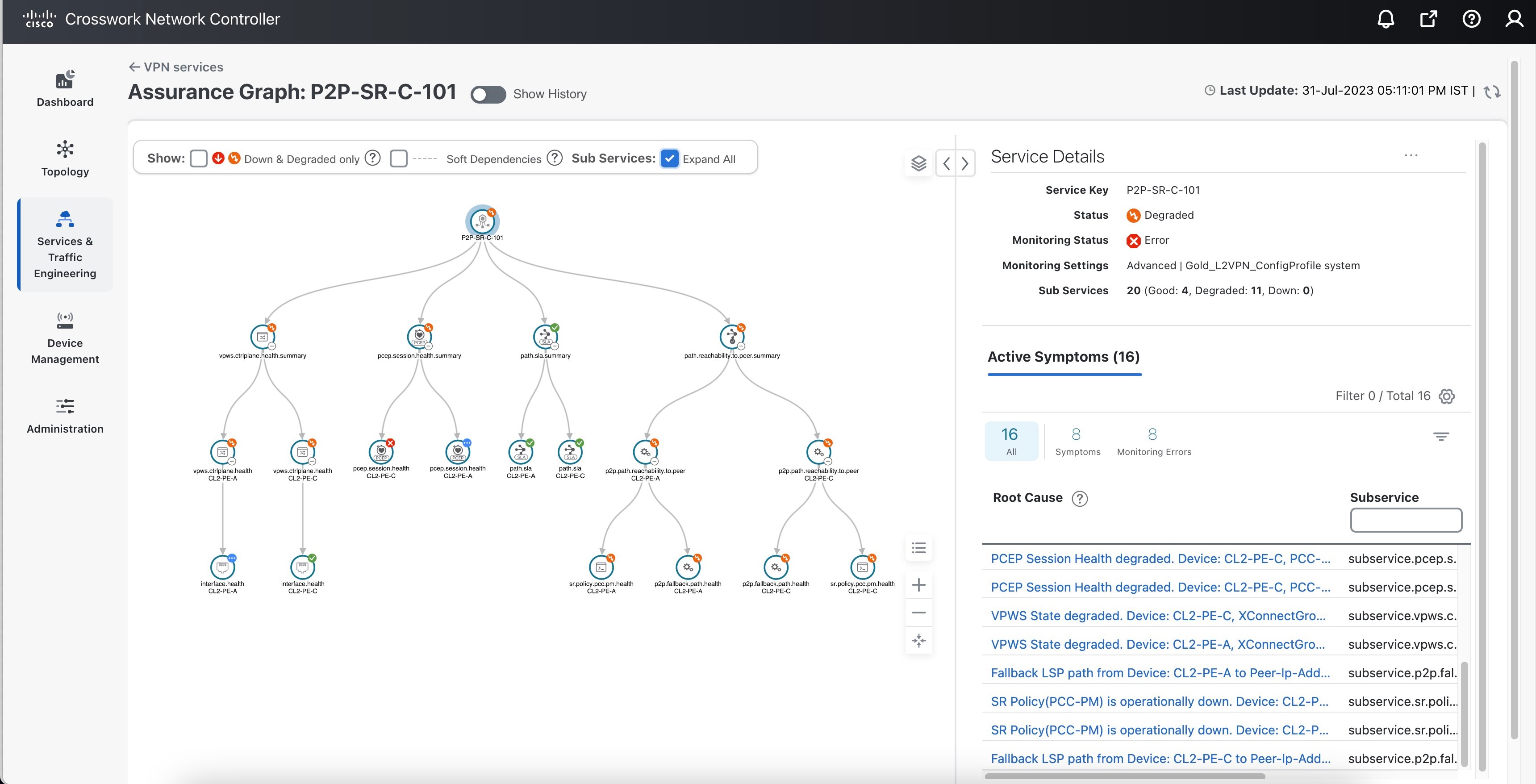
You can view the Monitoring Status of a service from its Service Details page.
From the main menu, choose Services & Traffic Engineering > VPN Services. Locate the service that you are interested in and under the Actions column, click View Details. This page displays the Monitoring Status and the Health status of the service.
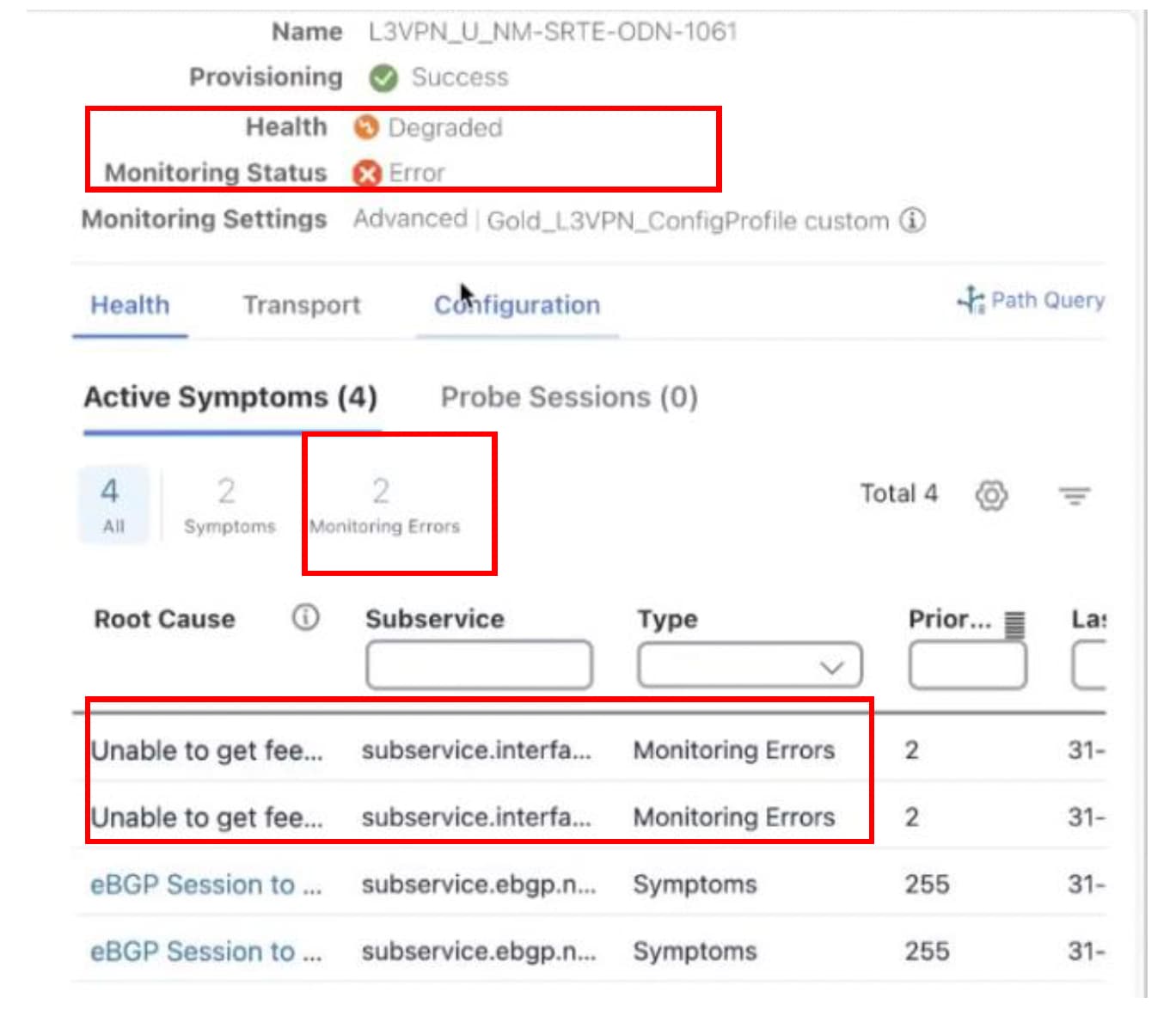
Monitoring status for a service can be either Healthy or Error.
-
Healthy: This means the end-to-end flow of monitoring the service is working as expected and Crosswork Network Controller is able to evaluate the health of the service successfully.
-
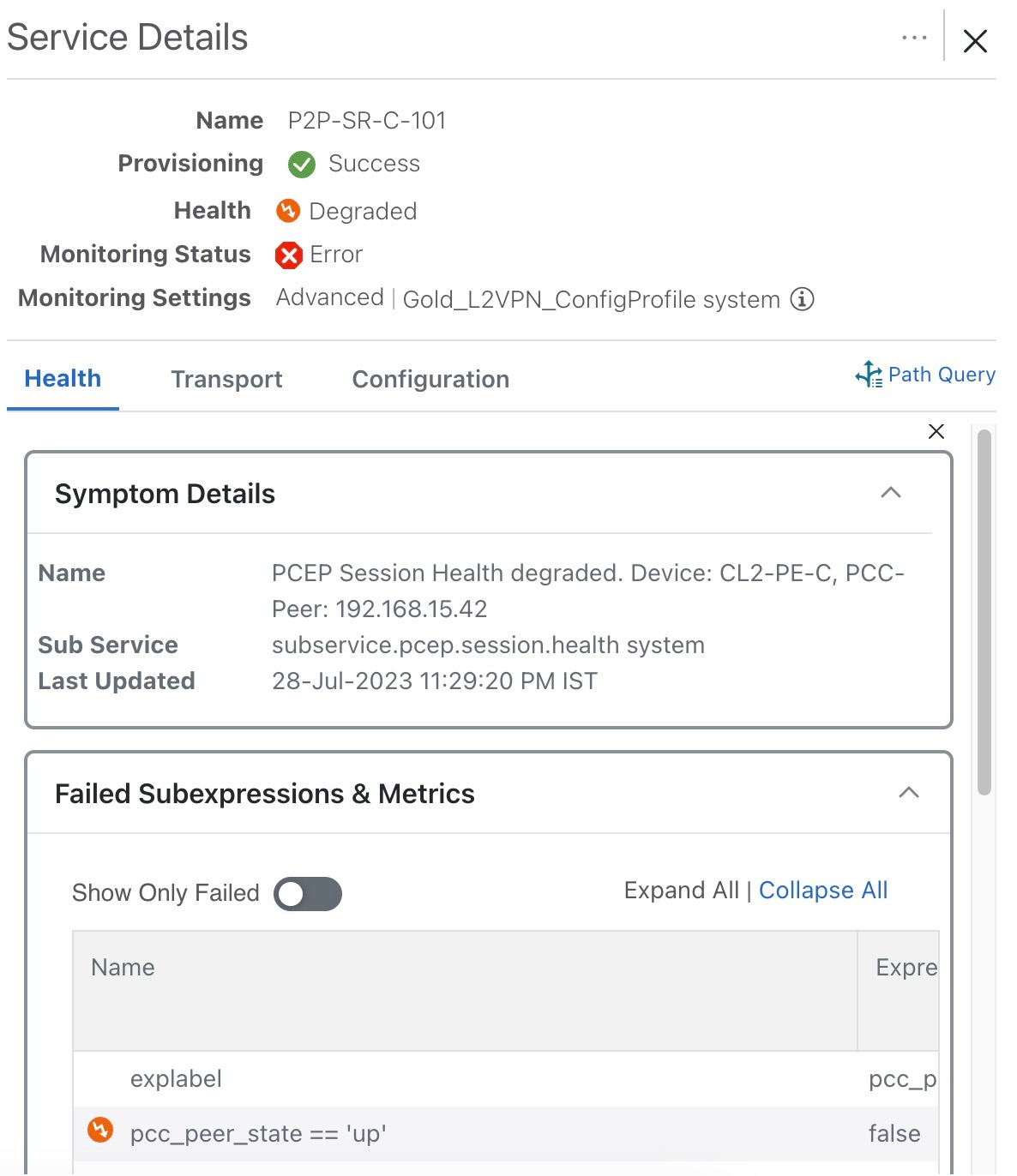
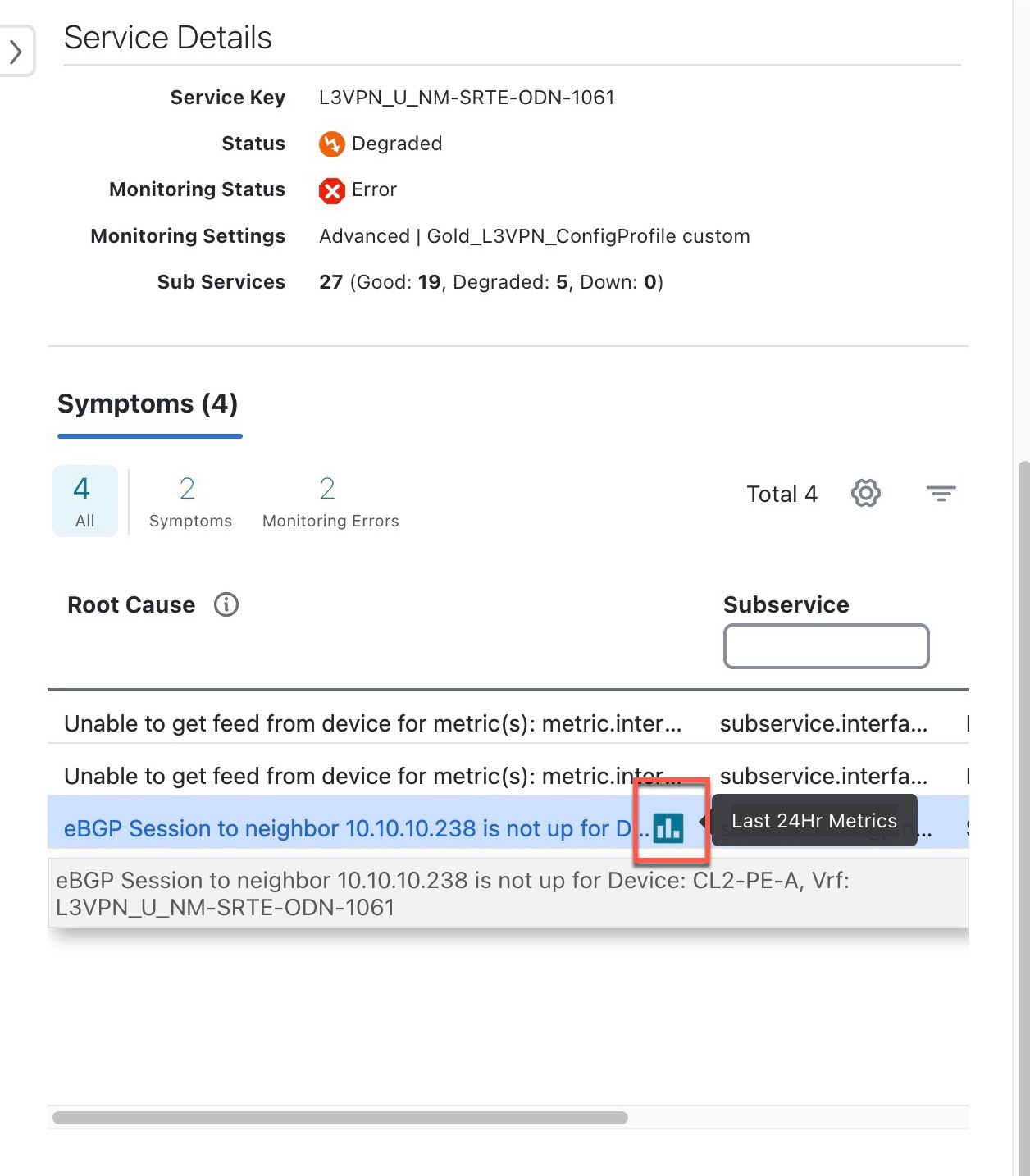
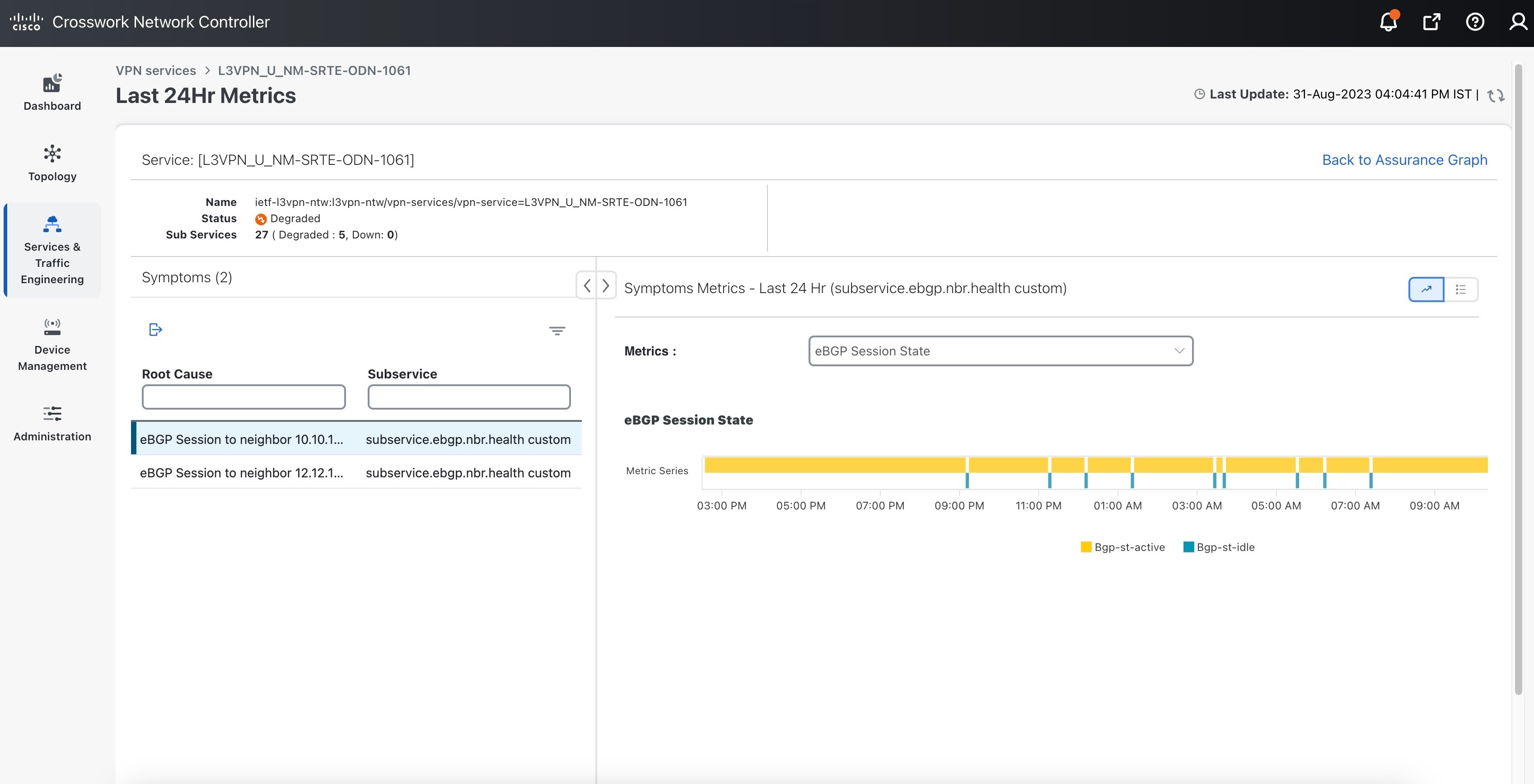
Error: This means Crosswork Network Controller is unable to monitor the current health of the service due to component failures, operational errors or device errors, and the health status that is displayed is the last known health of the service. You can filter monitoring errors using the mini dashboard or the filters.

Note
Monitoring errors reported on account of device health do not affect the overall health of the service.
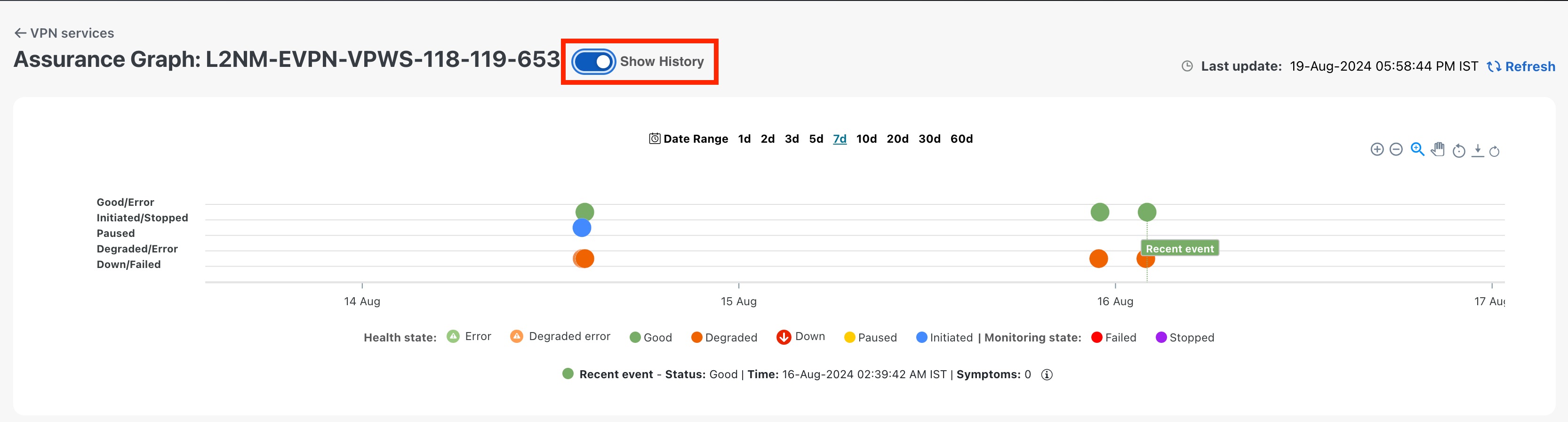
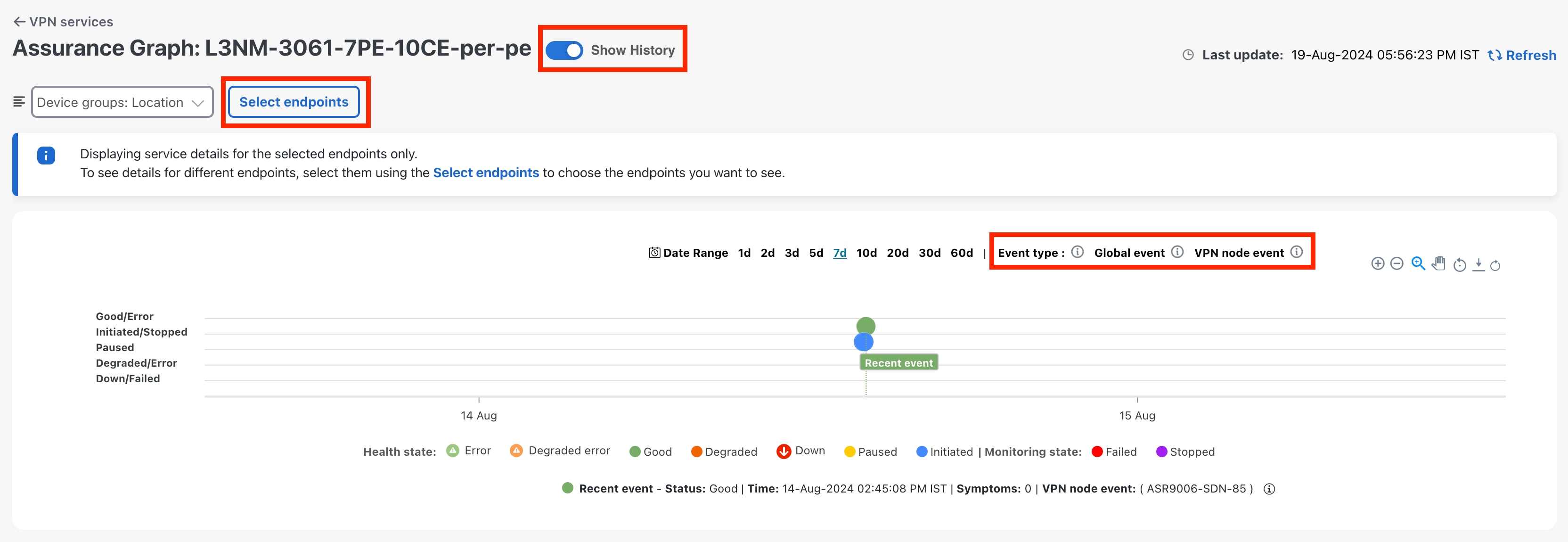
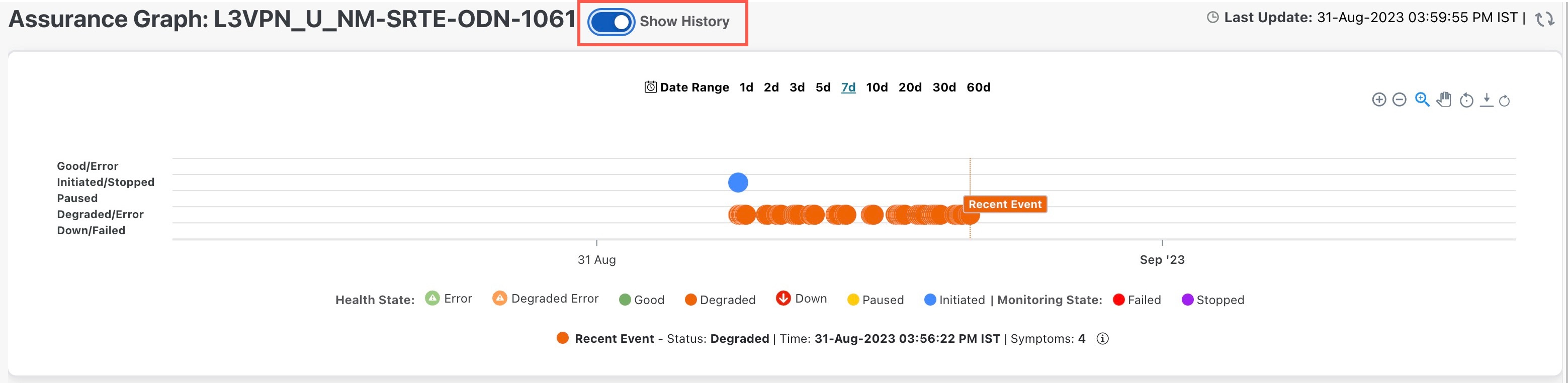
In the Historical Graph, Events of Significance (EoS) are displayed for monitoring errors as well. If the service is healthy but there are monitoring errors, a green warning icon is displayed. However, if the service is degraded and there are monitoring errors, then an orange warning icon is displayed. Clicking these icons provides you with the details in the symptoms table with type as Monitoring Errors.
 Note |
The Historical Graph displays monitoring errors only when the Monitoring Errors setting is enabled via API. There is no option to enable this setting from the UI. Once this setting is enabled, the system starts to log these monitoring errors as Events of Significance and display them in the historical graph. Refer to the API documentation on Cisco Devnet for more information. |
 Feedback
Feedback