Manage Certificates
What is a Certificate?
A certificate is an electronic document that identifies an individual, a server, a company, or another entity, and associates that entity with a public key. When a certificate is created with a public key, a matching private key is also generated. In TLS, the public key is used to encrypt data being sent to the entity and the private key is used to decrypt. A certificate is signed by an issuer or a "parent" certificate (Certificate Authority) - i.e. signed by the parent's private key. Certificates can also be self-signed. In a TLS exchange, a hierarchy of certificates is used to verify the validity of the certificate's issuer. This hierarchy is called a trust-chain and consists of 3 types of entities: a root CA certificate (self-signed), possibly multiple levels of intermediate CA certificates, and a server (or client) certificate (end-entity). The intermediate certificates act as a “link of trust” linking the server certificates to the CA’s root certificate and providing additional layers of security. Starting from the root certificate's private key, the private key for each certificate in the trust chain signs and issues the next certificate in the chain until finally signing an end entity certificate. The end-entity certificate is the last certificate in the chain and is used as a client or server certificate. For more details about these protocols, see X.509 Certificates and HTTPS.
How are Certificates Used in Crosswork?
Communication between Crosswork applications and devices as well as between various Crosswork components are secured using the TLS protocol. TLS uses X.509 certificates to securely authenticate devices and encrypt data to ensure its integrity from source to destination. Crosswork uses a mix of generated and client uploaded certificates. Uploaded certificates can be purchased from Certificate authorities (CA) or can be self-signed. For example, the Cisco Crosswork VM-hosted web server and the client browser-based user interface communicate with each other using Crosswork generated X.509 certificates exchanged over TLS.
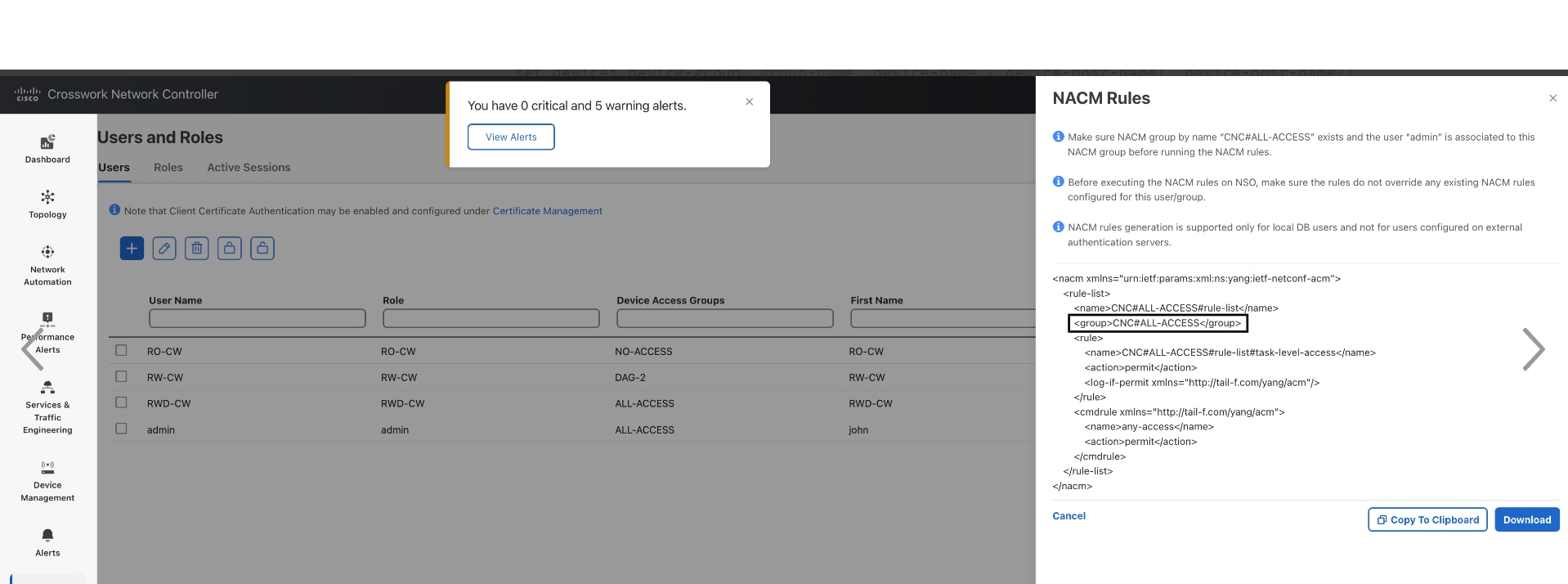
The Crosswork Cert Manager is a proxy for multiple microservices and services within the distributed framework and manages all the Crosswork certificates. The Certificate Management UI () allows you to view, upload, and modify certificates. The following figure displays the default certificates provided by Cisco Crosswork.
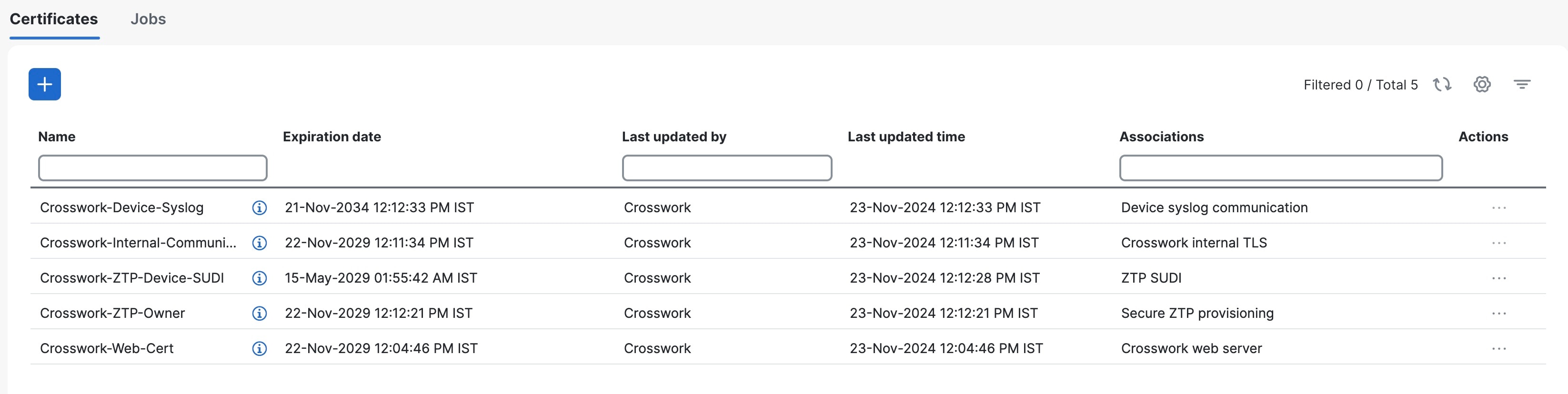
Certificate Types and Usage
The following figure shows how Crosswork uses certificates for various communication channels.
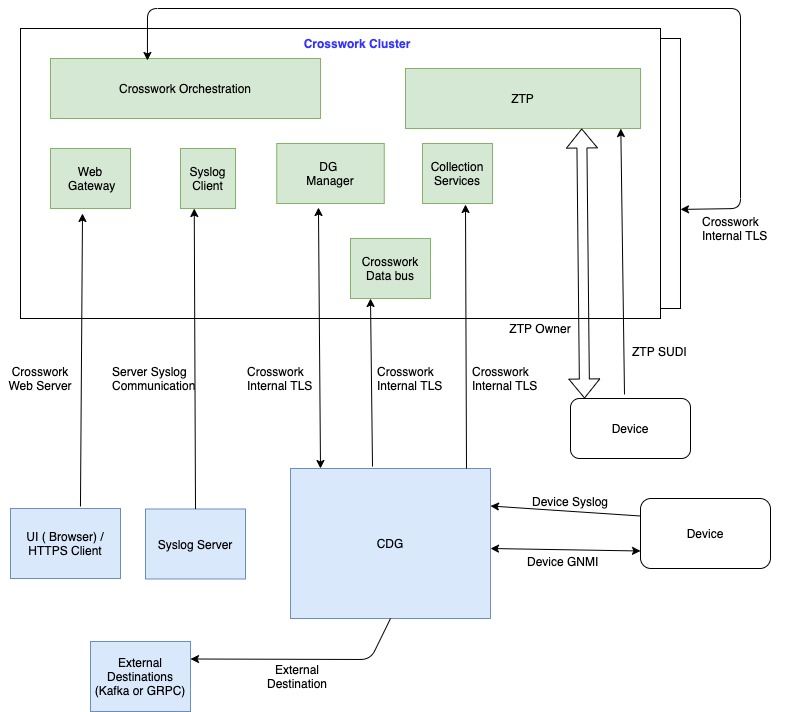
These certificates are classified into various roles with different properties depending on their use case as shown in the following table.
|
Role |
UI Name |
Description |
Server |
Client |
Allowed operations |
Default Expiry |
Allowed Expiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Crosswork (CW) Internal TLS |
CW-Internal- Communication |
|
Crosswork |
Crosswork Data Gateway Crosswork |
Download |
5 years |
— |
|
CW Web Server |
CW-Web-Certificate Server Authentication |
|
Crosswork Web Server |
User Browser or API Client |
|
5 years |
30 days to 5 years |
|
ZTP SUDI |
CW-ZTP-Device-SUDI |
|
Crosswork ZTP |
Device |
|
100 days |
31 days. This value is user-defined |
|
Secure ZTP Provisioning |
CW-ZTP-Owner |
|
Crosswork ZTP |
Device |
|
5 years |
31 days. This value is user-defined |
|
Device Syslog |
CW-Device-Syslog |
|
Crosswork Data Gateway |
Device |
Download |
5 years |
— |
|
Device gNMI Communication |
— |
Provides GNMI telemetry communications between devices and Crosswork Data Gateway. |
Crosswork Data Gateway |
Device |
|
Not Applicable |
31 days. This value is user-defined |
|
Server Syslog Communication |
— |
|
External Syslog Server |
Crosswork |
|
— |
31 days. This value is user-defined |
|
External Destination |
— |
Exports telemetry data from Crosswork Data Gateway to external destinations (Kafka or gRPC) after performing a mutual-authentication. |
External Destinations (Kafka or gRPC) |
Crosswork Data Gateway |
|
— |
31 days. This value is user-defined |
|
External Destination Server Auth |
— |
Exports telemetry data from Crosswork Data Gateway to external destinations (Kafka or gRPC) after performing a server-based authentication. |
External Crosswork Data Gateway Destinations (Kafka or gRPC) |
||||
|
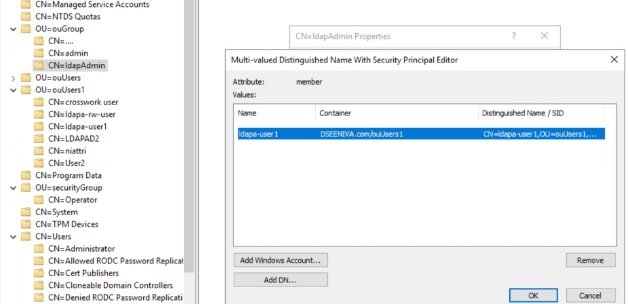
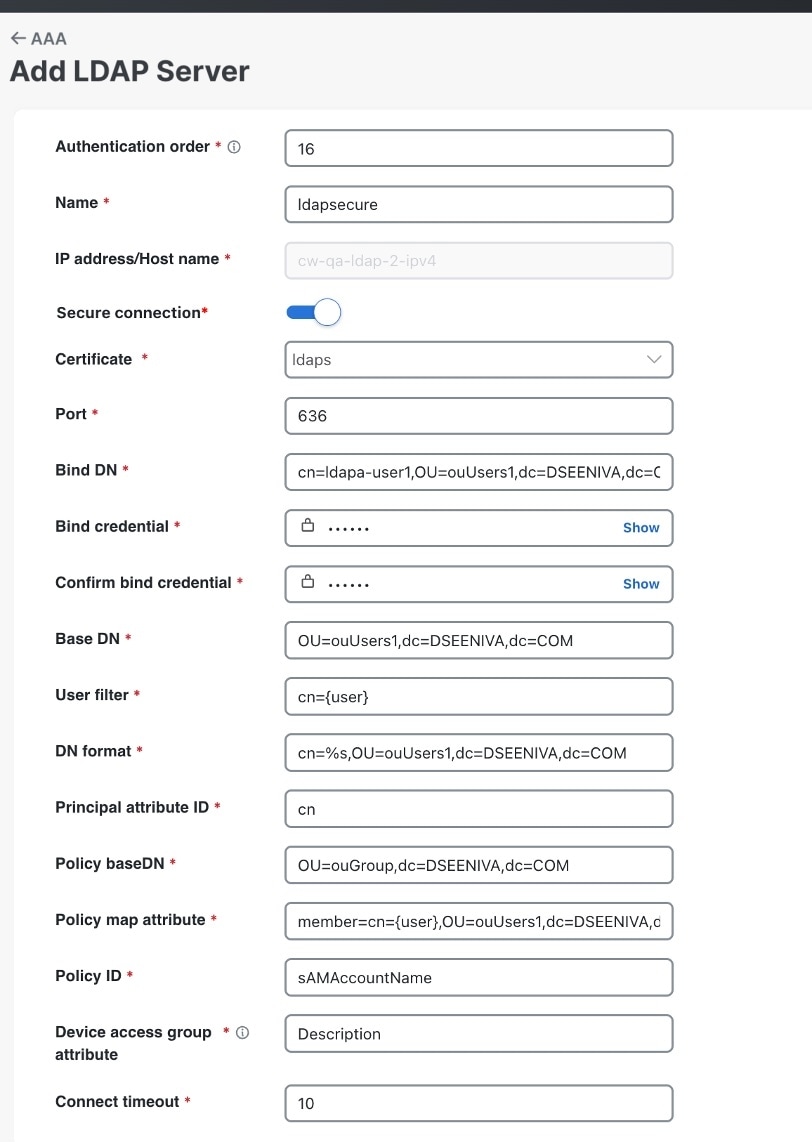
Secure LDAP Communication |
— |
Crosswork uses the trust chain of this certificate to authenticate the secure LDAP server. |
Secure LDAP server |
Crosswork |
|
— |
31 days. This value is user-defined |
|
Application External Destination |
— |
Exports telemetry data from Crosswork to an external Kafka destination. |
External Kafka Destinations |
Crosswork |
Upload |
— |
31 days. This value is user-defined |
There are two category roles in Crosswork:
-
Roles which allow you to upload or download trust chains only.
-
Roles that allow upload or download of both the trust chain and an intermediate certificate and key.
Add a New Certificate
This topic explains the steps to add a new certificate.
You can add certificates for these roles.
-
External Destination: Certificates uploaded for this role are used to secure communication between Crosswork Data Gateway and external destinations like Kafka servers. To enable mutual authentication, the user uploads a CA Certificate Trustchain that will be common to both Crosswork Data Gateway and the external server. This trust chain contains a root CA certificate and any number of optional intermediate CA certificates. The last intermediate certificate in the chain and its corresponding private key is uploaded separately in the UI using Intermediate key, Intermediate certificate, and optionally Passphrase (if one was used for generating the intermediate key). Crosswork internally creates a client certificate using this intermediate key for the Crosswork Data Gateways that connects to the external destination. The destination (for example: Kafka) server certificate trust needs to be derived from the same root CA certificate.
You can upload certificates to the External Destination role, the authentication type must be opted as Mutual-Auth on the Add Destination page. For more information about the authentication types, see Add or Edit a Data Destination.
-
Server Syslog Communication: The user uploads the trust chain of the Syslog server certificate. This trust chain is used by Crosswork to authenticate the Syslog server. Once this trust chain is uploaded and propagated within Crosswork, the user can add the syslog server () and associate the certificate to enable TLS. For more information, see Configure a Syslog Server.
-
Devices gNMI communication: The user uploads a bundle of trust chains used by Crosswork Data Gateway to authenticate the devices connecting to it. This trust chain and the device gNMI certificate must also be configured on the device. The trust chain file that is uploaded can contain multiple hierarchies of trust certificates as needed to allow all the devices in the network to connect. For more information, see Configure gNMI Certificate.
-
Secure LDAP Communication: The user uploads the trust chain of the secure LDAP certificate. This trust chain is used by Crosswork to authenticate the secure LDAP server. Once this trust chain is uploaded and propagated within Crosswork, the user can add the LDAP server (see Manage LDAP Servers) and associate the certificate.
-
External Destination Server Auth: The user uploads the root CA certificate. This certificate is used to establish a secure communication between Crosswork Data Gateway and external destinations like Kafka servers.
You can upload the certificates to the External Destination Server Auth role only when the authentication type is set to Server-Auth. For more information about the authentication types, see Add or Edit a Data Destination.
-
Application External Destination: The user can upload the application certificates to ensure secure transfer of telemetry data to an external Kafka destination. The Kafka channel is safeguarded through mutual TLS, and the TLS Manager is responsible for managing the certificates used by external Kafka.
For information on certificate types and usage, see Certificate Types and Usage.
 Note |
Cisco Crosswork does not receive a web certificate directly. It accepts an intermediate CA and intermediate Key to create a new web certificate, and apply it to the Web Gateway. |
If you prefer to upload your own ZTP and web certificates (instead of using the default certificates provided within Cisco Crosswork), use the Edit function (see Edit Certificates).
Before you begin
-
All certificates that are uploaded must be in Privacy Enhanced Mail (PEM) format. Note where these certificates are in the system so that you can navigate to them easily.
-
Trust chain files that are uploaded may contain the entire hierarchy (root CA and intermediate certificates) in the same file. In some cases, multiple chains are also allowed in the same file.
-
Intermediate Keys need to be either PKCS1 or PKCS8 format.
-
A data destination must be configured prior to adding a new certificate for an external destination. For more information, see Add or Edit a Data Destination.
-
Ensure there are no collection jobs configured for destinations when adding or updating a certificate with multiple destinations.
-
Ensure that the tyk service is in a healthy state.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
From the main menu, choose and click |
||
|
Step 2 |
Enter a unique name for the certificate. |
||
|
Step 3 |
From the Certificate Role drop-down menu, select the purpose for which the certificate is to be used. For more information, see Certificate Types and Usage.
|
||
|
Step 4 |
Click Browse, and navigate to the certificate trustchain. |
||
|
Step 5 |
In the case of an External Destination certificate, you must select one or more destinations and provide the CA certificate trustchain, intermediate certificate, and intermediate key. The passphrase field is optional and is used to create the intermediate key (if applicable). |
||
|
Step 6 |
Click Save.
|
Edit Certificates
Crosswork Network Controller allows you to update web certificates by importing an intermediate Certificate Authority (CA) certificate. You can edit certificates to add or remove connection destinations, and upload or replace expired or misconfigured certificates. This applies to user-provided certificates, ZTP certificates, and web certificates. However, system certificates provided by Cisco Crosswork cannot be modified and will not be available for selection.
Crosswork Network Controller also allows you to configure the client authentication for web certificates. Client authentication offers an alternative method for setting up user authentication in Crosswork, requiring both the client and server to present digital certificates to verify their identities. Enabling this feature can provide a more seamless login experience for users.
You can also “remove” a certificate by following this procedure to replace the certificate or by disabling security (disable Enable Secure Communication option) for any assigned destinations (see Add or Edit a Data Destination). Permanently deleting a certificate from the Cisco Crosswork system is not supported.
Before you begin
-
Updating the certificate can disrupt the existing trust chain of certificates used for client authentication if enabled, so proceed with caution.
-
This process requires the Crosswork server to be restarted, which will take several minutes to complete.
-
Set the AAA mode to Local to enable client authentication.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
From the main menu, choose to view the Certificate Management window. |
|
Step 2 |
To update a certificate: |
|
Step 3 |
To enable the client certificate authentication of a web certificate: |
|
Step 4 |
To update certificate and configure client authentication in a single step: |
Download Certificates
To export certificates, do the following:
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
From the main menu, choose . |
|
Step 2 |
Click 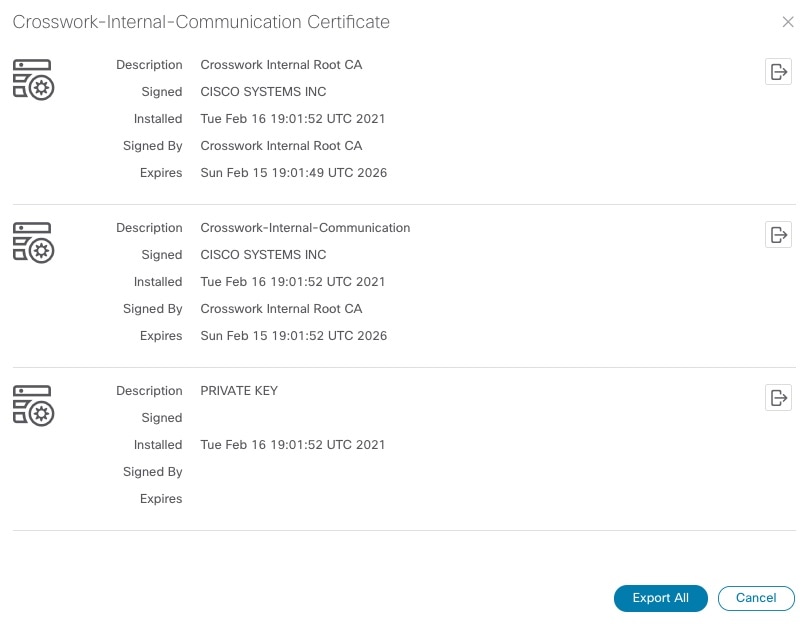
|
|
Step 3 |
To separately download the root certificate, intermediate certificate, and the private key, click |
Renew Certificates
Kubernetes certificate renewal
Certificates are valid for one year before they expire. After renewing the certificates, ensure that the pods are healthy before resuming other operations.
 Note |
When renewing certificates before expiry, it is recommended to perform this activity during a maintenance window as the cluster is in an operational state. |
To renew a certificate, perform the following:
Before you begin
-
Create a plain text file on your local machine (for example,
password.txt) that contains the SSH login password for the server. -
Keep the management IP addresses readily available for the hybrid and worker nodes in your cluster.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Create a backup of your Crosswork Network Controller. |
||
|
Step 2 |
Log in to one of your hybrid nodes. |
||
|
Step 3 |
Run the following command:
Replace the parameters with the management IP addresses of the nodes in your cluster.
Here are some examples:
|
||
|
Step 4 |
(Optional) Recover cluster: If multiple pods are stuck in Wait for the Once all the Calico pods are up and running, all other pods should recover and enter a running state. If any pods remain in a non-running state, wait at least 10 minutes after the Calico pods have started, and then run this command: |
Automatic Renewal of Internal Certificates
Crosswork CA generates TLS certificate chains, including root, intermediate CA, and leaf certificates, for day 0 deployments (Geo HA and non-Geo HA). The leaf certificates are valid for 2 years, while root and intermediate CA certificates are valid for 5 years. Customers with Crosswork deployments lasting beyond 2 years will face certificate expiry, disrupting TLS communication and impacting cluster operations. Auto-renewal applies to all Crosswork certificates generated internally, including NATS, Kafka, and any application-specific internal certificates.
The renewal alert is generated only when the expiry period is less than 60 days. When an internal certificate is expiring and renewed, all internal certificates of that type will be renewed. For example, when a leaf certificate is renewed, the process will also renew all other leaf certificates.
 Important |
For Geo HA deployment:
|
The certificate renewal process can cause a downtime of approximately 30 minutes to 1 hour. It is recommended to perform this activity during a maintenance window to avoid disrupting cluster operations.
To renew an internal certificate, perform the following:
Procedure
|
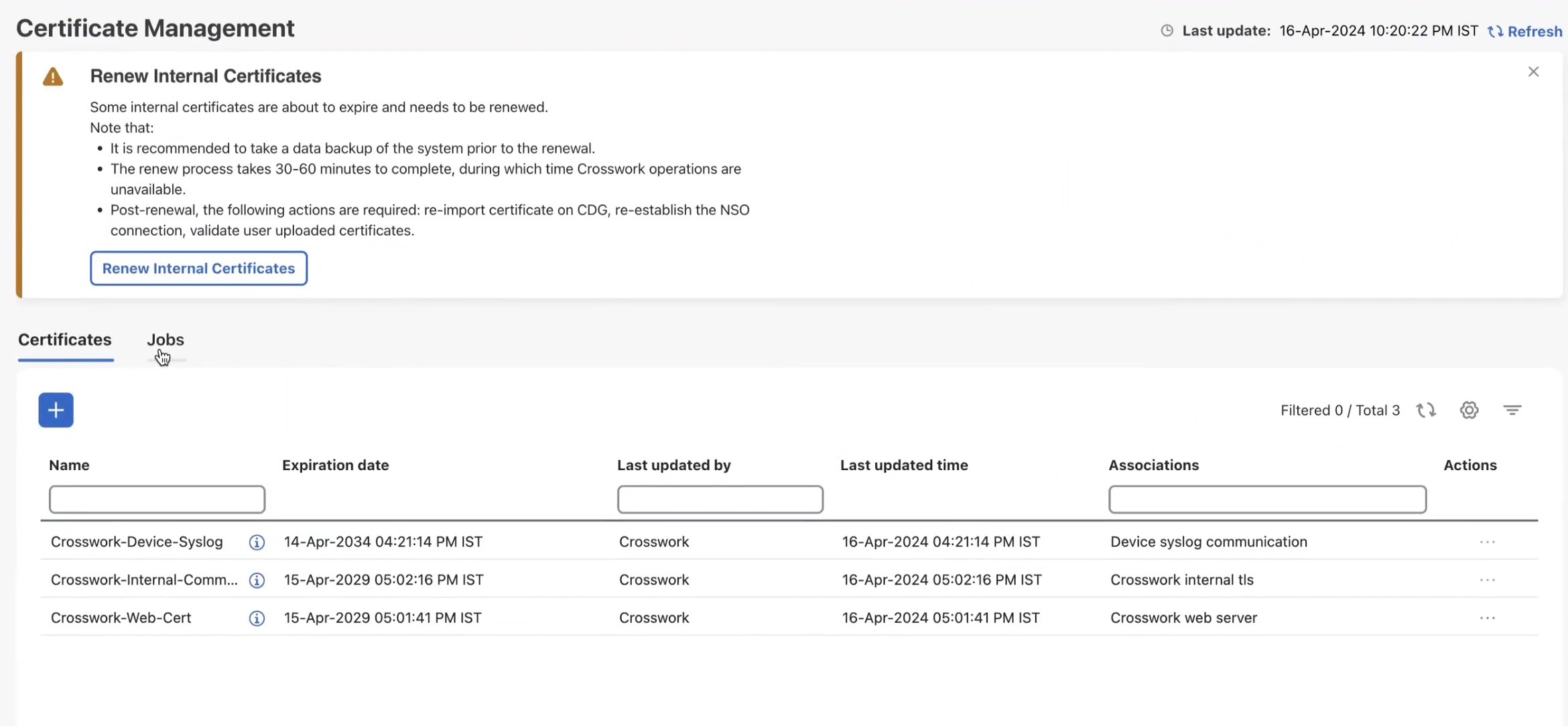
Step 1 |
From the main menu, choose . The Certificate Management window is displayed. If an internal certificate is about to be expired, a prompt is displayed for certificate renewal.
|
||
|
Step 2 |
Click Renew Internal Certificate. A confirmation popup is displayed. Click Renew to confirm. 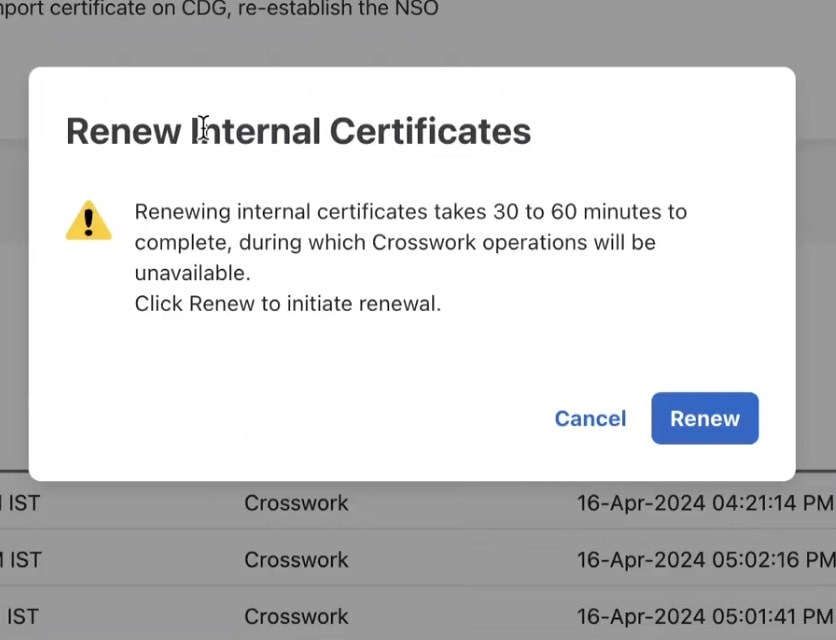
This action invokes the REST API (/v2/cert/renew) and initiates the certificate expiry check. A notification about the new renewal job is displayed on the Certificate Management window. 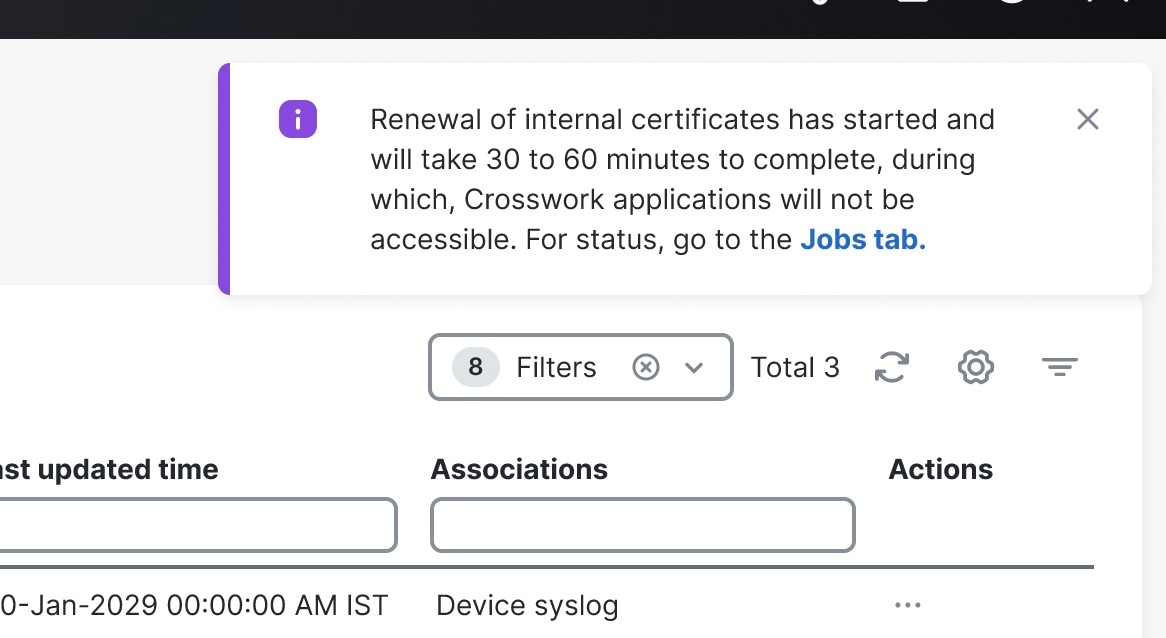
You can view progress of the renewal job from the Jobs tab. Once the job is complete, an Info alarm event is raised about the successful completion. You must manually clear this alarm to acknowledge the event. Any error during the process will result in job failure; however, the job can be triggered again as the API is repeatable. |
||
|
Step 3 |
In case of Geo HA deployment: After successfully completing the certificate renewal, run an on-demand or periodic sync across the active and standby clusters to ensure that asynchronous replication is re-established over a secure channel. |
||
|
Step 4 |
Once the renewal job is completed, perform the following steps to ensure TLS communication is maintained between Crosswork and other external components: |



 ) located at the top right corner of the window.
) located at the top right corner of the window.

 Feedback
Feedback