Creation and Configuration of a Rule for IPv6 Based Access Control List (ACL) on the WAP121 and WAP321 Access Points
Available Languages
Objective
An Access Control List (ACL) is a list of network traffic filters and correlated actions used to improve security. An access control list contains the hosts that are allowed or denied access to the network device. The QoS feature contains Differentiated Services (DiffServ) support that allows traffic to be classified into streams and given certain QoS treatment in accordance with defined per-hop behaviors.
This article explains how to create and configure IPv6 ACL on WAP121 and WAP321 Access Points.
Applicable Devices
• WAP121
• WAP321
Software Version
• v1.0.3.4
IPv6 Based ACL Configuration
IP ACLs classify traffic for Layers 3 in the IP stack. Each ACL is a set of up to 10 rules applied to traffic either sent from a wireless client or received by a wireless client. Each rule specifies whether the contents of a given field should be used to permit or deny access to the network. Rules can be based on various criteria and may apply to one or more fields within a packet, such as the source or destination IP address, the source or destination port, or the protocol carried in the packet.
Creation of IPv6 ACL
Step 1. Log in to the Access Point Configuration Utility and choose Client QoS > ACL. The ACL page opens.
Step 2. Enter the name of the ACL in the ACL Name field.
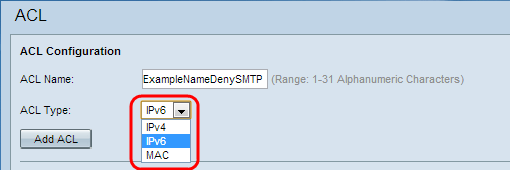
Step 3. Choose the IPv6 type for the ACL from the ACL Type drop-down list.
Step 4. Click Add ACL to create a new IPv6 ACL.
Configuration of a Rule for IPv6 ACL
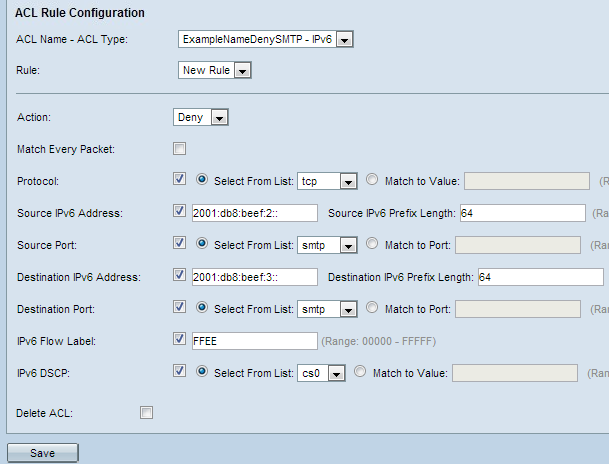
Step 1. Choose the ACL from the ACL Name-ACL Type drop-down list for which rule has to be configured.
Step 2. If a new rule has to be configured for the selected ACL, choose New Rule from the Rule drop-down list. Otherwise choose one of the present rules from the Rule drop-down list.
Note: Maximum of 10 rules can be created for a single ACL.
Step 3. Choose the action for the ACL rule from the Action drop-down list.
• Deny — Blocks all traffic that meets the rule criteria to enter or exit the WAP device.
• Permit — Allows all traffic that meets the rule criteria to enter or exit the WAP device.
Caution: You have to add a permit rule permits the traffic because if a permit or deny is chosen always there is an implicit deny at the end of every rule.
Step 4. Check the Match Every Packet checkbox to match the rule for every frame or packet regardless of its contents. If you want the configure any of the additional match criteria, then uncheck the Match Every Packet checkbox.
Timesaver: If you check Match Every Packet checkbox then skip to Step 12.
Step 5. Check the Protocol checkbox to enable L3 or L4 (Network and Transport layer of IP stack) protocol match condition based on the value of the IP Protocol field in IPv6 packets. If the Protocol checkbox is checked, click one of these radio buttons.
• Select From List — Choose a protocol from the Select From List drop-down list. The drop-down list has ip, icmp, igmp, tcp, udp protocols.
• Match to Value — For protocols not presented in the list. Enter a standard IANA-assigned protocol ID ranges from 0 to 255.
Step 6. Check the Source IPv6 Address checkbox to include an IP address of the source in the match condition. Enter the IPv6 address and the IPv6 prefix length of the source in the relative fields.
Step 7. Check the Source Port checkbox to include a source port in the match condition. If the Source Port check box is checked, click one of these radio buttons.
• Select From List — Choose a source port from the Select From List drop-down list. The drop-down list has ftp, ftpdata, http, smtp, snmp, telnet, tftp, www ports.
• Match to Port — For source port not presented in the list. Enter the port number which ranges 0 to 65535 and includes three different types of ports.
– 0 to 1023 — Well Known Ports. Port used by the server process as its contact port. The contact port is sometimes called a Well-Known Port.
– 1024 to 49151 — Registered Ports. It is a network port used for certain protocol or for an application.
– 49152 to 65535 — Dynamic and/or Private Ports. Dynamic ports are not managed by any governing body like IANA and have no special usage restrictions.
Step 8. Check the Destination IPv6 Address checkbox to include the IP address of the destination in the match condition. Enter the IPv6 address and the IPv6 prefix length of the destination in the relative fields.
Step 9. Check the Destination Port checkbox to include a destination port in the match condition. If the Destination Port check box is checked, click one of these radio buttons.
• Select From List — Choose a destination port from the Select From List drop-down list. The drop-down list has ftp, ftpdata, http, smtp, snmp, telnet, tftp, www ports.
• Match to Port — For destination port not presented in the list. Enter the port number which ranges 0 to 65535 and includes three different types of ports.
– 0 to 1023 — Well Known Ports.
– 1024 to 49151 — Registered Ports.
– 49152 to 65535 — Dynamic and/or Private Ports.
Step10. Check the IPv6 Flow label checkbox to include the IPv6 flow label in the match condition. The 20-bit flow label field in the IPv6 header can be used by a source to label a set of packets that belong to the same flow. Enter the number which ranges from 00000 to FFFFF in the IPv6 Flow label field.
Step 11. Check the IP DSCP checkbox to include the IP DSCP values in the match condition. If IP DSCP check box is checked, click one of these radio buttons.
• Select From List — IP DSCP value to choose from the Select From List drop-down list. The drop-down list has DSCP Assured Forwarding (AS), Class of Service (CS) or Expedited Forwarding (EF) values.
• Match to Value — To customize DSCP value which ranges from 0 to 63.
Step 12. (Optional) If you want to delete the configured ACL then, check the Delete ACL checkbox.
Step 13. Click Save to save the settings.
 Feedback
Feedback