Framework Mapping: Cisco Secure Network Analytics + CISA Zero Trust Model White Paper
Available Languages
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
U.S. Public Sector organizations are embarking on a Zero Trust roadmap—a structured and phased approach to transition its cybersecurity framework toward a more mature and resilient Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA). This roadmap aligns with best practices outlined in the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Special Publication 800-207 and the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) Zero Trust Maturity Model (ZTMM).
By leveraging these frameworks, U.S. Public Sector Organizations can adopt a comprehensive strategy to strengthen its security posture across all five CISA Zero Trust pillars—Identity, Device, Network/Environment, Application Workload, and Data.
1. Identity: Focuses on verifying and managing the identities of users, processes, and systems, ensuring access is granted only to authenticated and authorized entities based on least privilege principles.
2. Device: Ensures that all devices accessing the network are identified, monitored, and meet security compliance standards to reduce potential attack surfaces.
3. Network/Environment: Emphasizes secure network segmentation, dynamic access controls, and monitoring of traffic flows to limit lateral movement and protect resources within hybrid, cloud, and on-premises environments.
4. Application Workload: Protects applications and workloads by enforcing secure access, implementing runtime monitoring, and ensuring that interactions between applications are trusted and compliant.
5. Data: Focuses on protecting sensitive information through classification, encryption, monitoring, and policies that prevent unauthorized access or exfiltration.
The CISA Zero Trust Model also builds on the foundational capabilities of the cross-cutting pillars with Visibility and Analytics,[1] Automation and Orchestration,[2] and Governance[3] which support (acts as the Pillar Base) and enhance the maturity of each core pillar.
Cisco® provides proven solutions for accelerating Zero Trust adoption. In this document we discuss how Cisco Secure Network Analytics (SNA) meets the CISA ZTMM standard.
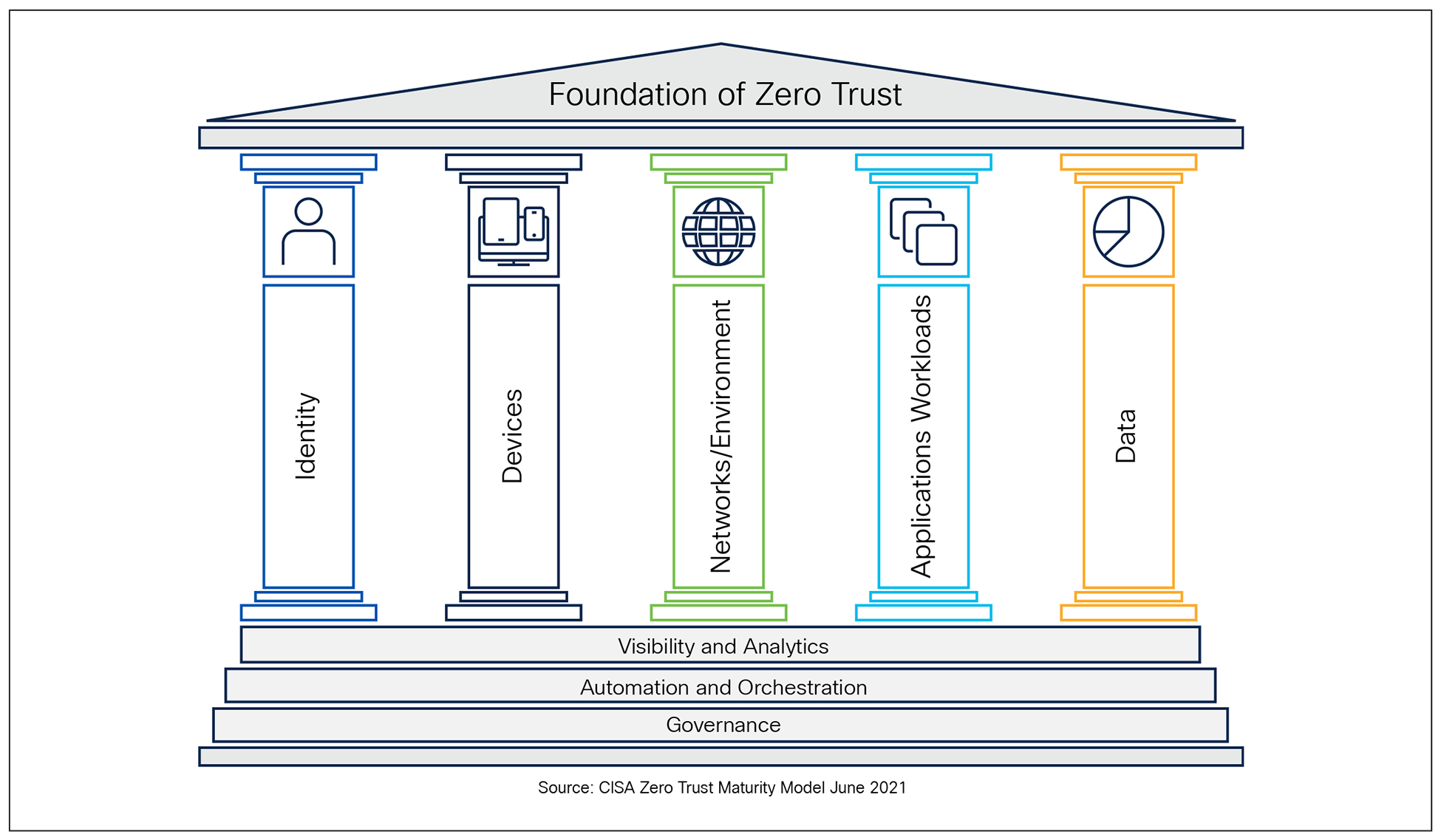
CISA Zero Trust Maturity Model
Cisco Secure Network Analytics plays a pivotal role in enabling the Zero Trust strategy by excelling in the Visibility & Analytics, Identity, and Application Workload pillars of the CISA model. Its advanced capabilities, including behavioral analytics, threat detection, and logging, provide deep visibility into network activity, user behavior, and application interactions. Secure Network Analytics continuously monitors network traffic for anomalies, enabling agencies to detect potential threats in real time and enforce security policies aligned with Zero Trust principles. By providing actionable insights, it empowers an organization to proactively mitigate risks and ensure compliance with stringent security standards.
In addition to its core strengths, Cisco Secure Network Analytics indirectly supports the Device and Data pillars by offering comprehensive insights into endpoint activity, data flows, and overall network behavior. While it does not directly enforce device compliance or data classification, its ability to detect anomalous activity and identify risks enhances the organization’s overall security posture. By integrating seamlessly with other Cisco security solutions, Secure Network Analytics ensures consistent monitoring and enforcement across the Zero Trust framework. As a critical component of an organization's Zero Trust roadmap, Cisco Secure Network Analytics enables the organization to achieve greater visibility, mitigate cyber risks, and align its security strategy with national standards and best practices.
Mapping to the CISA Zero Trust Five Pillars
Below is a detailed mapping of Cisco Secure Network Analytics capabilities to the CISA Zero Trust Five Pillars and their corresponding functions. This table provides a clear alignment between SNA's features and the foundational components of a Zero Trust architecture, illustrating how its capabilities support each pillar and enhance overall security. By breaking down each pillar, function, and capability, the table offers valuable context for understanding how SNA enables organizations to advance their Zero Trust maturity.
Table 1. Mapping Cisco Secure Network Analytics Capabilities to the CISA Zero Trust Identity Pillar
| CISA Zero Trust Pillar |
CISA Functions |
Cisco SNACapabilities |
Notes |
| Identity |
Enterprise Identity and Access Management |
Identity Anomaly Detection |
Cisco SNA enhances identity management by providing network behavior and monitoring activity patterns for anomalies and/or incidents. |
| Multi-Factor Authentication |
|
Cisco SNA does not directly enable MFA. |
|
| Privileged Access Management |
|
Indirectly supports privileged access management by detecting unusual activity patterns related to high-privilege accounts. |
|
| Least Privilege Access |
|
Cisco SNA can help ensure least privilege access by identifying anomalous access behaviors that suggest policy violations. |
Table 2. Mapping Cisco Secure Network Analytics Capabilities to the CISA Zero Trust Device Pillar
| CISA Zero Trust Pillar |
CISA Functions |
Cisco SNA Capabilities |
Notes |
| Device |
Device Inventory |
|
Cisco SNA supports an inventory of devices (via host groups); it identifies rogue devices and monitors device behavior and traffic for potential risks. |
| Device Security Posture |
|
Device posture is not directly assessed by Cisco SNA but can be inferred from traffic flows and anomalous activity. |
|
| Device Trust |
|
Cisco SNA indirectly contributes to device trust by monitoring and analyzing network traffic associated with devices. |
Table 3. Mapping Cisco Secure Network Analytics Capabilities to the CISA Zero Trust Network/Environment Pillar
| CISA Zero Trust Pillar |
CISA Functions |
Cisco SNA Capabilities |
Notes |
| Network / Environment |
Segmentation of Network |
|
Cisco SNA does not directly enforce segmentation but provides visibility into network traffic, enabling administrators to create informed segmentation policies. Cisco SNA supports the reporting of segmentation. |
| Secure Network Access |
Data Flow Mapping |
Cisco SNA maps data flows across the network, identifying potential risks and ensuring secure pathways for data transmission. |
|
| Encrypted Network Traffic |
|
Cisco SNA inspects encrypted network traffic by monitoring and analyzing behavior patterns for encrypted sessions. Cisco SNA can also verify secure encrypted algorithms. |
Table 4. Mapping Cisco Secure Network Analytics Capabilities to the CISA Zero Trust Application Workload Pillar
| CISA Zero Trust Pillar |
CISA Functions |
Cisco SNA Capabilities |
Notes |
| Application Workload |
Enterprise Application Inventory |
|
Cisco SNA does not maintain application inventories but monitors application-level traffic for anomalies. |
| Secure Application Access |
Continuous Monitoring |
Cisco SNA supports secure application access by continuously monitoring application traffic and identifying unauthorized (e.g., TrustSEC) or risky behavior. |
|
|
|
Ongoing Authorizations |
Provides ongoing analysis of network activity to ensure that application access remains compliant with policies. |
Table 5. Mapping Cisco Secure Network Analytics Capabilities to the CISA Zero Trust Data Pillar
| CISA Zero Trust Pillar |
CISA Functions |
Cisco SNA Capabilities |
Notes |
| Data |
Data Classification |
|
Cisco SNA does not classify data, but monitors data flows to identify potentially sensitive information being accessed or moved. |
| Data Discovery |
|
While Cisco SNA does not discover data directly, it provides insights into data movement across the network. |
|
| Encrypt Data at Rest and In Transit |
Data Encryption |
Cisco SNA complements data encryption by monitoring network traffic to ensure applications are not being misused or exfiltrated within encrypted data. |
|
| Prevent Data Exfiltration |
Data Flow Mapping |
Cisco SNA enables detection of unauthorized data movement or exfiltration by analyzing data flows and identifying anomalies. It works with Cisco ISE to quarantine hosts that violate policy |
Table 6. Mapping Cisco Secure Network Analytics Capabilities to the CISA Zero Trust Automation and Orchestration Supporting Pillar
| CISA Zero Trust Pillar |
CISA Functions |
Cisco SNA Capabilities |
Notes |
| Visibility & Analytics |
Security Monitoring and Visibility |
Log all Traffic (Network, Data, Apps, User) |
Cisco SNA provides robust traffic logging for all network activities, offering full visibility into users, devices, applications, and data flows. Cisco SNA does data analytics from firewalls (Syslog/NSEL). Note: Cisco SNA is not a PCAP (traffic recorder). |
|
|
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) |
Cisco SNA integrates with SIEM solutions to centralize security event data and facilitate analysis. Cisco SNA works with 3rd party solutions (e.g., Splunk, Firewalls) as an intelligence repository. |
|
|
|
Common Security and Risk Analytics |
Provides advanced analytics (behavioral, anomalous, and malicious) (MITRE ATT&CK) to identify risks and threats across the network |
|
|
|
User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) |
Cisco SNA uses UEBA to detect anomalies in user and device behavior, identifying potential threats or compromised accounts. |
1. Core Strengths in Visibility and Analytics:
● Cisco SNA excels in the Visibility and Analytics pillar, offering comprehensive logging, behavioral analytics (UEBA), and integration with SIEM solutions to centralize and analyze security data.
2. Identity and Application Monitoring:
● Cisco SNA supports the Identity pillar by providing behavioral context for user identity verification, detecting anomalies, and supporting continuous authentication.
● In the Application Workload pillar, Cisco SNA provides ongoing monitoring of application traffic and ensures compliance with access policies.
3. Contributions to Data Security:
● Cisco SNA contributes to the Data pillar by monitoring data flows across the network, identifying unauthorized movement, and complementing encryption efforts to prevent data exfiltration.
4. Limited Role in Device Management:
● While Cisco SNA does not directly manage device inventories or assess posture, it indirectly supports the Device pillar by monitoring device traffic and detecting anomalous behavior.
5. Visibility and Analytics:
● Cisco SNA is highly complementary to other Zero Trust tools like Cisco ISE and Secure Access, as it focuses on providing actionable visibility and analytics to enable policy enforcement and proactive threat detection.
Cisco Secure Network Analytics (SNA) is foundational for Zero Trust, aligning with the CISA Maturity Model. Its strengths lie in Visibility and Analytics, Identity, and Application Workload pillars, providing real-time monitoring, behavioral analytics, and comprehensive logging across users, devices, applications, and data flows. Cisco SNA enables threat detection, policy enforcement, and continuous authentication/authorization. It also contributes to the Data pillar by tracking flows and supports the Device pillar via anomaly monitoring. Integrating with other security tools, Cisco SNA enhances risk identification, streamlines incident response, and advances Zero Trust maturity.
Cisco Secure Network Analytics
Cisco Secure Network Analytics At-a-Glance
[1] Visibility and Analytics enable organizations to monitor and analyze behavior and events across the five pillars. This foundation capability provides the data-driven insights necessary to identify anomalies, detect threats, and enforce Zero Trust polices.
[2] Automation and Orchestration ensure that Zero Trust principles are implemented consistently and efficiently across the five pillars. By automating security tasks and orchestrating responses, organizations can reduce human error and improve reaction times to potential threats.
[3] Governance ensures that security policies, processes, and compliance requirements are well-defined and constantly applied across all pillars. It provides the overarching framework for decision-making, accountability, and adherence to organizational goals and regulatory mandates.