-
Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager Configuration Guide, Release 1.3 (from Release 1.3(1) through Release 1.3(6))
-
Index
-
New and Changed Information
-
Preface
-
Product Overview
-
Getting Started with Cisco Fabric Manager
-
Overview of Fabric Manager Components
-
Before You Begin
-
Obtaining and Installing Licenses
-
Initial Configuration
-
Configuring High Availability
-
Software Images
-
Managing Modules
-
Managing System Hardware
-
Configuring and Managing VSANs
-
Configuring Interfaces
-
Configuring Trunking
-
Configuring PortChannels
-
Configuring and Managing Zones
-
Configuring Inter-VSAN Routing
-
Managing FLOGI, Name Server, FDMI, and RSCN Databases
-
Configuring Switch Security
-
Configuring Fabric Security
-
Configuring Port Security
-
Configuring Fibre Channel Routing Services and Protocols
-
Configuring IP Services
-
Configuring FICON
-
Configuring IP Storage
-
Configuring Call Home
-
Configuring Domain Parameters
-
Configuring Traffic Management
-
Configuring System Message Logging
-
Discovering SCSI Targets
-
Monitoring Network Traffic Using SPAN
-
Advanced Features and Concepts
-
Configuring Fabric Configuration Servers
-
Monitoring System Processes and Logs
-
Troubleshooting the Fabric
-
Troubleshooting Fabric Manager Issues
-
Table Of Contents
Configuring Fabric Configuration Servers
Configuring Fabric Configuration Servers
This chapter describes the Fabric Configuration Server (FCS) feature provided in the Cisco MDS 9000 Family of directors and switches.
This chapter contains the following topics:
About FCS
The Fabric Configuration Server (FCS) provides discovery of topology attributes and maintains a repository of configuration information of fabric elements. A management application is usually connected to the FCS on the switch through an N port. The FCS views the entire fabric based on the following objects:
•
Interconnect element (IE) object—Each switch in the fabric corresponds to an IE object. One or more IE objects form a fabric.
•
Port object— Each physical port in an IE corresponds to a port object. This includes the switch ports (xE, Fx, and TL ports), and its attached Nx ports.
•
Platform object—A set of nodes may be defined as a platform object to make it a single manageable entity. These nodes are end-devices (host systems, storage subsystems) attached to the fabric. platform objects reside at the edge switches of the fabric.
Each object has its own set of attributes and their values. A null value may also be defined for some attributes.
In the Cisco MDS 9000 Family switch environment, multiple VSANs constitute a fabric, where one instance of the FCS is present per VSAN.
If you have attached a management application to a switch, all the frames directed towards the FCS in the switch is a part of the port VSAN in the switch port (Fx port). Hence your view of the management application is limited only to this VSAN. However information about other VSANs that this switch is part of can be obtained either through SNMP or CLI.
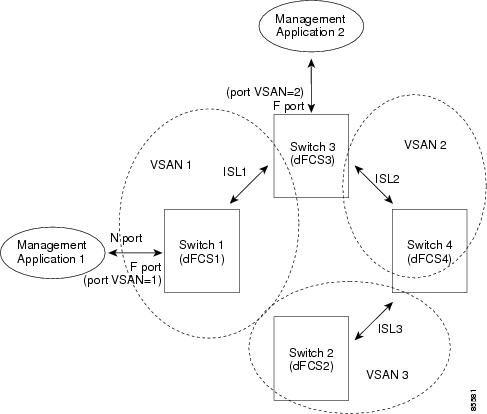
In Figure 32-1, Management Application 1 (M1) is connected through an F port with a port VSAN ID 1 and Management Application 2 (M2) is connected through an F port with a port VSAN ID 2. M1 can query FCS info of switches S1 and S3, and M2 can query switches S3 and S4. Switch S2 information is not known to both of them. FCS operations can be done only on those switches that are visible in the VSAN. Note that M2 can send FCS requests only for VSAN 2 even though S3 is also a part of VSAN 1.
Figure 32-1 FCSs in a VSAN Environment
Significance of FCS
The significance of FCSs are as follows:
•
Network Management
–
N port management application can query and obtain information about the fabric elements.
–
SNMP Manager--A SNMP Manager can use the FCS management information base (MIB) to start discovery and obtain information about the fabric topology.
•
FCSs supports TE and TL ports in addition to the standard F and E ports.
•
FCS can maintain a group of modes with a logical name and management address when a platform registers with it. FCSs maintain a backup of all registrations in secondary storage and updates it with every change. When a restart or switchover happens, FCSs retrieve the secondary storage information, and rebuild its database.
•
The SNMP manager can query FCSs for all the IEs, ports, and platforms in the fabric.

 Feedback
Feedback