-
Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager Configuration Guide, Release 1.3 (from Release 1.3(1) through Release 1.3(6))
-
Index
-
New and Changed Information
-
Preface
-
Product Overview
-
Getting Started with Cisco Fabric Manager
-
Overview of Fabric Manager Components
-
Before You Begin
-
Obtaining and Installing Licenses
-
Initial Configuration
-
Configuring High Availability
-
Software Images
-
Managing Modules
-
Managing System Hardware
-
Configuring and Managing VSANs
-
Configuring Interfaces
-
Configuring Trunking
-
Configuring PortChannels
-
Configuring and Managing Zones
-
Configuring Inter-VSAN Routing
-
Managing FLOGI, Name Server, FDMI, and RSCN Databases
-
Configuring Switch Security
-
Configuring Fabric Security
-
Configuring Port Security
-
Configuring Fibre Channel Routing Services and Protocols
-
Configuring IP Services
-
Configuring FICON
-
Configuring IP Storage
-
Configuring Call Home
-
Configuring Domain Parameters
-
Configuring Traffic Management
-
Configuring System Message Logging
-
Discovering SCSI Targets
-
Monitoring Network Traffic Using SPAN
-
Advanced Features and Concepts
-
Configuring Fabric Configuration Servers
-
Monitoring System Processes and Logs
-
Troubleshooting the Fabric
-
Troubleshooting Fabric Manager Issues
-
Table Of Contents
Managing Running Attributes for Domains
Viewing Domain Manager Statistics
Specifying a Preferred or Static Domain ID
Configuring Allowed Domain ID Lists
Disabling the fcdomain Feature
Configuring Persistent FC IDs Manually
Configuring Unique Area FC IDs for Some HBAs
Configuring Domain Parameters
The Fibre Channel domain (fcdomain) feature performs principal switch selection, domain ID distribution, FC ID allocation, and fabric reconfiguration functions as described in the FC-SW-2 standards. The domains are configured on a per VSAN basis.
CautionChanges to fcdomain parameters should not be performed on a daily basis. These changes should be made by an administrator or individual who is completely familiar with switch operations.
Tip
When you change the configuration, be sure to save the running configuration. The next time you reboot the switch, the saved configuration is used. If you do not save the configuration, the previously saved startup configuration is used.
This chapter contains the following topics:
•
Specifying a Preferred or Static Domain ID
•
Configuring Allowed Domain ID Lists
•
Disabling the fcdomain Feature
•
Configuring Persistent FC IDs
About fcdomain Phases
This section describes each fcdomain phase.
•
Principal switch selection—This phase guarantees the selection of a unique principal switch across the fabric.
•
Domain ID distribution—This phase guarantees each switch in the fabric obtains a unique domain ID.
•
FC ID allocation—This phase guarantees a unique FC ID assignment to each device attached to the corresponding switch in the fabric.
•
Fabric reconfiguration—This phase guarantees a resynchronization of all switches in the fabric to ensure they simultaneously restart a new principal switch selection phase.
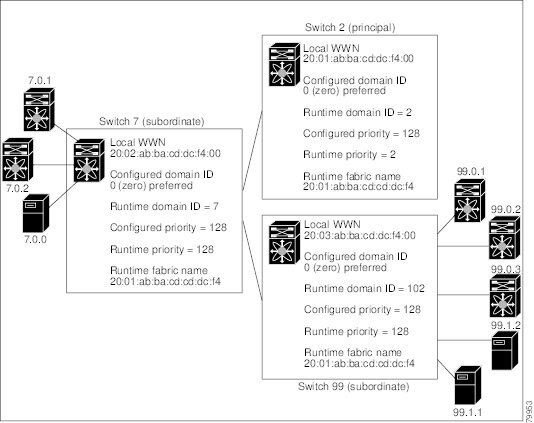
Figure 26-1 Sample fcdomain Configuration
Note
Domain IDs and VSAN values used in all procedures are only provided as examples. Be sure to use IDs and values that apply to your configuration.
Restarting the Domain
Fibre Channel domains can be started disruptively or nondisruptively. If you perform a disruptive restart, reconfigure fabric (RCF) frames are sent to other switches in the fabric. If you perform a nondisruptive restart, build fabric (BF) frames are sent to other switches in the fabric.
Note
A static domain is specifically configured by the user and may be different from the runtime domain. If the domain IDs are different, the runtime domain ID will change to take on the static domain ID after the next restart.
Tip
If a VSAN is in interop mode, you cannot restart the fcdomain for that VSAN disruptively.
Performing a Domain Restart
To restart the fabric disruptively or nondisruptively, follow these steps:
Step 1
Open Device Manager on a switch in the domain you want to restart.
Step 2
Choose FC > Domain Manager. You see the Domain Manager dialog box.
Step 3
Click in the Restart column for the VSAN ID for which you want to restart the domain. You see a drop-down list of options.
Step 4
Choose disruptive for a disruptive restart, or Non-disruptive for a non-disruptive restart.
Step 5
Click Apply to restart the domain.
Configuring the Domain
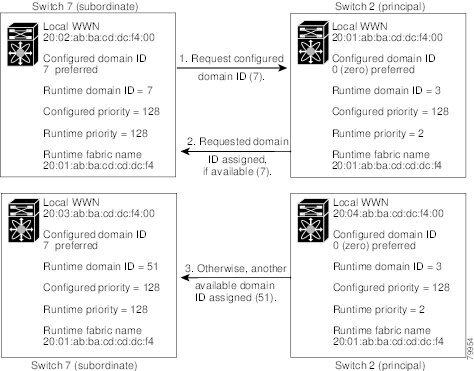
The configured domain ID can be preferred or static. By default, the configured domain is 0 and the configured type is preferred. If you do not configure a domain ID, the local switch sends a random ID in its request.
When a subordinate switch requests a domain, the following process takes place.
1.
The local switch sends a configured domain ID request to the principal switch.
2.
The principal switch assigns the requested domain ID if available, otherwise, it assigns another available domain ID.
Figure 26-2 Configuration Process Using the "preferred" Option
The behavior for a subordinate switch changes based on the allowed domain ID lists, on the configured domain ID, and on the domain ID that the principal switch has assigned to the requesting switch:
•
When the received domain ID is not within the allowed list, the requested domain ID becomes the runtime domain ID and all interfaces on that VSAN are isolated.
•
When the assigned and requested domain IDs are the same, the preferred and static options are not relevant, and the assigned domain ID becomes the runtime domain ID.
•
When the assigned and requested domain IDs are different, the following cases apply:
–
If the configured option is static, the assigned domain ID is discarded, all local interfaces are isolated, and the local switch assigns itself the configured domain ID, which becomes the runtime domain ID.
–
If the configured option is preferred, the local switch accepts the domain ID assigned by the principal switch and the assigned domain ID becomes the runtime domain ID.
CautionYou must restart the domain if you want to apply the configured domain changes to the runtime domain.
Configuring Domain Attributes
From this dialog box you can specify a fabric name for fabric logins on the VSAN and set the priority for the switch used in the principal switch selection process.
Configure the principal attributes for the domain.
To manage domain attributes from the Fabric Manager, choose FC > Domain Manager on the menu tree and click the Configuration tab. The Information pane from the Fabric Manager lets you manage domain attributes for multiple switches.
To manage domain attributes from the Device Manager, choose Domain Manager from the FC menu and click the Configuration tab. The Device Manager dialog box displays domain attributes for a single switch.
Configure the attributes for the domain.
Managing Running Attributes for Domains
To view running domain attributes from the Fabric Manager, choose FC > Domain Manager on the menu tree and click the Running tab. The Information pane from the Fabric Manager displays domain attributes for multiple switches.
To view running domain attributes from the Device Manager, choose Domain Manager from the FC menu and click the Running tab. The Domain Manager dialog box, with the Running tab selected, displays domain attributes for a single switch.
Viewing Domain Information
To view domain information from the Device Manager, choose Domain Manager from the FC menu and click the Domains tab. The dialog box displays domain information for a single switch
Viewing Domain Manager Statistics
To monitor domain manager statistics from the Fabric Manager, choose FC > Domain Manager on the menu tree and click the Statistics tab. The Information pane from the Fabric Manager displays domain statistics for multiple switches.
To monitor domain manager statistics from the Device Manager, choose Domain Manager from the FC menu and click the Statistics tab. The Domain Manager dialog box, with the Statistics tab selected, displays domain statistics for a single switch.
Configuring Domain Interfaces
To configure domain interfaces from the Fabric Manager, choose FC > Domain Manager on the menu tree and click the Interfaces tab. The Information pane from the Fabric Manager displays domain interfaces for multiple switches.
To configure domain interfaces from the Device Manager, choose Domain Manager from the FC menu and click the Interfaces tab. The Domain Manager dialog box, with the Interfaces tab selected, displays domain interfaces for a single switch.
Configure the attributes for domain interfaces.
Viewing Domain Areas
To monitor domain areas from the Device Manager, choose Domain Manager from the FC menu and click the Areas tab. The Domain Manager dialog box, with the Areas tab selected, displays domain areas for a single switch.
Viewing Domain Area Ports
To monitor area ports for domains from the Device Manager, choose Domain Manager from the FC menu and click the Area Ports tab. The Domain Manager dialog box, with the Area Ports tab, displays area ports for domains for a single switch.
Specifying a Preferred or Static Domain ID
If you change the configured domain ID, the change is only accepted if the new domain ID is included in all the allowed domain ID lists currently configured in the VSAN. Alternatively, you can also configure zero-preferred domain ID.
Note
The 0 (zero) value can be configured only if you use the preferred option.
While the static option can be applied to runtime after a disruptive or nondisruptive restart, the preferred option is applied to runtime only after a disruptive restart.
Tip
When the FICON feature is enabled in a given VSAN, the domain ID for that VSAN will remain in the static state. You can change the static ID value but you cannot change it to the preferred option.
Setting Switch Priority
By default, the configured priority is 128. The valid range to set the priority is between 1 and 254. Priority 1 has the highest priority. Value 255 is accepted from other switches, but cannot be locally configured.
Any new switch cannot become the principal switch when it joins a stable fabric. During the principal switch selection phase, the switch with the highest priority becomes the principal switch. If two switches have the same configured priority, the switch with the lower WWN becomes the principal switch.
Configuring Allowed Domain ID Lists
By default, the valid range for an assigned domain ID list is from 1 to 239. You can specify a list of ranges to be in the allowed domain ID list and separate each range with a comma. The principal switch ensures that the domain requested by any switch in the fabric is specified in the allowed list.
Tip
If you configure an allowed list on one switch in the fabric, we recommend you configure the same list in all other switches in the fabric to ensure consistency.
An allowed domain ID list must satisfy the following conditions:
•
If this switch is a principal switch, all the currently assigned domain IDs must be in the allowed list.
•
If this switch is a subordinate switch, the local runtime domain ID must be in the allowed list.
•
The locally-configured domain ID of the switch must be in the allowed list.
•
The intersection of the assigned domain IDs with other already-configured domain ID lists must not be empty.
Merging Stable Fabrics
By default, the auto-reconfigure option is disabled. When you join two switches belonging to two different stable fabrics that have overlapping domains, the following cases apply:
•
If the auto-reconfigure option is enabled on both switches, a disruptive reconfiguration phase is started.
•
If the auto-reconfigure option is disabled on either or both switches, the links between the two switches become isolated.
The auto-reconfigure option takes immediate effect at runtime; you do not need to restart the fcdomain. If a domain is currently isolated due to domain overlap, and you later enable the auto-reconfigure option on both switches, the fabric continues to be isolated. However, if you enable the auto-reconfigure option on both switches before connecting the fabric, a disruptive reconfiguration (RCF) occurs. A disruptive reconfiguration may affect data traffic. You can nondiruptively reconfigure the fcdomain by changing the configured domains on the overlapping links and getting rid of the domain overlap.
Assigning Contiguous Domains
By default, the contiguous-allocation option is disabled. When the subordinate switches request the principal switch for two or more domains and the domains are not contiguous, the following cases apply:
•
If the contiguous-allocation option is enabled in the principal switch, the principal switch locates contiguous domains and assigns them to the subordinate switches.
•
If the contiguous-allocation option is disabled in the principal switch, the principal switch assigns the available domains to the subordinate switches.
The contiguous-allocation option takes immediate effect at runtime; you do not need to restart the fcdomain.
Disabling the fcdomain Feature
By default, the fcdomain feature is enabled on each switch. If you disable the fcdomain feature in a switch, that switch can no longer participate with other switches in the fabric.
The fcdomain configuration is applied to runtime through a disruptive restart.
Setting the Fabric Name
By default the configured fabric name is 20:01:00:05:30:00:28:df.
•
When the fcdomain feature is disabled, the runtime fabric name is the same as the configured fabric name.
•
When the fcdomain feature is enabled, the runtime fabric name is the same as the principal switch WWN.
The fabric name is applied to runtime through a disruptive restart when the fcdomain is configured as disabled.
Stopping Incoming RCFs
The rcf-reject option is configured on a per-interface, per-VSAN basis. By default, the rcf-reject option is disabled (that is, RCF request frames are not automatically rejected).
The rcf-reject option takes immediate effect to runtime through a disruptive restart.
Configuring Persistent FC IDs
By default, the persistent FC_ID feature is disabled. When a N/NL-port logs into a switch, and gets assigned an FC ID, the WWN of the requesting N/NL-port and the assigned FC ID is retained and stored in a volatile cache (the content is lost after a reboot).
If the persistent FC ID feature is disabled, binding of the FC ID to the WWN is preserved on a best effort basis.
For example, after the disconnection of one N-Port from the switch, if its FC ID is requested by another device, the request is granted and the initial association WWN FC ID is released. Also, if the 4K entries of the volatile cache used to store the WWN-to- FC ID binding get completely filled up, a new (more recent) entry will overwrite the oldest one, losing the corresponding binding WWN to FC ID.
The behavior is different for an N-Port than for an NL-Port:
•
N-ports should receive the same FC IDs if unplugged and plugged back in any port of the same switch (as long as it belongs to the same VSAN)
•
NL-port should receive the same FC IDs only if connected back to the same interface on the switch it was connected originally.
The assigned FC IDs in a fcdomain can be activated to remain persistent, even after a reboot. This ensures that an attached N Port receives the same FC ID after a switch reboot. If you enable this feature, the following apply:
•
The currently "in-use" FC IDs in the fcdomain will be saved across reboots.
•
The fcdomain automatically populates the database with dynamic entries that the switch has learned about after a device (host or disk) is plugged into a port interface.
To configure persistent FC IDs from the Fabric Manager, choose FC > Domain Manager on the menu tree and click the Persistent FCIDs tab. The Information pane from the Fabric Manager displays persistent FC IDs for multiple switches.
To configure persistent FC IDs from the Device Manager, choose Domain Manager from the FC menu and click the Persistent FCIDs tab. The Domain Manager dialog box, with the Persistent FCIDs tab selected, displays persistent FC IDs for a single switch.
Configure the attributes for persistent FC IDs.
Before you can create persistent FC IDs, you must:
•
Configure a static domain ID in that VSAN
•
Ascertain that the static configured domain and the runtime domain are the same. You can verify this using the show fcdomain command. For information about using the command line interface (CLI), refer to the Cisco 9000 Family Configuration Guide.
Note
If you connect to the switch from an AIX or HP-UX host, be sure to create the persistent FC ID in the VSAN that connects these hosts.
Note
Persistent FC IDs with loop-attache devices (FL ports) need to remain connected to the same port in which they were configured.
Creating a Persistent FC ID
To create a new persistent FC ID, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click Create. You see the Create Domain Manager Persistent FCIDs dialog box.
Step 2
Enter the VSAN ID.
Step 3
Enter the WWN.
Step 4
Enter the FC ID.
Step 5
Choose the mask. The mask is the number of FC IDs which are assigned either statically or dynamically for this WWN on this VSAN. Possible values are Single, meaning just one FCI ID is assigned, or Area, meaning all of the FC IDs in the area that is specified are assigned.
Step 6
Choose the assignment. The assignment is the type of persistency of this FC ID (static or dynamic).
Step 7
Click Create to create the persistent FC ID, or click Close to return to the Domain Manager without creating the FC ID.
Deleting a Persistent FC ID
To delete a persistent FC ID, follow these steps:
Step 1
Choose the persistent FC ID you want to delete. This enables the Delete button.
Step 2
Click Delete to delete the FC ID.
Configuring Persistent FC IDs Manually
Once the persistent FC ID feature is enabled, you can enter the persistent FC ID submode and add static or dynamic entries in the FC ID database. By default, all added entries are static. Persistent FC IDs are configured on a per-VSAN basis. Follow these requirements to manually configure a persistent FC ID:
•
Ensure that the persistent FC ID feature is enabled in the required VSAN.
•
Ensure that the required VSAN is an active VSAN. Persistent FC IDs can only be configured on active VSANs.
•
Verify that the domain part of the FC ID is the same as the runtime domain ID in the required VSAN. If the software detects a domain mismatch, the command is rejected.
•
Verify that the port field of the FC ID is 0 (zero) when configuring an area.
•
Do not replace an FC ID that is already configured in another WWN. If you want to use a previously-configured WWN, first delete the configured WWN before proceeding with this procedure.
Note
You cannot configure persistent FC IDs in FICON-enabled VSANs.
Configuring Unique Area FC IDs for Some HBAs
Note
This section does not apply if either the HBA port or the storage port is connected to different switches.
Some HBA ports require a different area ID than storage ports when they are both connected to the same switch. For example, if the storage port FC ID is 0x6f7704, the area for this port is 77. In this case, the HBA port area can be anything other than 77. The HBA port FC ID must be manually configured to be different from the storage port FC ID.
Switches in the Cisco MDS 9000 Family facilitate this requirement with the FC ID persistence feature. You can use this feature to preassign an FC ID with a different area to either the storage port or the HBA port. The procedure in this example uses a switch domain of 111(6f hex). The HBA port connects to interface fc1/9 and the storage port connects to interface FCC 1/10 in the same switch.
Enabling Persistent FC IDs
Persistent FC IDs are disabled by default. You can enable this option globally or for each VSAN. If you choose to enable it globally, you can do so at any time using the initial setup routine or the setup command. When you enable this option globally, the switch remains in this state until you change the global configuration.
Note
If you enable this option during the initial switch setup, this option will be automatically enabled in all configured VSANs. If you enable this option at a later stage, this option will be automatically enabled in all VSANs configured after that stage. VSANs configured before that stage will remain unchanged.
When a N or NL port logs into a Cisco MDS 9000 Family switch, it is assigned a FC ID. By default, the persistent FC ID feature is disabled. If this feature is disabled, the following consequences apply:
•
A N or NL port logs into a Cisco MDS 9000 Family switch, the WWN of the requesting N or NL port and the assigned FC ID, are retained and stored in a volatile cache. The contents of this volatile cache are not saved across reboots.
•
The switch is designed to preserve the binding FC ID to the WWN, on a best-effort basis. For example, if one N port disconnects from the switch and its FC ID is requested by another device, this request is granted, and the WWN with the initial FC ID association is released.
•
The volatile cache stores up to 4000 entries of WWN to FC ID binding. If this cache is full, a new (more recent) entry overwrites the oldest entry in the cache. In this case, the corresponding WWN to FC ID association for the oldest entry is lost.
•
The switch connection behavior differs between N ports and NL ports:
–
N ports receive the same FC IDs if disconnected and reconnected to any port within the same switch (as long as it belongs to the same VSAN).
–
NL ports receive the same FC IDs only if connected back to the same port on the switch to which it was originally connected.
The assigned FC IDs in a fcdomain can be enabled to remain persistent even after a reboot. This ensures that an attached N port receives the same FC IDs after a reboot. If you enable this feature, the following consequences apply:
•
The currently in-use FC IDs in the fcdomain are saved across reboots.
•
The fcdomain automatically populates the database with dynamic entries that the switch has learned about after a device (host or disk) is plugged into a port interface.
Note
If you connect to the switch from an AIX or HP-UX host, be sure to enable the persistent FC ID feature in the VSAN that connects these hosts.
Note
Persistent FC IDs with loop-attached devices (FL ports) need to remain connected to the same port in which they were configured.
A persistent FC ID assigned to an F port can be moved across interfaces and can continue to maintain the same persistent FC ID.
Purging Persistent FC IDs
Persistent FC IDs can be purged selectively. Static entries and FC IDs currently in use cannot be deleted. Table 26-1 identifies the FC ID entries that can be deleted.
Table 26-1 Purged FC IDs
static
in use
Not deleted
static
not in use
Not deleted
dynamic
in use
Not deleted
dynamic
not in use
deleted
Default Settings
Table 26-2 lists the default settings for all fcdomain parameters.

 Feedback
Feedback