Core Components
A Cisco Wireless network consists of the following core components:
-
Cisco Wireless Controllers: Cisco Wireless Controllers (controllers) are enterprise-class high-performance wireless switching platforms that support 802.11a/n and 802.11b/g/n protocols. They operate under control of the AireOS operating system, which includes the radio resource management (RRM), creating a Cisco Wireless solution that can automatically adjust to real-time changes in the 802.11 radio frequency (802.11 RF) environment. Controllers are built around high-performance network and security hardware, resulting in highly reliable 802.11 enterprise networks with unparalleled security.
The following controllers are supported:
-
Cisco Access Points: Cisco access points (APs) can be deployed in a distributed or centralized network for a branch office, campus, or large enterprise. For more information about APs, see https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/wireless/access-points/index.html
-
Cisco Prime Infrastructure (PI): Cisco Prime Infrastructure can be used to configure and monitor one or more controllers and associated APs. Cisco PI has tools to facilitate large-system monitoring and control. When you use Cisco PI in your Cisco wireless solution, controllers periodically determine the client, rogue access point, rogue access point client, radio frequency ID (RFID) tag location and store the locations in the Cisco PI database. For more information about Cisco PI, see https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/cloud-systems-management/prime-infrastructure/series.html.
-
Cisco Connected Mobile Experiences (CMX): Cisco Connected Mobile Experiences (CMX) acts as a platform to deploy and run Cisco Connected Mobile Experiences (Cisco CMX). Cisco Connected Mobile Experiences (CMX) is delivered in two modes—the physical appliance (box) and the virtual appliance (deployed using VMware vSphere Client) . Using your Cisco wireless network and location intelligence from Cisco MSE, Cisco CMX helps you create personalized mobile experiences for end users and gain operational efficiency with location-based services. For more information about Cisco CMX, see https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/wireless/connected-mobile-experiences/series.html.
-
Cisco DNA Spaces: Cisco DNA Spaces is a multichannel engagement platform that enables you to connect, know, and engage with visitors at their physical business locations. It covers various verticals of business such as retail, manufacturing, hospitality, healthcare, education, financial services, enterprise work spaces, and so on. Cisco DNA Spaces also provides solutions for monitoring and managing the assets in your premises.
The Cisco DNA Spaces: Connector enables Cisco DNA Spaces to communicate with multiple Cisco Wireless Controller (controller) efficiently by allowing each controller to transmit high intensity client data without missing any client information.
For information about how to configure Cisco DNA Spaces and the Connector, see https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/wireless/dna-spaces/products-installation-and-configuration-guides-list.html.
For more information about design considerations for enterprise mobility, see the Enterprise Mobility Design Guide at:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/wireless/controller/8-5/Enterprise-Mobility-8-5-Design-Guide/Enterprise_Mobility_8-5_Deployment_Guide.htmlOverview of Cisco Mobility Express
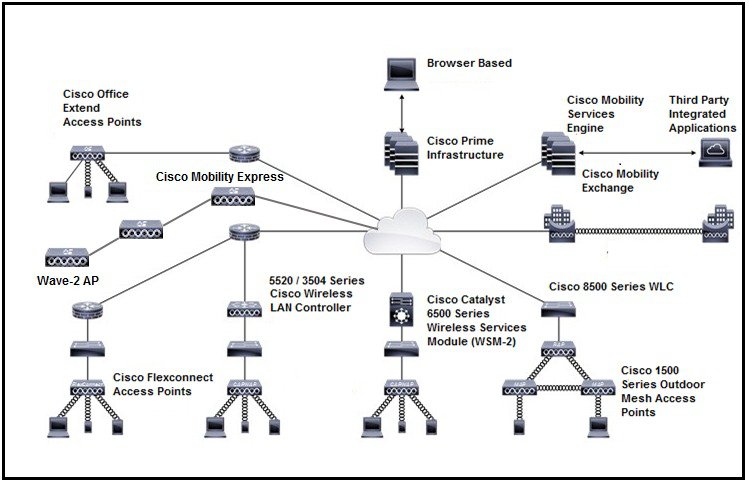
The Cisco Mobility Express wireless network solution comprises of at least one Cisco Wave 2 AP with an in-built software-based wireless controller managing other Cisco APs in the network.
The AP acting as the controller is referred to as the primary AP while the other APs in the Cisco Mobility Express network, which are managed by this primary AP, are referred to as subordinate APs.
In addition to acting as a controller, the primary AP also operates as an AP to serve clients along with the subordinate APs.
Cisco Mobility Express provides most features of a controller and can interface with the following:
-
Cisco Prime Infrastructure: For simplified network management, including managing AP groups
-
Cisco Identity Services Engine: For advanced policy enforcement
-
Connected Mobile Experiences (CMX): For providing presence analytics and guest access using Connect & Engage
For more information about using Cisco Mobility Express, see the user guide for relevant releases at: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/wireless/mobility-express/products-installation-and-configuration-guides-list.html
Single-Controller Deployments
A standalone controller can support lightweight access points across multiple floors and buildings simultaneously and support the following features:
-
Autodetecting and autoconfiguring lightweight access points as they are added to the network.
-
Full control of lightweight access points.
-
Lightweight access points connect to controllers through the network. The network equipment may or may not provide Power over Ethernet (PoE) to the access points.
Some controllers use redundant Gigabit Ethernet connections to bypass single network failures.
 Note |
Some controllers can connect through multiple physical ports to multiple subnets in the network. This feature can be helpful when you want to confine multiple VLANs to separate subnets. |
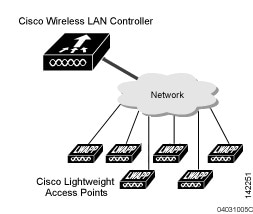
Multiple-Controller Deployments
Each controller can support lightweight access points across multiple floors and buildings simultaneously. However, full functionality of the Cisco wireless LAN solution occurs when it includes multiple controllers. A multiple-controller system has the following additional features:
-
Autodetecting and autoconfiguring RF parameters as the controllers are added to the network.
-
Same-subnet (Layer 2) roaming and inter-subnet (Layer 3) roaming.
-
Automatic access point failover to any redundant controller with a reduced access point load.
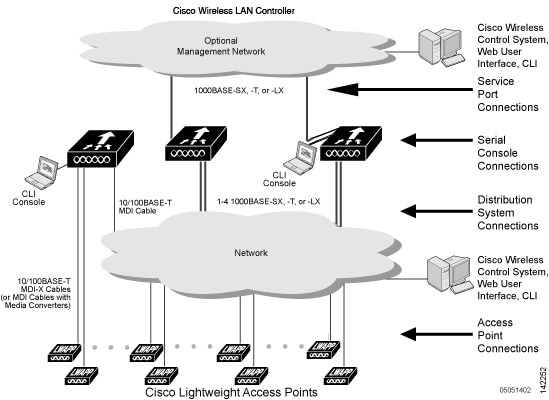
The following figure shows a typical multiple-controller deployment. The figure also shows an optional dedicated management network and the three physical connection types between the network and the controllers.
 Feedback
Feedback