- New and Changed Information
- Jabber Overview
- Configuration and Installation Workflows
- Configure Directory Integration
- Set Up Certificate Validation
- Service Discovery
- Configure a Service Profile
- Configure the IM and Presence Service
- Configure Voice and Video Communication
- Configure Voicemail
- Configure Conferencing
- Configure Client
- Integrate with Directory Sources
- Install Client
- Remote Access
- Troubleshooting
- Cisco Jabber Options
- Cisco Jabber Reference Information
Service Discovery
Configuration URL Workflow
| Command or Action | Purpose |
|---|
Configuration URL
To enable users to launch Cisco Jabber without having to manually enter service discovery information, create and distribute a configuration URL to users.
You can provide a configuration URL link to users by emailing the link to the user directly, or by posting the link to a website.
-
ServicesDomain—Required. Every configuration URL must include the domain of the IM and presence server that Cisco Jabber needs for service discovery.
-
VoiceServiceDomain—Required only if you deploy a hybrid cloud-based architecture where the domain of the IM and presence server differs from the domain of the voice server. Set this parameter to ensure that Cisco Jabber can discover voice services.
-
ServiceDiscoveryExcludedServices—Optional. You can exclude any of the following services from the service discovery process:
-
WEBEX—When you set this value, the client: -
CUCM—When you set this value, the client: -
CUP—When you set this value, the client:
You can specify multiple, comma-separated values to exclude multiple services.
If you exclude all three services, the client does not perform service discovery and prompts the user to manually enter connection settings.
-
-
ServicesDomainSsoEmailPrompt—Optional. Specifies whether the user is shown the email prompt for the purposes of determining their home cluster.
-
EnablePRTEncryption—Optional. Specifies that the PRT file is encrypted. Applies to Cisco Jabber for Mac.
-
PRTCertificateName—Optional. Specifies the name of the certificate. Applies to Cisco Jabber for Mac.
-
InvalidCertificateBehavior—Optional. Specifies the client behavior for invalid certificates.
-
PRTCertificateUrl—Specifies the name of a certificate with a public key in the trusted root certificate store. Applies to Cisco Jabber mobile clients.
-
Telephony_Enabled—Specifies whether the user has phone capability or not. The default is true. -
ForceLaunchBrowser—Used to force user to use the external browser. Applies to Cisco Jabber mobile clients. 
Note
ForceLaunchBrowser is used for client certificate deployments and for devices with Android OS below 5.0.
ciscojabber://provision?ServicesDomain=<domain_for_service_discover> &VoiceServicesDomain=<domain_for_voice_services> &ServiceDiscoveryExcludedServices=<services_to_exclude_from_service_discover> &ServicesDomainSsoEmailPrompt=<ON/OFF>
 Note |
-
ciscojabber://provision?ServicesDomain=cisco.com
-
ciscojabber://provision?ServicesDomain=cisco.com &VoiceServicesDomain=alphauk.cisco.com
-
ciscojabber://provision?ServicesDomain=service_domain &VoiceServicesDomain=voiceservice_domain&ServiceDiscoveryExcludedServices=WEBEX
-
ciscojabber://provision?ServicesDomain=cisco.com &VoiceServicesDomain=alphauk.cisco.com&ServiceDiscoveryExcludedServices=CUCM,CUP
-
ciscojabber://provision?ServicesDomain=cisco.com &VoiceServicesDomain=alphauk.cisco.com&ServiceDiscoveryExcludedServices=CUCM,CUP &ServicesDomainSsoEmailPrompt=OFF
Provide Users with Configuration URL from a Website
You can provide a configuration URL link to users by emailing the link to the user directly, or by posting the link to a website.
 Note | Due to a limitation of the Android operating system, Cisco Jabber for Android users can encounter an issue if they open the configuration URL directly from an Android application. To work around this issue, we recommend that you distribute your configuration URL link using a website. |
If you want to use the website explore option for URL provisioning, we recommended you to use Mozilla Firefox.
Use the following procedure to distribute the link from a website.
Mobile Configuration Using Enterprise Mobility Management
You can configure Cisco Jabber using EMM on Cisco Jabber for Android and Cisco Jabber for iPhone and iPad. For more information on setting up EMM, refer to the instructions for administrators provided by the EMM provider.
If you want Jabber to run only on managed devices, then you can deploy certificate-based authentication, and enroll the client certificate through EMM.
Manual Connection Settings
Manual connection settings provide a fallback mechanism when Service Discovery is not used.
When you start Cisco Jabber, you can specify the authenticator and server address in the Advanced settings window. The client caches the server address to the local application configuration that loads on subsequent starts.
-
On-Premises with Cisco Unified Communications Manager release 9.x and Later — If the client cannot get the authenticator and server addresses from the service profile.
-
Cloud-Based or On-Premises with Cisco Unified Communications Manager release 8.x — If you do not set the authenticator in the bootstrap file. The client also prompts users to enter server addresses in the Advanced settings window if you do not set server addresses in the bootstrap file or with SRV records.
Settings that you enter in the Advanced settings window take priority over any other sources including SRV records and bootstrap settings.
If you select either Cisco IM & Presence or Cisco Communications Manager 8.xoptions, the client retrieves UC services from Cisco Unified Presence or Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service. The client does not use service profiles or SSO discovery.
 Note | For Cisco Jabber for Windows, service discovery stops after 20 seconds regardless of the number of servers the SRV record resolves to. During service discovery, once Cisco Jabber finds _cisco-uds, it attempts to connect to the first 2 servers within 20 seconds. Cisco Jabber doesn't attempt to connect to any servers after it's attempted service discovery for the highest 2 priority servers. Users can manually point to the working server or re-order SRV priorities to at least one of the top two priority servers available for service discovery. |
- Automatic Connection Setting for Service Discovery
- Manual Connection Settings for On-Premises Deployments
- Manual Connection Settings for On-Premises Deployments in Phone Mode
- Manual Connection Settings for Cloud-Based Deployments
Automatic Connection Setting for Service Discovery
Users can select the Automatic option in the Advanced settings window to discover servers automatically.
The Automatic option allows users change from manually setting the service connection details to using service discovery. For example, on the initial launch, you manually set the authenticator and specify a server address in the Advanced settings window.
The client always checks the cache for manual settings. The manual settings take higher priority over SRV records, and for Cisco Jabber for Windows, the bootstrap file. For this reason, if you decide to deploy SRV records and use service discovery, you override the manual settings from the initial launch.
Manual Connection Settings for On-Premises Deployments
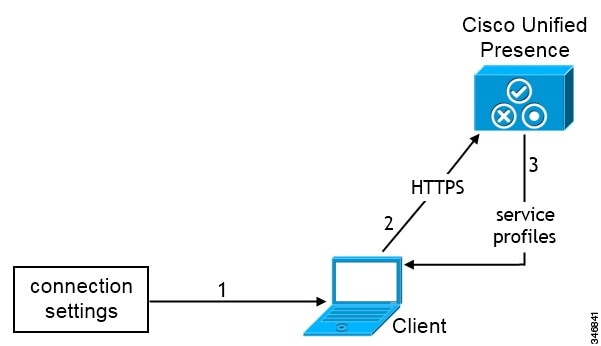
Users can set Cisco Unified Presence or Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service as the authenticator and specify the server address in the Advanced settings window.
You can automatically set the default server address with the _cuplogin SRV record.
Manual Connection Settings for On-Premises Deployments in Phone Mode
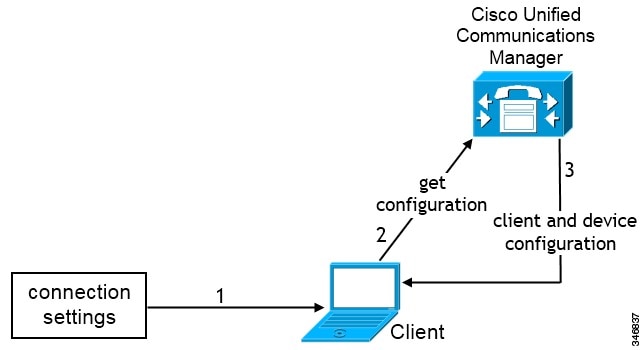
Users can set Cisco Unified Communications Manager as the authenticator and specify the following server addresses in the Advanced settings window:
Manual Connection Settings for Cloud-Based Deployments
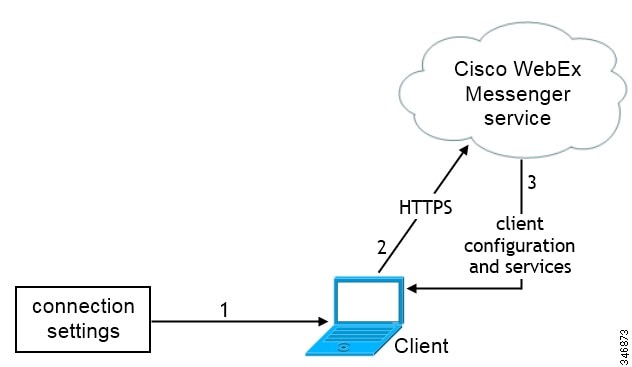
Users can set the Cisco WebEx Messenger service as the authenticator and specify the CAS URL for login in the Advanced settings window.
Installer Switches: Cisco Jabber for Windows
When you install Cisco Jabber, you can specify the authenticator and server addresses. The installer saves these details to a bootstrap file. When users launch the client for the first time, it reads the bootstrap file. The bootstrap file takes priority if service discovery is deployed.
Bootstrap files provide a fallback mechanism for service discovery in situations where service discovery has not been deployed and where you do not want users to manually specify their connection settings.
The client only reads the bootstrap file on the initial launch. After the initial launch, the client caches the server addresses and configuration, and then loads from the cache on subsequent launches.
We recommend that you do not use a bootstrap file, and instead use service discovery, in on-premises deployments with Cisco Unified Communications Manager release 9.x and later.
- Bootstrap Settings for On-Premises Deployments
- Bootstrap Settings for On-Premises Deployments in Phone Mode
- Bootstrap Settings for Cloud-Based Deployments
Bootstrap Settings for On-Premises Deployments
|
Product Mode |
Server Releases |
Argument Values |
|---|---|---|
|
Full UC (Default Mode) |
|
Use the following installer switches and values: |
|
Full UC (Default Mode) |
|
Use the following installer switches and values: |
|
IM Only (Default Mode) |
|
Use the following installer switches and values: |
|
IM Only (Default Mode) |
|
Use the following installer switches and values: |
-
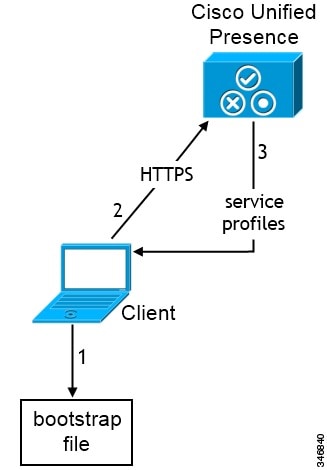
The client retrieves settings from the bootstrap file.
The client starts in default mode and determines that Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service is the authenticator. The client also gets the address of the presence server, unless Service Discovery results dictate otherwise.
-
The client authenticates to Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service .
-
The client retrieves service profiles from the presence server.
Bootstrap Settings for On-Premises Deployments in Phone Mode
-
Set CUCM as the value for AUTHENTICATOR.
-
Set phone_mode as the value for PRODUCT_MODE.
-
Set the TFTP server address as the value for TFTP.
-
Set the CTI server address as the value for CTI.
-
Set the CCMCIP server address as the value for CCMCIP.
Cisco Unified Communications Manager release 9.x and earlier—If you enable Cisco Extension Mobility, the Cisco Extension Mobility service must be activated on the Cisco Unified Communications Manager nodes that are used for CCMCIP. For information about Cisco Extension Mobility, see the Feature and Services guide for your Cisco Unified Communications Manager release.
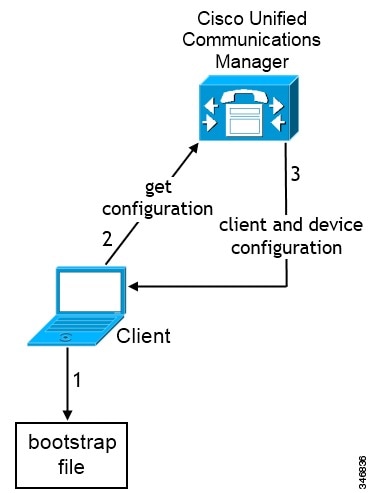
-
The client retrieves settings from the bootstrap file.
The client starts in phone mode and determines that Cisco Unified Communications Manager is the authenticator. The client also gets the addresses for the TFTP server (and CTI servers for Jabber for Windows and Jabber for Mac), unless Service Discovery results dictate otherwise.
-
The client authenticates to Cisco Unified Communications Manager and gets configuration.
-
The client retrieves device and client configuration.
Bootstrap Settings for Cloud-Based Deployments
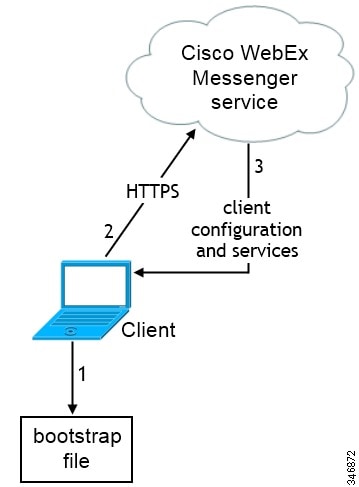
-
The client retrieves settings from the bootstrap file.
The client starts in default mode and determines that the Cisco WebEx Messenger service is the authenticator, unless Service Discovery results dictate otherwise.
-
The client authenticates to the Cisco WebEx Messenger service.
-
The client retrieves configuration and services.
 Feedback
Feedback