Cisco IP Phone Hardware Overview
The Cisco IP Phone 7800 Series provides voice communication over an Internet Protocol (IP) network. The CiscoIPPhone functions much like a digital business phone, allowing you to place and receive phone calls and to access features such as mute, hold, transfer, speed dial, call forward, and more. In addition, because the phone connects to your data network, it offers enhanced IP telephony features, including access to network information and services, and customizable features and services.
The Cisco IP Phone 7841 supports Gigabit ethernet connectivity.
When adding features to the phone line keys, you are limited by the number of line keys available. You cannot add more features than the number of line keys on your phone.
|
Phone |
Supported Line Keys |
|---|---|
|
Cisco IP Phone 7811 |
0 |
|
Cisco IP Phone 7821 |
2 |
|
Cisco IP Phone 7841 |
4 |
|
Cisco IP Phone 7861 |
16 |
-
G.711 a-law
-
G.711 mu-law
-
G.722
-
G722.2 AMR-WB
-
G.729a
-
G.729ab
-
iLBC
-
Opus
-
G.711 a-law
-
G.711 mu-law
-
G.722
-
G.729
-
G.729a
-
G.729b
-
G.729ab
-
iLBC
-
Opus
 Caution |
Use of a cell, mobile, or GSM phone, or two-way radio in close proximity to a CiscoIP Phone might cause interference. For more information, see the manufacturer documentation of the interfering device. As with other network devices, you must configure Cisco IP Phones to prepare them to access Cisco Unified Communications Manager and the rest of the IP network. By using DHCP, you have fewer settings to configure on a phone. If your network requires it, however, you can manually configure information such as: an IP address, TFTP server, and subnet information. Cisco IP Phones can interact with other services and devices on your IP network to provide enhanced functionality. For example, you can integrate Cisco Unified Communications Manager with the corporate Lightweight Directory Access Protocol 3 (LDAP3) standard directory to enable users to search for coworker contact information directly from their IP phones. You can also use XML to enable users to access information such as weather, stocks, quote of the day, and other web-based information. |
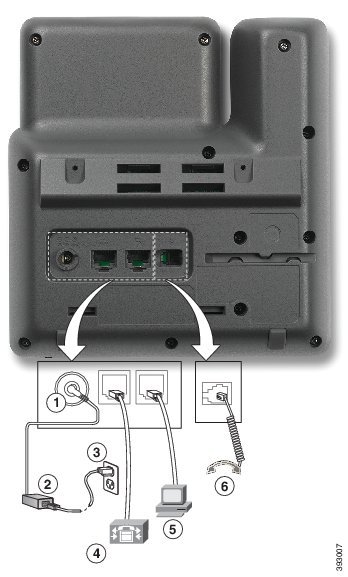

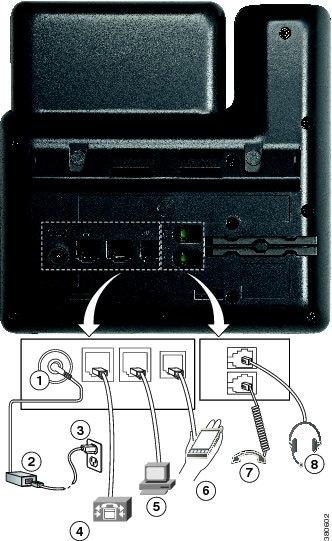
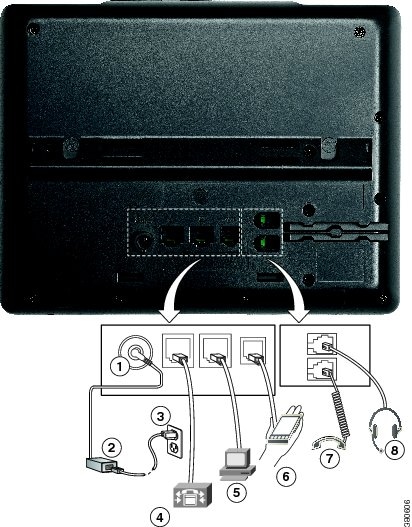

 Feedback
Feedback