Information About MRP
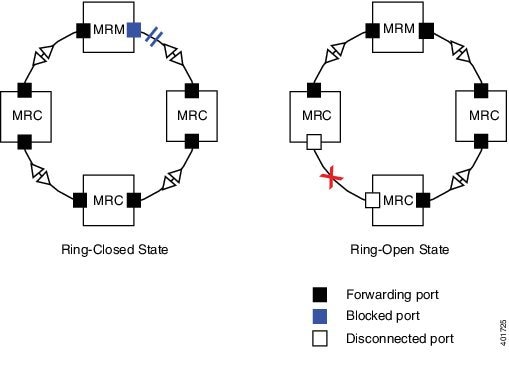
Media Redundancy Protocol (MRP), defined in International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standard 62439-2, provides fast convergence in a ring network topology for Industrial Automation networks. MRP Media Redundancy Manager (MRM) defines its maximum recovery times for a ring in the following range: 10 ms, 30 ms, 200 ms and 500 ms.
 Note |
The default maximum recovery time on the Cisco IE switch is 200 ms for a ring composed of up to 50 nodes. You can configure the switch to use the 30 ms or the 500 ms recovery time profile as described in Configuring MRP Manager. The 10 ms recovery time profile is not supported. |
MRP is supported on the following switches:
-
Cisco Catalyst IE3x00 Rugged Series Switches (IE3200, IE3300, and IE3400)
-
Cisco Catalyst IE3400 Heavy Duty Series Switches
-
Cisco Catalyst IE3100 Rugged Series Switches (IE3100 and IE3105)
 Note |
MRP is not supported on Cisco Catalyst ESS3300 Switches. |
MRP operates at the MAC layer and is commonly used in conjunction with the PROFINET standard for industrial networking in manufacturing.
|
Feature |
Release information |
Feature description |
|---|---|---|
|
PTP over MRP |
Release 17.18.1 |
From Cisco IOS-XE 17.18.1 onwards, PTP support over Media Redundancy Protocol (MRP) is introduced. |
 Feedback
Feedback