- Preface
- Overview
- Configuring Fibre Channel Domain Parameters
- Configuring and Managing VSANs
- DPVM
- Configuring VSAN Trunking
- Configuring and Managing Zones
- Distributing Device Alias Services
- Configuring Fibre Channel Routing Services and Protocols
- Managing FLOGI, Name Server, FDMI, and RSCN Databases
- Advanced Fibre Channel Features
- Configuring FC-SP and DHCHAP
- Configuring Port Security
- Configuring Fabric Binding
- Configuring Port Tracking
- Index
IVR Zones and Zonesets
- Information about IVR Zones and Zonesets
- Default Settings
- Licensing Requirements
- Guidelines and Limitations
- Configuring IVR Zones and Zonesets
- Verifying IVR Configuration
- Feature History
Information about IVR Zones and Zonesets
As part of the IVR configuration, you need to configure one or more IVR zones to enable cross-VSAN communication. To achieve this result, you must specify each IVR zone as a set of (pWWN, VSAN) entries. Like zones, several IVR zone sets can be configured to belong to an IVR zone. You can define several IVR zone sets and activate only one of the defined IVR zone sets.
 Note |
The same IVR zone set must be activated on all of the IVR-enabled switches |
| IVR Zones | Zones |
|---|---|
| IVR zone membership is specified using the VSAN and pWWN combination. | Zone membership is specified using pWWN, fabric WWN, sWWN, or the AFID. |
| Default zone policy is always deny (not configurable). | Default zone policy is deny (configurable). |
As part of the IVR configuration, you need to configure one or more IVR zone to enable cross-VSAN communication. To achieve this, you must specify each IVR zone as a set of (pWWN, VSAN) entries. Different IVR zone sets can contain the same IVR zone, because IVR zones can be members of one or more IVR zone sets.
Automatic IVR Zone Creation
To allow pwwn1 to communicate with pwwn2, they must be in the same zone in VSAN 1, as well as in VSAN 2. If they are not in the same zone, then the hard-zoning ACL entries will prohibit pwwn1 from communicating with pwwn2.
A zone corresponding to each active IVR zone is automatically created in each edge VSAN specified in the active IVR zone. All pWWNs in the IVR zone are members of these zones in each VSAN.
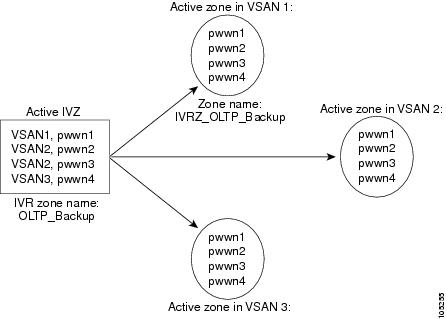
The zones are created automatically by the IVR process when an IVR zone set is activated. They are not stored in a full zone set database and are lost when the switch reboots or when a new zone set is activated. The IVR feature monitors these events and adds the zones corresponding to the active IVR zone set configuration when a new zone set is activated. Like zone sets, IVR zone sets are also activated nondisruptively.
 Note |
If pwwn1 and pwwn2 are in an IVR zone in the current as well as the new IVR zone set, then activation of the new IVR zone set does not cause any traffic disruption between them. |
If pwwn1 and pwwn2 are in an IVR zone in the current as well as the new IVR zone set, then activation of the new IVR zone set does not cause any traffic disruption between them.
Default Settings
| Parameters | Default |
|---|---|
| IVR feature | Disabled |
| IVR NAT | Disabled |
| IVR distribution | Disabled |
| IVR Autotopology | Disabled |
| IVR VSANs | Not added to virtual domains |
| QoS for IVR Zones | Low |
Licensing Requirements
| Product | License |
|---|---|
| Cisco Nexus 7000 Series. | IVR requires the FCoE license for each F-series module. FCoE enabled in a storage VDC does not require the Advanced Services License. IVR also requires the Storage Enterprise License. For a complete explanation of the Cisco NX-OS licensing scheme and how to obtain and apply licenses, see the Cisco NX-OS Licensing Guide. |
Guidelines and Limitations
When interop mode is enabled, consider the following IVR configuration guidelines:
-
When a member's native VSAN is in interop mode (for example, when the interop mode is 2, 3, or 4), then ReadOnly, the QoS attribute, and LUN zoning are not permitted
-
When a member’s VSAN is already in interop mode and an attempt is made to configure ReadOnly, the QoS attribute, or LUN zoning, a warning message is displayed to indicate that the configuration is not permitted.
-
When you configure ReadOnly, the QoS attribute, or LUN zoning first, and then change the member’s VSAN interop mode, a warning message is displayed to indicate the configuration is not permitted. You are then prompted to change the configuration.
switch(config)# vsan database switch(config-vsan-db)# vsan 2 switch(config-vsan-db)# vsan 2 interop 2 switch(config-vsan-db)# exit switch(config)# ivr zoneset name ivr_zs1 switch(config-ivr-zoneset)# zone name ivr_z1 switch(config-ivr-zoneset-zone)# member pwwn 21:00:00:14:c3:3d:45:22 lun 0x32 vsan 2 VSAN is in interop mode, and LUN zoning cannot be set. switch(config)# ivr zoneset name ivr_zs1 switch(config-ivr-zoneset)# zone name ivr_z1 switch(config-ivr-zoneset-zone)# member pwwn 21:00:00:14:c3:3d:45:22 vsan 2 switch(config-ivr-zoneset-zone)# attribute read-only VSAN is in interop mode and zone member has been configured, zone cannot be set to READ-ONLY. switch(config-ivr-zoneset-zone)# attribute qos priority medium VSAN is in interop mode and zone member has been configured, QoS cannot be assigned to zone.
Configuring IVR Zones and Zonesets
- Configuring IVR Zones
- Configuring IVR Zone Sets
- Configuring LUNs in IVR Zoning
- Configuring the QoS Attribute
- Configuring Read-only Zoning
Configuring IVR Zones
3.
member pwwn pwwn vsan vsan-id
4.
(Optional) show ivr pending-diff
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | configure terminal Example: switch# configure terminal switch(config)# |
Enters configuration mode. |
| Step 2 | ivr zone name zonename Example: switch(config)# ivr zone name sample_vsan2-3 switch(config-ivr-zone)# |
Creates the IVR zone and enters IVR zone configuration mode. The zonename can be any case-sensitive, alphanumeric string up to 59 characters. |
| Step 3 | member pwwn pwwn vsan vsan-id Example: switch(config-ivr-zone)# member pwwn 21:00:00:20:37:c8:5c:6b vsan 2 |
Adds the specified pWWN in VSAN 2 as an IVR zone member. The pwwn is in colon-separated hexadecimal format. The vsan range is from 1 to 4093. |
| Step 4 | show ivr pending-diff Example: switch(config-ivr-zone)# show ivr pending-diff |
(Optional) Displays information about the pending changes to the IVR database. This displays changes that have not been committed yet. |
| Step 5 | show ivr zone Example: switch(config-ivr-zone)# show ivr zone |
(Optional) Displays information about the zones in the active zone database. |
| Step 6 | ivr commit Example: switch(config-ivr-zone)# ivr commit |
(Optional) Commits all pending changes to IVR to the active IVR database and distributes these changes to all IVR-enabled switches in the fabric. |
You must commit the IVR changes to make these changes permanent and distribute the changes to all IVR-enabled switches in the fabric.
Configuring IVR Zone Sets
2.
ivr zoneset name zoneset-name
4.
(Optional) show ivr pending-diff
5.
(Optional) show ivr zoneset
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | configure terminal Example: switch# configure terminal switch(config)# |
Enters configuration mode. |
| Step 2 | ivr zoneset name zoneset-name Example: switch(config)# ivr zoneset name ivrZoneset1 switch(config-ivr-zoneset)# |
Creates the IVR zone set and enters IVR zone set configuration mode. The zoneset-name can be any case-sensitive, alphanumeric string up to 59 characters. |
| Step 3 | member zonename Example: switch(config-ivr-zoneset)# member sample_vsan2-3 |
Adds the specified IVR zone as an IVR zone set member. The zoneset-name can be any case-sensitive, alphanumeric string up to 59 characters. |
| Step 4 | show ivr pending-diff Example: switch(config-ivr-zoneset)# show ivr pending-diff |
(Optional) Displays information about the pending changes to the IVR database. This displays changes that have not been committed yet. |
| Step 5 | show ivr zoneset Example: switch(config-ivr-zoneset)# show ivr zoneset |
(Optional) Displays information about the zone sets in the active zone set database. |
| Step 6 | ivr commit Example: switch(config-ivr-zoneset)# ivr commit |
(Optional) Commits all pending changes to IVR to the active IVR database and distributes these changes to all IVR-enabled switches in the fabric. |
You must commit the IVR changes to make these changes permanent and distribute the changes to all IVR-enabled switches in the fabric. You must also activate the zone set.
Configuring LUNs in IVR Zoning
LUN zoning can be used between members of active IVR zones. You can configure the service by creating and activating LUN zones between the desired IVR zone members in all relevant edge VSANs using the zoning interface or you can use LUN zoning directly supported by IVR.
3.
member pwwn pwwn lun lun-id vsan vsan-id [ autonomous-fabric-id afid]
4.
(Optional) show ivr pending-diff
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | configure terminal Example: switch# configure terminal switch(config)# |
Enters configuration mode. |
||
| Step 2 | ivr zone name zonename Example: switch(config)# ivr zone name ivrLunZone switch(config-ivr-zone)# |
Creates the IVR zone and enters IVR zone configuration mode. The zonename can be any case-sensitive, alphanumeric string up to 59 characters. |
||
| Step 3 | member pwwn pwwn lun lun-id vsan vsan-id [ autonomous-fabric-id afid] Example: switch(config-ivr-zone)# member pwwn 21:00:00:20:37:c8:5c:6b lun 0x64 vsan 2 |
Configures an IVR zone member based on the specified pWWN and LUN value.
The pwwn is in colon-separated hexadecimal format. The lun-id is in hexadecimal notation. The vsan range is from 1 to 4093. |
||
| Step 4 | show ivr pending-diff Example: switch(config-ivr-zone)# show ivr pending-diff |
(Optional) Displays information about the pending changes to the IVR database. This displays changes that have not been committed yet. |
||
| Step 5 | show ivr zone Example: switch(config-ivr-zone)# show ivr zone |
(Optional) Displays information about the zones in the active zone database. |
||
| Step 6 | ivr commit Example: switch(config-ivr-zone)# ivr commit |
(Optional) Commits all pending changes to IVR to the active IVR database and distributes these changes to all IVR-enabled switches in the fabric. |
Configuring the QoS Attribute
3.
attribute qos priority { low | medium | high}
4.
(Optional) show ivr pending-diff
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | configure terminal Example: switch# configure terminal switch(config)# |
Enters configuration mode. |
| Step 2 | ivr zone name zonename Example: switch(config)# ivr zone name sample_vsan2-3 switch(config-ivr-zone)# |
Creates the IVR zone and enters IVR zone configuration mode. The zonename can be any case-sensitive, alphanumeric string up to 59 characters. |
| Step 3 | attribute qos priority { low | medium | high} Example: switch(config-ivr-zone)# attribute qos priority medium |
Configures the QoS for IVR zone traffic. |
| Step 4 | show ivr pending-diff Example: switch(config-ivr-zone)# show ivr pending-diff |
(Optional) Displays information about the pending changes to the IVR database. This displays changes that have not been committed yet. |
| Step 5 | show ivr zone Example: switch(config-ivr-zone)# show ivr zone |
(Optional) Displays information about the zones in the active zone database. |
| Step 6 | ivr commit Example: switch(config-ivr-zone)# ivr commit |
(Optional) Commits all pending changes to IVR to the active IVR database and distributes these changes to all IVR-enabled switches in the fabric. |
Configuring Read-only Zoning
 Note |
Read-only zoning cannot be configured in an IVR zone set setup. |
4.
(Optional) show ivr pending-diff
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | configure terminal Example: switch# configure terminal switch(config)# |
Enters configuration mode. |
| Step 2 | ivr zone name zonename Example: switch(config)# ivr zone name sample_vsan2-3 switch(config-ivr-zone)# |
Enters IVR zone configuration mode. The zonename can be any case-sensitive, alphanumeric string up to 59 characters. |
| Step 3 | attribute read-only Example: switch(config-ivr-zone)# attribute read-only |
Configures the QoS for IVR zone traffic. |
| Step 4 | show ivr pending-diff Example: switch(config-ivr-zone)# show ivr pending-diff |
(Optional) Displays information about the pending changes to the IVR database. This displays changes that have not been committed yet. |
| Step 5 | show ivr zone Example: switch(config-ivr-zone)# show ivr zone |
(Optional) Displays information about the zones in the active zone database. |
| Step 6 | ivr commit Example: switch(config-ivr-zone)# ivr commit |
(Optional) Commits all pending changes to IVR to the active IVR database and distributes these changes to all IVR-enabled switches in the fabric. |
Verifying IVR Configuration
To display the IVR configuration, perform one of the following tasks:
| Command |
Purpose |
|---|---|
show ivr |
Displays the status for the IVR configuration. |
| show ivr diagnostics |
Displays information about IVR diagnostics. |
show ivr merge status |
Displays information the last IVR merge event. |
show ivr pending |
Displays information about the IVR pending database. |
show ivr pending-diff |
Displays the differences between the pending database and the config database. |
show ivr vsan-topology [active | configured] |
Displays the IVR VSAN topology. |
show ivr session status |
Displays information about IVR CFS session. |
show ivr virtual-domains |
Displays information about IVR virtual domains for all local VSANs. |
show ivr zone |
Displays information about IVR zones. |
show ivr zoneset |
Displays information about IVR zone sets. |
show ivr service-group active |
Displays information about the active service group. |
| show ivr service-group configured | Displays information about the configured service group. |
| show autonomous-fabric-id database | Displays information about the AFIDs. |
| show ivr virtual-fcdomain-add-status | Displays the status of the IVR virtual domain configuration. |
Feature History
| Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
| IVR |
5.2(1) |
This feature was introduced. |
 Feedback
Feedback