Licensing Requirements
For a complete explanation of Cisco NX-OS licensing recommendations and how to obtain and apply licenses, see the Cisco NX-OS Licensing Guide.
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
This chapter contains the following sections:
For a complete explanation of Cisco NX-OS licensing recommendations and how to obtain and apply licenses, see the Cisco NX-OS Licensing Guide.
The Ethernet ports can operate as standard Ethernet interfaces connected to servers or to a LAN.
The Ethernet interfaces are enabled by default.
You can enable the various capabilities of the Ethernet interfaces on a per-interface basis using the interface command. When you enter the interface command, you specify the following information:
Interface type—All physical Ethernet interfaces use the ethernet keyword.
Slot number:
Slot 1 includes all the fixed ports.
Slot 2 includes the ports on the upper expansion module (if populated).
Slot 3 includes the ports on the lower expansion module (if populated).
Slot 4 includes the ports on the lower expansion module (if populated).
Port number— Port number within the group.
The interface numbering convention is extended to support use with a Cisco Nexus Fabric Extender as follows:
switch(config)# interface ethernet [chassis/]slot/port
The chassis ID is an optional entry that you can use to address the ports of a connected Fabric Extender. The chassis ID is configured on a physical Ethernet or EtherChannel interface on the switch to identify the Fabric Extender discovered through the interface. The chassis ID ranges from 100 to 199.
The Cisco-proprietary Unidirectional Link Detection (UDLD) protocol allows ports that are connected through fiber optics or copper (for example, Category 5 cabling) Ethernet cables to monitor the physical configuration of the cables and detect when a unidirectional link exists. When the switch detects a unidirectional link, UDLD shuts down the affected LAN port and alerts the user. Unidirectional links can cause a variety of problems, including spanning tree topology loops.
UDLD is a Layer 2 protocol that works with the Layer 1 protocols to determine the physical status of a link. At Layer 1, autonegotiation takes care of physical signaling and fault detection. UDLD performs tasks that autonegotiation cannot perform, such as detecting the identities of neighbors and shutting down misconnected LAN ports. When you enable both autonegotiation and UDLD, Layer 1 and Layer 2 detections work together to prevent physical and logical unidirectional connections and the malfunctioning of other protocols.
A unidirectional link occurs whenever traffic transmitted by the local device over a link is received by the neighbor but traffic transmitted from the neighbor is not received by the local device. If one of the fiber strands in a pair is disconnected, and if autonegotiation is active, the link does not stay up. In this case, the logical link is undetermined, and UDLD does not take any action. If both fibers are working normally at Layer 1, then UDLD at Layer 2 determines whether those fibers are connected correctly and whether traffic is flowing bidirectionally between the correct neighbors. This check cannot be performed by autonegotiation, because autonegotiation operates at Layer 1.
A Cisco Nexus device periodically transmits UDLD frames to neighbor devices on LAN ports with UDLD enabled. If the frames are echoed back within a specific time frame and they lack a specific acknowledgment (echo), the link is flagged as unidirectional and the LAN port is shut down. Devices on both ends of the link must support UDLD in order for the protocol to successfully identify and disable unidirectional links.
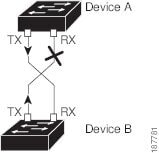
The following figure shows an example of a unidirectional link condition. Device B successfully receives traffic from Device A on the port. However, Device A does not receive traffic from Device B on the same port. UDLD detects the problem and disables the port.
The following table shows the default UDLD configuration.
|
Feature |
Default Value |
|---|---|
|
UDLD global enable state |
Globally disabled |
|
UDLD aggressive mode |
Disabled |
|
UDLD per-port enable state for fiber-optic media |
Enabled on all Ethernet fiber-optic LAN ports |
|
UDLD per-port enable state for twisted-pair (copper) media |
Disabled on all Ethernet 10/100 and 1000BASE-TX LAN ports |
UDLD aggressive mode is disabled by default. You can configure UDLD aggressive mode only on point-to-point links between network devices that support UDLD aggressive mode. If UDLD aggressive mode is enabled, when a port on a bidirectional link that has a UDLD neighbor relationship established stops receiving UDLD frames, UDLD tries to reestablish the connection with the neighbor. After eight failed retries, the port is disabled.
To prevent spanning tree loops, nonaggressive UDLD with the default interval of 15 seconds is fast enough to shut down a unidirectional link before a blocking port transitions to the forwarding state (with default spanning tree parameters).
When you enable the UDLD aggressive mode, the following occurs:
One side of a link has a port stuck (both transmission and receive)
One side of a link remains up while the other side of the link is down
In these cases, the UDLD aggressive mode disables one of the ports on the link, which prevents traffic from being discarded.
Cisco Nexus 3000 Series switches have a number of fixed 10-Gigabit ports; each is equipped with SFP+ interface adapters. Cisco Nexus 3100 Series switches have 32 Quad Same Factor Pluggable (QSFP) ports and 4 SFP+ interface adapters. The default speed for these 32 ports is 40 Gbps.
 Note |
If you set a port configuration that does not use all of the ports, the unused ports are left in the removed state. For example, if you configure 96 x 25G + 32 x 100G on a Cisco Nexus 3264C-E platform switch, the configuration uses 56 ports and leaves 8 ports in the removed state. Where:
|
You can operate QSFP ports as either 40-Gigabit Ethernet or 4 x10-Gigabit Ethernet modes on Cisco Nexus 3132 and Cisco Nexus 3172 switches. By default, there are 32 ports in the 40-Gigabit Ethernet mode. These 40-Gigabit Ethernet ports are numbered in a 2-tuple naming convention. For example, the second 40-Gigabit Ethernet port is numbered as 1/2. The process of changing the configuration from 40-Gigabit Ethernet to 10-Gigabit Ethernet is called breakout and the process of changing the configuration from 10-Gigabit Ethernet to Gigabit Ethernet is called breakin. When you break out a 40-Gigabit Ethernet port into 10-Gigabit Ethernet ports, the resulting ports are numbered using a 3-tuple naming convention. For example, the break-out ports of the second 40-Gigabit Ethernet port are numbered as 1/2/1, 1/2/2, 1/2/3, 1/2/4.
You can break out the 40-Gigabit Ethernet port into four 10-Gigabit Ethernet ports by using the speed 10000 command and using a splitter cable to connect to multiple peer switches. You can break in four 10-Gigabit Ethernet ports to a 40-Gigabit Ethernet port by using the speed 40000 command. The configuration change from 40-Gigabit Ethernet to 10-Gigabit Ethernet and from 10-Gigabit Ethernet to 40-Gigabit Ethernet takes effect immediately. You do not need to reload the switch. A QSFP transceiver security check is also performed.
 Note |
When you break out from 40-Gigabit Ethernet to 10-Gigabit Ethernet, or break in from 10-Gigabit Ethernet to 40-Gigabit Ethernet, all interface configurations are reset, and the affected ports are administratively unavailable. To make these ports available, use the no shut command. |
 Note |
Starting with Release 6.0(2)U5(1), a new QSFP+ 40-Gb transceiver is now supported on the Cisco Nexus 3000 Series switches. The new QSFP+ (40-Gb) transceiver has a cable that splits into four 10Gb SFP-10G-LR transceivers. To use it, you need the port to be in 4x10G mode. If you are using the breakout cable, you need to run that 40G port in 4x10G mode. |
The ability to break out a 40-Gigabit Ethernet port into four 10-Gigabit Ethernet ports and break in four 10-Gigabit Ethernet ports into a 40-Gigabit Ethernet port dynamically allows you to use any of the breakout-capable ports to work in the 40-Gigabit Ethernet or 10-Gigabit Ethernet modes without permanently defining them.
For Cisco Nexus 3132Q switches, when the Ethernet interface 1/1 is in the 40-Gigabit Ethernet mode, the first QSFP port is active. After breakout, when the Ethernet interface 1/1/1-4 is in the 10-Gigabit Ethernet mode, you can choose to use either QSFP ports or SFP+ ports. However, both the first QSFP port and the four SFP+ ports cannot be active at the same time.
When using a QSFP-40G-CR4 on Cisco Nexus 3000 switches, you must configure the default speed as 40G in the auto-negotiation parameters. Otherwise, the interface may not be able to bring the link up.
| Nexus 3100 Series Switches | Ports | Port Modes |
|---|---|---|
| Cisco Nexus 3132Q | 32 x QSFP ports and 4 SFP+ ports |
The Fixed32x40G port mode does not support breakout. |
| Cisco Nexus 3132Q-V | 32 x 40G QSFP ports |
|
| Cisco Nexus 31108PC-V | 48 x 10G SFP+ ports and 6 x 100G QSFP ports |
The following two port modes are supported:
The following features are specific to port mode-1:
The following features are specific to port mode-2:
|
| Cisco Nexus 31108TC-V | 48 x 10GBase-T and 6 x 100G ports |
The following two port modes are supported:
The following features are specific to port mode-1:
The following features are specific to port mode-2:
|
| Cisco Nexus 3172PQ | 6 x QSFP ports and 48 SFP+ ports |
|
The Switch Virtual Interface (SVI) represents a logical interface between the bridging function and the routing function of a VLAN in the device. By default, when a VLAN interface has multiple ports in the VLAN, the SVI goes to the down state when all the ports in the VLAN go down.
Autostate behavior is the operational state of an interface that is governed by the state of the various ports in its corresponding VLAN. An SVI interface on a VLAN comes up when there is at least one port in that vlan that is in STP forwarding state. Similarly, this interface goes down when the last STP forwarding port goes down or goes to another STP state.
By default, Autostate calculation is enabled. You can disable Autostate calculation for an SVI interface and change the default value.
 Note |
Nexus 3000 Series switches do not support bridging between two VLANs when an SVI for one VLAN exists on the same device as the bridging link. Traffic coming into the device and bound for the SVI is dropped as a IPv4 discard. This is because the BIA MAC address is shared across VLANs/SVIs with no option to modify the MAC of the SVI. |
The Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) is a device discovery protocol that runs over Layer 2 (the data link layer) on all Cisco-manufactured devices (routers, bridges, access servers, and switches) and allows network management applications to discover Cisco devices that are neighbors of already known devices. With CDP, network management applications can learn the device type and the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) agent address of neighboring devices that are running lower-layer, transparent protocols. This feature enables applications to send SNMP queries to neighboring devices.
CDP runs on all media that support Subnetwork Access Protocol (SNAP). Because CDP runs over the data-link layer only, two systems that support different network-layer protocols can learn about each other.
Each CDP-configured device sends periodic messages to a multicast address, advertising at least one address at which it can receive SNMP messages. The advertisements also contain time-to-live, or holdtime information, which is the length of time a receiving device holds CDP information before discarding it. Each device also listens to the messages sent by other devices to learn about neighboring devices.
The switch supports both CDP Version 1 and Version 2.
The following table shows the default CDP configuration.
|
Feature |
Default Setting |
|---|---|
|
CDP interface state |
Enabled |
|
CDP timer (packet update frequency) |
60 seconds |
|
CDP holdtime (before discarding) |
180 seconds |
|
CDP Version-2 advertisements |
Enabled |
An interface is in the error-disabled (err-disabled) state when the inteface is enabled administratively (using the no shutdown command) but disabled at runtime by any process. For example, if UDLD detects a unidirectional link, the interface is shut down at runtime. However, because the interface is administratively enabled, the interface status displays as err-disabled. Once an interface goes into the err-disabled state, you must manually reenable it or you can configure an automatic timeout recovery value. The err-disabled detection is enabled by default for all causes. The automatic recovery is not configured by default.
When an interface is in the err-disabled state, use the errdisable detect cause command to find information about the error.
You can configure the automatic err-disabled recovery timeout for a particular err-disabled cause by changing the time variable.
The errdisable recovery cause command provides automatic recovery after 300 seconds. To change the recovery period, use the errdisable recovery interval command to specify the timeout period. You can specify 30 to 65535 seconds.
To disable recovery of an interface from the err-disabled state, use the no errdisable recovery cause command.
all—Enables a timer to recover from all causes.
bpduguard—Enables a timer to recover from the bridge protocol data unit (BPDU) Guard error-disabled state.
failed-port-state—Enables a timer to recover from a Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) set port state failure.
link-flap—Enables a timer to recover from linkstate flapping.
pause-rate-limit—Enables a timer to recover from the pause rate limit error-disabled state.
udld—Enables a timer to recover from the Unidirectional Link Detection (UDLD) error-disabled state.
loopback—Enables a timer to recover from the loopback error-disabled state.
If you do not enable the err-disabled recovery for the cause, the interface stays in the err-disabled state until you enter the shutdown and no shutdown commands. If the recovery is enabled for a cause, the interface is brought out of the err-disabled state and allowed to retry operation once all the causes have timed out. Use the show interface status err-disabled command to display the reason behind the error.
You can use the default interface feature to clear the configured parameters for both physical and logical interfaces such as the Ethernet, loopback, management, VLAN, and the port-channel interface.
The debounce timer delays notification of a link change, which can decrease traffic loss due to network reconfiguration. You can configure the debounce timer separately for each Ethernet port and specify the delay time in milliseconds. The delay time can range from 0 milliseconds to 5000 milliseconds. By default, this parameter is set for 100 milliseconds, which results in the debounce timer not running. When this parameter is set to 0 milliseconds, the debounce timer is disabled.
 Caution |
Enabling the debounce timer causes the link-down detections to be delayed, which results in a loss of traffic during the debounce period. This situation might affect the convergence and reconvergence of some Layer 2 and Layer 3 protocols. |
The switch does not fragment frames. As a result, the switch cannot have two ports in the same Layer 2 domain with different maximum transmission units (MTUs). A per-physical Ethernet interface MTU is not supported. Instead, the MTU is set according to the QoS classes. You modify the MTU by setting class and policy maps.
 Note |
When you show the interface settings, a default MTU of 1500 is displayed for physical Ethernet interfaces. |
See the following information on the configuration, packet size, incremented counter values, and traffic.
|
Configuration |
Packet Size |
Incremented Counters |
Traffic |
|---|---|---|---|
|
L2 port – without any MTU configuration |
6400 and 10000 |
Jumbo, giant, and input error |
Dropped |
|
L2 port – with jumbo MTU 9216 in network-qos configuration |
6400 |
Jumbo |
Forwarded |
|
L2 port – with jumbo MTU 9216 in network-qos configuration |
10000 |
Jumbo, giant, and input error |
Dropped |
|
Layer 3 port with default Layer 3 MTU and jumbo MTU 9216 in network-qos configuration |
6400 |
Jumbo |
Packets are punted to the CPU (subjected to CoPP configs), get fragmented, and then they are forwarded by the software. |
|
Layer 3 port with default Layer 3 MTU and jumbo MTU 9216 in network-qos configuration |
6400 |
Jumbo |
Packets are punted to the CPU (subjected to CoPP configs), get fragmented, and then they are forwarded by the software. |
|
Layer 3 port with default Layer 3 MTU and jumbo MTU 9216 in network-qos configuration |
10000 |
Jumbo, giant, and input error |
Dropped |
|
Layer 3 port with jumbo Layer 3 MTU and jumbo MTU 9216 in network-qos configuration |
6400 |
Jumbo |
Forwarded without any fragmentation. |
|
Layer 3 port with jumbo Layer 3 MTU and jumbo MTU 9216 in network-qos configuration |
10000 |
Jumbo, giant, and input error |
Dropped |
|
Layer 3 port with jumbo Layer 3 MTU and default L2 MTU configuration |
6400 and 10000 |
Jumbo, giant, and input error |
Dropped |
 Note |
|
You can operationally enable uplink SFP+ ports before downlink RJ-45 ports after a reload on a Cisco Nexus 3048 switch. You must delay enabling the RJ-45 ports in the hardware until the SFP+ ports are enabled.
You can configure a timer that during reload enables the downlink RJ-45 ports in hardware only after the specified timeout. This process allows the uplink SFP+ ports to be operational first. The timer is enabled in the hardware for only those ports that are admin-enable.
Downlink delay is disabled by default and must be explicitly enabled. When enabled, if the delay timer is not specified, it is set for a default delay of 20 seconds.
The following table lists the default settings for all physical Ethernet interfaces:
|
Parameter |
Default Setting |
|---|---|
|
Duplex |
Auto (full-duplex) |
|
Encapsulation |
ARPA |
|
MTU1 |
1500 bytes |
|
Port Mode |
Access |
|
Speed |
Auto (10000) |
You can configure normal or aggressive unidirectional link detection (UDLD) modes for Ethernet interfaces on devices configured to run UDLD. Before you can enable a UDLD mode for an interface, you must make sure that UDLD is already enabled on the device that includes the interface. UDLD must also be enabled on the other linked interface and its device.
To use the normal UDLD mode, you must configure one of the ports for normal mode and configure the other port for the normal or aggressive mode. To use the aggressive UDLD mode, you must configure both ports for the aggressive mode.
 Note |
Before you begin, UDLD must be enabled for the other linked port and its device. |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 2 |
switch(config)# feature udld |
Enables UDLD for the device. |
| Step 3 |
switch(config)# no feature udld |
Disables UDLD for the device. |
| Step 4 |
switch(config)# show udld global |
Displays the UDLD status for the device. |
| Step 5 |
switch(config)# interface type slot/port |
Specifies an interface to configure, and enters interface configuration mode. |
| Step 6 |
switch(config-if)# udld {enable | disable | aggressive} |
Enables the normal UDLD mode, disables UDLD, or enables the aggressive UDLD mode. |
| Step 7 |
switch(config-if)# show udld interface |
Displays the UDLD status for the interface. |
This example shows how to enable UDLD for the switch:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# feature udld
This example shows how to enable the normal UDLD mode for an Ethernet port:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# interface ethernet 1/4
switch(config-if)# udld enable
This example shows how to enable the aggressive UDLD mode for an Ethernet port:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# interface ethernet 1/4
switch(config-if)# udld aggressive
This example shows how to disable UDLD for an Ethernet port:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# interface ethernet 1/4
switch(config-if)# udld disable
This example shows how to disable UDLD for the switch:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# no feature udld
You can manually trigger the link state consistency checker to compare the hardware and software link status of an interface and display the results. To manually trigger the link state consistency checker and display the results, use the following command in any mode:
| Command or Action | Purpose |
|---|---|
|
switch# show consistency-checker link-state module slot |
Starts a link state consistency check on the specified module and displays its results. |
This example shows how to trigger a Link State consistency check and display its results:
switch# show consistency-checker link-state module 1
Link State Checks: Link state only
Consistency Check: FAILED
No inconsistencies found for:
Ethernet1/1
Ethernet1/2
Ethernet1/3
Ethernet1/4
Ethernet1/5
Ethernet1/6
Ethernet1/7
Ethernet1/8
Ethernet1/9
Ethernet1/10
Ethernet1/12
Ethernet1/13
Ethernet1/14
Ethernet1/15
Inconsistencies found for following interfaces:
Ethernet1/11You can configure a Quad small form-factor pluggable (QSFP+) port by using the hardware profile portmode command. To restore the defaults, use the no form of these commands. The Cisco Nexus 3172PQ switch has 48x10g+breakout6x40g as the default port mode.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
||
| Step 2 |
switch(config)# copy running-config bootflash: my-config.cfg |
Copies the running configuration to the bootflash. You can use this file to configure your device later. |
||
| Step 3 |
switch(config)# write erase |
Removes all the interface configurations. |
||
| Step 4 |
switch(config)# reload |
Reloads the Cisco NX-OS software. |
||
| Step 5 |
switch(config)# [no] hardware profile portmode portmode |
Changes the interface port mode. |
||
| Step 6 |
(Optional) switch(config)# hardware profile portmode portmode 2-tuple |
(Optional)
Displays the port names in 2-tuple mode instead of the default 3-tuple convention mode. |
||
| Step 7 |
(Optional) switch(config)# copy running-config startup-config |
(Optional)
Saves the change persistently through reboots and restarts by copying the running configuration to the startup configuration. |
||
| Step 8 |
switch(config)# reload |
Reloads the Cisco NX-OS software. Manually apply all the interface configuration. You can refer to the configuration file that you saved earlier.
|
This example shows how to change the port mode to 48x10g+breakout6x40g for QSFP+ ports:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# copy running-config bootflash:my-config.cfg
switch(config)# write erase
switch(config)# reload
WARNING: This command will reboot the system
Do you want to continue? (y/n) [n] y
switch(config)# hardware profile portmode 48x10g+breakout6x40g
Warning: This command will take effect only after saving the configuration and reload!
Port configurations could get lost when port mode is changed!
switch(config)# copy running-config startup-config
switch(config)# reload
WARNING: This command will reboot the system
Do you want to continue? (y/n) [n] yThis example shows how to change the port mode to 48x10g+4x40g for QSFP+ ports:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# copy running-config bootflash:my-config.cfg
switch(config)# write erase
switch(config)# reload
WARNING: This command will reboot the system
Do you want to continue? (y/n) [n] y
switch(config)# hardware profile portmode 48x10g+4x40g
Warning: This command will take effect only after saving the configuration and reload!
Port configurations could get lost when port mode is changed!
switch(config)# copy running-config startup-config
switch(config)# reload
WARNING: This command will reboot the system
Do you want to continue? (y/n) [n] yThis example shows how to change the port mode to 48x10g+4x40g for QSFP+ ports and verify the changes:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# hardware profile portmode 48x10g+4x40g
Warning: This command will take effect only after saving the configuration and r
eload! Port configurations could get lost when port mode is changed!
switch(config)# show running-config
!Command: show running-config
!Time: Thu Aug 25 07:39:37 2011
version 5.0(3)U2(1)
feature telnet
no feature ssh
feature lldp
username admin password 5 $1$OOV4MdOM$BAB5RkD22YanT4empqqSM0 role network-admin
ip domain-lookup
switchname BLR-QG-5
ip access-list my-acl
10 deny ip any 10.0.0.1/32
20 deny ip 10.1.1.1/32 any
class-map type control-plane match-any copp-arp
class-map type control-plane match-any copp-bpdu
:
:
control-plane
service-policy input copp-system-policy
hardware profile tcam region arpacl 128
hardware profile tcam region ifacl 256
hardware profile tcam region racl 256
hardware profile tcam region vacl 512
hardware profile portmode 48x10G+4x40G
snmp-server user admin network-admin auth md5 0xdd1d21ee42e93106836cdefd1a60e062
<--Output truncated-->
switch#This example shows how to restore the default port mode for QSFP+ ports:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# no hardware profile portmode
Warning: This command will take effect only after saving the configuration and r
eload! Port configurations could get lost when port mode is changed!
switch(config)# Note |
If the interface and transceiver speed is mismatched, the SFP validation failed message is displayed when you enter the show interface ethernet slot/port command. For example, if you insert a 1-Gigabit SFP transceiver into a port without configuring the speed 1000 command, you will get this error. By default, all ports are 10 Gbps. |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 2 |
switch(config)# interface type slot/port |
Enters interface configuration mode for the specified interface. This interface must have a 1-Gigabit Ethernet SFP transceiver inserted into it. |
| Step 3 |
switch(config-if)# speed speed |
Sets the speed on the interface.
|
This example shows how to set the speed for a 1-Gigabit Ethernet port:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# interface ethernet 1/4
switch(config-if)# speed 1000By default, all ports on Cisco Nexus 3132 switches are 40-Gigabit Ethernet. You can break out a 40-Gigabit Ethernet port to four x10-Gigabit Ethernet ports.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
||
| Step 2 |
switch(config)# interface type slot/port-range |
|
||
| Step 3 |
switch(config-if)# speed 10000 |
Sets the speed on the interface to 10-Gigabit per second.
|
This example shows how to set the speed to 10-Gigabit per second on Ethernet interface 1/2:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# interface ethernet 1/49
switch(config-if)# speed 10000
switch(config-if)# sh running-config | grep port
limit-resource port-channel minimum 0 maximum 511
interface breakout module 1 port 49 map 10g-4x ------------------------------------------> interface breakout is added on "speed" config
hardware profile portmode 48x10g+breakout6x40g
(config-if)#
(config)# int ethernet 1/49/1
(config-if)#no speed 10000 ------------------------------------> on "no speed", the interface breakout cmd is removed.
(config-if)# sh running-config | grep port
limit-resource port-channel minimum 0 maximum 511
hardware profile portmode 48x10g+breakout6x40g
You can break in four x 10-Gigabit Ethernet ports to a 40-Gigabit Ethernet port.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
||
| Step 2 |
switch(config)# interface type slot/port |
|
||
| Step 3 |
switch(config-if)# speed 40000 |
Sets the speed on the interface to 40 Gbps. |
This example shows how to set the speed to 40 Gbps on Ethernet interface 1/2/1:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# interface ethernet 1/2/1
switch(config-if)# speed 40000When you break out ports into the 10-GbE mode, you can switch between the first QSFP port and SFP+ ports 1 to 4. Either the first QSFP port or the four SFP+ ports can be active at any time. QSFP is the default port with an interface speed of 40 Gbps.
When the first QSFP port is in the 40-GbE mode, you cannot switch the port to four SFP+ ports and the first QSFP port will be active until you break out the port into the 10-GbE mode. This is because SFP+ ports do not support the 40-GbE mode.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
||
| Step 2 |
switch(config)# [no] hardware profile front portmode qsfp | sfp-plus |
The no form of this command activates the QSFP port.
|
||
| Step 3 |
switch(config)# interface breakout module module number port port rangemap 10g-4x |
Enables you to configure the module in 10g mode. When you are changing the portmode from QSFP to SFP+, the hardware profile front portmode command takes effect only after breaking out the first QSFP port as displayed in this command. |
||
| Step 4 |
(Optional) switch(config)# copy running-config startup-config |
(Optional)
Saves the change persistently through reboots and restarts by copying the running configuration to the startup configuration. |
This example shows how to change the portmode from QSFP to SFP+:
switch# show int e1/1 tranceiver
Ethernet1/1
transceiver is present
type is QSFP-40G-SR
name is CISCO
part number is AFBR-79EIPZ-CS1
revision is 02
serial number is AVP1645S1QT
nominal bitrate is 10300 MBit/sec per channel
Link length supported for 50/125um fiber is 30 m
Link length supported for 50/125um fiber is 100 m
cisco id is --
cisco extended id number is 16
switch# show running-config | inc portmode
hardware profile portmode 32X40G
hardware profile front portmode qsfp
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# hardware profile front portmode sfp-plus
switch(config)# interface breakout module 1 port 1 map 10g-4x
switch(config)# copy running-config startup-config
This example shows how to make the QSFP port active:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# hardware profile front portmode qsfp
switch(config)# copy running-config startup-config
By default, auto-negotiation is enabled on all 1G SFP+ and 40G QSFP ports and it is disabled on 10G SFP+ ports. Auto-negotiation is by default enabled on all 1G and 10G Base-T ports. It cannot be disabled on 1G and 10G Base-T ports.
This command is equivalent to the Cisco IOS speed non-negotiate command.
 Note |
|
 Note |
You usually configure Ethernet port speed and duplex mode parameters to auto to allow the system to negotiate the speed and duplex mode between ports. If you decide to configure the port speed and duplex modes manually for these ports, consider the following:
|
 Note |
For 1G SFP with autonegotiation enabled, Auto Speed mode is not compatible to linkup with a peer having 100M speed. |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
||
| Step 2 |
switch(config)# interface ethernet slot/port |
Selects the interface and enters interface mode. |
||
| Step 3 |
switch(config-if)# no negotiate auto |
Disables link negotiation on the selected Ethernet interface (1-Gigabit port). |
||
| Step 4 |
(Optional) switch(config-if)# negotiate auto |
(Optional)
Enables link negotiation on the selected Ethernet interface. The default for 1-Gigabit Ethernet ports is enabled.
|
This example shows how to disable auto-negotiation on a specified Ethernet interface (1-Gigabit port):
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# interface ethernet 1/1
switch(config-if)# no negotiate auto
switch(config-if)#This example shows how to enable auto-negotiation on a specified Ethernet interface (1-Gigabit port):
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# interface ethernet 1/5
switch(config-if)# negotiate auto
switch(config-if)#You can configure a SVI to remain active even if no interfaces are up in the corresponding VLAN. This enhancement is called Autostate Disable.
When you enable or disable autostate behavior, it is applied to all the SVIs in the switch unless you configure autostate per SVI .
 Note |
Autostate behavior is enabled by default. |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 2 |
switch(config)# feature interface-vlan |
Enables the interface-vlan feature. |
| Step 3 |
switch(config)# system default interface-vlan [no] autostate |
Configures the system to enable or disable the Autostate default behavior. |
| Step 4 |
(Optional) switch(config)# interface vlan interface-vlan-number |
(Optional)
Creates a VLAN interface. The number range is from 1 to 4094. |
| Step 5 |
(Optional) switch(config-if)# [no] autostate |
(Optional)
Enables or disables Autostate behavior per SVI. |
| Step 6 |
(Optional) switch(config)# show interface-vlan interface-vlan |
(Optional)
Displays the enabled or disabled Autostate behavior of the SVI. |
| Step 7 |
(Optional) switch(config)# copy running-config startup-config |
(Optional)
Saves the change persistently through reboots and restarts by copying the running configuration to the startup configuration. |
This example shows how to disable the systems Autostate default for all the SVIs on the switch:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# feature interface-vlan
switch(config)# system default interface-vlan no autostate
switch(config)# interface vlan 50
switch(config-if)# no autostate
switch(config)# copy running-config startup-configThis example shows how to enable the systems autostate configuration:
switch(config)# show interface-vlan 2
Vlan2 is down, line protocol is down, autostate enabled
Hardware is EtherSVI, address is 547f.ee40.a17c
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 1000000 Kbit, DLY 10 usec
The default interface feature allows you to clear the existing configuration of multiple interfaces such as Ethernet, loopback, management, VLAN, and port-channel interfaces. All user configuration under a specified interface will be deleted. On a Cisco Nexus C3408-S switch, the number of interfaces you can configure using the default interface ethernet command, at a time, is limited to a maximum of 64 ports.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 2 |
switch(config)# default interface type interface number |
|
| Step 3 |
switch(config)# exit |
|
This example shows how to delete the configuration of an Ethernet interface and revert it to its default configuration:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# default interface ethernet 1/3
.......Done
switch(config)# exitYou can configure the frequency of Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) updates, the amount of time to hold the information before discarding it, and whether or not to send Version-2 advertisements.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 2 |
(Optional) switch(config)# [no] cdp advertise {v1 | v2 } |
(Optional)
Configures the version to use to send CDP advertisements. Version-2 is the default state. Use the no form of the command to return to its default setting. |
| Step 3 |
(Optional) switch(config)# [no] cdp format device-id {mac-address | serial-number | system-name} |
(Optional)
Configures the format of the CDP device ID. The default is the system name, which can be expressed as a fully qualified domain name. Use the no form of the command to return to its default setting. |
| Step 4 |
(Optional) switch(config)# [no] cdp holdtime seconds |
(Optional)
Specifies the amount of time a receiving device should hold the information sent by your device before discarding it. The range is 10 to 255 seconds; the default is 180 seconds. Use the no form of the command to return to its default setting. |
| Step 5 |
(Optional) switch(config)# [no] cdp timer seconds |
(Optional)
Sets the transmission frequency of CDP updates in seconds. The range is 5 to 254; the default is 60 seconds. Use the no form of the command to return to its default setting. |
This example shows how to configure CDP characteristics:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# cdp timer 50
switch(config)# cdp holdtime 120
switch(config)# cdp advertise v2
You can enable or disable CDP for Ethernet interfaces. This protocol works only when you have it enabled on both interfaces on the same link.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 2 |
switch(config)# interface type slot/port |
Enters interface configuration mode for the specified interface. |
| Step 3 |
switch(config-if)# cdp enable |
Enables CDP for the interface. To work correctly, this parameter must be enabled for both interfaces on the same link. |
| Step 4 |
switch(config-if)# no cdp enable |
Disables CDP for the interface. |
This example shows how to enable CDP for an Ethernet port:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# interface ethernet 1/4
switch(config-if)# cdp enable
This command can only be applied to a physical Ethernet interface.
You can enable error-disable (err-disabled) detection in an application. As a result, when a cause is detected on an interface, the interface is placed in an err-disabled state, which is an operational state that is similar to the link-down state.
 Note |
Base ports in Cisco Nexus 5500 never get error disabled due to pause rate-limit like in the Cisco Nexus 5020 or 5010 switch. |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 2 |
switch(config)# errdisable detect cause {all | link-flap | loopback} |
Specifies a condition under which to place the interface in an err-disabled state. The default is enabled. |
| Step 3 |
switch(config)# shutdown |
Brings the interface down administratively. To manually recover the interface from the err-disabled state, enter this command first. |
| Step 4 |
switch(config)# no shutdown |
Brings the interface up administratively and enables the interface to recover manually from the err-disabled state. |
| Step 5 |
switch(config)# show interface status err-disabled |
Displays information about err-disabled interfaces. |
| Step 6 |
(Optional) switch(config)# copy running-config startup-config |
(Optional)
Saves the change persistently through reboots and restarts by copying the running configuration to the startup configuration. |
This example shows how to enable the err-disabled detection in all cases:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# errdisable detect cause all
switch(config)# shutdown
switch(config)# no shutdown
switch(config)# show interface status err-disabled
switch(config)# copy running-config startup-configYou can specify the application to bring the interface out of the error-disabled (err-disabled) state and retry coming up. It retries after 300 seconds, unless you configure the recovery timer (see the errdisable recovery interval command).
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 2 |
switch(config)# errdisable recovery cause {all | udld | bpduguard | link-flap | failed-port-state | pause-rate-limit | loopback} |
Specifies a condition under which the interface automatically recovers from the err-disabled state, and the device retries bringing the interface up. The device waits 300 seconds to retry. The default is disabled. |
| Step 3 |
switch(config)# show interface status err-disabled |
Displays information about err-disabled interfaces. |
| Step 4 |
(Optional) switch(config)# copy running-config startup-config |
(Optional)
Saves the change persistently through reboots and restarts by copying the running configuration to the startup configuration. |
This example shows how to enable err-disabled recovery under all conditions:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# errdisable recovery cause loopback
switch(config)# show interface status err-disabled
switch(config)# copy running-config startup-configYou can use this procedure to configure the err-disabled recovery timer value. The range is from 30 to 65535 seconds. The default is 300 seconds.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 2 |
switch(config)# errdisable recovery interval interval |
Specifies the interval for the interface to recover from the err-disabled state. The range is from 30 to 65535 seconds. The default is 300 seconds. |
| Step 3 |
switch(config)# show interface status err-disabled |
Displays information about err-disabled interfaces. |
| Step 4 |
(Optional) switch(config)# copy running-config startup-config |
(Optional)
Saves the change persistently through reboots and restarts by copying the running configuration to the startup configuration. |
This example shows how to enable err-disabled recovery under all conditions:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# errdisable recovery interval 32
switch(config)# show interface status err-disabled
switch(config)# copy running-config startup-configYou can disable recovery of an interface from the err-disabled state.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 2 |
switch(config)# no errdisable recovery cause {all | udld | bpduguard | link-flap | failed-port-state | pause-rate-limit | loopback} |
Specifies a condition under which the interface reverts back to the default err-disabled state. |
| Step 3 |
(Optional) switch(config)# show interface status err-disabled |
(Optional)
Displays information about err-disabled interfaces. |
| Step 4 |
(Optional) switch(config)# copy running-config startup-config |
(Optional)
Saves the change persistently through reboots and restarts by copying the running configuration to the startup configuration. |
This example shows how to disable err-disabled recovery:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# no errdisable recovery cause loopback
switch(config)# show interface status err-disabled
switch(config)# copy running-config startup-configYou can enable the debounce timer for Ethernet ports by specifying a debounce time, in milliseconds (ms), or disable the timer by specifying a debounce time of 0. By default, the debounce timer is set to 100 ms, which results in the debounce timer not running.
 Note |
The link state of 10G and 100G ports may change repeatedly when connected to service provider network. As a part of link reset or break-link functionality, it is expected that the Tx power light on the SFP to change to N/A state, at an event of link state change. However, to prevent this behavior during the link state change, you may increase the link debounce timer to start from 500ms and increase it in 500ms intervals until the link stabilizes. On the DWDM, UVN, and WAN network, it is recommended to disable automatic link suspension (ALS) whenever possible. ALS suspends the link on the WAN when the Nexus turn off the link. |
You can show the debounce times for all of the Ethernet ports by using the show interface debounce command.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 2 |
switch(config)# interface type slot/port |
Enters interface configuration mode for the specified interface. |
| Step 3 |
switch(config-if)# link debounce time milliseconds |
Enables the debounce timer for the amount of time (1 to 5000 ms) specified. Disables the debounce timer if you specify 0 milliseconds. |
This example shows how to enable the debounce timer and set the debounce time to 1000 ms for an Ethernet interface:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# interface ethernet 3/1
switch(config-if)# link debounce time 1000This example shows how to disable the debounce timer for an Ethernet interface:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# interface ethernet 3/1
switch(config-if)# link debounce time 0You can provide textual interface descriptions for the Ethernet ports.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 2 |
switch(config)# interface type slot/port |
Enters interface configuration mode for the specified interface. |
| Step 3 |
switch(config-if)# description test |
Specifies the description for the interface. |
This example shows how to set the interface description to Server 3 interface:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# interface ethernet 1/3
switch(config-if)# description Server 3 InterfaceYou can shut down and restart an Ethernet interface. This action disables all of the interface functions and marks the interface as being down on all monitoring displays.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 2 |
switch(config)# interface type slot/port |
Enters interface configuration mode for the specified interface. |
| Step 3 |
switch(config-if)# shutdown |
Disables the interface. |
| Step 4 |
switch(config-if)# no shutdown |
Restarts the interface. |
This example shows how to disable an Ethernet port:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# interface ethernet 1/4
switch(config-if)# shutdown
This example shows how to restart an Ethernet interface:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# interface ethernet 1/4
switch(config-if)# no shutdown
You can operationally enable uplink SFP+ ports before downlink RJ-45 ports after a reload on a Cisco Nexus 3048 switch by delaying enabling the RJ-45 ports in the hardware until the SFP+ ports are enabled.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 2 |
switch(config)# downlink delay enable | disable [timeout time-out] |
Enables or disables downlink delay and configures the timeout. |
This example shows how to enable downlink delay and configure the delay timeout on the switch:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# downlink delay enable timeout 45To view configuration information about the defined interfaces, perform one of these tasks:
|
Command |
Purpose |
|---|---|
| switch# show interface type slot/port |
Displays the detailed configuration of the specified interface. |
| switch# show interface type slot/port capabilities |
Displays detailed information about the capabilities of the specified interface. This option is available only for physical interfaces. |
| switch# show interface type slot/port transceiver |
Displays detailed information about the transceiver connected to the specified interface. This option is available only for physical interfaces. |
| switch# show interface brief |
Displays the status of all interfaces. |
| switch# show interface flowcontrol |
Displays the detailed listing of the flow control settings on all interfaces. |
The show interface command is invoked from EXEC mode and displays the interface configurations. Without any arguments, this command displays the information for all the configured interfaces in the switch.
This example shows how to display the physical Ethernet interface:
switch# show interface ethernet 1/1
Ethernet1/1 is up
Hardware is 1000/10000 Ethernet, address is 000d.eca3.5f08 (bia 000d.eca3.5f08)
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 10000000 Kbit, DLY 10 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 190/255, rxload 192/255
Encapsulation ARPA
Port mode is trunk
full-duplex, 10 Gb/s, media type is 1/10g
Input flow-control is off, output flow-control is off
Auto-mdix is turned on
Rate mode is dedicated
Switchport monitor is off
Last clearing of "show interface" counters never
5 minute input rate 942201806 bytes/sec, 14721892 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 935840313 bytes/sec, 14622492 packets/sec
Rx
129141483840 input packets 0 unicast packets 129141483847 multicast packets
0 broadcast packets 0 jumbo packets 0 storm suppression packets
8265054965824 bytes
0 No buffer 0 runt 0 Overrun
0 crc 0 Ignored 0 Bad etype drop
0 Bad proto drop
Tx
119038487241 output packets 119038487245 multicast packets
0 broadcast packets 0 jumbo packets
7618463256471 bytes
0 output CRC 0 ecc
0 underrun 0 if down drop 0 output error 0 collision 0 deferred
0 late collision 0 lost carrier 0 no carrier
0 babble
0 Rx pause 8031547972 Tx pause 0 reset
This example shows how to display the physical Ethernet capabilities:
switch# show interface ethernet 1/1 capabilities
Ethernet1/1
Model: 734510033
Type: 10Gbase-(unknown)
Speed: 1000,10000
Duplex: full
Trunk encap. type: 802.1Q
Channel: yes
Broadcast suppression: percentage(0-100)
Flowcontrol: rx-(off/on),tx-(off/on)
Rate mode: none
QOS scheduling: rx-(6q1t),tx-(1p6q0t)
CoS rewrite: no
ToS rewrite: no
SPAN: yes
UDLD: yes
MDIX: no
FEX Fabric: yes
This example shows how to display the physical Ethernet transceiver:
switch# show interface ethernet 1/1 transceiver
Ethernet1/1
sfp is present
name is CISCO-EXCELIGHT
part number is SPP5101SR-C1
revision is A
serial number is ECL120901AV
nominal bitrate is 10300 MBits/sec
Link length supported for 50/125mm fiber is 82 m(s)
Link length supported for 62.5/125mm fiber is 26 m(s)
cisco id is --
cisco extended id number is 4
This example shows how to display a brief interface status (some of the output has been removed for brevity):
switch# show interface brief
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Ethernet VLAN Type Mode Status Reason Speed Port
Interface Ch #
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Eth1/1 200 eth trunk up none 10G(D) --
Eth1/2 1 eth trunk up none 10G(D) --
Eth1/3 300 eth access down SFP not inserted 10G(D) --
Eth1/4 300 eth access down SFP not inserted 10G(D) --
Eth1/5 300 eth access down Link not connected 1000(D) --
Eth1/6 20 eth access down Link not connected 10G(D) --
Eth1/7 300 eth access down SFP not inserted 10G(D) --
...
This example shows how to display the CDP neighbors:
switch# show cdp neighbors
Capability Codes: R - Router, T - Trans-Bridge, B - Source-Route-Bridge
S - Switch, H - Host, I - IGMP, r - Repeater,
V - VoIP-Phone, D - Remotely-Managed-Device,
s - Supports-STP-Dispute
Device ID Local Intrfce Hldtme Capability Platform Port ID
d13-dist-1 mgmt0 148 S I WS-C2960-24TC Fas0/9
n5k(FLC12080012) Eth1/5 8 S I s N5K-C5020P-BA Eth1/5
|
MIB |
MIB Link |
|---|---|
|
IF-MIB |
To locate and download MIBs, go to the following URL: http://www.cisco.com/public/sw-center/netmgmt/cmtk/mibs.shtml |
|
MAU-MIB
|