Fibre Channel Connectivity Overview
A switch is in NPV mode after enabling NPV. NPV mode applies to an entire switch. All end devices connected to a switch that are in NPV mode must log in as an N port to use this feature (loop-attached devices are not supported). All links from the edge switches (in NPV mode) to the NPV core switches are established as NP ports (not E ports), which are used for typical inter-switch links.
FC NPV Benefits
FC NPV provides the following:
-
Increased number of hosts that connect to the fabric without adding domain IDs in the fabric
-
Connection of FC and FCoE hosts and targets to SAN fabrics using FC interfaces
-
Automatic traffic mapping
-
Static traffic mapping
-
Disruptive automatic load balancing
FC NPV Mode
Feature-set fcoe-npv in ACI will be enabled automatically by default when first FCoE/FC configuration is pushed.
FC Topology
The topology of a typical configuration supporting FC traffic over the ACI fabric consists of the following components:
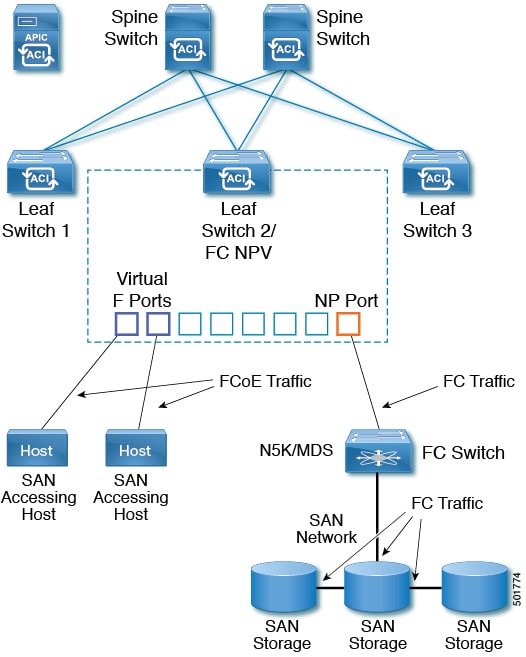
-
A Leaf can be connected to a FC switch by using FCoE NP port or native FC NP port.
-
An ACI Leaf can be directly connected with a server/Storage using FCoE links.
-
FC/FCoE traffic is not sent to fabric/spine. A Leaf switch does not do local switching for FCoE traffic. The switching is done by a core switch which is connected with a leaf switch via FC/FCoE NPV link.
-
Multiple FDISC followed by Flogi is supported with FCoE host and FC/FCoE NP links.

 Feedback
Feedback